烟草野火病菌Pseudomonas syringae pv. tabaci yuexi-1信号肽预测及分析
王铁霖,李晶,杨玉文,赵廷昌
中国农业科学院植物保护研究所,植物病虫害生物学国家重点实验室,北京 100193
烟草野火病菌Pseudomonas syringaepv.tabaciyuexi-1信号肽预测及分析
王铁霖,李晶,杨玉文,赵廷昌
中国农业科学院植物保护研究所,植物病虫害生物学国家重点实验室,北京 100193
利用SignalP 4.0、 LipoP 1.0 及TMHMM v2.0对烟草野火病菌Pseudomonas syringaepv.tabaciyuexi-1菌株基因组中信号肽的数量、长度和氨基酸组成进行了预测及分类。结果确定其中432个ORFs (Open reading frame) 所编码的N 端有信号肽序列,占全部ORFs的8.81%。其中351条分泌型信号肽 (SPI),81条脂蛋白型信号肽 (SPII)。在分泌型信号肽中,信号肽的长度为11~42个氨基酸,以长度为22个氨基酸的信号肽最多。同源性分析结果显示,具有相同信号肽序列的不同蛋白序列之间是高度保守的。该研究提供了野火病原菌致病因子的备选基因,提高该病菌致病因子的筛选效率。
Pseudomonas syringaepv.tabaci;信号肽;SignalP 4.0;LipoP 1. 0;TMHMM v2.0
烟草野火病是烟草生产上一种重要的叶部细菌性病害。该病害在苗期、大田期均可发生,主要危害烟草叶片,也可危害幼茎、蒴果、萼片等器官,给烟草种植业造成了巨大的经济损失[1-2]。大部分病原菌的毒素、细胞壁降解酶等致病因子为分泌蛋白。而信号肽在分泌蛋白跨膜、 转运及识别植物受体蛋白过程中起着非常重要的作用[3-4]。
信号肽一般由10~40个氨基酸残基组成,通常大致分为3个区段:其中N端为碱性氨基末端,通常由带正电荷的氨基酸组成;中间为疏水中心,主要由20个或以上的中性氨基酸组成;C端为加工区,含有被信号肽酶裂解的部位,其中小分子氨基酸如甘氨酸、丙氨酸、丝氨酸较多[5,6]。
本实验室对分离自四川越西县烟草病样上的一株致病力很强的烟草野火病菌株 yuexi-1进行了全基因组测序, 结果显示其基因组含有 5701个开放阅读框(open reading frame,ORFs)。本研究根据野火病菌株Pseudomonas syringaepv. tabaciyuexi-1的全基因组测序结果,利用 3 种在线生物信息学分析工具 SignalP 4.0、LipoP 1. 0 和 TMHMM v2.0 对该病菌的信号肽进行预测和分析,为该菌株致病因子的筛选提供备选基因。
1 实验材料及方法
1.1 实验材料
从Genbank上获得Pseudomonas syringaepv. tabaciyuexi-1菌株基因组序列(序列号JWJF00000000) 的fasta 文件和 gb文件。
1.2 预测方法
(1) 使用 SignalP 4.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/SignalP/) 在Gram-negative bacteria选项下预测 yuexi-1菌株基因组所有ORFs的N端氨基酸序列是否存在信号肽。(2) 使用 LipoP 1.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/LipoP/) 分析N端氨基酸序列,预测蛋白质类型。(3) 使用TMHMM Server v. 2.0 (http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM/) 验证预测结果。预测标准根据相关文献执行[19~23]。
2 结果与分析
综合SignalP 4.0、 LipoP 1. 0和TMHMM Server v.2.0的预测结果,对P. syringaepv. tabaciyuexi-1编码蛋白基因的序列分析结果如下:
2.1 信号肽的数量和长度
经预测,yuexi-1菌株基因组有432个ORFs具有信号肽,占全部ORFs的8.81%。信号肽所在的ORFs长度最小为41个氨基酸,最大为1649个氨基酸,平均长度为340个氨基酸,ORFs长度分布在101~200个氨基酸范围内数量最多(图1) 。
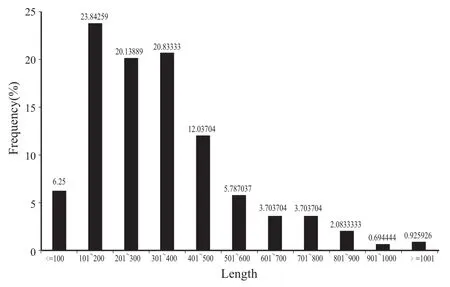
图1 含信号肽的ORFs长度分布Fig. 1 Length distribution of the ORFs containing signals peptides
信号肽的长度在11~41个氨基酸之间,以21~24个氨基酸居多,其中长度为22个氨基酸的信号肽最多,共66条,占15.30%(图2)。
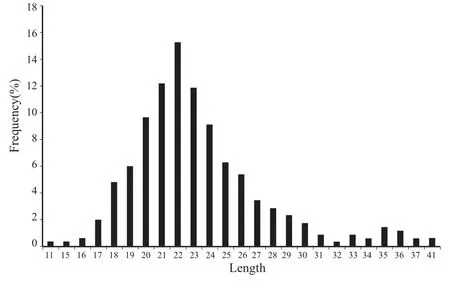
图2 信号肽长度(氨基酸)分布Fig. 2 Length (amino acids) distribution of signal peptide
2.2 氨基酸种类分析
经LipoP 1. 0分析,根据信号肽氨基酸组成及切割位点信号肽识别序列的不同将信号肽分为4种类型:第一类信号肽酶I型 (SPI) 信号肽最为典型[7-9];第二类为信号肽酶II型 (SPII),通常在脂蛋白中出现[10];第三类为IV型菌毛 (Type IV pilin peptidase);第四类通常与细菌素和信息素的合成有关,由ABC转运系统转运[11-13]。
对P. syringaepv. tabaciyuexi-1菌株中的432条信号肽分类结果表明,共有351条SPI型信号肽和81条SPII型信号肽。
2.2.1 信号肽酶I型( SPI型)
SPI型信号肽通常在从分泌蛋白被转运至细胞膜途中或转运至细胞膜后,被切割[14,15]。此类信号肽中存在分泌类信号肽 (Sec-type),其典型结构: N-端由2~3个带正电荷的氨基酸 (K或R) 组成,也有的由5~11个带正电荷的氨基酸组成。N-domain 由平均19个氨基酸构成。C-domain (切割位点前3 位的氨基酸) 的典型结构为A-X-A (A 为丙氨酸, X 指任意一种氨基酸)。
在预测得到的351条SPI型信号肽中,200条信号肽具有A-X-A的典型结构,长度在11~41个氨基酸之间。另一类信号肽具有典型的双精氨酸结构,引导分泌蛋白参与双精氨酸 (Tat) 转运途径,这一类信号肽具有RR-X-## ( X为任意氨基酸,## 指疏水氨基酸) 的保守序列[16-18]。在P. syringepv.tabaciyuexi-1菌株的基因组中, 有 27 条信号肽具有RR-motif 的保守区段,其长度在17-42个氨基酸之间。其中17 条信号肽的C-domain 中出现A-X-A 典型结构 (表1)。如表 1 所示, 这些信号肽参与ABC蛋白转运途径等多种不同分泌途径和相关酶合成代谢途径。
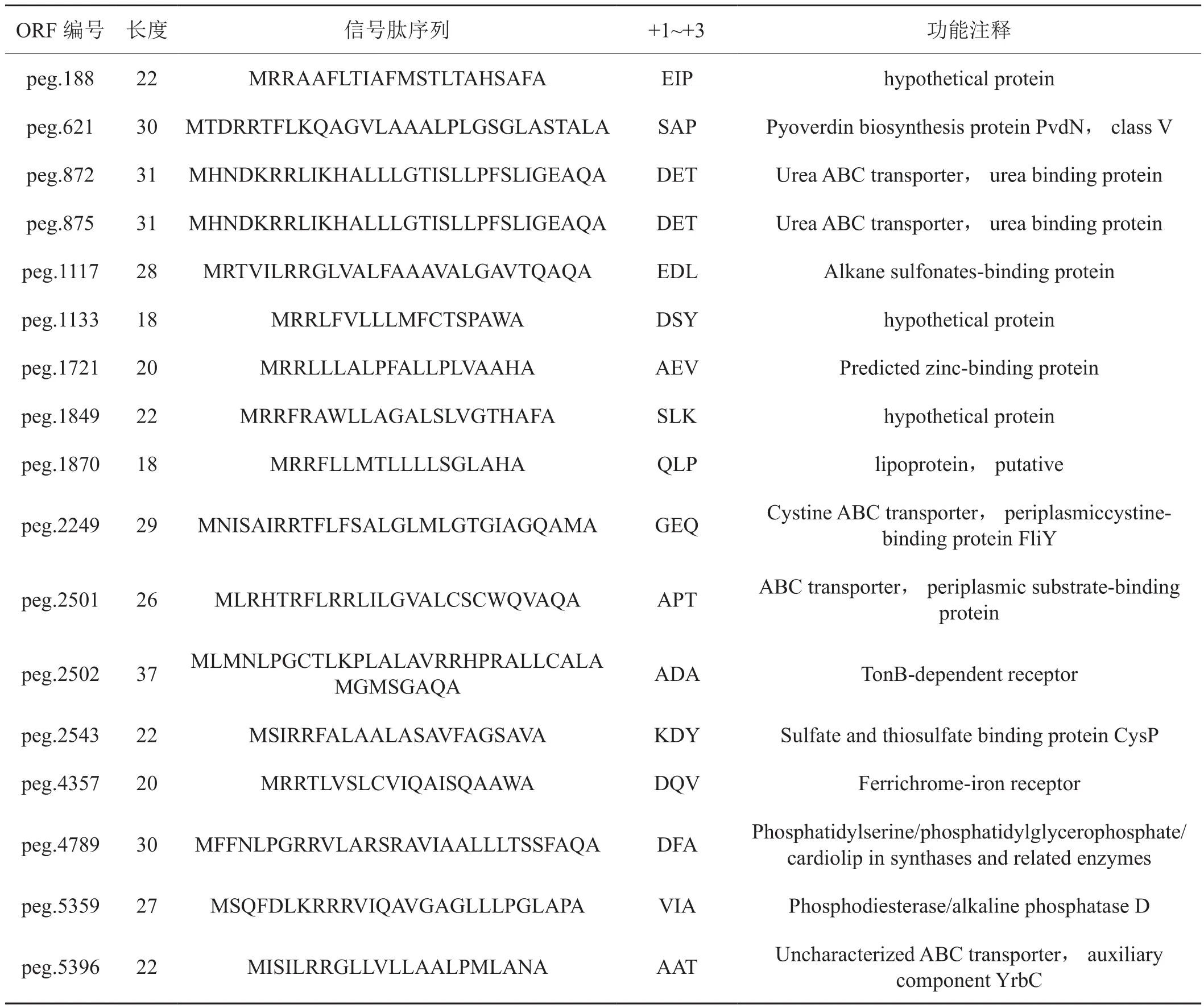
表1 具有典型A-X-A结构的RR-motif型信号肽Tab. 1 RR-motif signal peptides with the typical structure of A-X-A
2.2.2 脂蛋白型信号肽
SPII型信号肽也称为脂蛋白信号肽,其典型结构C-domain为: L-(A /S) -(A /G),在切割位点后+ 1位氨基酸为半胱氨酸(C),这样就形成了保守的L-(A /S)-(A /G)-C的Li-pobox典型结构,该结构使脂蛋白被切割后依然能够锚定在质膜上。该类信号肽通常比分泌型信号肽短。
在P. syringaepv.tabacistrain yuexi-1中,共有81个脂蛋白型信号肽,其长度在14~36个氨基酸之间。其中有 37 (1.32%) 条信号肽具有Li-pobox典型结构(表2)。
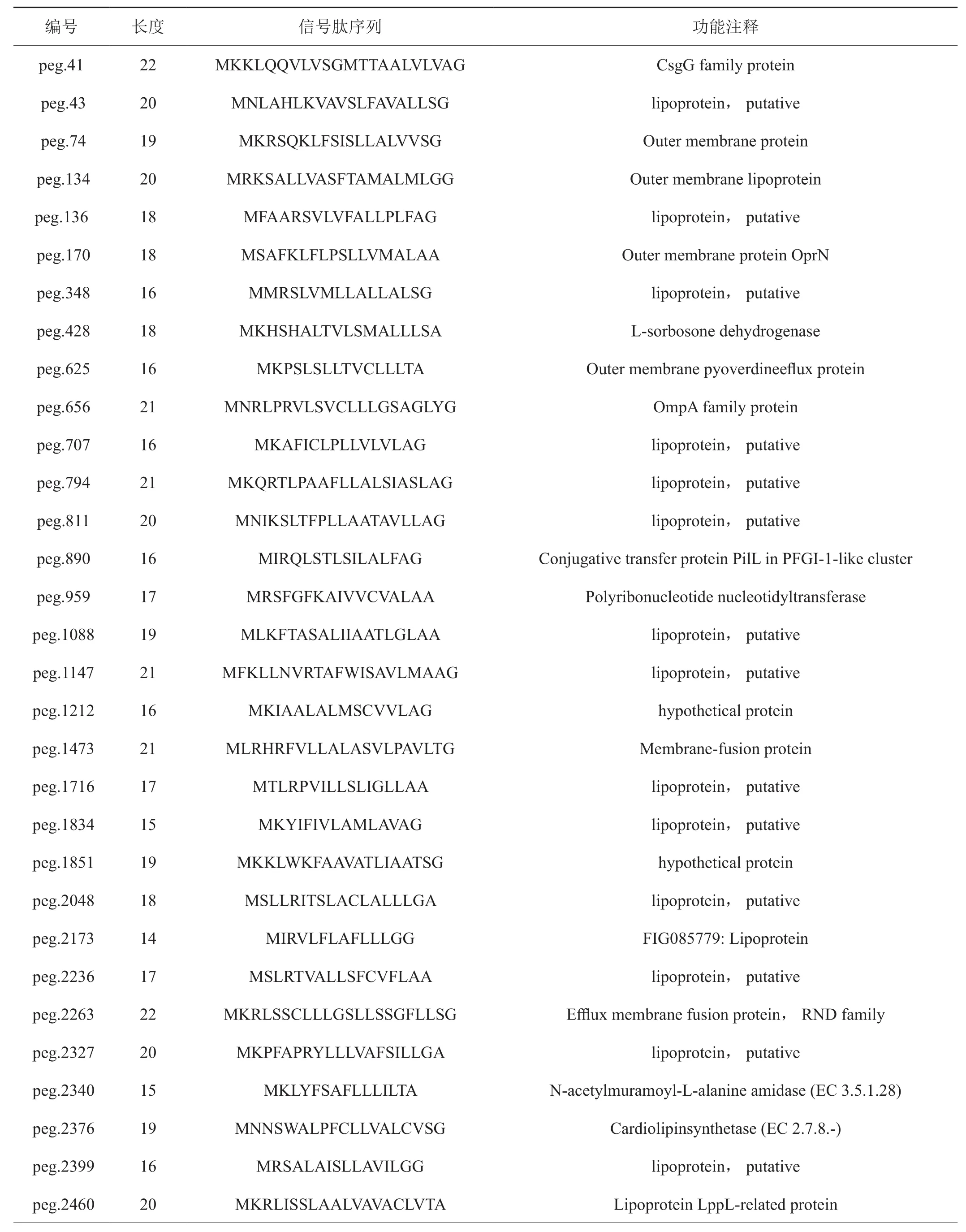
表2 烟草野火病菌yuexi-1菌株基因组脂蛋白类型信号肽Tab. 2 Lipoprotein signal peptide in P. syringaepv.tabaci strain yuexi-1

续表2
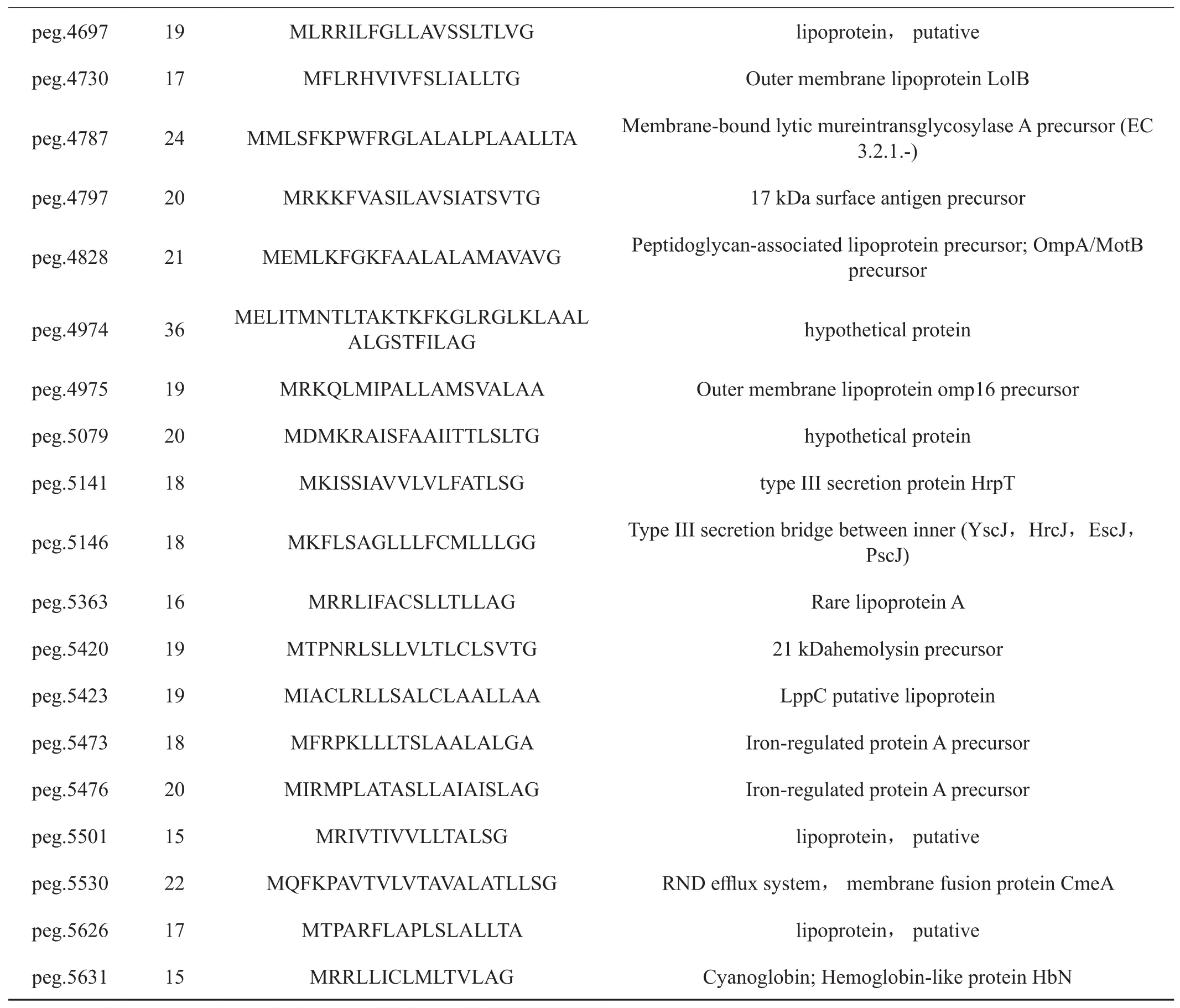
续表2
在P.pv. tabaciyuexi-1菌株的基因组中,存在不同的分泌蛋白具有相同信号肽序列的现象。据统计,共30条SPI型信号肽和2条SPII型信号肽(表3)存在这种情况,而这些分泌蛋白具有类似的功能描述并参与相同生物过程。我们对含有相同信号肽序列的氨基酸序列进行比对发现,其中8 组分泌蛋白,ORF 的编号分别为:peg.886 与peg.2670,peg.3721 与peg.3724, peg.3810、peg.4062与peg.4068, peg.3812、peg.4064 与 peg.4070, peg.4111 与 peg.4113,peg.170 与peg.4165, peg.2692 与 peg.2779, peg.2796 与 peg.2803,核酸序列比对的一致性在 99%~100%,可能为多拷贝基因。其它含有相同信号肽的蛋白序列的长度和同源性的差异很大,但有功能相近,这些分泌蛋白序列呈现很高的同源性并高度保守,因此判断这一类基因为平行进化的同源基因。

表3 相同序列信号肽Tab. 3 Signal peptides with the same sequences
3 讨论
本研究运用 3 种生物信息学分析软件对P.syringaepv. tabaci yuexi-1 菌株的全基因组序列进行分析。P. syringaepv. tabaciyuexi-1 菌株中共有432条信号肽,其中351条SPI型信号肽和81条SPII型信号肽。通过比较分析,SPII 型信号肽与 SPI 型信号肽存在以下不同:首先,脂蛋白的信号肽,其 C 端包含 Lipobox 共识序列L-(A /S)-(A/G)-C,其结构比分泌信号肽更保守(表 2),说明在脂蛋白的修饰过程中,多肽变化极少。另外,SPI型信号肽平均长度为26 个氨基酸,SPII 型信号肽的平均长度为 20 个氨基酸左右,较 SPI 型信号肽短。
烟草野火病菌 yuexi-1 有较强的致病力,其基因组测序的完成, 使得从全基因组水平分析和研究该菌株的信号肽和分泌蛋白成为可能。本研究中,结合多种生物信息学软件,优化预测方法,对基因组中具有信号肽的分泌蛋白进行了预测分析,使预测结果更准确,为该菌株基因组特征的描述及该病菌致病机制的研究提供了理论依据。前期报道,细菌的大多数分泌蛋白中其致病性关系密切。其中, 参与 Tat 分泌途径的RR-motif信号肽与植物病原细菌的致病性关系尤为密切。Rodríguez等利用生物信息学软件对Dickeya dadantii3937的全基因组序列进行信号肽预测分析,并筛选假定 Tat 底物进行突变体,结果发现,TatC 突变体的致病力降低[24]。梨火疫病菌 (Erwinia amylovora) Tat途径中的分泌蛋白参与病菌的生长速度、 致病力生理特性[25]。本研究中,在 yuexi-1信号肽预测结果中, 得到 26 条与Tat 系统相关的信号肽。同时,在分析分泌蛋白功能时发现,预测得到的信号肽中存在参与 III 型分泌系统等与致病力关系密切的分泌系统,以上所得到的这些信号肽所对应的基因是否也与其致病力等密切相关也需要进一步证实。
尽管本研究利用结合多种软件,提高预测的准确性,但预测结果与实际分泌到菌体外的蛋白在数量和种类上有一定的差距,在预测信号肽蛋白中,哪些是真正的分泌蛋白、分泌状态及其功能需进一步验证。后期研究工作中,结合预测结果对感兴趣的分泌蛋白进行功能验证,提高验证分泌蛋白功能效率。
[1] Gasson M J. Indicator technique for antimetabolic toxin production by phytopathogenic species ofPseudomonas[J].Applied and environmental microbiology, 1980, 39(1): 25-29.
[2] Thomas M D, Uchytil TF, Durbin RD. et al. Inhibition of glutamine synthetase from pea by tabtoxinine-beta-lactam[J]. Plant physiology, 1983, 71(4): 912-5.
[3] Emanuelsson O, von Heijne G. Prediction of organellar targeting signals [J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Molecular Cell Research, 2001, 1541(1): 114-119.
[4] Baldi P, Brunak S, Chauvin Y, et al. Assessing the accuracy of prediction algorithms for classi fi cation: an overview [J].Bioinformatics, 2000, 16(5): 412-424.
[5] Heijne G. Patterns of amino acids near signal‐sequence cleavage sites [J]. European journal of biochemistry, 1983,133(1): 17-21.
[6] Von Heijne G. Signal sequences: the limits of variation [J].Journal of molecular biology, 1985, 184(1): 99-105.
[7] 王铁霖,严婉荣,闫莎莎,等. 瓜类果斑病菌 (Acidovorax citrulli) 基因组信号肽预测分析[J]. 中国瓜菜, 2012,25(1): 1-6.
[8] Tjalsma H, van den Dolder J, Meijer WJ, et al. The Plasmid-Encoded Signal Peptidase SipP Can Functionally Replace the Major Signal Peptidases SipS and SipT of Bacillus subtilis [J]. Journal of bacteriology, 1999, 181(8):2448-2454 .
[9] Tjalsma H, Zanen G, Venema G, et al. The potential active site of the lipoprotein-speci fi c (type II) signal peptidase of Bacillus subtilis [J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1999,274(40): 28191-28197.
[10] Prágai Z, Tjalsma H, Bolhuis A, et al. The signal peptidase II (Isp) gene of Bacillus subtilis [J]. Microbiology, 1997,143(4): 1327-1333.
[11] Banerjee S, Hansen JN. Structure and expression of a gene encoding the precursor of subtilin, a small protein antibiotic[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1988, 263(19): 9508-9514.
[12] Paik S H, Chakicherla A, Hansen J N. Identification and characterization of the structural and transporter genes for,and the chemical and biological properties of, sublancin 168, a novel lantibiotic produced by Bacillus subtilis 168[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1998, 273(36): 23134-23142.
[13] Weiner J H, Bilous P T, Shaw G M, et al. A novel and ubiquitous system for membrane targeting and secretion of cofactor-containing proteins [J]. Cell, 1998, 93(1): 93-101.
[14] Dalbey R E, von Heijne G. Signal peptidases in prokaryotes and eukaryotes-a new protease family [J]. Trends in biochemical sciences, 1992, 17(11): 474-478.
[15] Dalbey R E, Lively M O, Bron S, et al. The chemistry and enzymology of the type I signal peptidases [J]. Protein Science, 1997, 6(6): 1129-1138.
[16] Berks B C, Sargent F, Palmer T. The Tat protein export pathway [J]. Molecular microbiology, 2000, 35(2): 260-274.
[17] Berks B C. A common export pathway for proteins binding complex redox cofactors?[J]. Molecular microbiology,1996, 22(3): 393-404.
[18] Cristóbal S, de Gier J W, Nielsen H, et al. Competition between Sec‐and TAT - dependent protein translocation inEscherichia coli[J]. The EMBO journal, 1999, 18(11):2982-2990.
[19] Petersen T N, Brunak S, von Heijne G, et al. SignalP 4.0:discriminating signal peptides from transmembrane regions[J]. Nature methods, 2011, 8(10): 785-786.
[20] Dyrløv Bendtsen J, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, et al.Improved prediction of signal peptides: SignalP 3.0[J].Journal of molecular biology, 2004, 340(4): 783-795.
[21] Juncker A S, Willenbrock H, Von Heijne G, et al. Prediction of lipoprotein signal peptides in Gram‐negative bacteria[J]. Protein Science, 2003, 12(8): 1652-1662.
[22] Paetzel M, Dalbey R E, Strynadka NCJ. Crystal structure of a bacterial signal peptidase in complex with a β-lactam inhibitor [J]. Nature, 1998, 396(6707): 186-190.
[23] Käll L, Krogh A, Sonnhammer ELL. Advantages of combined transmembrane topology and signal peptide prediction-the Phobius web server [J]. Nucleic acids research, 2007, 35(suppl 2): W429-W432.
[24] Rodríguez-Sanz M, Antúnez-Lamas M, Rojas C, et al.The Tat pathway of plant pathogen Dickeya dadantii 3937 contributes to virulence and fi tness [J]. Fems Microbiology Letters,2010,302(2):151-158.
[25] 于洋洋, 刘倩倩, 徐恩丽, 胡白石. 梨火疫病菌(Erwinia amylovora)双精氨酸运输系统基因(tatC)的功能分析[J].农业生物技术学报, 2011,19 (6): 1081-1088.
Analysis of coding region for proteins containing signal peptides ofPseudomonas syringaepv.tabaciyuexi-1 strain
WANG Tielin, LI Jing, YANG Yuwen, ZHAO Tingchang
State Key Laboratory for Biology of Plant Diseases and Insect Pests, Institute of Plant Protection, Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, Beijing 100193
This paper predicted and analyzed the number, length and amino acid components in the genome ofPseudomonas syringaepv.tabaciyuexi-1, a strain of tobacco fi re blight pathogen, by using SignalP 4.0, LipoP 1.0 and TMHMM v2.0. Results showed that 432 ORFs(8.81% of all the ORFs) contained N- terminal signal peptides, of which 351 signal peptides were SPI type and 81 signal peptides were SPII type. Among the SPI peptides, length was between 11 to 42 amino acids and the majority was 22 amino acids in length. In addition,the proteins that share the same signal peptide sequences were highly conserved in the homologue analysis. This study provided candidate genes for virulence factors of the tobacco fi re blight pathogen, and promoted the efficiency for screening the virulence factors.
Pseudomonas syringaepv.tabaci; signal peptide; SignalP 4.0; LipoP 1. 0; TMHMM v2.0
王铁霖,李晶,杨玉文,等. 烟草野火病菌Pseudomonas syringaepv. tabaciyuexi-1信号肽预测及分析[J]. 中国烟草学报,2016,22(1)
烟草病虫害检测与综合治理重点开放实验室开放课题经费(项目号:bc2011 );中国烟草总公司科技重点项目 (项目号 110201202002 )
王铁霖,博士,Email:wtl82@163.com
赵廷昌,研究员,Email:zhaotgcg@163.com
2015-04-23
:WANG Tielin, LI Jing, YANG Yuwen, et al. Analysis of coding region for proteins containing signal peptides ofPseudomonas syringaepv.tabaciyuexi-1 strain [J]. Acta Tabacaria Sinica, 2016,22(1)

