肌骨超声在类风湿关节炎评估中的应用研究*
唐鸿鹄 王英 刘毅 奉丽丽 刘艺 林辉
(四川大学华西医院 风湿免疫科, 四川 成都 610041)
·论著·
肌骨超声在类风湿关节炎评估中的应用研究*
唐鸿鹄 王英 刘毅 奉丽丽 刘艺 林辉
(四川大学华西医院 风湿免疫科, 四川 成都 610041)
目的 通过肌骨超声评估类风湿关节炎(RA)患者关节受累情况,探讨肌骨超声半定量评价与类风湿关节炎自身抗体、实验室指标、临床评估的相关性,探索类风湿关节炎新的评价体系,完善类风湿关节炎患者的个体化治疗模式。方法 纳入2014年2月至2015年2月间在四川大学华西医院风湿免疫科病房住院的RA患者共30例,用肌骨超声对患者的双手、双腕、双膝的关节分别从关节积液、滑膜增生、腱鞘炎、骨侵蚀四个方面进行扫查和评估,记录超声半定量评价分数。对采集的数据进行分析和比较。结果 在30例 RA患者中,合并关节痛20名(66.7%),不伴关节痛的患者有10名(33.3%)。统计结果显示RA患者受累关节的频率从大到小分别是腕关节、掌指关节(MCP)[MCP2>MCP5>MCP1>MCP3>MCP4]、近端指间关节(PIP)[PIP2>PIP3>PIP1>PIP5>PIP4]、膝关节。RA患者的肌骨超声评分与炎性指标(血沉、C反应蛋白)、自身抗体(RF、CCP)、DAS28评分以及IL-6水平相关(P<0.01)。结论 肌骨超声作为评估和预测患者关节和肌腱受累的有力工具,具有安全、无创、廉价、接受度高等优点,是风湿性疾病的重要诊疗手段之一。肌骨超声对于评估RA患者的亚临床滑膜炎的敏感度高,其评分与RA患者的自身抗体、血白介素6水平、DAS28评分呈正相关。以肌骨超声做为基础,我们的研究离探索出新的关节炎的评价体系更近了一步。
类风湿关节炎; 关节受累; 肌骨超声; 白介素6
类风湿关节炎(Rheumatoid arthritis,RA)是一类慢性致残性疾病,发病率接近0.5%,以异常的自身免疫、炎症以及纤维血管组织导致的滑膜增生及关节破坏为主要特征[1]。血管的异常增生和扩张是RA患者血管翳形成的早期表现,特别是血管增生,是滑膜炎存在和进展的基础[2]。关节及关节周围的滑膜炎以及随之发生的关节结构损伤是RA的主要病理特征[3]。无论在临床试验还是实践中,准确的监测关节滑膜炎对治疗疾病预后都是至关重要的。
在类风湿关节炎患者的关节评估中,影像学检查是一项重要的工具。在RA的早期,放射学影像检查可以显示关节周围软组织(手、足)、近关节的骨质减少、骨质硬化。然而放射学对早期骨侵蚀的检测并不敏感,在软骨和软组织的成像上则存在明显的局限性[4]。炎症的早期控制、持续损伤的阻断有赖于早期探测疾病活动度和损伤的高敏感成像技术的发展。近十年,随着影像学的发展,磁共振和肌骨超声已经逐渐替代X射线用于评估早期RA的结构改变,有利于 RA的早期诊断、治疗和预后的监测[5-6]。因此,本研究选择高频肌骨超声对RA患者进行关节评估,探讨肌骨超声半定量评价与RA患者自身抗体、实验室指标、临床评估的相关性。
1 对象和方法
1.1 研究对象 本研究纳入2014年2月至2015年2月间在四川大学华西医院风湿免疫科病房住院的RA患者共30例,其中男性患者7例,女性患者23例; 年龄18岁~68岁,平均年龄(43.57±12.26)岁;RA患者就诊时病程3~80月,平均(22.67±20.94)月。按是否有关节痛分为RA关节痛组(n=20)和RA无关节痛组(n=10)。所有纳入患者均符合1987年美国风湿病学会(ACR)修订的RA分类标准,排除合并其他结缔组织病包括系统性红斑狼疮、脊柱关节炎等,排除近期合并重症感染的患者。本研究获得了四川大学华西医院伦理委员会批准,且取得受试者的知情同意。
1.2 研究仪器 本研究采用了Esaote MyLab20 超声仪器(探头频率分别为8~12 MHz、12~18 MHz)。
1.3 研究方法
1.3.1 超声评估半定量 OMERACT (Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials)第七次会诊发表了超声在类风湿关节炎患者的关节评估定义包括关节积液、滑膜炎、腱鞘炎/腱周炎、骨质侵蚀[7]。在本研究中,我们也借鉴了该项定义及关节的半定量评分系统。
1.3.2 RA患者临床资料 收集包括患者年龄、性别、发病时间、发病年龄、临床表现、体格检查、治疗方案;检测所有RA患者的血沉、CRP、RF、CCP、血清IL-6。
1.3.3 RA患者的临床评估 对所有RA患者进行DAS28评估。
1.3.4 统计学方法 采用SPSS 20统计软件进行分析,计量资料使用平均值±标准差,计数资料使用百分比或者频数分别进行描述,完成正态分布检验、独立样本t检验,Kruskal-Wallis检验,对参数进行Spearman相关分析,P<0.01有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1 RA患者的一般资料 两组患者在性别、年龄、病程、CCP抗体的滴度方面的差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);在血沉、CRP、RF滴度、IL-6水平、DAS28评分及超声评分方面的差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05),见表1。

表1 RA患者的临床资料
注:RF:类风湿因子;CCP:抗环瓜氨酸抗体;ESR:血沉;CRP:C反应蛋白
2.2 RA患者关节受累特点
2.2.1 RA患者关节受累的频率 在扫查的30例 RA患者共420个关节中,我们发现受累频率最高的是腕关节 28例(93.3%),其次分别是掌指关节(MCP)、近端指间关节(PIP)、膝关节。其中MCP1 17例(56.7%)、MCP2 24例(80.0%)、MCP3 13例(43.3%)、MCP4 8例(26.7%)、MCP5 20例(66.7%);PIP1 8例(26.7%)、PIP2 14例(46.7%)、PIP3 11例(36.7%)、PIP4 3例(10.0%)、PIP5 5例(16.7%)、膝关节受累有14例(46.7%)。RA患者受累关节的频率从大到小分别是腕关节、MCP(MCP2>MCP5>MCP1>MCP3>MCP4)、PIP(PIP2>PIP3>PIP1>PIP5>PIP4)、膝关节(图1)。
2.2.2 RA患者关节受累的类型 我们在RA患者的关节中探查到了滑膜炎、关节积液、腱鞘炎以及骨质侵蚀。在这420个关节中,我们发现受累类型最多的是关节积液288/420(68.6%),其次分别是滑膜炎209/420(49.8%)、腱鞘炎132/420 (31.4%)、骨质侵蚀45/420 (10.7%)。图2显示腕关节滑膜炎的肌骨超声声像表现特征。
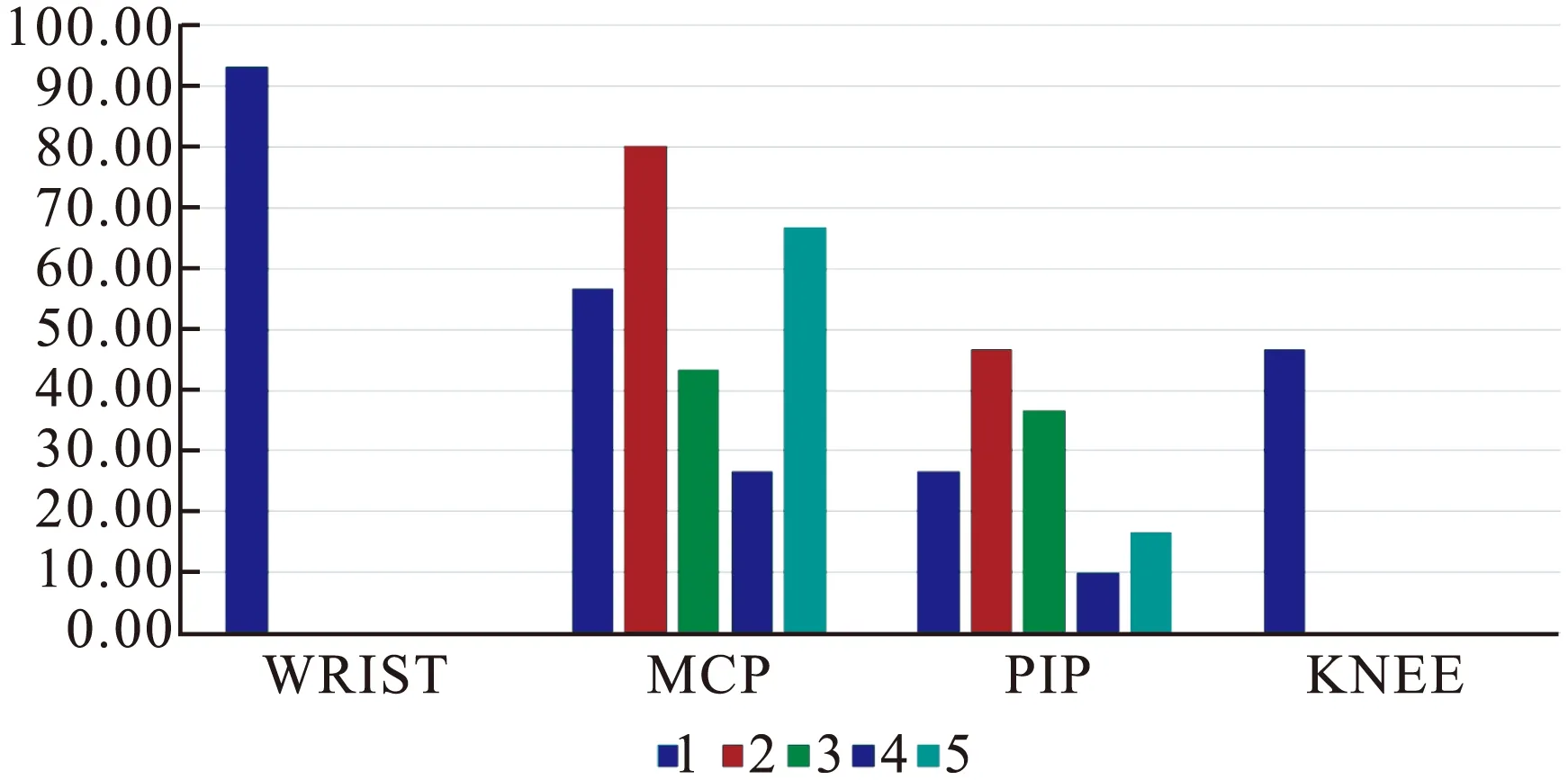
图1 RA患者关节受累的频率[n(×10-2)]
Figure 1 The frequency of joints involved in RA patients
注:Wrist:腕关节;MCP:掌指关节;PIP:近端指间关节;knee:膝关节
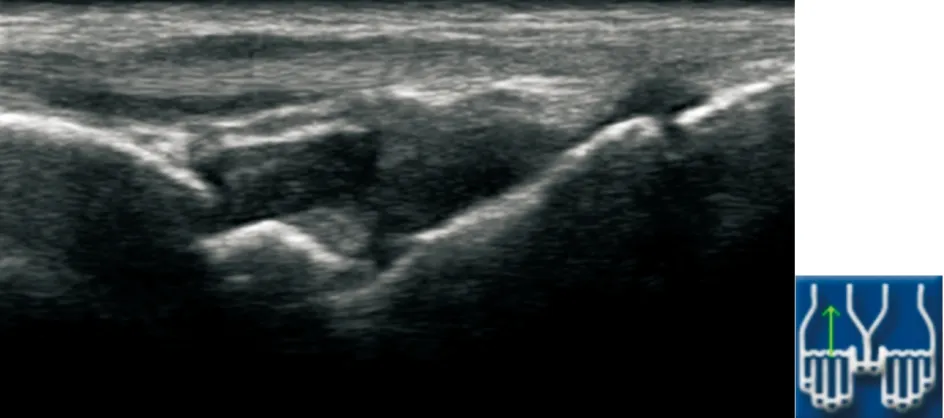
图2 腕关节滑膜炎超声图
Figure 2 Ultrasound pictures of wrist synovitis
2.3 RA患者肌骨超声评分与实验室指标、DAS28评分的相关性 RA患者肌骨超声评分与自身抗体(RF、CCP)、炎性指标(血沉、CRP)、血清IL-6水平、DAS28评分均呈正相关(P<0.01),见表2。
表2 RA超声评分与实验室指标、DAS28评分的相关性
Table 2 The correlation between US evaluation and laboratory indexes, DAS28 in RA patients

RA超声评分rPRF0.8190.000CCP0.5860.001ESR0.8750.000CRP0.9050.000DAS280.8960.000IL-60.9050.000
3 讨论
肌肉骨骼超声(Musculoskeletal ultrasound,MSUS)利用高频超声波(13~17 MHz)构架机体的软组织和骨架,以达到病理诊断或者指导实时介入程序的目的[8]。风湿科医生可以利用高频超声波诊断肌腱炎、部分或全层肌腱撕裂、神经截留、肌肉拉伤、韧带扭伤、关节积液以及介入手术治疗[9]。在过去的十年间,超声的应用体现了以下的优势:①有限的成本。②最小的风险。③重现性好。④敏感度高。因此,在风湿病患者的评估上,超声已逐渐取代了临床常用的成像模式如放射学(X线)、计算机断层扫描(CT)等。
近年MSUS在炎性关节病尤其是RA的患者中的应用越来越多,积累了庞大的数据库[10-13]。有研究显示,对于早期和慢性期的患者而言,掌指关节、近端指间关节以及跖趾关节的评估对疾病整体的评价很有帮助[12,14-15]。应用能量多普勒和彩色多普勒技术可以帮助临床医生区分滑膜增厚是否处于炎症活跃期。研究发现与放射学相比,超声在RA患者中可以探测到更多骨质侵蚀[16-19]。
本研究关注肌骨超声在RA患者的关节评估中的作用,我们通过超声发现在RA患者中,关节受累频率从高到低分别是腕关节、掌指关节、近端指间关节、膝关节,而受累类型以关节积液和滑膜炎为主,这与临床实际相符。在RA患者中,合并关节痛和无关节痛的两组病人之间,超声评分、RF滴度、CRP、血沉、IL-6水平以及DAS28评分均有差异。尽管超声评分在不合并关节痛的RA患者中普遍偏低,但我们通过超声仍然发现关节及关节周围组织异常,包括关节积液、滑膜炎、腱鞘炎,甚至骨质侵蚀,这也表明MSUS探测RA亚临床滑膜炎的可能性较大。
在研究中,我们还探索了肌骨超声评分与自身抗体、炎性指标、细胞因子、临床评分系统的相关性,结果显示,RA患者的超声评分与RF滴度、CCP抗体滴度、血沉、CRP、血清IL-6水平、DAS28评分均呈正相关。简而言之,肌骨超声半定量评分可以充分的反应RA患者的关节情况,成为RA病情评估体系的重要组成部分。
4 结论与启示
肌骨超声作为一项新兴的影像技术,对于风湿性疾病尤其是关节和肌腱异常的评估方面发挥着重要的作用[20-21]。我们的研究旨在建立一套更为完善全面的RA诊断和关节评估体系,但还存在一定的局限性:①样本量太少,探测的关节数目局限,得到的结果可能不够精准。②没有涉及RA的具体治疗策略,因为RA的治疗方案包括非甾体类抗炎药、激素以及慢作用药物,这些药物都对关节炎的评估有一定的影响,属于研究的不可控因素。③单中心研究,且年龄层次不够丰满。
[1]Salaffi F, De Angelis R, Grassi W. Prevalence of musculoskeletal conditions in an Italian pop- ulation sample: results of a regional community-based study. I. The MAPPING study[J]. Clin Exp Rheumatol, 2005,23(6):819-828.
[2]Walsh DA. Angiogenesis and arthritis[J]. Rheumatology, 1999,38(2):103-112.
[3]Conaghan PG, O′Connor P, McGonagle D,etal. Elucidation of the relationship between synovitis and bone damage: a randomized magnetic resonance imaging study of individual joints in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2003,48(1):64-71.
[4]Iagnocco A, Ceccarelli F, Perricone C,etal. The role of ultrasound in rheumatology[J]. Ultrasound CT MR, 2011,32(2):66-73.
[5]Combe B, Dougados M, Goupille P,etal. Prognostic factors for radiographic damage in early rheumatoid arthritis: a multiparameter prospective study[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2001,44(8):1736-1743.
[6]Drossaers-Bakker KW, de Buck M, van Zeben D,etal. Long-term course and outcome of functional capacity in rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of disease activity and radiologic damage over time[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1999,42(9):1854-1860.
[7]Ohrndorf S, Backhaus M. Advances in sonographic scoring of rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2013,72(Suppl 2):ii69-ii75.
[8]Kremkau F. Diagnostic Ultrasound: Principles and Instruments[M]. 6th ed.Philadelphia, PA: WB Saunders, 2002:428.
[9]Smith J,Finnoff JT.Diagnostic and interventional musculoskeletal ultrasound:part1. Fundamentals[J]. PM R, 2009,1(1):64-75.
[10] Grassi W, Cervini C: Ultrasonography in rheumatology: An evolving technique[J]. Ann Rheum Dis,1998,57(5):268-270.
[11] Wakefield RJ, Brown AK, O′Connor PJ,etal. Musculoskeletal ultrasonography:What is it and should training be compulsory for rheumatologists?[J]. Rheumatology, 200,43(7):821-822.
[12] Backhaus M, Kamradt T, Sandrock D,etal. Arthritis of the finger joints:A comprehensive approach comparing conventional radiography, scintigraphy,ultrasound, and contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging[J].Arthritis Rheum,1999,42(6):1232-1245.
[13] Kane D, Balint PV, Sturrock RD. Ultrasonography is superior to clinical examination in the detection and localization of knee joint effusion in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. J Rheumatol,200, 30(5):966-971.
[14] Szkudlarek M, Narvestad E, Klarlund M,etal. Ultrasonography of the metatarsophalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography, and clinical examination[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2004, 50(7):2103-2112.
[15] Szkudlarek M, Klarlund M, Narvestad E,etal. Ultrasonography of the metacarpophalangeal and proximal interphalangeal joints in rheumatoid arthritis: A comparison with magnetic resonance imaging, conventional radiography and clinical examination[J]. Arthritis Res Ther,2006,8(2):R52.doi:10.1186/ar1904.
[16] Backhaus M, Burmester GR, Sandrock D,etal. Prospective two year follow up study comparing novel and conventional imaging procedures in patients with arthritic finger joints[J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2006, 61(5):895-904.
[17] Scheel AK, Hermann KG, Ohrndorf S,etal. Prospective 7 year follow up imaging study comparing radiography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging in rheumatoid arthritis finger joints[J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2006, 65(5):595-600.
[18] Naredo E, Collado P, Cruz A,etal. Longitudinal power Doppler ultrasonographic assessment of joint inflammatory activity in early rheumatoid arthritis: Predictive value in disease activity and radiologic progression[J].Arthritis Rheum,2007, 57(1):116-124.
[19] Taylor PC, Steuer A, Gruber J,etal. Comparison of ultrasonographic assessment of synovitis and joint vascularity with radiographic evaluation in a randomized, placebo-controlled study of infliximab therapy in early rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2004, 50(4):1107-1116.
[20] Scheel AK, Hermann KG, Kahler E,etal. A novel ultrasonographic synovitis scoring system suitable for analyzing finger joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis[J]. Arthritis Rheum,2005, 52(3):733-743.
[21] Naredo E, Bonilla G, Gamero F,etal. Assessment of inflammatory activity in rheumatoid arthritis: A comparative study of clinical evaluation with grey scale and power Doppler ultrasonography[J]. Ann Rheum Dis,2005, 64(3):375-381.
Musculoskeletal ultrasound application in rheumatoid arthritis joint assessment research
TANG Honghu,WANG Ying,LIU Yi,et al
(DepartmentofRheumatologyandImmunology,WestChinaHospital,SichuanUniversity,Chengdu610041,China)
Objective To evaluate the joint involvement in Rheumatoid arthritis(RA) through musculoskeletal ultrasound(MSUS), analyze the relationship between ultrasound assessment and autoantibodies, inflammatory biomarkers and clinical scoring system, explore the evaluation system for lupus arthritis and consummate the individual treatment strategy for RA. Methods 30 patients with RA (7 male patients, 21 female patients) was included in February 2014 to February 2015 in Rheumatology Department, West China Hospital, Sichuan University. We used MSUS to evaluate the hands, wrists and knees from four aspects (joint effusion, synovial hyperplasia, tenosynovitis, bone erosion) respectively and recorded ultrasonic semi-quantitative evaluation scores. All of the datas were collected for analysis and comparising. Results In 30 RA patients, there were 20 cases with painful joints (66.7%) and 10 cases without painful joints(33.3%). In assessments of 420 joints, the frequency of involvement from high to low was wrist, MCP(MCP2>MCP5>MCP1>MCP3>MCP4), PIP(PIP2>PIP3>PIP1>PIP5>PIP4) and knee. We analyze the correlation between the semi-quantitative evaluation of MSUS and autoantibodies, laboratory data, the clinical score. We have found MSUS scores and inflammatory indexes (blood sedimentation, c-reactive protein), DAS28 ratings, the level of IL - 6 are significantly correlated in RA patients.(P<0.01). Conclusion Musculoskeletal ultrasound is a powerful tool to evaluate and predict the affected joints and tendons.MSUS is one of the important diagnostic methods of the rheumatic diseases with safe, noninvasive, cheap, and highly acceptance. Musculoskeletal ultrasound is highly sensitive to evaluate the RA patients with subclinical synovitis. The MSUS scores of patients are positively correlated with RA autoantibodies, the level of interleukin 6 and DAS28 scores. Our study proved the value of new evaluation system of arthritis by musculoskeletal ultrasound.
Rheumatoid arthritis; Joints involvement; Musculoskeletal ultrasound; Interleukin 6
国家自然科学基金(81102274);四川省科技厅国际合作项目(2014HH0027);成都市科技攻关项目(10GGYB644SF-023)
刘毅,教授,博士生导师,本刊常务编委,E-mail:yi2006liu@163.com
R 593.22
A
10.3969/j.issn.1672-3511.2016.11.011
2016-07-01; 编辑: 张文秀)

