Fucose-appended dendrimer/α-cyclodextrin conjugate as a novel NF-κB decoy carrier to Kupffer cells infulminant hepatitis mice induced by lipopolysaccharide
,Chiho Ako,Ryosuke Mitsuysu, Tishi Higshi,Hidetoshi Arim,b,
aGraduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Kumamoto University,5-1 Oe-honmachi,Chuo-ku,Kumamoto, Japan
bProgram for Leading Graduate Schools“HIGO(Health Life Science:Interdisciplinary and Glocal Oriented) Program,”Kumamoto University,5-1 Oe-honmachi,Chuo-ku,Kumamoto,Japan
Fucose-appended dendrimer/α-cyclodextrin conjugate as a novel NF-κB decoy carrier to Kupffer cells infulminant hepatitis mice induced by lipopolysaccharide
Keiichi Motoyamaa,Chiho Akaoa,Ryosuke Mitsuyasua, Taishi Higashia,Hidetoshi Arimaa,b,*
aGraduate School of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Kumamoto University,5-1 Oe-honmachi,Chuo-ku,Kumamoto, Japan
bProgram for Leading Graduate Schools“HIGO(Health Life Science:Interdisciplinary and Glocal Oriented) Program,”Kumamoto University,5-1 Oe-honmachi,Chuo-ku,Kumamoto,Japan
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 25 November 2015
Cyclodextrins
Dendrimer
Fucose
Fulminant hepatitis
NF-κB decoy
Fulminant hepatitis is a serious,life-threatening disorder and is associated with infammatory cytokines produced by Kupffer cells.However,a number of clinical trials for the treatment of fulminant hepatitis did not show enough substantial benefts.Since NF-κB is a key mediator of infammatory response in Kupffer cells,NF-κB decoy would be an attractive candidate for the treatment of fulminant hepatitis.Recently, Opanasopit et al.revealed that fucosylated protein is preferentially taken up by Kupffer cells via a fucose receptor(Fuc-R).Therefore,the fucosylation to NF-κB decoy carrier is one of the prominent approaches for Kupffer cell-selective delivery. We recently reported that thioalkylated mannose-modifed star burst polyamidoamine(PAMAM)dendrimer/α-cyclodextrin conjugates(Man-S-α-CDE(G3))has the potential for a novel antigen presenting cell-selective siRNA carrier[1].However,there is no report on fucose-appended α-CDE as a Kupffer cell-selective NF-κB decoy carrier.Therefore,in the present study,we newly synthesized fucosyl-oxypropyl-thio-propionylated α-CDE(Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2)(Fig.1A))and evaluated the potential of Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2)/NF-κB decoycomplex for the treatment of fulminant hepatitis[2].
Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2,average degree of substitution of fucose (DSF)2)/NF-κB decoy complex signifcantly suppressed nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-α(TNF-α)production from lipopolysaccharide(LPS)-simulated NR8383 cells,a rat alveolar macrophage cell line,by adequate physicochemical properties and fucose receptor-mediated cellular uptake.Intravenous injection of Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2,DSF2)/NF-κB decoy complexextended the survival of LPS-induced fulminant hepatitis model mice,compared to those of NF-κB decoy alone and jetPEI™-Macrophage/NF-κB decoy complex(Fig.1B).In addition,Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2,DSF2)/NF-κB decoy complex administered intravenously highly accumulated in the liver,compared to naked NF-κB decoy alone.Furthermore,the liver accumulation of Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2,DSF2)/NF-κB decoy complex was inhibited by the pretreatment with GdCl3,a specifc inhibitor of Kupffer cell uptake.Also,the serum aspartate aminotransferase(AST),alanine aminotransferase(ALT)andTNF-α levels in LPS-induced fulminant hepatitis model mice were signifcantly attenuated by the treatment with Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2,DSF2)/ NF-κB decoy complex,compared with naked NF-κB decoy alone. Taken together,these results suggest that Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2, DSF2)has the potential for a novel Kupffer cell-selective NF-κB decoy carrier for the treatment of LPS-induced fulminant hepatitis in mice.
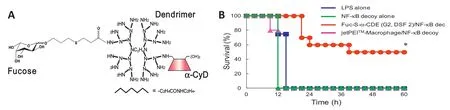
Fig.1–Chemical structure of Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2)(A)and effects of Fuc-S-α-CDE(G2,DSF2)/NF-κB decoy complex on survival curve of fulminant hepatitis mice induced by LPS.Each line represents the survival of 4–10 mice.*P<0.05 versus LPS alone (B).
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Motoyama K,Mitsuyasu R,Akao C,et al.Design and evaluation of thioalkylated mannose-modifed dendrimer (G3)/a-cyclodextrin conjugates as antigen-presenting cellselective siRNA carriers.AAPS J 2014;16:1298–1308.
[2]Akao C,Tanaka T,Onodera R,et al.Potential use of fucoseappended dendrimer/α-cyclodextrin conjugates as NF-κB decoy carriers for the treatment of lipopolysaccharideinduced fulminant hepatitis in mice.J Control Release 2014;193:35–41.
*E-mail address:arimah@gpo.kumamoto-u.ac.jp.
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.11.080
1818-0876/©2016 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
