高龄髋膝关节置换术后致假体周围感染的相关因素分析
臧泽林,李鹏飞,曹海泉
(南充市中心医院重症医学科,四川 南充637000)
高龄髋膝关节置换术后致假体周围感染的相关因素分析
臧泽林,李鹏飞,曹海泉
(南充市中心医院重症医学科,四川 南充637000)
目的 分析高龄髋膝关节置换术后致假体周围感染发生的相关因素,以期为高龄患者术后感染的控制提供依据。方法 选取2013年1月至2015年10月我院重症医学科收治的31例高龄髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染患者为观察组,同期的31例未发生感染患者为对照组,比较两组患者的年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平、基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史率,同时以Logistic回归分析上述指标与感染的关系。结果 观察组患者的年龄、BMI值、手术时间、基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史率分别为(78.42±5.21)岁、(25.16±2.32)kg/m2、(2.56±0.30)h、58.06%、35.48%、(31.64±2.76)h及32.26%,均高于对照组的(72.60±4.81)岁、(22.87±2.14)kg/m2、(1.98±0.22)h、32.26%、12.90%、(24.08±2.53)h及12.90%,血清白蛋白水平为(31.82±3.85)g/L,低于对照组的(37.67±4.25)g/L,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),且经Logistic回归分析结果显示,上述指标均为术后假体周围感染发生的危险因素(P<0.05)。结论 年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平、基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史率均是高龄髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染发生的相关因素,临床上应给予充分的重视,及时采用干预措施。
高龄;髋膝关节置换术;假体;感染;相关因素
髋膝关节置换术是近年来临床中应用较广泛的治疗方式,关于本治疗方式的研究较多,其中关于高龄髋膝关节置换患者术后感染,尤其是假体周围感染的临床研究并不少见[1-2],但是有关高龄患者术后导致假体周围感染的相关因素研究却较少,相关研究指标的差异也较大[3]。为此,本文就高龄髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染发生的相关因素进行分析,以期为高龄患者术后感染的控制提供依据,现将结果报道如下:
1 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料 选取2013年1月至2015年10月我院重症医学科收治的31例高龄髋膝关节置换术后致假体周围感染患者为观察组,同期的31例未发生感染患者为对照组。对照组患者中,单侧置换者27例,双侧置换者4例;骨关节炎者25例,其他患者6例。观察组患者中,单侧置换者26例,双侧置换者5例;骨关节炎者24例,其他患者7例。两组患者的置换位置及疾病种类比较差异均无统计学意义(χ2=0.241,0189,P>0.05)。
1.2 资料收集 采用回顾性方法收集两组患者的年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平、基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史率并进行比较。
1.3 统计学方法 应用SAS5.0统计学软件进行数据分析,计量资料以均数±标准差(±s)表示,组间比较采用t检验,计数资料比较采用χ2检验,采用多因素Logistic回归分析法分析各项指标与感染的关系,以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 两组患者的年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平及引流管留置时间比较 观察组患者的年龄、BMI值及手术时间均高于对照组,血清白蛋白水平低于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。
表1 两组患者的年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平及引流管留置时间比较(±s)

表1 两组患者的年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平及引流管留置时间比较(±s)
组别对照组(n=31)观察组(n=31) t值P值年龄(岁) 72.60±4.81 78.42±5.21 6.243<0.05 BMI(kg/m2) 22.87±2.14 25.16±2.32 5.972<0.05手术时间(h) 1.98±0.22 2.56±0.30 6.459<0.05血清白蛋白水平(g/L) 37.67±4.25 31.82±3.85 6.213<0.05引流管留置时间(h) 24.08±2.53 31.64±2.76 5.880<0.05
2.2 两组患者的基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率及髋膝部位创伤史率比较 观察组患者的基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率及髋膝部位创伤史率均高于对照组,差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表2。
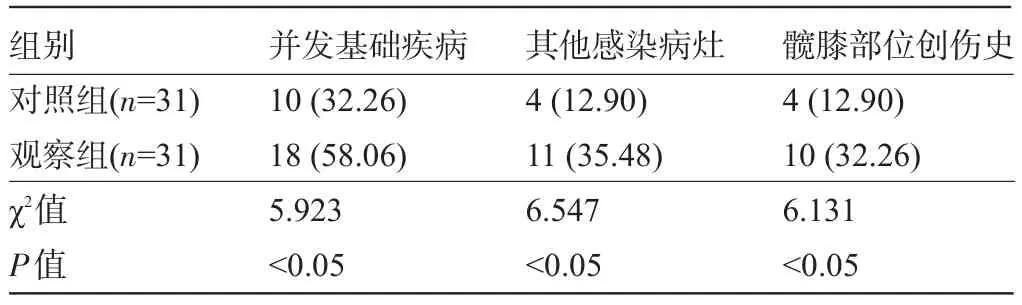
表2 两组患者的基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率及髋膝部位创伤史率比较[例(%)]
2.3 各项指标与术后假体周围感染的关系 经多因素Logistic回归分析结果显示,年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平、并发基础疾病、存在其他感染病灶、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史均与术后假体周围感染发生率有密切的关系,见表3。

表3 观察指标与术后假体周围感染的关系
3 讨论
髋膝关节置换术是临床中用于髋膝关节治疗的常用术式,临床中对于此类手术的相关研究较多见,对于影响患者最终治疗效果的因素的研究也极为常见[4-5]。其中各类围术期并发症是严重影响患者最终治疗效果的重要因素。而假体周围感染作为其中极为重要且危害极大甚至可导致患者置换术失败的一类并发症[6-7],临床对其控制及治疗的重视程度极高。再者,有研究认为假体周围感染不仅仅可导致局部炎性状态的发生,对于下肢的微循环及其他方面状态也有较大的不良影响,因此进一步提升了对假体周围感染防控的必要性。临床中关于假体周围感染的研究虽不少见,但是关于其发生的相关影响因素研究却仍相对不足,而高龄患者作为此类手术患者中较为突出且要求较高的一类人群,对其进行术后假体周围感染相关影响因素的进一步研究价值相对更高[8-9]。
本文中我们就高龄髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染发生的相关因素进行探究,结果显示,此类手术患者术后假体周围感染者较未发生感染者存在明显差异,表现为年龄、BMI值、手术时间、基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史率相对更高,血清白蛋白水平相对更低等方面,且经Logistic回归分析显示,上述指标均与感染的发生有密切的关系,分析原因,我们认为高龄患者本身免疫状态相对较差,其易于发生感染,加之BMI值较高者承重力较高,微循环相对较差等使其假体受到的不良影响更小[10],因此更易于发生感染,再者,手术时间较长者大大延长了病原菌接触时间,因此更易于发生感染,白蛋白较低者营养状态较差[11],存在其他感染病灶及引流管留置时间较长者接触病原菌概率提高,髋膝部位创伤史者其康复速度相对较慢,效果可能相对更差,也更易于发生感染[12]。
综上所述,笔者认为年龄、BMI值、手术时间、血清白蛋白水平、基础疾病并发率、其他感染病灶存在率、引流管留置时间及髋膝部位创伤史率均是高龄髋膝关节置换术后假体周围感染发生的相关因素,应给予充分的重视及干预。
[1]Weber-Spickschen TS,Alfke D,Agneskirchner JD.The use of a modular system to convert an anatomical total shoulder arthroplasty to a reverse shoulder arthroplasty:clinical and radiological results[J]. Bone Joint J,2015,97(12):1662-1667.
[2]McArthur BA,Abdel MP,Taunton MJ,et al.Seronegative infections in hip and knee arthroplasty:periprosthetic infections with normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate and C-reactive protein level[J].Bone Joint J,2015,97(7):939-944.
[3]Rudert M,Holzapfel BM,von Rottkay E,et al.Impaction bone grafting for the reconstruction of large bone defects in revision knee arthroplasty[J].Oper Orthop Traumatol,2015,27(1):35-46.
[4]李勇,魏宪会.全髋关节置换术假体周围感染的危险因素及治疗措施的研究[J].中国实用医刊,2014,41(15):76-77.
[5]Helito CP,Junqueira JJ,Gobbi RG,et al.Effect of postoperative use of nasal oxygen catheter supplementation in wound healing following total knee arthroplasty[J].Clinics(Sao Paulo),2014,69(11): 735-739.
[6]Sprowson AP,Jensen CD,Parsons N,et al.The effect of triclosan coated sutures on rate of surgical site infection after hip and knee replacement:a protocol for a double-blind randomised controlled trial[J].BMC Musculoskelet Disord,2014,14(15):237.
[7]李朔,郭常安,阎作勤.人工关节假体周围感染诊疗的研究进展[J].中国临床医学,2014,21(5):613-616.
[8]Hamaji A,Hajjar L,Caiero M,et al.Volume replacement therapy during hip arthroplasty using hydroxyethyl starch(130/0.4)compared to lactated Ringer decreases allogeneic blood transfusion and postoperative infection[J].Braz JAnesthesiol,2013,63(1):27-35.
[9]Pajarinen J,Jamsen E,Konttinen YT,et al.Innate immune reactions in septic and aseptic osteolysis around hip implants[J].J Long Term Eff Med Implants,2014,24(4):283-296.
[10]Nakano S,Yoshioka S,Tezuka F,et al.New surgical treatment using a docking nail for postoperative periprosthetic femoral fracture after total hip arthroplasty[J].JArthroplasty,2013,28(2):326-330.
[11]Alfargieny R,Bodalal Z,Bendardaf R,et al.Nutritional status as a predictive marker for surgical site infection in total joint arthroplasty [J].Avicenna J Med,2015,5(4):117-122.
[12]Anthony VF,Brian SP,Irving MS.Capturing orthopaedic surgical site infection data and assessing dental recommendations with respect to total joint arthroplasty[J].The Journal of theAmericanAcademy of Orthopaedic Surgeons,2015,23(Supp1):S55-59.
Related factors of infection around the prosthesis of patients with advanced age after hip and knee arthroplasty.
ZANG Ze-lin,LI Peng-fei,CAO Hai-quan.Intensive Care Unit,Nanchong Central Hospital,Nanchong 637000,Sichuan, CHINA
ObjectiveTo analyze the related factors of infection around the prosthesis of patients with advanced age after hip and knee arthroplasty,in order to provide evidence for the control of postoperative infection of patients with advanced age.MethodsA total of 31 patients of advanced age with infection around the prosthesis after hip and knee arthroplasty,who admitted to Intensive Care Unit(ICU)of our hospital from January 2013 to October 2015,were selected as the observation group.At the same time,31 patients without infection were selected as the control group.Then the ages,body mass index(BMI)value,operation time,serum albumin level,basic disease rates,other infection sites rates,drainage tube indwelling time,trauma history rates of hip and knee of the two groups were compared, and the relationship between those indexes and infection were analyzed by the logistic regression analysis.ResultsThe age,BMI value,operation time,basic disease rates,other infection sites rates,drainage tube indwelling time,trauma history rates of hip and knee of the observation group were respectively(78.42±5.21)years,(25.16±2.32)kg/m2,(2.56± 0.30)h,58.06%,35.48%,(31.64±2.76)h and 32.26%,which were all higher than(72.60±4.81)years,(22.87±2.14)kg/m2, (1.98±0.22)h,32.26%,12.90%,(24.08±2.53)h and 12.90%of the control group;while the serum albumin level(31.82± 3.85)g/L of the observation group was lower than(37.67±4.25)g/L of the control group;all of the above differences were statistically significant(P<0.05).Logistic regression analysis showed that those indexes all had close relationship with the postoperative infection around the prosthesis(P<0.05).ConclusionThe age,BMI value,operation time,serum albumin level,basic disease rates,other infection sites rates,drainage tube indwelling time,trauma history rates of hip and knee are all the related factors of infection around the prosthesis of patients with advanced age after hip and knee arthroplasty,so the indexes should be paid enough attention,and timely intervention measures should be taken.
Advanced age;Hip and knee arthroplasty;Prosthesis;Infection;Related factors
R687.4
A
1003—6350(2017)02—0302—03
10.3969/j.issn.1003-6350.2017.02.044
2016-07-15)
臧泽林。E-mail:zweigxy@163.com

