Development of charged liposomal delivery system for enhanced algicidal effect of DP-92
Yu Jin Cho,Jun-Pil Jee
College of Pharmacy,Chosun University,Gwangju 501-759,Republic of Korea
Development of charged liposomal delivery system for enhanced algicidal effect of DP-92
Yu Jin Cho,Jun-Pil Jee*
College of Pharmacy,Chosun University,Gwangju 501-759,Republic of Korea
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 25 November 2015
Harmful algae
Liposome
Algicidal activity
Delivery system
Harmful algal blooms(HABs)known as red tides have brought serious problems in marine environments and aquaculture industries,and have threatened marine organisms and human health.Several methods have been studied to treat HABs such as clay focculants,bioresources and chemical algicides.Although the usage of chemical algicides is the most common method for the management of HABs effects,the undesirable toxicity and economical cost limit the wide application of chemical algicides[1].
We have chemically synthesized series of thiazolidinedione (TD)derivatives to manage the HABs.The TD derivatives exhibited remarkable algicidal effect on HABs,especially green tide,however,did not exhibit the effect on red tide.To treat red tide,new algicidal agent,N-[(3,4-dichlorophenyl)methyl]cyclohexanamine(DP-92), was synthesized.DP-92 induced a high degree of selective algicidal effect on red tide.However,DP-92 was not soluble in aqueous solution and improvement of its solubility was needed to enhance its algicidal effect and wide application in marine environment[2,3].
In order to improve algicidal effect of DP-92,we designed the charged liposomal delivery system for DP-92 and evaluated the algicidal effects of DP-92 loaded liposomal delivery systems.
Liposomes were prepared with phospholipids,cholesterol and algicidal agent DP-92.L-α-phosphatidylcholine(EggPC),1,2-di-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine(DOPC)or 1,2-di-(9Z-octadecenoyl)-3-trimethylammonium-propane chloride salt(DOTAP)was employed to prepare different surfacecharged liposomes.The properties of liposomes were characterized such as mean diameter,zeta potential and encapsulation effciency(EE%).To evaluate the algicidal effect of the charged liposomes,Heterosigma akashiwo(H.akashiwo),a type of red tide,was exposed to DP-92 loaded liposomes at fnal DP-92 concentrations of 0.05,0.1,0.2,0.4,0.5 and 1 μM for 24 h, and IC50value was calculated.Mean diameter of the liposomes composed of Egg PC,DOPC and DOTAP were 179.4±0.3, 136.7±0.09 and 166.6±0.22 nm,respectively,and their zeta potential value were−32.5±0.8,−5.7±0.5 and+25.6±1.2 mV, respectively.EE%values of the liposomes were 95,95 and 98%, respectively.IC50values of DP-92 in liposomes against H.akashiwo were lower than that of free DP-92 in DMSO (0.62 μM).Especially,DP-92 in positively charged liposome had the lowest IC50value as 0.51 μM.The charge–chargeinteraction between the positively charged surface of the liposomes and the negatively charged wall of H.akashiwo results in more effcient delivery DP-92 to H.akashiwo and higher algicidal effect compared to those of neutral or negatively charged liposome.
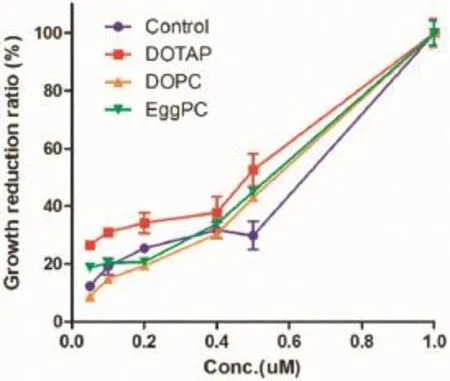
Fig.1–Algicidal effciency of liposomal delivery system for DP-92(means±S.D.,n=3).
In conclusion,the positively charged liposomal delivery system for DP-92 appeared to be effective to enhance the effcacy of DP-92 and showed great potential as an effective tool for treatment of HABs.
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Kim YM,Wu Y,Duong TU,et al.Algicidal activity of thiazolidinedione derivatives against harmful algal blooming species.Mar Biotechnol(NY)2012;14(3):312–322.
[2]Han HK,Kim YM,Lim SJ,et al.Enhanced effcacy of TD53,a novel algicidal agent,against the harmful algae via the liposomal delivery system.Int J Pharm 2011;405(1–2):137–141.
[3]Son M,Baek SH,Shin K,et al.Effects of the algicide, thiazolidinedione derivative TD49,on microbial communities in a mesocosm experiment.Environ Monit Assess 2015;187(4):163.
*E-mail address:jee@chosun.ac.kr.
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.11.081
1818-0876/©2016 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
