Microemulsion-based hydrogels of itraconazole: Evaluation of characteristics and stability
Sugitt Sngdungyng Suttip SukswtVeerwt Teernchideekul
aFaculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Prince of Songkla University,Songkla,Thailand
bFaculty of Pharmacy,Mahidol University,Bangkok,Thailand
Microemulsion-based hydrogels of itraconazole: Evaluation of characteristics and stability
Prapaporn Boonmea,*,Jarika Kaewbanjonga,Sugitta Sangduangyanga, Suttipa Suksawata,Veerawat Teeranachaideekulb
aFaculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Prince of Songkla University,Songkla,Thailand
bFaculty of Pharmacy,Mahidol University,Bangkok,Thailand
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 24 November 2015
Itraconazole
Microemulsion-based hydrogels
Gelling agent
Stability
Itraconazole(ITZ)is a broad spectrum triazole antifungal drug and commercially available as oral forms.However,effective topical forms are interesting to avoid systemic adverse effects, to directly deliver antifungal drugs to the target sites and to enhance patient compliance[1].Microemulsion-based hydrogel(MBH),a semisolid form of microemulsion(ME),is one of novel formulations practically used as topical drug carriers[2]. This study aimed to develop formulations of ITZ-loaded MBHs having advantageous properties and high stability.
Phase diagram of a system containing Tween 80(T80),propylene glycol(PG),ethyl oleate(EO)and water(W)was constructed by water titration method to obtain ME region. Blank oil-in-water(o/w)ME was selected from the region and prepared by simply mixing.Blank MBHs were then produced by combining ME with a hydrophilic gelling agent,i.e.,carbomer 934(C934),hydroxypropyl methylcellulose 1500(HPMC)or xanthan gum(XG),at various concentrations.They were characterized for appearance,pH,conductivity and viscosity. Satisfed formulations were incorporated with 0.5%ITZ. Subsequently,ITZ-loaded MBHs were evaluated for physical and chemical properties before and after being stored in clear glass containers at room temperature for 8 weeks.The drug content was quantitatively determined by UV spectrophotometric technique[3].Briefy,ITZ in each sample was extracted with methanol and then measured absorbance against methanol at 262 nm.The drug content of the sample was calculated using the calibration curve.All experiments were performed in triplicate.Selected o/w ME was composed of 50%3:1 T80:PG,8% EO and 42%W as shown in Fig.1A.MBHs prepared from 1% HPMC or 1%XG were desirable in terms of physical characteristics.Thus,ITZ-HPMC-MBH and ITZ-XG-MBH containing 0.5%ITZ were prepared and evaluated.Both ITZ-loaded MBHs were translucent yellowish gels.Their results of physical stability were exhibited in Fig.1B.A slightly decrease in the pH of both formulations with signifcantly increasing conductivity and viscosity(P-value<0.05,paired t-test)was observed during storage.After stability study,the percent ITZ remaining in ITZ-HPMC-MBH and ITZ-XG-MBH dramatically reducedto be 46.65%and 87.45%,respectively.The results indicated that type of hydrophilic gelling agent affected characteristics and stability of the obtained ITZ-loaded MBHs.
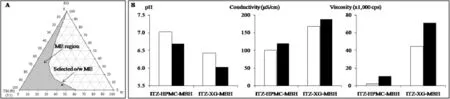
Fig.1–Phase diagram of studied system(A)and characteristics of ITZ-HPMC-MBH and ITZ-XG-MBH before(clear bar)and after(opaque bar)stability study(B).
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the fnancial support received from the Faculty of Pharmaceutical Sciences,Prince of Songkla University and the Nanotec-PSU Center of Excellence on Drug Delivery System,Thailand.ITZ was a gift from Unison Laboratories Co.,Ltd.,Thailand.
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Güngör S,Erdal MS,Aksu B.New formulation strategies in topical antifungal therapy.JCDSA 2013;3:56–65.
[2]Souto EB,Doktorovova S,Boonme P.Lipid-based colloidal systems(nanoparticles,microemulsions)for drug delivery to the skin:materials and end-product formulations.J Drug Deliv Sci Tech 2011;21(1):43–54.
[3]Parikh SK,Patel AD,Dave JB,et al.Development and validation of UV spectrophotometric method for estimation of itraconazole bulk drug and pharmaceutical formulation.Int J Drug Dev Res 2011;3(2):324–328.
*E-mail address:prapaporn@pharmacy.psu.ac.th
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.11.110
1818-0876/©2016 Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
