Doxorubicin:The dogma and the bone
,Pornsk Srimornsk,Crispin R.Dss,
aSchool of Pharmacy,Curtin University,Bentley 6102,Australia
bDepartment of Pharmaceutical Technology,and Pharmaceutical Biopolymer Group(PBiG), Faculty of Pharmacy,Silpakorn University,Nakhon Pathom 73000,Thailand
Doxorubicin:The dogma and the bone
JiaY.Wonga,Pornsak Sriamornsakb,Crispin R.Dassa,*
aSchool of Pharmacy,Curtin University,Bentley 6102,Australia
bDepartment of Pharmaceutical Technology,and Pharmaceutical Biopolymer Group(PBiG), Faculty of Pharmacy,Silpakorn University,Nakhon Pathom 73000,Thailand
A R T I C L E I N F O
Article history:
Available online 23 November 2015
Doxorubicin
Cancer
Tumour
Apoptosis
Cardiotoxicity
Doxorubicin is an anthracycline drug used as frontline chemotherapy of osteosarcoma among other types of cancers. While quite effective in providing a good control over the tumours in some patients,it can cause signifcant toxicity to organs such as the heart[1].Attempts to ameliorate this toxicity with agents such as dexrazoxane have been successful, but not without complications[2]as will be discussed in this talk.Pigment epithelium-derived factor(PEDF),a potent antiangiogenic and osteogenetic protein[3],was used to reduce this side-effect,together with an analysis of levels of adenosine triphosphate(ATP)and reactive oxygen species(ROS).The effects of low dose doxorubicin in a clinically relevant dosing model will be discussed.
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the support of a Curtin Academic 50 scheme and various members of his lab for data generated.
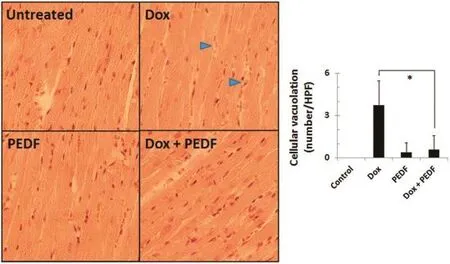
Fig.1 PEDF reduces extent of doxorubicin-induced cellular vacuolation in cardiomyocytes.
R E F E R E N C E S
[1]Tacar O,Sriamornsak P,Dass CR.Doxorubicin:an update on anticancer molecular action,toxicity and novel drug delivery systems.J Pharm Pharmacol 2013;65:157–170.
[2]Bryant J,Picot J,Levitt G,et al.Cardioprotection against the toxic effects of anthracyclines given to children with cancer:a systematic review.Health Technol Assess 2007;11:1–84.
[3]Alcantara MB,Nemazannikova N,Elahy M,et al.Pigment epithelium-derived factor upregulates collagen I and downregulates matrix metalloproteinase 2 in osteosarcoma cells,and colocalises to collagen I and heat shock protein 47 in fetal and adult bone.J Pharm Pharmacol 2014;66:1586–1592.
*E-mail address:Crispin.Dass@curtin.edu.au.
Peer review under responsibility of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ajps.2015.10.016
1818-0876/©2016 The Authors.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.on behalf of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
 Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences2016年1期
- Asian Journal of Pharmacentical Sciences的其它文章
- Determination of the antidepressant effect of mirtazapine augmented with caffeine using Swiss-albino mice
- Photosafety testing of dermally-applied chemicals based on photochemical and cassette-dosing pharmacokinetic data
- Biopharmaceutics classifcation system(BCS)-based biowaiver for immediate release solid oral dosage forms of moxifoxacin hydrochloride (Moxifox GPO)manufactured by the Government Pharmaceutical Organization(GPO)
- Bioequivalence study of abacavir/lamivudine (600/300-mg)tablets in healthy Thai volunteers under fasting conditions
- Evaluation of cytotoxic and infammatory properties of clove oil microemulsion in mice
- Analytical method development of pregabalin and related substances in extended release tablets containing polyethylene oxide
