基于修正简易模型的陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力分布特征
钟莉娜,王军,赵文武
(1.中国地质大学(北京)土地科学技术学院,100083,北京;2.国土资源部土地整治中心土地整治重点实验室,100035,北京;3.北京师范大学资源学院,100875,北京)
基于修正简易模型的陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力分布特征
钟莉娜1,2,王军2†,赵文武3
(1.中国地质大学(北京)土地科学技术学院,100083,北京;2.国土资源部土地整治中心土地整治重点实验室,100035,北京;3.北京师范大学资源学院,100875,北京)
降雨侵蚀力经典模型计算结果准确,但计算过程繁琐、数据量大且难获取;简易模型计算便捷,但结果不够准确。本文分析了8种黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力模型的差异,并对简易模型进行修正。以经典模型为基准值,对与经典模型结果最为接近的简易模型进行修正,基于修正后的简易模型分析黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力的时空分布特征。在此过程中用到的方法主要是数理统计法和模型差异分析方法。经典模型更能准确估算陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力;拟合模型y=0.849x-29.651可以提高章文波降雨侵蚀力简易模型的模拟精度(拟合优度0.734);陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区2006—2012年间降雨侵蚀力总体呈现上升趋势;汾川河流域、清涧河流域上游降雨侵蚀力较高,下游次之;延河流域、大理河流域下游降雨侵蚀力较高,上游次之。降雨侵蚀力简易算法经修正后可以较好的估算黄土丘陵沟壑区的降雨侵蚀力的时空分布特征,陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区2006—2012年间降雨侵蚀力时空分布不均,降雨侵蚀力整体较高。
降雨侵蚀力;简易算法修正;时空分布;陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区
降雨侵蚀力(R因子)是通用土壤流失方程USLE及其修正版RUSLE中的一个基础因子[1]。土壤侵蚀与植被覆盖和降雨因子密切相关,短历时、高强度降雨是引起土壤侵蚀的主要因素,特别是在地表相对裸露的坡地[2];因此,降雨侵蚀力计算结果的准确性将直接影响土壤侵蚀的定量研究。
EI30算法是美国通用土壤流失方程中土壤侵蚀力因子R的经典计算方法,在全球有广泛的应用,也受到广大学者普遍认可。降雨侵蚀力简易算法也多以EI30算法为精度的衡量标准。由于基于降雨强度和降雨动能建立的降雨侵蚀力计算模型已被广泛应用且应用效果良好,有学者称之为降雨侵蚀力的经典算法[3]。经典算法基于降雨强度和对应的降雨动能计算降雨侵蚀力,需要长期且连续的降雨过程数据,计算繁琐费时,不适合较大时空尺度上的土壤侵蚀评价[4]。为此,国内外许多学者提出利用年、月、日降雨量等常规降雨资料估算降雨侵蚀力的模型,并在各地区得到广泛应用[5-6]。用年、月、日降雨量等常规降雨资料估算降雨侵蚀力模型的简易算法且已为广大学者普遍接受。许多学者在分析降雨侵蚀力时空分布规律时往往直接采用现有的简易模型,并未考虑模型在研究区是否适用,是否需要修正;另外,现有的降雨侵蚀力模型有很多,在进行相关研究时如何选择也是学者需要关注的问题。
目前用于计算黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力的公式有很多,但不同类型的降水资料提供的信息丰富程度不同,降雨侵蚀力的估算精度也有所差别。本文整理了多种曾用于黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力估算的简易算法和经典算法,分别计算安塞集水区的降雨侵蚀力,分析不同算法计算结果的差异,并以经典算法为基准值,对与之结果最为接近的简易算法进行修正,用修正后的简易算法分析黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力的时空分布特征。
1 研究区概况
选择水土流失比较严重的陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区作为研究区域,位于E 108°45′~110°25′,N 36°10′~37°55′N之间,总面积17 488 km2,包括延河流域、清涧河流域、汾川河流域和无定河流域中的大理河流域,主要涉及延安、延长、安塞、子长、清涧等县市。研究区气候属于中温带大陆性半干旱季风气候,四季变化明显,干湿分明,年温差大[7]。90%以上的降水集中在5—9月,6—9月为汛期,多暴雨。地表为黄土层,黄土颗粒细,土质松软,在流水侵蚀的作用下极易造成土壤侵蚀。
2 数据与方法
2.1 数据来源
以土地利用变化较小的1980—1989年为研究时段,收集安塞集水区内镰刀湾、杨山、化子坪、谭家营、坪桥、安塞和郝家坪降水站点的雨量资料和降雨过程资料(图1),包括7个站点全年的降雨过程数据(包括次降雨持续时间及30min最大降雨强度数据)、日降雨数据以及月降雨数据。1980—1989年安塞水文站的年含沙量及输沙量数据。2006—2012年大理河、清涧河、汾川河、延河流域57个降雨站点的空间分布见图1。数据源于《中华人民共和国水文年鉴·黄河流域水文资料》。
2.2 研究方法
2.2.1 降雨侵蚀力因子计算方法 分析统计8种曾用于估算黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力的计算方法。采用不同方法计算1980—1989年安塞集水区内镰刀湾等7个降水站点的降雨侵蚀力,统计区域平均值得到基于不同算法的安塞集水区年降雨侵蚀力(表1)。各计算公式的单位不一致,本文对各公式的计算结果进行标准化处理之后,将安塞年降雨侵蚀力与安塞水文站的年含沙量、输沙量数据进行相关分析,选择较适合的降雨侵蚀力计算方法。
2.2.2 模型差异分析方法 模型的有效系数Ef越高,表明模型与基准值的差异性越小,准确度越高[16],该指标由J.E.Nash等提出[16]:

图1 安塞集水区降雨站点分布Fig.1 Spatial distribution of rainfall stations in Ansai watershed


式中:Er为相对偏差,Robsn和Rcalm为模型估算和基准月平均降雨侵蚀力,MJ·mm/(km2·h)。相对偏差可以用来衡量模型的估算值对基准值的偏离程度[17]。
3 结果与分析

表1 降雨侵蚀力计算方法Tab.1 Methods of rainfall erosivity
3.1 基于不同算法的降雨侵蚀力计算结果比较
将基于不同计算方法得到的年降雨侵蚀力与安塞集水区水文资料(输沙量和含沙量)进行相关分析,得到不同计算方法的年降雨侵蚀力与安塞集水区水文资料的相关系数,其结果如图2所示。另外,从图2中也可以看出经典算法(R7、R8)与水文要素(输沙量与含沙量)的相关系数明显高出简易算法(R1—R6)与水文要素的相关系数。江忠善等[14]建立的降雨侵蚀力公式R7较王万忠[15]的降雨侵蚀力公式R8与水文要素的相关性更高,更能准确反映安塞集水区的土壤侵蚀状况。简易算法中,章文波等[9]的降雨侵蚀力公式R2与水文要素具有更高的相关性。综合考虑降雨侵蚀力估算结果的准确性和数据的可获得性,选择章文波的降雨侵蚀力公式R2来估算研究区的降雨侵蚀力。为进一步提高章文波降雨侵蚀力公式计算结果的准确度,本文分析江忠善建立的降雨侵蚀力经典算法R7与章文波建立的降雨侵蚀力简易算法R2的差异性,并基于R7对R2进行修正。

表1 (续)Continued from Tab.1

图2 不同降雨侵蚀力因子计算方法与水文数据的相关性Fig.2 Correlation between different calculation models of rainfall erosivity and hydrological data
3.2 经典算法R7与简易算法R2的差异性分析
以经典算法R7估算的月降雨侵蚀力作为基准值,利用有效系数和相对偏差来分析R2与R7的差异。统计1981—1989年6—9月的月平均降雨量和降雨侵蚀力数据,并分析R2相对R7的有效系数和相对偏差(表2)。1981—1989年期间月平均降雨量为8月>7月>9月>6月。R2相对于R7的有效系数为9月>6月>7月>8月,而研究期间,安塞集水区各月侵蚀性降雨(>12 mm)次数排序为8月>7月>6月>9月,二者排序恰好相反,说明R2的准确度与侵蚀性降雨的次数成反比。另外,R2的相对偏差月份之间相差不大,有效系数越大,相对偏差越小说明模型的模拟精度越高;因此R2对黄土丘陵沟壑区9月份降雨侵蚀的模拟精度相对较高。
R2与R7产生差异的主要原因是R2采用日降雨量和月降雨量因子估算降雨侵蚀力,并未明显包含降雨强度概念,与EI经典算法的物理意义不相接近;同时,黄土丘陵沟壑区土质松散,遇水容易溶解,一场十几毫米的短历时、高强度局地性暴雨要比七八十毫米的长历时、低强度区域性暴雨的侵蚀量大得多:因此,降雨强度因素对黄土丘陵沟壑区水土流失的影响程度要比雨量因子大得多。
3.3 简易算法R2的修正
以R2为自变量,以R7为因变量,建立R2与R7的拟合模型,对降雨侵蚀力简易算法R2进行修正。由图3看出,R2与R7的关系满足线性分布,拟合模型为R7=0.849R2-29.651,拟合优度为0.734,即

式中:R为月降雨侵蚀力,MJ·mm/(hm2·h);D为第j日侵蚀性降雨量,mm(降雨量≥12 mm,否则以0计算);K为侵蚀性降雨时间,d。

式中:Pd12为日雨量≥12mm的日平均雨量,mm;Py12为日雨量≥12mm的年平均雨量,mm。
3.4 黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力的时空分布特征

表2 R2相对于R7的差异比较Tab.2 Comparison of the differences between R2and R7
降雨侵蚀力空间变化分析计算研究区降雨侵蚀力2006—2012年的多年平均值均值得到图4,可以看出:汾川河流域、清涧河流域上游降雨侵蚀力较高,下游次之;延河流域、大理河流域下游降雨侵蚀力较高,上游次之。总体来说,延河和大理河流域降雨侵蚀力较低,而清涧河和汾川河流域降雨侵蚀力较高。研究区降雨侵蚀力存在2个高值区,分别是清涧河上游地区和汾川河上游地区,低值区分别位于大理河中游和延河流域上中游。
降雨侵蚀力时间变化分析统计研究区2006—2012年的降雨侵蚀力得到图5。可以看出,2006—2012年间降雨侵蚀力总体呈现上升趋势,但由于2008年和2010年降雨量较小导致2008年和2010年的降雨侵蚀力较低。
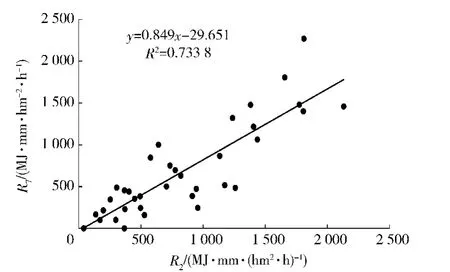
图3 R2与R7的拟合模型Fig.3 Fitting model of R2and R7

图4 多年降雨侵蚀力均值空间分布(MJ·mm·hm-2·h-1·a-1)Fig.4 Spatial distribution ofmean annual rainfall erosivity
4 结论
1)相对于降雨侵蚀力简易算法,经典算法更能准确估算陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀力。章文波等[9]的降雨侵蚀力简易算法对9月份陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区降雨侵蚀的模拟精度相对较高。简易算法与经典算法差异存在的主要原因是降雨强度因素对黄土丘陵沟壑区土壤侵蚀的影响程度要比雨量因子大的多,而简易算法采用日降雨量和月降雨量因子估算降雨侵蚀力,并未明显包含降雨强度概念。

图5 降雨侵蚀力年际变化Fig.5 Interannual variation of rainfall erosivity
2)江忠善等[14]的降雨侵蚀力经典算法与章文波等[9]的降雨侵蚀力简易算法满足线性分布,拟合模型y=0.849x-29.651可以提高章文波的降雨侵蚀力简易算法的模拟精度(拟合优度0.734)。
3)陕北黄土丘陵沟壑区2006—2012年间降雨侵蚀力总体呈现上升趋势。汾川河流域、清涧河流域上游降雨侵蚀力较高,下游次之;延河流域、大理河流域下游降雨侵蚀力较高,上游次之。
修正后的降雨侵蚀力简易算法可以较好的估算黄土丘陵沟壑区的降雨侵蚀力。相较于经典算法,简易算法既节约人力物力,也节省时间成本,同时也有较好的模拟精度,可以在大尺度上推广使用。
[1] LAIR L.Soil degradation by erosion[J].Land Degradation&Development,2001,12(12):519.
[2] 杨韶洋,刘霞,姚孝友,等.沂蒙山区降雨侵蚀力空间分布推算方法[J].中国水土保持科学,2015,13(2):1. Yang Shaoyang,Liu Xia,Yao Xiaoyou,et al.Calculat-ing methods of rainfall erosivity spatial distribution in Yimeng Mountain Area[J].Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2015,13(2):1.(in Chinese)
[3] 胡续礼,潘剑君,杨树江,等.几种降雨侵蚀力模型的比较研究[J].水土保持通报,2006,26(1):68. Hu Xuli,Pan Jianjun,Yang Shujiang,et al.Comparative study on rainfall erosivity models using daily rainfall amounts[J].Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2006,26(1):68.(in Chinese)
[4] Oliveira P T S,Wend land E,Nearing M A.Rainfall erosivity in Brazil:A review[J].Catena,2013,100(2):139.
[5] Fiener P,Neuhaus P,Botschek J.Long-term trends in rainfall erosivity-analysis of high resolution precipitation time series(1937- 2007)from Western Germany[J]. Agricultural and Forest Meteorology,2013,171/172(8):115.
[6] Maetens W,Vanmaercke M,Poesen J,et al.Effects of land use on annual runoff and soil loss in Europe and the Mediterranean A meta-analysis of plot data[J].Progress in Physical Geography,2012,36(5):599.
[7] 王浩,张光辉,张永萱,等.黄土高原小流域次降雨径流深预报模型[J].中国水土保持科学,2015,13(5):31. Wang Hao,Zhang Guanghui,Zhang Yongxuan,et al. Rainfall event based runoff prediction model for small watersheds in the Loess Plateau[J].Science of Soil and Water Conservation,2015,13(5):31.(in Chinese)
[8] 殷水清,谢云.黄土高原降雨侵蚀力时空分布[J].水土保持通报,2005,25(4):29. Yin Shuiqing,Xie Yun.Temporal and spatial variations of rainfall erosivity in the Loess Plateau[J].Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2005,25(4):29.(in Chinese)
[9] 章文波,付金生.不同类型雨量资料估算降雨侵蚀力[J].资源科学,2003,25(1):35. Zhang Wenbo,Fu Jinsheng.Rainfall erosivity estimation under different rainfall amount[J].Resources Science,2003,25(1):35.(in Chinese)
[10]刘秉正.渭北地区R的估算及分布[J].西北林学院学报,1993,8(2):21. Liu Binzheng.Estimation and distribution of rainfall erosive power index[J].Journal of Northwest Forestry University,1993,8(2):21.(in Chinese)
[11]Wischmeier HW,Smith D D.Rainfall energy and its relationship to soil loss[J].Transactions American Geophysical Union,1958,39(2):285.
[12]孙保平,赵廷宁,齐实.USLE在西吉县黄土丘陵沟壑区的应用[J].中国科学院水利部西北水土保持研究所集刊:黄土高原试验区土壤侵蚀和综合治理减沙效益研究专集,1990,12:50. Sun Baoping,Zhao Tingnin,Qi Shi.Application of USLE in Xiji county in Loess Hilly Gully Region[J].Research of Soil and Water Conservation,1990,12:50.(in Chinese)
[13]赵文武,徐海燕,解纯营.黄土丘陵沟壑区延河流域降雨侵蚀力的估算[J].农业工程学报,2008,24(S1):38. Zhao Wenwu,Xu Haiyan,Xie Chunying.Estimation of rainfall erosivity watershed in Yanhe River of Loess Hilly Gully Region[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2008,24(S1):38.(in Chinese)
[14]江忠善,李秀英.黄土高原土壤流失预报方程中降雨侵蚀力和地形因子的研究[J].中国科学院西北水土保持研究所集刊,1988,7:40. Jiang Zhongshan,Li Xiuying.Study on rainfall erosivity and topographic factors in soil erosion in Loess Plateau prediction equation[J].Memoir of Northwestern Institute of Soil and Water Conservation Academia Sinica,1988,7:40.(in Chinese)
[15]王万忠.黄土地区降雨侵蚀力R指标的研究[J].中国水土保持,1987,12:34. Wang Wangzhong.Study on index of erosivity(R)of rainfall in loess area[J].Soil and Water Conservation in China,1987,12:34.(in Chinese)
[16]Nash JE,Sutcliffe JV.River flow forecasting through conceptualmodels part:a discussion of principles[J]. Journal of Hydrology,1970,10(3):282.
[17]Stoyanow S V,Rachev S T,Ortobeli S,et al.Relative deviation metrics and the problem of strategy replication[J].Journal of Banking&Finance,2008,32(2):199.
Tem poral and spatial distribution characteristics of rainfall erosivity in loess hilly region of Northern Shaanxi based on the modified simplified models
Zhong Lina1,2,Wang Jun2,Zhao Wenwu3
(1.School of Land Science and Technology,China University of Geosciences,100083,Beijing,China;2.Key Laboratory of Land Consolidation and Rehabilitation,Ministry of Land and Resources,100035,Beijing,China;3.College of Resources Science and Technology,Beijing Normal University,100875,Beijing,China)
[Background]Universal Soil Loss Equation(USLE)is an empirical model widely used in the domain of soil erosion by water.And the rainfall erosivity(R factor)is a basic factor in USLE and the revised universal soil loss equation(RUSLE).The soil erosion and rainfall factors are closely related.The accuracy of the calculated results of rainfall erosivity will directly affect the quantitative study of soil erosion.The calculated results by the classical models are accurate,however,the calculation process is cumbersome,and the data used in the calculation is large and difficult to be obtained. Calculation of rainfall erosivity using simplified models is convenient,but the result is not accurate enough.[Methods]The differences of rainfall erosivity calculated by 8 different models were analyzed,then the simplified models generating the closest values with classical models were modified,and then the simplified models after modification were used to analyze the temporal and spatial distribution characteristics of rainfall erosivity.The main methods used in this process were mathematical statistics and model difference analysis.[Results]1)Compared to the simplified models,classical models were more accurate to estimate the rainfall erosivity in the loess hilly and gully region,the main reasons resulting in this were as,the impact degree of rainfall intensity factor was much higher than the rainfall factor on soil erosion in the loess hilly and gully region,while rainfall intensity was not considered as an impact factor in the simplified models,and the calculation in the simplified models was carried out by daily rainfall and monthly rainfall data.2)The fitting model y=0.849x-29.651 improved the simulation precision of the simplified model of rainfall erosivity by Zhang Wenbo(Goodness of fit was 0.734).The rainfall erosivity of the loess hilly and gully region of Northern Shaanxi Province during 2006- 2012 showed a rising trend.The rainfall erosivity of the upstream of Fenchuan River Basin and Qingjian River Basin was relatively high and the rainfall erosivity of the downstream was in second;the rainfall erosivity of the downstream of Yan he Basin and Dali River Basin was relatively high,and the rainfall erosivity of the upstream was in second.[Conclusions]The simplified rainfall erosivity models after modification may be used to better estimate the rainfall erosivity in the loess hilly and gully region,and by which the manpower,time and costwould be saved;moreover,the favorable simulation accuracy can be obtained,thus they can be used in large scale and provide a scientific basis for the soil and water conservation work in the loess hilly and gully region and even the country-scale investigation of soil erosion.The rainfall erosivity in the loess hilly gully region is calculated better by simplified model after modification,as result,the temporal and spatial distribution of rainfall erosivity in the loess hilly and gully region are high and uneven as a whole from 2006 to 2012.
rainfall erosivity;modification of simplified model;temporal and spatial distribution;loess hilly and gully region of Northern Shaanxi
F301.2
A
1672-3007(2016)05-0008-07
10.16843/j.sswc.2016.05.002
2016- 02- 16
2016- 05- 05
项目名称:国家自然科学基金“松嫩平原西部土地整理的时空格局及生态效应”(41171152),“土地利用格局与土壤流失关系的尺度效应分析与尺度转换”(41171069)
钟莉娜(1989—),女,博士研究生。主要研究方向:景观生态和土地整治。E-mail:zhong_lina@163.com
†通信作者简介:王军(1970—),男,博士,研究员。主要研究方向:景观生态学,土地可持续利用与土地整治。E-mail:wangjun@lcrc.org.cn

