GRAPHIC ABSTRACT
Acta Mechanica Sinica, Volume 32, Number 5, October 2016
GRAPHIC ABSTRACT
Acta Mechanica Sinica, Volume 32, Number 5, October 2016
FLUID MECHANICS
Hydrodynamic interactions of water waves with a group of independently oscillating truncated circular cylinders
Xiaohui Zeng · Min Shi · Shanlin Huang
The water wave radiation by arrays of truncated circular cylinders is studied, as each cylinder can oscillate independently in any rigid oscillation mode (including translational and rotational modes, such as surge, sway, heave, pitch, roll, and their combinations) with prescribed amplitude. The orthogonal test method is employed to investigate the effects of several infl uential factors on convergence. Effects of evanescent modes on the hydrodynamic coefficients are revealed.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 773-791 (2016)
Numerical evaluation of passive control of shock wave/boundary layer interaction on NACA0012 airfoil using jagged wall
Mojtaba Dehghan Manshadi · Ramin Rabani
This paper is focused to appraise the practicability of weakening the shock wave and reducing the wave drag in transonic regime using jagged wall. For a simple NACA0012 airfoil, the interaction between the shock wave and boundary layer causes a rapid increase in the boundary layer thickness and large separation bubble formation, but applying the Jagged wall on the upper surface of the airfoil causes the large separation bubble to disintegrate and break down into several weak bubbles which in turn causes a gradual reduction in Mach number.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 792-804 (2016)
SOLID MECHANICS
Measurement of residual stress in a multi-layer semiconductor heterostructure by micro-Raman spectroscopy
Wei Qiu · Cui-Li Cheng · Ren-Rong Liang · Chun-Wang Zhao · Zhen-Kun Lei ·
Yu-Cheng Zhao · Lu-Lu Ma · Jun Xu · Hua-Jun Fang · Yi-Lan Kang
This work presented a methodological study on the measurement of residual stress in a multi-layer semiconductor heterostructure. (a) Scanning electron microscopy,(b) micro-Raman spectroscopy, and (c) transmission electron microscopy were applied to measure the geometric parameters of the multilayer structure. (d) The relationship between the Raman spectrum and the stress/strain on the [110] crystal orientations of C-Si and GexSi1-xwere determined to enable the residual stress analyses. Based on the Raman mapping results, the distribution of residual stress along the depth of the multi-layer heterostructure was successfully obtained.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 805-812 (2016)
Stress analysis of thermally affected rotating nanoshafts with varying material properties
Keivan Kiani
Analytical expressions of thermo-elastic fields within rotating nanoshafts with varying material properties are obtained. Using the surface elasticity theory of Gurtin-Murdoch, the non-classical fixed-free and free-free boundary conditions are enforced. The effects of material properties variation, environment’s temperature, angular velocity, outer radius, and surface effect on the resulted radial displacement, hoop stress, and radial stress are explored. This work can be regarded as a pivotal step towards rational design of thermally affected nano-scaled rotors or nanomachines with rotating tube-like elements or hollow nanowires.
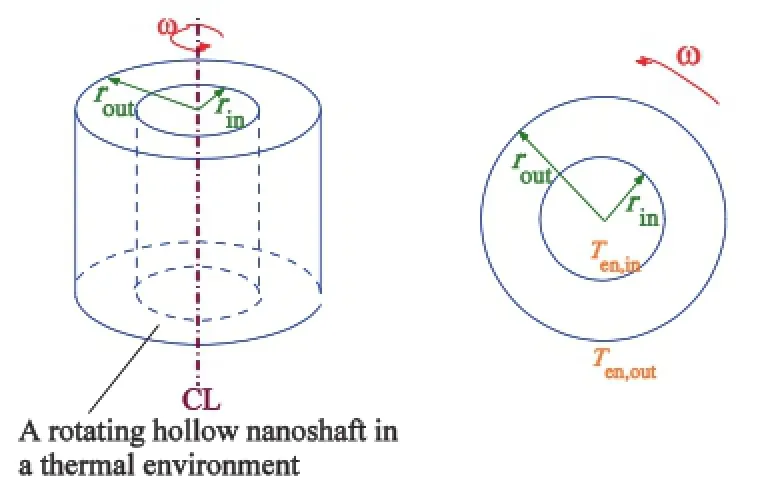
Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 813-827 (2016)
Acoustomechanical constitutive theory for soft materials
Fengxian Xin · Tian Jian Lu
Acoustic wave propagation from surrounding medium into a soft material can generate acoustic radiation stress due to acoustic momentum transfer inside the medium and material as well as at the interface between the two. To analyze acoustic-induced deformation of soft materials, we establish an acoustomechanical constitutive theory by combining the acoustic radiation stress theory and the nonlinear elasticity theory of soft materials. The acoustic radiation stress tensor is formulated by time averaging the momentum equation of particle motion, which is then introduced into the nonlinear elasticity constitutive relation to construct the acoustomechanical constitutive theory of soft materials. Considering a specified case of soft material sheet subjected to two counterpropagating acoustic waves, we demonstrate the nonlinear large deformation of the soft material and analyze the interaction between acoustic waves and material deformation under the conditions of total refl ection, acoustic transparent and acoustic mismatch.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 828-840 (2016)
Nonlocal vibration analysis of circular double-layered graphene sheets resting on an elastic foundation subjected to thermal loading
Reza Ansari · Jalal Torabi
The nonlocal vibration behavior of embedded circular double-layered graphene sheets (DLGSs) is studied in thermal environment. The governing equation is derived on the basis of Eringen’s nonlocal elasticity and the classical plate theory. Using the generalized differential quadrature method and periodic differential operators in radial and circumferential directions, respectively, the governing equation is discretized. The effects of various parameters such as elastic medium coefficients, radius-to-thickness ratio, thermal loading and nonlocal parameter are examined on natural frequencies of DLGS.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 841-853 (2016)
Extended Kantorovich method for local stresses in composite laminates upon polynomial stress functions
Bin Huang · Ji Wang · Jianke Du · Yan Guo · Ting feng Ma · Lijun Yi
We report a polynomial stress function based extended Kantorovich method for predicting local stresses in composite laminate under axial tensile load. The local stress concentration could lead to undesired delamination or crack failure in laminated structures. The proposed appraoch can accurately and efficiently predict the local stress distributions though the iterations. The resutls are also well verified by the results of 3D finite element method (FEM). The proposed appraoch can be considered as an useful candidate tool for local stress analysis in composite laminates.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 854-865 (2016)
Tuning of non-uniform switch toughening in ferroelectric composites by an electric field
Xiaodong Xia · Zheng Zhong
This paper deals with a mode III interfacial crack subject to anti-plane stress and in-plane electric fields. The analysis concentrates on the tuning of fracture toughness from non-uniform domain switching by an electric field. The electric loading changes the size of asymmetric switching zone. We obtain the electricallydependent switch toughening for stationary and quasi-static growing interfacial cracks, respectively. Numerical results are presented on electric field tuning of the critical applied stress intensity factor. The research gives us ideas to optimize fracture properties of ferroelectric composites by altering the electric field.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 866-880 (2016)
A phase-field study on the oxidation behavior of Ni considering heat conduction
Chao Wang · Shigang Ai · Daining Fang
High temperature oxidation experiments and phase field modeling for pure Ni were performed in air under atmospheric pressure at 600°C, 700°C, and 800°C. By interactive algorithm, the dependence of the coefficient of Cahn-Hilliard equation Lc on the temperature T was conducted. Then, the oxidation behavior of Ni was investigated when considering heat conduction and the infl uences of temperature boundaries on the oxidation degree, oxide film thickness and specific weight gain were discussed.
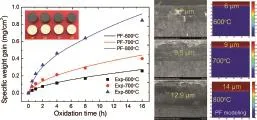
Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 881-890 (2016)
Contact force and mechanical loss of multistage cable under tension and bending
Yanyun Ru · Huadong Yong · Youhe Zhou
A 3D theoretical model is proposed to analyze the strain and stress states and mechanical loss of strand structures. A global and local analysis method is established, which can be applied to multistage strand structures. The contact forces between the strands are obtained under bending. For the different twist pitches of second stage cable, there is a phase difference between the contact forces.
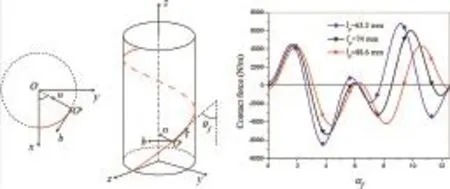
Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 891-904 (2016)
Numerical study on the deformation of soil stratum and vertical wells with gas hydrate dissociation
Xudong Chen · Xuhui Zhang · Xiaobing Lu · Wei Wei · Yaohong Shi
Gas hydrate (GH) dissociation leads to the deformation of soil stratum and vertical wells. The results of numerical simulations in FLAC3D software show that the relative affected zone in the over layer expands with the increase of the dissociation zone while keeps constant after the dissociation zone reaches two times the thickness of over layer. The interaction becomes significant when the length of dissociation zone is over 1/2 of the distance between the two wells. The hydrostatic pressure constrains the horizontal displacement of soil stratum and wells.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 905-914 (2016)
Reliability assessment on interfacial failure of thermal barrier coatings Jin-Wei Guo · Li Yang · Yi-Chun Zhou · Li-Min He · Wang Zhu · Can-Ying Cai ·
Chun-Sheng Lu
This study aims at establishing a reliability assessment method to analyze the interface failure of TBCs. The interface failure of two kinds of TBCs with different mechanisms is analyzed. It is shown that the failure probabilities are 40.64% and 46.92%, respectively. The interfacial failure of TBCs is significantly affected by the thermal mismatch of material properties and the temperature drop in service.
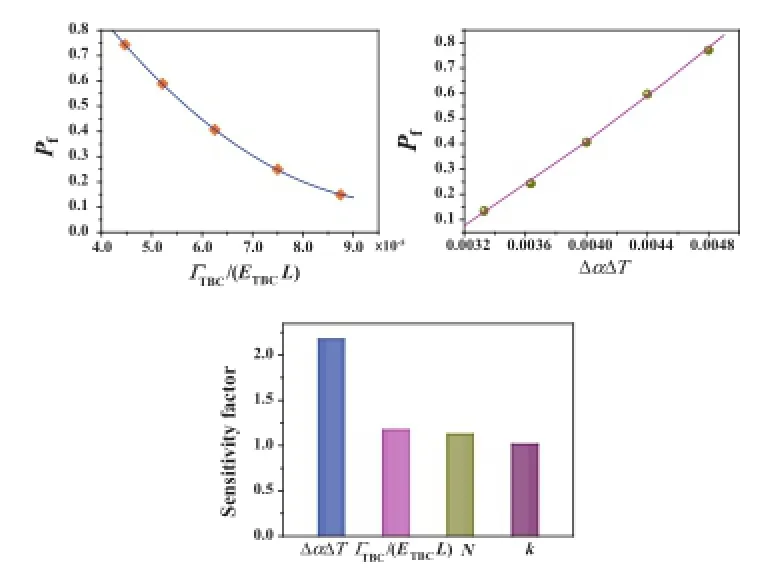
Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 915-924 (2016)
DYNAMICS, VIBRATION, AND CONTROL
Nonlinear integral resonant controller for vibration reduction in nonlinear systems
Ehsan Omidi · S.Nima Mahmoodi
A new nonlinear integral resonant controller (NIRC) is introduced in this paper to suppress vibration in nonlinear oscillatory smart structures. The NIRC consists of a first-order resonant integrator that provides additional damping in the closedloop system response to reduce high-amplitude nonlinear vibration around the fundamental resonance frequency. The controlled system via the NIRC does not show any high-amplitude peaks in the neighboring frequencies of the resonant mode, unlike conventional second-order compensation methods. This makes the NIRC controlled system robust to excitation frequency variations.

Ac ta Me ch an i ca Si ni ca 32, 9 25-9 3 4 (2 0 16)
Gradient systems and mechanical systems
Fengxiang Mei · Huibin Wu
All kinds of gradient systems and their properties will be discussed. Two problems connected with gradient systems and mechanical systems will be studied. One is the direct problem which transforming the mechanical system into a gradient system, and the other is the inverse problem which transforming the gradient system into a mechanical system.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 935-940 (2016)
A direct probabilistic approach to solve state equations for nonlinear systems under random excitation
Zheng Lv · Zhiping Qiu
To analysis dynamic response of nonlinear systems excited by environmental loads, a direct probabilistic approach (DPA) is presented to formulate and solve moment equations, which is completely independent from the Itô/filtering approach. Meanwhile, a multi-scale algorithm for the numerical solution of moment equations is exploited in order to improve computational efficiency and avoid much wall-clock time. DPA has the advantage of obtaining the response’s moments directly from initial condition and statistical characteristics of the external excitations. A comparison of the results with Monte Carlo simulation gives good matching.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 941-958 (2016)
BIOMECHANICS
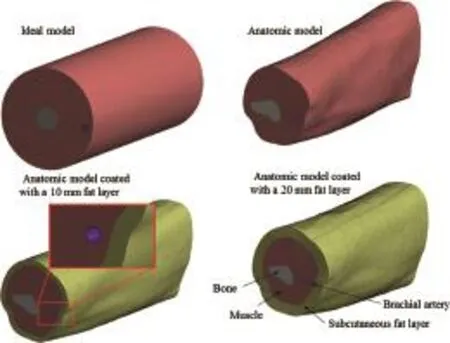
Numerical analysis of stress distribution in the upper arm tissues under an infl atable cuff: Implications for noninvasive blood pressure measurement
Zhipeng Deng · Fuyou Liang
Finite element models were constructed to investigate factors dominating pressure distribution in the upper arm under an infl atable cuff. Obtained results showed that the magnitude of cuff pressure and small variations in mechanical properties of arm soft tissues had little infl uence on the efficiency of pressure transmission in arm tissues. In the meantime, it was found that thickening of the subcutaneous fat layer significantly reduced the effective pressure transmitted to the brachial artery, which may explain why pressure overestimation occurs more frequently in obese subjects in noninvasive blood pressure measurement.
Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 959-969 (2016)
Entropic force between biomembranes
Long Li · Fan Song
An entropic force, stemming from thermal excited fl uctuations, has been reexamined. A novel expression of the force is presented, and its validity is proved by the existing experimental data. The existing seemingly controversial results are proved to be available in the sufficiently small separations and to be separately the upper and lower bounds of the present results. The effective acting distance of the entropic force is first presented. The study here is helpful to understand deeply the interaction between matters.

Acta Mechanica Sinica 32, 970-975 (2016)
- Acta Mechanica Sinica的其它文章
- Entropic force between biomembranes
- Numerical analysis of stress distribution in the upper arm tissues under an inflatable cuff:Implications for noninvasive blood pressure measurement
- A direct probabilistic approach to solve state equations for nonlinear systems under random excitation
- Gradient systems and mechanical systems
- Nonlinear integral resonant controller for vibration reduction in nonlinear systems
- Reliability assessment on interfacial failure of thermal barrier coatings

