Formulation development of nifedipine controlled-release coated tablets
Ananya Ubonratana,Sirachaya Choosakul,Nara Nilnakara, Chaisan Sriwichupong,Garnpimol Ritthidej
Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy,Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Chulalongkorn University,Bangkok 10330,Thailand
Formulation development of nifedipine controlled-release coated tablets
Ananya Ubonratana*,Sirachaya Choosakul,Nara Nilnakara, Chaisan Sriwichupong,Garnpimol Ritthidej
Department of Pharmaceutics and Industrial Pharmacy,Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Chulalongkorn University,Bangkok 10330,Thailand
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 24 November 2015
Nifedipine
Extended release tablet
Matrix
Sodium alginate
HPMC
Due to frequent administration of oral nifedipine tablet,controlled or sustained release of the drug will improve patient compliance,stable blood level and side effect decrement[1,2]. Various extended release nifedipine products have been commercially available.In this study,extended release tablets of this drug were formulated using sodium alginate, hydroxypropylmethylcellulose(HPMC)as controlled release matrix materials.Small scale production of 200 tablets and scale-up production to 5000 tablets were performed by manual and electrical single punch tableting machines.The tablets were then flm coated.Physicochemical evaluation was followed USP 32 including assay,content uniformity and impurities analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography. The effect of amount of the polymers and lactose on drug release was compared.Moreover,stability study of the selected formulation was performed at room temperature (25°C).
The obtained core tablets had satisfactory appearance with yellowish color due to color of the nifedipine raw material.After coating,smooth surface and white color of titanium dioxide was yielded in order to preventing light-exposure.All tested samples had hardness of about 11 kg,uniformed tablet weight with low%friability.The drug assay,content uniformity and impurities were within compendial criteria.Dissolution testing using Apparatus 2 revealed that formulation with lower ratio of sodium alginate to HPMC increased the initial release compared to the formulation with higher ratio(Fig.1b vs Fig.1a) while formulation without lactose further improved the dissolution even though with higher concentration of matrix polymers(Fig.1c).Large scale production could have higheror deviated drug release possibly due to different compression force and speed.However,optimized formulation could be obtained and comparable to commercial tablet(Fig.1d).
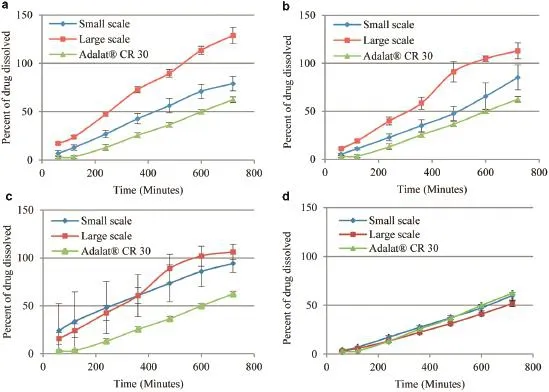
Fig.1–Dissolution profle of the selected formulations prepared with small scale and large scale production:sodium alginate:HPMC:lactose=50:90:30(a),sodium alginate:HPMC:lactose=80:60:30(b),sodium alginate:HPMC:lactose=90:110:0 (c),sodium alginate:HPMC:lactose=50:60:90(d)compared to commercial tablet.
Acknowledgements
Research funding from TCELS(Thailand Center of Excellence for Life Sciences)was greatly appreciated.
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Kojima H,Yoshihara K,Sawada T,et al.Extended release of a large amount of highly water soluble diltiazem hydrochloride by utilizing counter polymer in polyethylene oxides(PEO)/ polyethylene glycol(PEG)matrix tablets.Eur J Pharm Biopharm 2008;70:556–562.
[2]Maderuelo C,Zarzuelo A,Lanao JM.Critical factors in the release of drugs from sustained release hydrophilic matrices. J Control Release 2011;154:2–19.
*E-mail address:ppearpair.au@gmail.com.
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.11.098
1818-0876/©2016 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
