Optimization of indomethacin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers
,S.P.Srinivs,Wree Tiyoonchi,
aDepartment of Pharmaceutical Technology,Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Naresuan University, Phitsanulok,Thailand
bIndiana University,School of Optometry,Bloomington,IN,USA
Optimization of indomethacin loaded nanostructured lipid carriers
Pattravee Niamprema,S.P.Srinivasb,Waree Tiyaboonchaia,*
aDepartment of Pharmaceutical Technology,Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Naresuan University, Phitsanulok,Thailand
bIndiana University,School of Optometry,Bloomington,IN,USA
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 25 November 2015
Indomethacin
Ocular drug delivery
Nanostructured lipid carrier
Mucoadhesive
Non-steroidal anti-infammatory
Topical administration is the most common and acceptable use for the treatment of ocular disease.However,the major problem of ocular drug delivery is the rapid drug elimination from the pre-ocular area leading to poor ocular bioavailability[1]. Nanostructure lipid carriers(NLC)possess a signifcant enhancement in ocular bioavailability by increasing the permeability and mucoadhesive property[2].In this study,indomethacin(IND),non-steroidal anti-infammatory,was used as a model drug[3].Thus,IND loaded NLC(IND-NLC)were developed and characterized.In addition,the mucoadhesive property of IND-NLC was investigated.
IND-NLC were prepared by high pressure homogenization (HPH)technique with various types of solid lipid and surfactant.The mean particle size,Zeta potential and polydispersity index were observed.The entrapment effcacy of IND-NLC was determined by HPLC method.Ex vivo mucoadhesive test was investigated using porcine eye cornea.The particle size of INDNLC was in a range of 40–250 nm with a narrow distribution. The surface of particle exhibited negatively charge of 20–30 mV.The high entrapment effcacy within the range of 60–70%was observed.In addition,IND-NLC exhibited a 2-fold mucoadhesive property than IND solution.This study indicated that the mucoadhesiveness of IND-NLC was successfully prepared by HPH technique.The encapsulation procedure was successfully developed with entrapment effcacy higher than 60%.Therefore,NLC could reasonably be considered as a promising for ocular drug delivery system.
Acknowledgement
The authors acknowledge the fnancial support received from Naresuan University,Thailand.
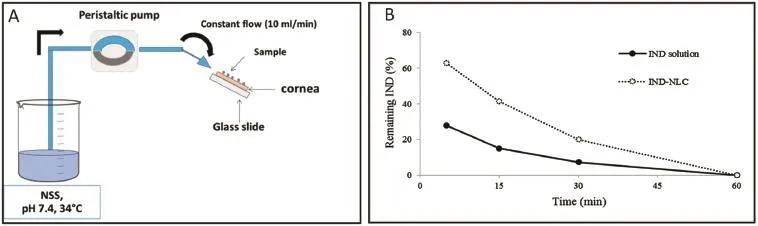
Fig.1–Schematic drawing of the apparatus for ex vivo mucoadhesive tests(A)and ex vivo mucoadhesive of IND-NLC on porcine cornea(B).
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Urtti A.Challenges and obstacles of ocular pharmacokinetics and drug delivery.Adv Drug Deliv Rev 2006;58(11):1131–1135.
[2]Tian BC,Zhang WJ,Xu HM,et al.Further investigation of nanostructured lipid carriers as an ocular delivery system:in vivo transcorneal mechanism and in vitro release study. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 2013;102:251–256.
[3]Badawi AA,El-Laithy HM,El Qidra RK,et al.Chitosan based nanocarriers for indomethacin ocular delivery.Arch Pharm Res 2008;31(8):1040–1049.
*E-mail address:wareet@nu.ac.th.
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.11.053
1818-0876/©2016 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
