芦丁在Au-TiO2修饰电极上的电化学行为及其测定
邢瑞敏,赵晓宇,许银霞,刘 勇,刘绣华,何建英,刘山虎
(河南大学 化学化工学院,河南 开封 475004)
芦丁在Au-TiO2修饰电极上的电化学行为及其测定
邢瑞敏,赵晓宇,许银霞,刘 勇,刘绣华,何建英,刘山虎
(河南大学 化学化工学院,河南 开封 475004)
利用沉淀沉积法合成了纳米金-二氧化钛(Au-TiO2)复合纳米材料.构建了Au-TiO2复合材料修饰的电化学传感器,并对芦丁进行了检测.通过扫描电镜(SEM),X射线衍射(XRD)对Au-TiO2复合材料进行表征,利用循环伏安(CV)和电流时间曲线(Amperometrici-tCurve)考察了其对芦丁的电催化性能.在最优条件下对芦丁进行检测,检测范围为0.1~10 μmol/L,灵敏度为1.47 μA·μmol·L-1·cm-2,信噪比为3时检测限为0.083 μmol/L.
Au;TiO2;芦丁;电化学传感器
作为一种天然黄酮衍生物,芦丁具有很多药理活性,例如降血压、抗氧化、消炎杀菌、抗肿瘤活性等[1-3],经常用于一些疾病的治疗.建立一种快速、简便、灵敏、选择性好的分析方法,对药物和植物中芦丁检测有重要意义[4-6].目前有很多分析方法用于芦丁的测定,如紫外可见分光光度法[7]、高效液相色谱法[8]、化学发光法[9]、毛细管电泳[10-11]、高效液相色谱质谱连用技术[12]等.但这些传统检测方法不易实现“现场”分析,往往需要复杂的样品前处理制备步骤,这使它们在实践操作中不方便.电化学方法具有快速、选择性好及灵敏等特性,可以较好地满足检测要求[13-15].
电化学方法的进步依赖于新材料的发展,发现新材料或新方法来提高电化学传感的敏感度、选择性依旧是一个挑战[16-17].二氧化钛因其化学稳定性、催化活性高、无毒廉价易得等优点,被用来作为负载贵金属纳米材料[18].贵金属纳米粒子,例如金纳米粒子,具有非凡的电导率,比表面积大,常用于电化学催化反应[19].本文中我们利用液相沉积法合成了金/二氧化钛复合纳米材料,构建了Au-TiO2复合材料修饰的电化学传感器,对芦丁进行了检测.在最佳条件下,用计时电流法测定芦丁的峰电流,线性范围0.1~10 μmol/L,灵敏度为1.47 μA·μmol·L-1·cm-2.
1 实验部分
1.1 仪器和试剂
电化学实验采用CHI660D型电化学工作站(上海辰华仪器公司),使用三电极体系:玻碳电极为工作电极,Ag/AgCl电极为参比电极,Pt为辅助电极.粉末X射线衍射分析法(Powder X-ray Diffraction)采用德国Bruker公司公司出产的 D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪, 2θ范围为10°~90°,探测器为林克斯阵列探测器和林克斯XE阵列探测器,Cu靶标准尺寸光管,管电压40 kV.扫描电子显微镜(SEM) 使美国FEI公司Nova Nano SEM 450型号的电镜.
二氧化钛获赠于CRISTAL ACTIV公司;氯金酸(HAuCl4)和磷酸二氢钾(KH2PO4)购于国药化学试剂有限公司;磷酸氢二钠(Na2HPO3)购于天津科密欧公司;Nafion 购于Alfa Aesar公司;芦丁购于大连美仑生物有限公司.所有试剂采用分析纯,水采用二次蒸馏水.
1.2 Au-TiO2纳米材料的制备
Au-TiO2纳米材料的制备采用沉积沉淀法.实验过程如下:配制1 g/L的氯金酸溶液20 mL用氢氧化钠调节pH为7.0,水浴加热至65 ℃,上述溶液中不断搅拌下加入0.2 g二氧化钛粉末.搅拌4 h,离心洗涤,200 ℃干燥.即可得到Au-TiO2纳米材料.
1.3 修饰电极的制备
首先将裸玻碳电极在均相纸上打磨,然后在麂皮上用1.0、0.3和0.05 μmol/Lα-Al2O3悬浊液做进一步的抛光处理,最后依次用1∶1 HNO3、无水乙醇、二次水超声清洗以得到光洁、平滑的电极表面,电极吹干后备用.将2 g/L的Au-TiO2悬浊液通过滴涂法负载在玻碳电极表面,晾干备用.
2 结果与讨论
2.1 材料的表征
运用X射线衍射对样品的晶体结构进行表征,如图1(A)所示,在复合材料的衍射峰除了二氧化钛纯品出现的锐钛矿衍射峰(JCPDS file No.21-1 272)外,还有4个衍射峰38.2°,44.5°,64.7°,81.9°,分别对应金纳米粒子的(111),(200),(220)和(311)晶面(JCPDS file No.65-860)[20].通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)对Au-TiO2的形态特征进行了表征.从图1(B)中可以看出,金纳米粒子均匀的沉积在二氧化钛上,无明显聚集.
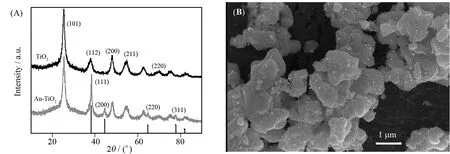
图1 Au-TiO2纳米材料的XRD图谱(A)和扫描(SEM)电镜(B)Fig.1 XRD (A) and SEM (B) pattern of Au-TiO2 nanocomposite
2.2 Au-TiO2-Nafion传感器用于芦丁检测的循环伏安特征
图2(A)显示的是芦丁在不同的修饰电极上的循环伏安曲线.在0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(PBS,pH=3.0)中,芦丁在Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极上氧化还原峰电流高于芦丁在TiO2/GCE,空白GCE电极上氧化还原峰电流,这表明芦丁在Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极上发生了较强的吸附和较快的电化学反应.芦丁在Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极上出现一对氧化还原峰,峰电位是0.59 V和0.54 V,说明芦丁的电化学氧化还原反应是可逆的.由于二氧化钛负载金纳米材料的催化能力较好,可提高电子传输速率,能有效促进芦丁进行电化学反应.通过图2(B)同一电极不同溶液的对比试验,可以看出该修饰电极可以检测芦丁溶液.

图2 (A)含0.1 mmol/L 芦丁的不同电极的循环伏安图,扫速:100 mV/s.a:空白电极 b:TiO2-Nafion修饰电极 c:Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极 (B) Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极在a:0.1 mol/L PBS (pH=3) b:0.1 mmol/L 芦丁PBS(0.1 mol/L,pH=3)中的循环伏安图Fig.2 (A) CVs on different types of electrodes in the presence of 0.1 mmol/L rutin at 100 mV/s.a:bare b:TiO2-Nafion/GCE c:Au-TiO2-Nafion/GEC (B) CVs on Au-TiO2-Nafion modified GCE in a:0.1 mol/L PBS (pH=3) b:0.1 mmol/L rutin PBS(0.1 mol/L,pH=3)
2.3 Au-TiO2-Nafion传感器响应的优化条件
2.3.1 纳米材料的滴涂量对传感器的影响
电极上所修饰的纳米粒子的量的多少直接影响到传感器表面对芦丁的吸附能力及电子传递的难易.图3所示为不同Au-TiO2滴涂量的影响.随滴涂量从5 μL到13 μL,氧化峰电流由增变减,其中9 μL时,氧化峰电流最大,最优的滴涂量是9 μL,原因可能是,当滴涂量超过9 μL,多余的Au-TiO2-Nafion会阻碍修饰材料与溶液之间的电荷转移,不利于芦丁的电催化氧化.
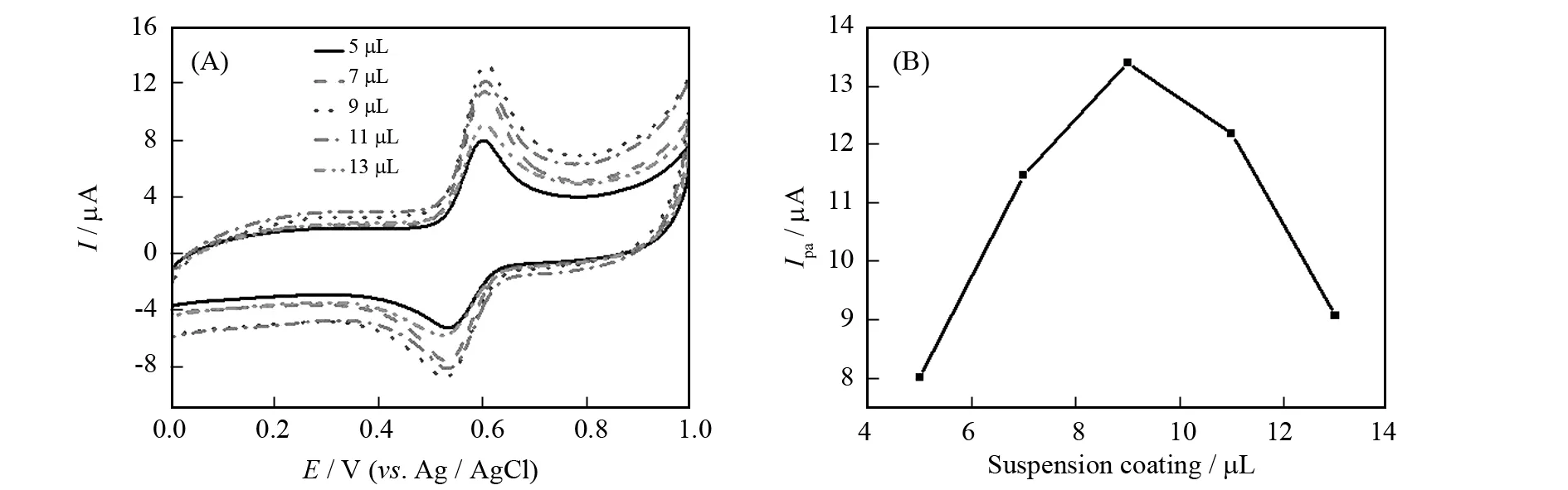
图3 0.1 mmol/L芦丁在0.1 mol/L PBS (pH=3.0)不同修饰量Au-TiO2-Nafion电极上的循环伏安图,扫速100 mV/sFig.3 CVs of 0.1 mmol/L rutin in 0.1 mol/L PBS (pH=3.0) with different Au-TiO2-Nafion suspension coating on bare GCE at 100 mV/s
2.3.2 pH对传感器的影响
在Au-TiO2-Nafion/GCE上,研究了0.1 mmol/L芦丁在0.1 mol/L缓冲液中不同pH时的电化学行为.试验结果如图4所示,当pH从2.0逐渐增加到8.0时,芦丁的氧化峰电位逐渐负移,同时,芦丁的氧化峰电位与pH之间具有良好的线性关系(见图4(B)),其线方程为Epa/V = 0.772 45-0.054 21pH (R2=0.995 6),因氧化电位可用下式表述:
EP=E0-m/n0.059pH
EP为实际电位,E0为标准电势,m代表参加反应质子的数量,n代表参加反应的电子数量,pH代表溶液酸碱度,根据该方程的斜率-0.054 V·pH-1接近理论值-0.059 V·pH-1,可以推断出,参与电化学反应的电子数与质子数相等[11].在pH为2~8的范围内,随着pH的增加,芦丁氧化峰电流先增大后减小,当pH=3.0时达到最大值.当pH过大时,阳极峰电流变小.随着pH的增大,电位向负向移动,这种试验现象的发生是由于质子参与了电极反应[1],根据以上实验结论,本实验中芦丁的测定最佳pH为3.0.

图4 (A):0.1 mmol/L芦丁在Au-TiO2-Nafion/GCE电极上,0.1 mol/L磷酸盐底液中不同pH (2~8)下的循环伏安图 (B):Ipa 和 Epa与pH的线性关系图Fig.4 (A) CVs of Au-TiO2-Nafion modified GC electrode in a 0.1 mol/L PBS with 0.1 mmol/L rutin at different solution pHs (pH 2-8).(B) Influence of pH on current response of Au-TiO2 nanocomposite modified GC electrode to rutin oxidation in PBS
2.3.3 扫速对传感器的影响
Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极在0.1 mmol/L芦丁在0.1 mol/L磷酸盐缓冲液(pH 3.0)中,不同扫描速率时对其峰电流的影响如图5(A)所示.扫描速率,从10 mV·s-1逐渐增加到100 mV·s-1时,芦丁的氧化峰电位都随着扫描速率的增加而正移,并且芦丁的氧化峰电流与扫描速率(v)成正比(见图5(B)),具有良好的线性关系,说明该反应受传质控制.

图5 0.1 mmol/L芦丁(0.1 mol/LPBS,pH=3.0)不同扫速时在Au-TiO2-Nafion/GCE上的循环伏图Fig.5 CVs on Au-TiO2-Nafion/GCE in the presence of 0.1 mmol/L rutin (0.1 mol/LPBS,pH=3.0) at different sweep rates
2.4 Au-TiO2-Nafion传感器对芦丁的检测
i-t曲线法具有较高的灵敏度和较好的与背景电流分离的能力,所以采用i-t曲线法来实现芦丁测定.如图6在+0.6 V(pH=3.0,0.1 mol/L PBS)下,研究芦丁浓度与峰电流之间的关系.当芦丁浓度在0.1~10 μmol/L之间,峰电流与芦丁浓度之间呈线性关系,相关系数0.9950,灵敏度1.47μA·μmol·L-1·cm-2,信噪比为3时检测限为0.083 μmol/L.

图6 Au-TiO2-Nafion修饰电极的i-t 曲线,pH 3.0;工作电压:+0.59 V,插入图:芦丁的线性曲线Fig.6 Amperometric response of Au-TiO2-Nafion /GCE at 0.59 V upon successive addition of 1 mmol/L rutin to 50 mL of 0.1 mol/L PBS (pH 3.0).Inset shows a plot of electro-catalytic current against rutin concentration
2.5 Au-TiO2-Nafion传感器的抗干扰能力
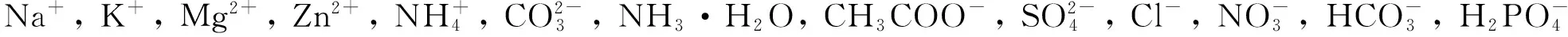
2.6 重现性和稳定性
将上述修饰电极在含有1 mmol/L芦丁磷酸缓冲液中连续扫描10次,其循环伏安中的峰电流的相对标准偏差3.8%.表明该传感器用于芦丁测定具有好的重现性.在修饰电极制备完成的1 w后,用该传感器对1 mmol/L芦丁进行扫描.发现电流的响应值为初始电流的87%.这说明该传感器具有良好的稳定性.
3 结论
利用沉淀沉积方法成功制备了Au-TiO2复合材料,在此基础上构建了电化学传感器.研究了芦丁在该修饰电极上的电化学行为,在最优条件下可实现芦丁的灵敏检测.该传感器具有较高的选择性和稳定性,为芦丁的实际分析提供了可能.
[1] LIU M,DENG J,CHEN Q,et al.Sensitive detection of rutin with novel ferrocene benzyne derivative modified electrodes [J].Biosensors & Bioelectronics,2013,41:275-281.
[2] GHOLIVAND M B,MOHAMMADI-BEHZAD L,HOSSEINKHANI H.Application of a Cu-chitosan/multiwalled carbon nanotube film-modified electrode for the sensitive determination of rutin [J].Analytical Biochemistry,2016,493:35-43.
[3] YANG S,WANG G,LI G,et al.Decoration of graphene modified carbon paste electrode with flower-globular terbium hexacyanoferrate for nanomolar detection of rutin [J].Electrochimica Acta,2014,144:268-274.
[4] LIU Z,XUE Q,GUO Y.Sensitive electrochemical detection of rutin and isoquercitrin based on SH-beta-cyclodextrin functionalized graphene-palladium nanoparticles [J].Biosensors & Bioelectronics,2016,89:444-452.
[5] ZHANG K,XU J,ZHU X,et al.Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanorods grown on graphene oxide sheets as electrochemical sensing platform for rutin [J].Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry,2015,739:66-72.
[6] 岳莹,梁卿,郭勇,等.介孔碳纳米纤维修饰电极用于黄酮类化合物芦丁的电化学测定[J].分析测试学报,2012,31(8):915-921.
YUE Y, LIANG Q, GUO Y,et al.Electrochemical determination of the flavonoid:rutin using a mesoporous carbon nanofiber-modified electrode [J].Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2012,31(8):915-921.
[7] GONG A,PING W,WANG J,et al.Cyclodextrin polymer/Fe3O4nanocomposites as solid phase extraction material coupled with UV-vis spectrometry for the analysis of rutin [J].Spectrochimica Acta A,2014,122:331-336.
[8] LIU D,MEI Q,WAN X,et al.Determination of rutin and isoquercetin contents in Hibisci mutabilis Folium in diffe-rent collection periods by HPLC [J].Journal of Chromatographic Science,2015,53:1680-1684.
[9] LI S,ZHANG L,CHEN L,et al.Determination of rutin by chemiluminescence based on a luminol-potassium periodate-ZnSe system [J].Analytical Methods,2016,8:4056-4063.
[10] WANG W,LIN P,MA L,et al.Separation and determination of flavonoids in three traditional chinese medicines by capillary electrophoresis with amperometric detection [J].Journal of Separation Science,2016,39:1357-1362.
[11] SUN W,WANG X,ZHU H,et al.Graphene-MnO2nanocomposite modified carbon ionic liquid electrode for the sensitive electrochemical detection of rutin [J].Sensors & Actuators B-Chemical,2013,178:443-449.
[12] SOARES M S,DA SILVA D F,FORIM M R,et al.Quantification and localization of hesperidin and rutin in Citrus sinensis grafted on C.Limonia after Xylella fastidiosa infection by HPLC-UV and MALDI imaging mass spectrometry [J].Phytochemistry,2015,115:161-170.
[13] LI J,QU J,YANG R,et al.A sensitive and selective electrochemical sensor based on graphene quantum dot/gold nanoparticle nanocomposite modified electrode for the determination of quercetin in biological samples [J].Electroanalysis,2016,28:1322-1330.
[14] YAN L J ,NIU X L,WANG W C.Electrochemical sensor for rutin detection with graphene oxide and multi-walled carbon nanotube nanocomposite modified electrode [J].International Journal of Electrochemical Science,2016:1738-1750.
[15] 孙伟, 王丹,张媛媛,等.电化学沉积纳米金和石墨烯修饰离子液体碳糊电极检测芦丁的研究[J].分析化学,2013,41(5):709-713.
SUN W,WANG D,ZHANG Y Y,Electrochemical deposition of gold and graphene modified ionic liquid carbon paste electrode detection research of rutin [J].Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2013,41(5):709-713.
[16] CUI R,HAN Z,PAN J,et al.Direct electrochemistry of glucose oxidase and biosensing for glucose based on helical carbon nanotubes modified magnetic electrodes [J].Electrochimica Acta,2011,58:179-183.
[17] 赵建军,潘勇,秦莫林,等.纳米金属金属氧化物在电化学传感器中的应用进展[J].化学传感器,2010,30(3):22-29.
ZHAO J J,PAN Y,QIN M L,et al.Progress of electrochemical sensors involving nano-metal/metal oxides [J].Chemical Sensors,2010,30(3):22-29.
[18] AMPELLI C,LEONARDI S G,GENOVESE C,et al.Monitoring of glucose in fermentation processes by using Au/TiO2composites as novel modified electrodes [J].Journal of Applied Electrochemistry,2015,45:943-951.
[19] HU L,FONG C C,ZHANG X,et al.Au nanoparticles decorated TiO2nanotube arrays as a recyclable sensor for photoenhanced electrochemical detection of bisphenol A [J].Environmental Science & Technology,2016,50:4430-4438.
[20] FENG F,MA Z.Sensitive electrochemical detection of hydrazine based on hollow core-satellite hZnS@Au nanoparticles [J].Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical,2016,232:9-15.
[责任编辑:吴文鹏]
Electrochemical behavior and detection of rutin on Au-TiO2modified electrode
XING Ruimin*,ZHAO Xiaoyu,XU Yinxia,LIU Yong,LIU Xiuhua,HE Jianying,LIU Shanhu
(CollegeofChemistryandChemicalEngineering,HenanUniversity,Kaifeng475004,Henan,China)
Au-TiO2nanoparticles were synthesized by deposition-precipitation and used for electrochemical detection of rutin.Emission scanning electron microscopy (SEM),and X-ray powder diffraction (XRD) patterns were used to characterize the morphology,structure and properties of this nanocomposite.Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and amperometrici-tcurve were used to the catalytic performance of Au-TiO2.Under the optimal conditions,the Au-TiO2-Nafion modified GC electrode can be used to determine rutin concentration in a wide linear range from 0.1 μmol/L to 10 μmol/L,and the sensitivity and the detection limit were estimated to be 1.47 μA·μmol·L-1·cm-2and 0.083 μmol/L,respectively,at a signal-to-noise ratio=3 (S/N=3).
Au; TiO2; rutin; electrochemical sensor
2016-09-19.
国家自然科学基金(21105021),河南省高校科技创新团队项目(14IRTSTHN030).
邢瑞敏(1980-),女,副教授,研究方向为纳米材料控制合成及其相关应用.*
,E-mail:xingenjoy@163.com.
O657.1
A
1008-1011(2017)01-0064-06

