具时间依赖边界条件的热传导方程的近似解法研究
廖秋明,李丹霞
(肇庆学院 数学与统计学院,广东 肇庆 526061)
具时间依赖边界条件的热传导方程的近似解法研究
廖秋明,李丹霞
(肇庆学院 数学与统计学院,广东 肇庆 526061)
研究了求解具时间依赖边界条件的热传导方程的近似解。首先,对温度边界条件为时间的幂函数的情况,采用标准的多项式温度近似函数,结合热平衡积分法及改进的热平衡积分法,求得时间的次数和温度近似函数的指数之间的关系,从而确定温度近似解函数;然后,对复杂的时间依赖的边界条件,应用线性微分方程叠加原理,构建近似解表达式。实验结果表明,这种方法既简便又具有良好的计算精度,能较好地模拟传热过程。
时间依赖边界条件;热传导方程;热平衡积分解法;叠加原理;近似解
0 引言
热平衡积分法(heat balance integral method,HBIM),是1958年由T.R.Goodman[1]提出的求解导热问题的有效方法。由于其计算简便、速度快,且计算精度较高,从而得到了广泛应用。改进的热平衡积分法(refined integral method,RIM)是N.Sadoun等[2]提出的一种改进方法。即通过对导热微分方程关于空间变量积分2次,并结合传统的热平衡积分方程,得到一个新的积分方程,所求得的近似解具有更高的精确性。但是,用热平衡积分法求解具时间依赖边界条件的热传导问题时,往往难以得到计算精度良好的近似解。为此,人们提出了各种改进方法及应用[3-9]。如D.Langford[3]采用最小误差测量函数来确定温度近似函数,显示出更高的精确性。T.G.Myers[4-5]利用D.Langford 提出的函数,求得了非整数形式的HBIM 和RIM 最优多项式次数,并将之应用到标准的导热问题及相变导热问题中。但标准的多项式温度近似解,只能解决温度边界条件随着时间递增的情况。S.L.Mitchell等[6]提出了用对数表达式表示近似解以及时间依赖的指数,以解决边界温度随着时间递减情况下的导热近似。Ling Feng等[7]提出了一种优化多项式温度近似解指数的积分方法。J.Hristov[8-9]改进热平衡积分法,并应用于非线性传热问题。
本文采用标准的多项式温度近似函数,当温度边界条件为时间的幂函数时,结合HBIM 和RIM获得时间和温度近似函数的指数之间的关系,从而确定温度近似解表达式,并应用线性微分方程叠加原理,构建近似解,以解决复杂的时间依赖边界条件,以得到简便又计算精度良好的近似解。
1 模型问题
一个半无限大的平板,当时间t>0时,在边界(x=0)处的温度设为(t) ;在有限的时间内,边界的热扰动将渗透到平板有限厚度范围内,即渗透深度记作(t)。半无限大的平板的热传导问题无量纲形式的数学模型为
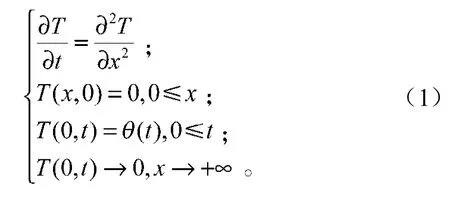
式中:T表示温度;
x表示空间坐标;
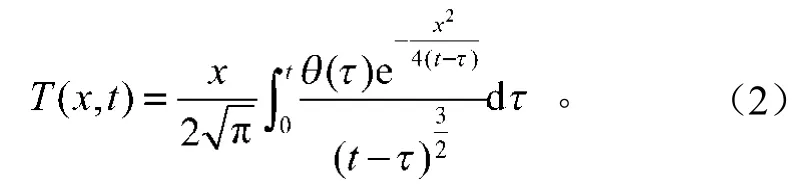
利用余误差函数,可得到精确解:
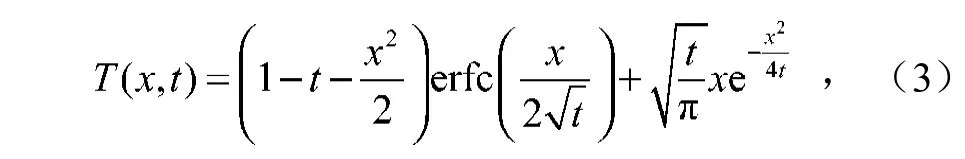
2 问题的近似解
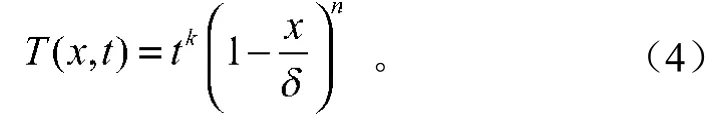
下面结合热平衡积分法及改进的热平衡积分法,求时间t的次数k和n之间的函数关系。
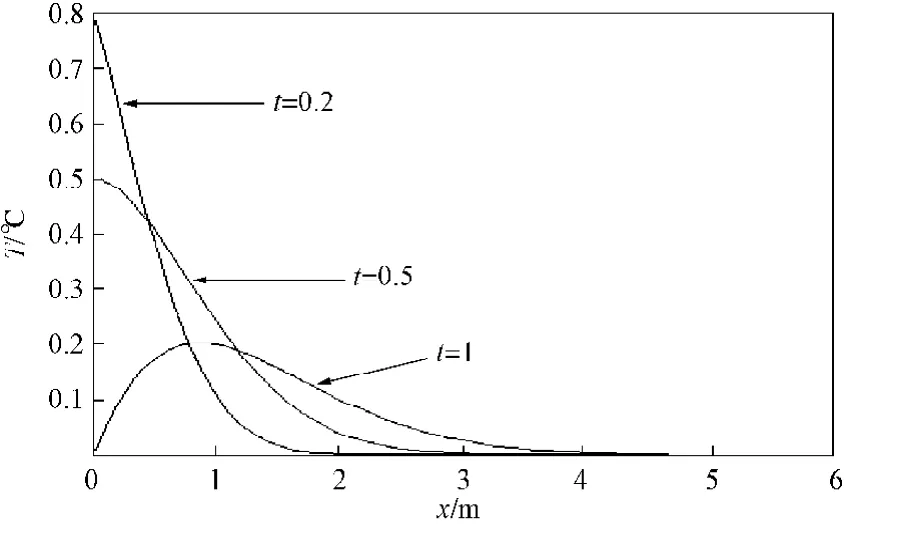
图1 当(t)=1-t时,不同t值下的精确解曲线Fig.1 Exact solution curves under the condition of(t)=1-t with t the variable
对问题(1)关于空间变量x进行积分,得到热平衡积分


下面以本文方法得到的近似解(12)和精确解以及HBIM,RIM的近似解进行实验对比,结果如图2和图3所示。其中HBIM,RIM的近似解同样采用标准的多项式,其指数n依赖时间变化[6],这里不失一般性取t=0.8。
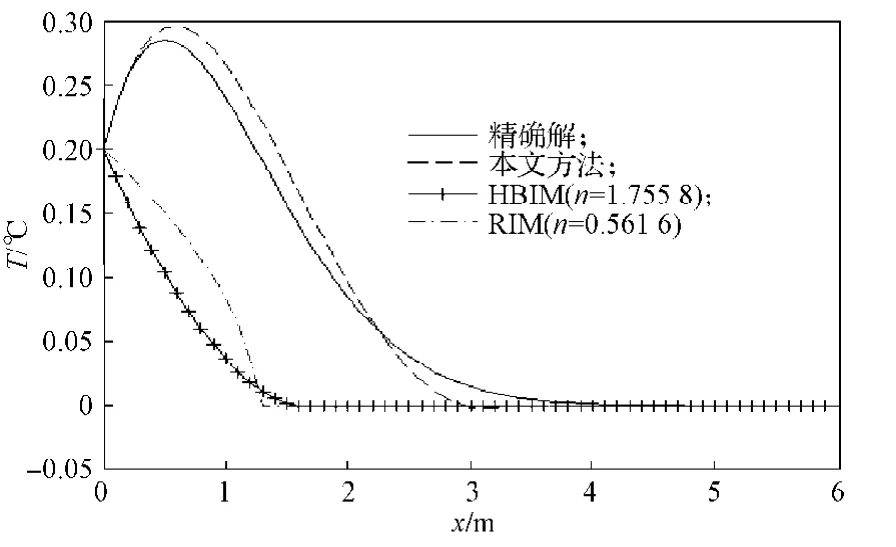
图2 当(t)=1-t , t = 0.8时,本文方法,HBIM,RIM近似解与精确解曲线的比较Fig.2 Curves for the approximate solution of HBIM, RIM and the presented approach as contrast to the exact solution curve when(t)=1-t with t = 0.8
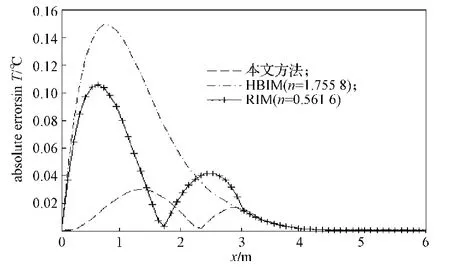
图3 当(t)=1-t,t=0.8时,本文方法,HBIM,RIM近似解与精确解之间的绝对误差比较Fig.3 Curves for the approximate solution of HBIM,RIM and the presented approach as contrast to the absolute error curve when(t)=1-t with t = 0.8
从图2和图3可以看出,采用本文方法得到的近似解和精确解很接近,绝对误差小于0.03,计算精度比HBIM和RIM的近似解更高。
3 结语
在温度边界随时间变化的条件下,采用标准的多项式温度近似函数,首先解决当温度边界条件为时间的基本幂函数时的近似解,结合HBIM和RIM,求得时间的次数和近似解函数的指数之间的关系,从而确定热平衡积分温度近似函数;然后应用线性微分方程叠加原理,构建近似解。该方法简便,得到的近似解精度高。用积分方法求出来的温度近似解不是唯一的,只有计算精度良好的近似解才具实用价值。本文的近似解法能较好地模拟当边界温度随着时间递减情况下传热过程中出现的拐点现象。在本文研究的基础上,可以解决更复杂的传热问题,如相变传热问题、高维传热问题等。
[1] GOODMAN T R.The Heat Balance Integral and Its Application to Problems Involving a Change of Phase[J].Trans ASME Journal of Heat Transfer,1958,80(1/2) :335-342.
[2]SADOUN N,SI-AHMEDE K,COLINET P.On the Refined Integral Method for the One-Phase Stefan Problem with Time-Dependent Boundary Conditions[J].Applied Mathematical Modeling,2006,30(6) :531-544.
[3] LANGFORD D.The Heat Balance Integral Method[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,1973,16(12) :2424-2428.
[4]MYERS T G.Optimal Exponent Heat Balance and Refined Integral Methods Applied to Stefan Problems[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2010, 53(5/6) :1119-1127.
[5]MYERS T G.Optimizing the Exponentin the Heat Balance and Refined Integral Methods[J]. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer,2009,36(2) :143-147.
[6]MITCHELL S L,MYERS T G.Improving the Accuracy of Heat Balance Integral Methods Applied to Thermal Problems with Time Dependent Boundary Conditions[J].International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer,2010,53(17/18) :3540-3551.
[7]LING Feng,LIAO Qiuming.A Novel Optimal Power Approach in Heat Balance Integral Method and Refined Integral Method[J].Int.J.Pacific Journal of Applied Mathematics,2014,5(3) :41-52.
[8]HRISTOV J.An Approximate Analytical (Integral-Balance)Solution to a Nonlinear Heat Diffusion Equation[J].Thermal Science,2015,19(2) :723-733.
[9]HRISTOV J.Diffusion Models with Weakly Singular Kernels in the Fading Memories: How the Integral-Balance Method can be Applied[J].Thermal Science,2015,19(2) :947-957.
[10]CARSLAW H S,JAEGER J C.Conduction of Heat in Solids[M].Oxford:Clarendon Press,1950 :50-91.
(责任编辑 :邓光辉)
On an Approximate Solution of the Heat Equation Under Time-Dependent Boundary Conditions
LIAO Qiuming, LI Danxia
(School of Mathematics and Statistics,Zhaoqing University,Zhaoqing Guangdong 526061,China)
In order to find an approximate solution of the heat equation under time-dependent boundary conditions,a research has been conducted as shown in the following steps.Firstly, with the power function of time being the temperature boundary condition, combined with the heat balance and refined integral methods, the standard polynomial approximation solution to the temperature equation has been adopted so as to obtain the relationship between the power of the approximate solution and the power of the temperature boundary function, thus working out the approximate solution.Secondly, an approximate solution expression will be constructed based on the application of the principle of superposition of linear differential equation, with the complex time dependent boundary condition taken into consideration.The experimental results show that this simple method, characterized with a better calculation accuracy, proves to be very effective in simulating the heat transfer process.
time-dependent boundary condition ;equation of heat conduction ;heat balance integral method ;principle of superposition ;approximate solution
O175.29
A
1673-9833(2016)04-0078-04
10.3969/j.issn.1673-9833.2016.04.015
2016-06-08
广东省自然科学基金资助项目(2015A030313704)
廖秋明(1972-),男,广东肇庆人,肇庆学院副教授,主要研究方向为偏微分方程理论及应用,E-mail:lqmzqu@163.com

