Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
Jin Seob Oh,Seo Hyun Lim,Sung Ha Ryu,Kyung Hun Kim, Kyung Soo Lee,Woo Heon Song,Jun Sang Park
GL PharmTech Corporation,#714,Jungang Induspia V,137,Sagimakgol-ro,Jungwon-gu,Seongnam, Gyeonggi-do,Republic of Korea
Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
Jin Seob Oh,Seo Hyun Lim,Sung Ha Ryu,Kyung Hun Kim, Kyung Soo Lee,Woo Heon Song,Jun Sang Park*
GL PharmTech Corporation,#714,Jungang Induspia V,137,Sagimakgol-ro,Jungwon-gu,Seongnam, Gyeonggi-do,Republic of Korea
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 25 November 2015
Pregabalin
Polyethylene oxide
Related compound
HPLC
Pregabalin,(S)-3-amino methyl hexanoic acid,is a structural analogue of γ-amino butyric acid(GABA)which has been widely used to treat partial seizures and neuropathic pain[1].It is soluble in aqueous solution and sparingly soluble in organic solvents such as ethanol,DMSO and DMF.Polyethylene oxide(PEO)has a strong negative effect on analysis of hydrophilic active ingredient and its relative substances due to extremely high viscosity of PEO in aqueous media.The aim of this study is to develop a fast and precise method for the determination of pregabalin and its relative substances in extended release tablets including PEO using sodium sulfate for the treatment of sample solution.
In order to remove effect of PEO in aqueous media,sodium sulfate solution in the range of 0.2–1.0 mol/L was pretreated. Viscosity of solution was evaluated by a viscometer for the determination of optimal concentration of sodium sulfate(Fig.1). Identifcation of precipitate after the pretreatment of sodium sulfate was evaluated by Raman spectroscopy[2].The separation of HPLC for 100 μL of sample solution was accomplished on a Capcellpak C18(4.6×250 mm,5 μm)column using gradient mobile phase consisting of pH 6.5 ammonium phosphate buffer and acetonitrile at the fow rate of 0.8 mL/min.The wavelength of UV detection was set at 210 nm.The chromatographic parameters monitored were peak retention time and theoretical plate number.The developed method was validated for specifcity,linearity,accuracy and precision according to the USP 35 and ICH guideline.
More than 0.5 mol/L of sodium sulfate effciently precipitated PEO to signifcantly reduce viscosity of aqueous solution from 4300–4500 g/cm·s to 1.4–1.5 g/cm·s.Precipitated PEO was identifed by Raman spectroscopy.The linearity of pregablin and its related substances over the range of 1.5–18.0 μg/mL was proven to show superior correlation coeffcient more than 0.997. The limit of detection and quantifcation were 0.10 μg/mL and 0.31 μg/mL respectively.Recovery between 96.6 and 107.7%at three concentration levels and%RSD of precision between 0.2 and 2.3%were obtained[3].As a result,this method was proven to be validated.Compared with the previous methods,this pretreatment method using sodium sulfate is superior withrespect to effcient removal of PEO effect for analysis of pregabalin and its related substances.This established method from the research is expected to contribute to adequate quality control through accurate and simple analysis of hydrophilic compounds in extended release dosage forms containing PEO.
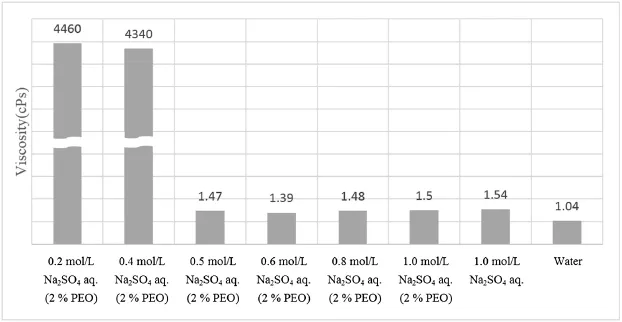
Fig.1–Comparison of the viscosity depending on the concentration of sodium sulfate.
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Jung YE,Chae JH.Pharmacotherapy of generalized anxiety disorder and pregabalin.Korean J Psychopharmacol 2008;19:136–146.
[2]Maxfeld J,Shepherd I.Conformation of poly(ethylene oxide) in the solid state,melt and solution measured by Raman scattering.Polymer 1975;16:505–509.
[3]Sripathi S,Somesetti NR,Veeramalla R,et al.Synthesis and characterization of impurities of an anticonvulsant drug, Pregabalin.ARKIVOC 2010;10:266–275.
*E-mail address:jspark@glpt.co.kr.
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.11.022
1818-0876/©2016 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Factors affecting formation of nanoemulsions containing modifed coconut oil and spearmint oil
