ERα特异性抑制剂对KM小鼠植入前胚体外发育的影响*
张燕琴,王世鄂
(1.泉州医学高等专科学校 人体解剖学教研室,福建 泉州 362010;2.福建医科大学 解剖学与组织胚胎学系,福建 福州 350100)
基础医学研究
ERα特异性抑制剂对KM小鼠植入前胚体外发育的影响*
张燕琴1,王世鄂2
(1.泉州医学高等专科学校 人体解剖学教研室,福建 泉州362010;2.福建医科大学 解剖学与组织胚胎学系,福建 福州350100)
目的 探讨ERα在KM小鼠植入前胚体外发育中的作用。方法 以空白M16培养液为对照组,观察不同浓度的ER抑制剂(ICI182780)、ERα特异性抑制剂(MPP)、ERβ特异性抑制剂(PHTPP)和ERα特异性抗体对KM小鼠1-细胞胚体外发育至4-细胞胚和囊胚的影响。结果 与M16对照组比较,0.5和1 μmol/L 的ICI182780、10 μmol/L的MPP明显降低4-细胞胚的发育率,导致囊胚发育失败(P<0.01);25和50 μmol/L的MPP、1 μg/mL的ERα特异性抗体将1-细胞胚阻滞在2-细胞阶段,并且50 μmol/L的MPP对细胞有毒性作用(P<0.01);0.5 μg/mL的ERα特异性抗体使细胞丧失发育至囊胚的能力(P<0.01);各浓度的PHTPP均未被观察到有上述作用(P>0.05)。结论 ER抑制剂、ERα特异性抑制剂和ERα特异性抗体均能抑制小鼠1-细胞胚的体外发育。
雌激素受体α;昆明小鼠;MPP;植入前胚;发育阻滞
雌激素受体α(estrogen receptor alpha,ERα),是类固醇激素受体的一类转录因子,在细胞核中有赖于配体的激活, 对雌激素诱导的细胞增殖、分化和发育具有调节作用,对与生长、发育和稳定内环境相关基因的表达有调控作用[1-3]。
不管是在生殖系统中还是在非生殖系统中或者是在非雌激素作用的组织细胞中,ERα对目的组织的增殖、分化作用均表现为调控相关基因的表达[4]。在植入前胚中,ERα mRNA和蛋白质的表达呈阶段特异性,2-细胞期、4-细胞期和囊胚期均可被检出,8-细胞期却未能检查到[5]。课题组的前期研究发现一定剂量的表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(-)(epigallo catechin gallate,EGCG)能够提高胚胎在体外的发育能力,同时使2-细胞胚中ERα的表达增强[6],可见,在小鼠胚胎发育过程中,ERα具有一定功能,但其具体作用尚不清楚。本实验以昆明(kunming,KM)小鼠植入前胚为研究对象,观测雌激素受体(estrogen receptor,ER)抑制剂(ICI182780)、ERα特异性抑制剂(MPP)、ERβ特异性抑制剂(PHTPP)以及ERα特异性抗体在小鼠2-细胞胚至4-细胞胚体外发育过程中的作用,为深入探讨ERα在植入前胚中的作用机制奠定实验基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1实验动物KM雌鼠4~6 周,KM雄鼠8 周以上,由上海斯莱克实验动物有限公司提供。
1.2主要药品及试剂人绒毛膜促性腺激素(hCG,美国Sigma公司),孕马血清促性腺激素(PMSG,以色列ProSpec TechnoGene公司),M2培养液、M16培养液(北京迈晨公司),ER抑制剂(ICI 182780)、ERα特异性抑制剂(MPP)、ERβ特异性抑制剂(PHTPP)(英国Tocris Bioscience公司),ERα特异性抗体(美国Santa cruz公司)。
1.3主要仪器倒置显微镜(日本Nikon公司,型号:C-DS),水套式二氧化碳培养箱(力康公司,型号:HF160W)。
1.4胚胎培养采用腹腔注射给药法,雌鼠给予6IU PMSG后46~48 h再给予6IU hCG进行促排卵,然后一对一跟雄鼠配对;第2天早晨查看雌鼠阴道是否有阴栓,有阴栓者判断为受精成功。于hCG注射后27~28 h,从有阴栓雌鼠输卵管中收集1-细胞胚,经M2洗涤,M16漂洗3次,将形态完好的1-细胞胚分别移至预孵育好的M16培养液(对照组)以及培养液滴中含有不同浓度ICI 182780(0.5和1 μmol/L)、MPP (0.1、1、10、25和50 μmol/L)、PHTPP (10、25和50 μmol/L)和ERα特异性抗体(0.25、0.5和1 μg/mL)中进行体外培养,培养条件设置为37 ℃、5% CO2、饱和湿度;观察并记录2-细胞胚、4-细胞胚和囊胚的发育状况。实验重复3次以上。
1.5数据分析及处理因卵母细胞未受精会导致发育差异,所以均选用2-细胞胚作基数,统计4-细胞胚及囊胚的发育率,所有数据采用SPSS 18.0软件进行χ2检验,以P<0.05认为有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1ICI182780阻滞1-细胞胚的体外发育KM小鼠1-细胞胚在0.5和1 μmol/L的ICI182780培养液滴中发育至4-细胞胚和囊胚的比率均低于M16对照组(P<0.01,见表1,图1B和2B)。
表11-细胞胚在不同浓度抑制剂(ICI、MPP和PHTPP)中的发育情况
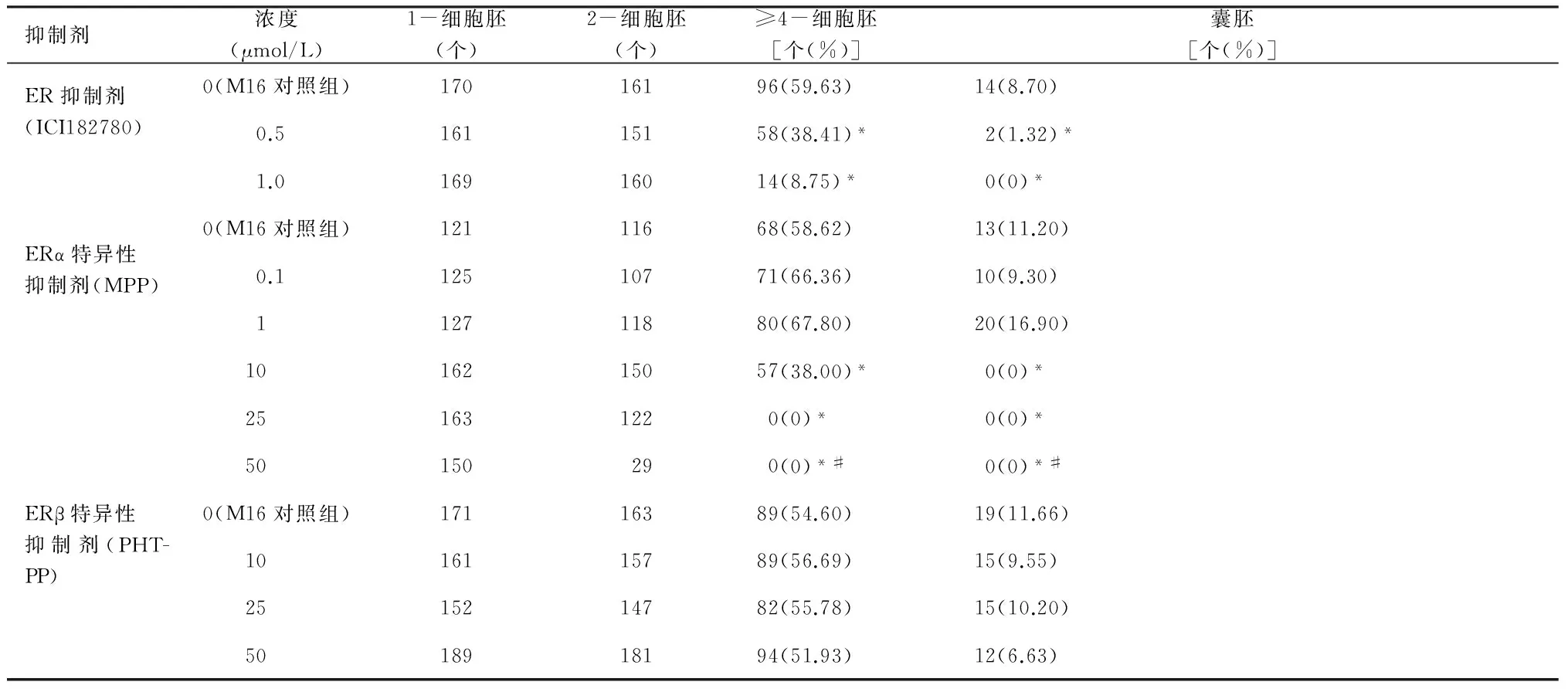
抑制剂浓度(μmol/L)1-细胞胚(个)2-细胞胚(个)≥4-细胞胚[个(%)]囊胚[个(%)]0(M16对照组)17016196(59.63)14(8.70)ER抑制剂(ICI182780)0.516115158(38.41)*2(1.32)*1.016916014(8.75)*0(0)*0(M16对照组)12111668(58.62)13(11.20)0.112510771(66.36)10(9.30)112711880(67.80)20(16.90)ERα特异性抑制剂(MPP)1016215057(38.00)*0(0)*251631220(0)*0(0)*50150290(0)*#0(0)*#0(M16对照组)17116389(54.60)19(11.66)1016115789(56.69)15(9.55)ERβ特异性抑制剂(PHT-PP)2515214782(55.78)15(10.20)5018918194(51.93)12(6.63)
*:与M16对照组比较,P<0.01。#:对细胞具有毒性作用。
2.2MPP使1-细胞胚的体外发育受阻表1中MPP的实验结果表明,与M16对照组相比较,10 μmol/L的MPP显著抑制小鼠2-细胞胚体外发育至4-细胞胚,同时使细胞失去发育至囊胚的能力(P<0.01),当培养液滴浓度为25 μmol/L时,1-细胞胚几乎全部不能发育至4-细胞胚(P<0.01,见图1C),hCG后112 h,细胞已呈坏死状态(见图2C)。而50 μmol/L的培养液滴中,1-细胞胚至2-细胞胚的发育率极低,同时于4-细胞期(hCG后64 h)可观测到细胞已表现为皱缩、发黑的坏死状态(见图1F)。
2.3PHTPP不影响1-细胞胚的体外发育与M16对照组比较,均未观察到10、25和50 μmol/L的PHTPP在小鼠植入前胚体外发育过程中的影响作用(P>0.05,见表1,图1D,2D)。

A: M16培养液(空白对照); B: ICI182780 1 μmol/L; C: MPP 25 μmol/L; D: PHTPP 50 μmol/L; E: ERα特异性抗体1 μg/mL; F: MPP 50 μmol/L。图1 KM小鼠1-细胞胚在含不同试剂浓度的培养液滴中体外发育至4-细胞胚(hCG后64 h)的培养图片
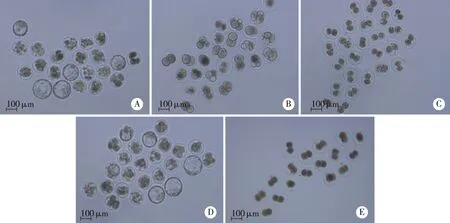
A: M16培养液(空白对照); B: ICI182780 1 μmol/L; C: MPP 25 μmol/L; D: PHTPP 50 μmol/L; E: ERα特异性抗体1 μg/mL。 图2 KM小鼠1-细胞胚在含不同试剂浓度的培养液滴中体外发育至囊胚(hCG后112 h)的培养图片
2.4ERα特异性抗体抑制1-细胞胚的体外发育当培养浓度为1 μg/mL时,1-细胞胚绝大部分被阻滞在2-细胞阶段(P<0.01,见图1E),hCG后112 h,细胞已呈坏死状态(见图2E)。而0. 5 μg/mL的培养浓度则使细胞失去发育至囊胚的能力(P<0.01,见表2)。
表21-细胞胚在不同浓度的ERα特异性抗体中的发育情况
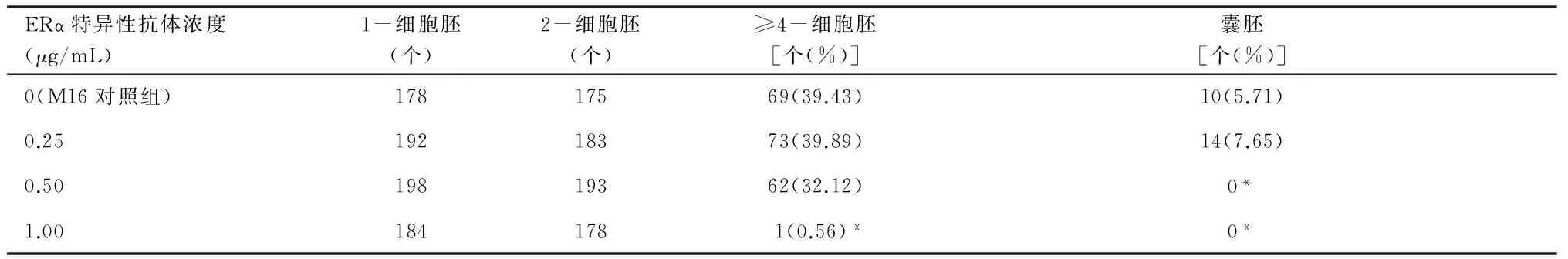
ERα特异性抗体浓度(μg/mL)1-细胞胚(个)2-细胞胚(个)≥4-细胞胚[个(%)]囊胚[个(%)]0(M16对照组)17817569(39.43)10(5.71)0.2519218373(39.89)14(7.65)0.5019819362(32.12)0*1.001841781(0.56)*0*
*:与M16对照组比较,P<0.01。
3 讨论
胚胎的发育不仅对各种各样的环境有害物质敏感,同时对内环境的各种刺激也是敏感的,任何影响因素都不利于胚胎发育成健康的、有活力的有机体甚至导致畸胎或死胎[7-9]。小鼠2-细胞中期之前,胚胎的生长有赖于母型调控,即其发育所需的mRNA和蛋白主要来自卵母细胞在其生长发育和成熟过程中所合成且累积的;但随着胚胎的进一步发育,母型mRNA和蛋白质快速降解,胚胎的后续发育则转为合子型调控,即其生长所需的mRNA和蛋白来源于合子基因组激活后所合成的;只有母型调控顺利转化为合子型调控,胚胎的生长发育才能得以继续[10]。胚胎自身合成mRNA和蛋白开始于2-细胞中期,而4-细胞时期的ERα可能来自母型,也可能来自合子型[5]。2-细胞胚发育至4-细胞胚的过程可能也是母型ERα转化为合子型ERα的过程,任何影响因素都可能导致转化失败。本研究选用ER抑制剂(ICI182780)进行胚胎体外培养发现ICI182780显著阻滞1-细胞胚的体外发育,这一结果与相关文献[11]报道一致。ICI182780和雌激素受体的亲和力很强,其利用改变受体的结构使得基因发生异常转录从而发挥其抑制功能,存在剂量依赖,被认为是“纯雌激素对抗剂”[12]。ERα和ERβ为ER的2种亚型,这2种亚型在多种组织与细胞中均有表达,研究表明,ERα和ERβ与配体的结合方式各不相同,在不同组织中发挥着各自的主导作用[13-16]。为了鉴别这2种亚型在小鼠胚胎发育过程中的功能,本实验将KM小鼠1-细胞胚分别置于MPP与PHTPP的各种浓度中,培养观测显示,MPP抑制1-细胞胚的体外发育,并存在剂量依赖性,而PHTPP不影响1-细胞胚的体外发育能力,这一结果提示,与ERβ相比较,ERα在小鼠植入前胚体外发育中发挥着更为重要的作用。MPP是ERα特异性抑制剂,彼此的亲和力很强,MPP通过影响ERα的不同基因调控位点,导致ERα激活基因转录的能力丧失[17]。进一步的研究显示,ERα特异性抗体同样使1-细胞胚的体外发育出现“阻滞”现象,说明不管是屏蔽ERα结合位点或者是降低ERα活性,均可抑制植入前胚的体外发育。
综上所述,ERα在KM小鼠植入前胚2-细胞胚至4-细胞胚体外发育的过程中具有重要作用,而ERβ未被观察到有显著作用,但ERα的具体影响机制有待进一步探讨。
[1] Candelaria N R, Liu K, Lin C Y. Estrogen receptor alpha: Molecular mechanisms and emerging insights[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2013, 114(10): 2203-2208.
[2] Teng J, Wang Z, Jarrard D F, et al. Roles of estrogen receptor alpha and beta in modulating urothelial cell proliferation[J]. Endocrine-Related Cancer, 2008, 15(1): 351-364.
[3] Christina L, Siewit B G E V, Louie A M C. Cadmium promotes breast cancer cell proliferation by potentiating the interaction between ERalpha and c-Jun[J]. Molecular Endocrinology, 2010, 24(5): 981-992.
[4] Couse J F, Korach K S. Estrogen receptor null mice: what have we learned and where will they lead us?[J]. Endocr Rev, 1999, 20(3): 358-417.
[5] Hiroi H, Momoeda M, Inoue S, et al. Stage-specific expression of estrogen receptor subtypes and estrogen responsive finge protein in preimplantational mouse embryos[J]. Endocrine Journal, 1999, 46(1): 153-158.
[6] 张卫玉, 吕俊杰, 林翠英, 等. EGCG对昆明小鼠早胚体外发育的影响[J]. 解剖科学进展, 2010, 16(2):101-104.
[7] Padmanabhan R A, Nirmala L, Murali M, et al. CrkL is a co-activator of estrogen receptor alpha that enhances tumorigenic potential in cancer[J]. Mol Endocrinol, 2011, 25(9): 1499-1512.
[8] Mattsson A, Olsson J A, Brunstrom B. Activation of estrogen receptor alpha disrupts differentiation of the reproductive organs in chicken embryos[J]. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2011, 172(2): 251-259.
[9] Wang A, Ji L, Shang W, et al. Expression of GPR30, ERalpha and ERbeta in endometrium during window of implantation in patients with polycystic ovary syndrome: a pilot study[J]. Gynecol Endocrinol, 2011, 27(4): 251-255.
[10] Shin S W, Tokoro M, Nishikawa S, et al. Inhibition of the ubiquitin-proteasome system leads to delay of the onset of ZGA gene expression[J]. The Journal of Reproduction and Development, 2010, 56(6): 655-663.
[11] Greenlee A R, Quail C A, Berg R L. The antiestrogen ICI 182780 abolishes developmental injury for murine embryos exposed in vitro to o,p'-DDT(1)[J]. Reprod Toxicol, 2000, 14(3): 225-234.
[12] Wakeling A E. Use of pure antioestrogens to elucidate the mode of action of oestrogens[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 1995, 49(11): 1545-1549.
[13] Giddabasappa A, Bauler M, Yepuru M, et al. 17-βEstradiol protects ARPE-19 cells from oxidative stress through estrogen receptor-β.Invest[J]. Ophthalmol Vis Sci, 2010, 51(10): 5278-5287.
[14] Chai J, Lee K F, Ng E H, et al. Ovarian stimulation modulates steroid receptor expression and spheroid attachment in peri-implantation endometria: studies on natural and stimulated cycles[J]. Fertil Steril, 2011, 96(3): 764-768.
[15] Pedram A, Razandi M, Lewis M, et al. Membrane-localized estrogen receptor alpha Is required for normal organ development and function[J]. Dev Cell, 2014, 29(4): 482-490.
[16] Pawar S, Laws M J, Bagchi I C, et al. Uterine epithelial estrogen receptor-α controls decidualization via a paracrine mechanism[J]. Molecular Endocrinology, 2015, 29(9): 1362-1374.
[17] Sun J, Huang Y R, Harrington W R, et al. Antagonists selective for estrogen receptor alpha[J]. Endocrinology, 2002, 143(3): 941-947.
[收稿2016-04-14;修回2016-06-15]
(编辑:王静)
The influence of ERα-specific antagonist on KM mouse preimplantation embryos development in vitro
ZhangYanqin1,WangShi’e2
(1.Department of Human Anatomy,Quanzhou Medical College, Quanzhou Fujian 362010,China;2.Department of Anatomy and Histology,Fujian Medical University, Fuzhou Fujian 350100,China)
Objective The objective of this study was to determine whether ERα plays a role in KM mouse preimplantation embryos development in vitro.Methods With blank M16 cultures as the control group, we observed the effects of different concentrations of antiestrogen ICI182780, ERα-specific antagonist MPP, ERβ-specific antagonist PHTPP and ERα specific antibody on the development of KM 1-cell embryos to 4-cell and blastocysts in vitro.Results Compared with blank M16 culture group, 0.5 and 1 μmol/l concentrations of ICI182780, as well as 10 μmol/l concentration of MPP,had significantly decreased the developmental rate of 4-cell embryos and lead to come to nothing of blastocysts (P<0.01). And, 25 and 50 μmol/l concentrations of MPP, as well as 1 μg/ml concentration of ERα specific antibody, had blocked 1-cell embryos at the 2-cell stage. Meanwhile, 50 μmol/l concentration of MPP had a toxic effect on embryos (P<0.01). 0.5 μg/ml concentration of ERα specific antibody had made the embryos lose the ability of development to the blastocysts (P<0.01). Finally, any concentration of PHTPP had been observed to have not any effect on the development of preimplantation embryos in vitro (P>0.05).Conclusion Antiestrogen and ERα-specific antagonist, as well as ERα specific antibody, could inhibit the development of 1-cell embryos in vitro.
ERα; KM mouse; MPP; preimplantation embryos; development block
泉州医学高等专科学校校级课题(NO:XJ1514)。
R321.2
A
1000-2715(2016)04-0353-05

