基于无迹Kalman滤波的基波分量提取
吕思颖,黎 丹,要 航,裴 旵
基于无迹Kalman滤波的基波分量提取
吕思颖,黎 丹,要 航,裴 旵
(广西大学电气工程学院,广西 南宁 530004)
针对全波Fourier和Kalman滤波算法在提取基波分量时对频率偏移敏感和直流偏移量抑制能力差的缺点,提出了一种新的基波分量提取算法。首先以故障信号的直流偏移量、基波角频率和基波分量作为状态变量,建立信号的非线性状态空间模型。然后采用无迹Kalman滤波(Unscented Kalman Filter,UKF)在信号的非线性模型基础上估计出基波分量。此外,滤波算法还能够实时估计出信号的直流偏移量和基波频率。通过多个算例仿真对算法进行验证与测试,仿真结果证实了算法的可行性和有效性。仿真结果表明,算法对频率突变和直流偏移量突变具有良好的适应性,能快速准确地提取出基波分量。
基波分量提取;直流偏移量;基波角频率;非线性状态空间模型;无迹Kalman滤波
0 引言
在电力系统微机保护算法中,如何有效滤除故障信号中的暂态噪声并快速准确地提取出电参量是国内外学者研究热点问题[1-8]。目前普遍采用全波和半波Fourier算法[9-11]求取故障信号的基波分量进行故障判断。全波和半波Fourier无法滤除信号中的衰减直流分量和非整数次谐波分量,对频率偏移比较敏感,对测量噪声抑制能力差,计算时间长,响应速度慢。Girgis等人将Kalman滤波引入到微机保护领域,以期望提高滤波算法的精度和速度[12-13]。Kalman滤波[10-11,14]将各次谐波视为噪声,将衰减直流分量作为状态变量进行估计,能够有效抑制各次谐波和衰减直流分量,且算法只需要当前周期的采样值,计算量和储存量小,能够实时在线计算。
但是,传统的Kalman滤波普遍采用的线性状态空间方程没有考虑恒定直流分量以及频率偏移,影响滤波算法的估计精度和对频率偏移的适应性。文献[15]建立了含有直流偏移量和基波角频率的非线性状态模型,对状态方程线性化后采用线性的强跟踪Kalman滤波器估计状态,由于采用了线性化过程,降低了滤波器的估计精度。和扩展Kalman滤波、强跟踪Kalman滤波相比,UKF[16-17]不需要对非线性系统进行线性化,具有更高的估计精度,因此被广泛应用于非线性随机系统的状态估计。
针对基于Fourier变换或Kalman滤波等滤波算法的不足,本文建立含有直流偏移量和基波角频率的信号非线性状态空间模型,利用无迹Kalman滤波算法提取信号的基波分量,通过多个算例仿真对算法进行验证和测试。
1 信号的状态空间模型
考虑非线性离散系统,其状态方程为
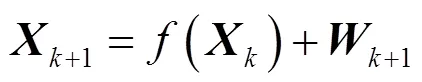
观测方程为
(2)
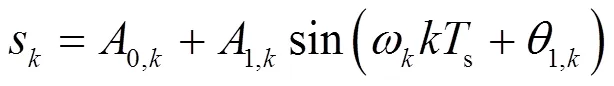

(5)
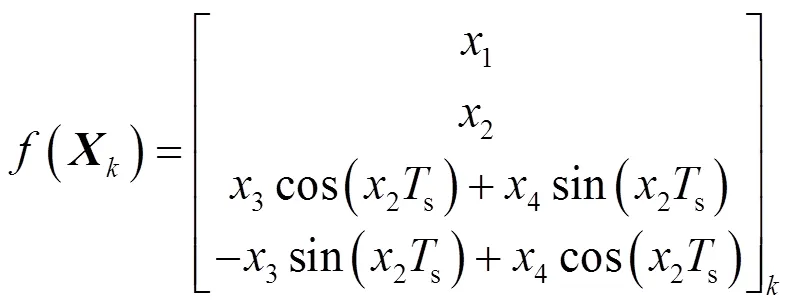
实际的电压或电流信号还包含谐波分量和测量噪声,将这些量的总和视为观测噪声。则在式(3)的基础上,得到系统观测方程用式(2)表示,其中,。
2 无迹Kalman滤波
2.1 算法原理
考虑非线性离散系统,其状态方程和观测方程分别为式(1)和式(2)。UKF算法主要有三个步骤:具体如下:
Step1:Sigma采样
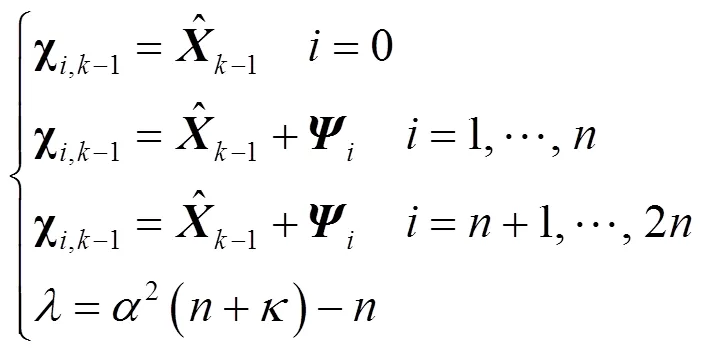
(7)
(8)
Step2:预测
预测协方差矩阵:
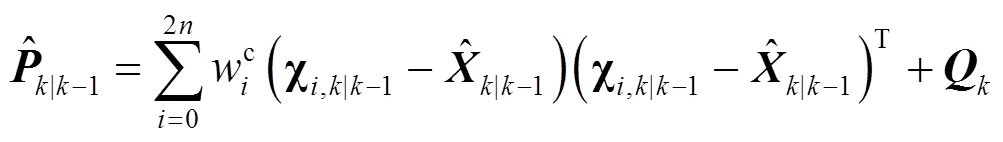
Step3:更新
计算自协方差矩阵:
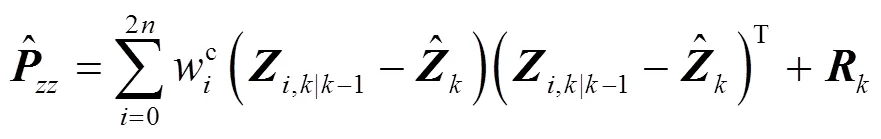
计算互协方差矩阵:
2.2 电参量提取
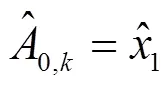
(10)
(11)
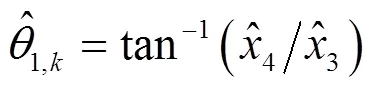
3 数值仿真实验
本节进行3个算例仿真,采用UKF算法提取三种不同测试信号的基波分量,并和传统的全波Fourier算法进行对比。定义电流测试信号:
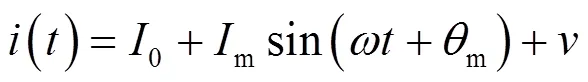
3.1 频率突变
本算例是仿真比较电力信号频率突变对全波Fourier算法和UKF算法的影响。设置电流测试信号的基波角频率在时由变化为,即基波频率由50 Hz增加到51 Hz,仿真结果如图1所示。
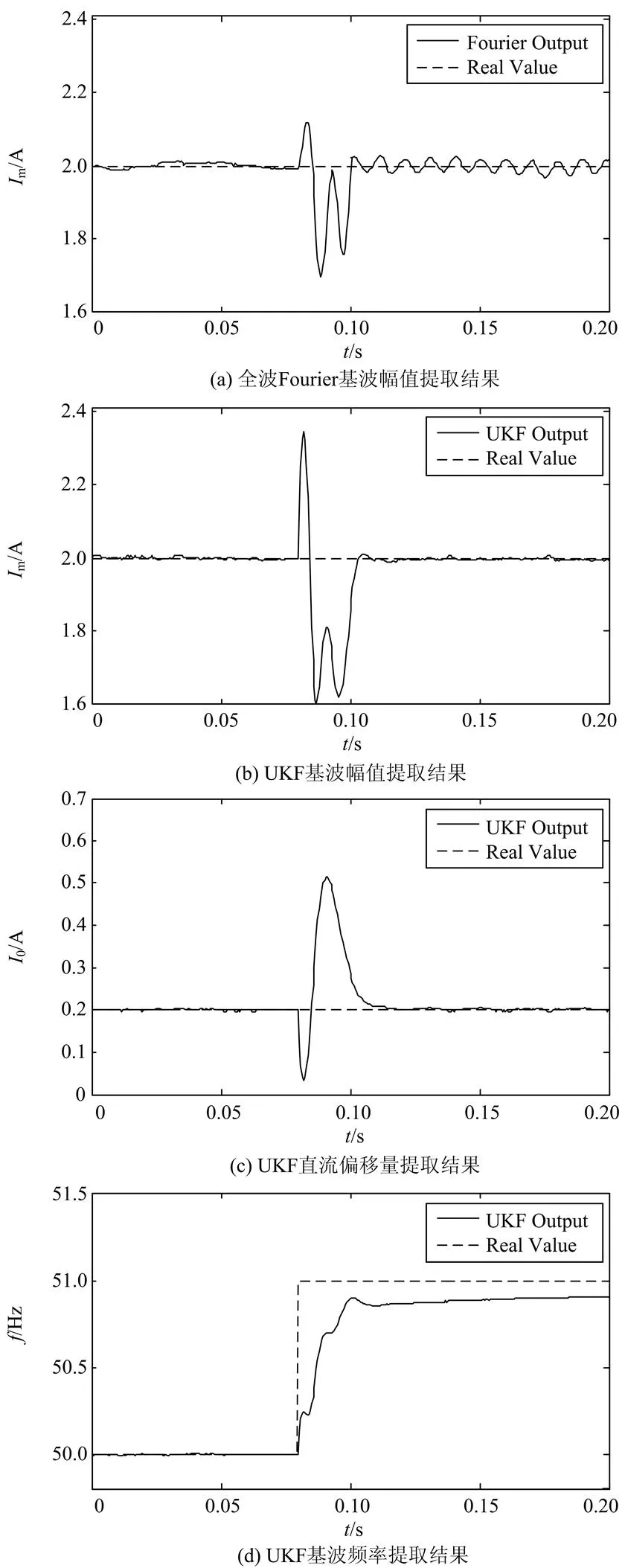
图1 信号基波频率突变时仿真结果
对比图1(a)和图1(b)可知,频率突变前,受到测量噪声的影响,全波Fourier算法基波幅值估计曲线呈现一定的振荡,而UKF算法和全波Fourier相比,其基波幅值估计曲线比较平滑,体现了UKF算法对测量噪声较强的抑制能力。频率突变后,全波Fourier最后收敛为一个持续振荡的曲线,而UKF算法和全波Fourier算法相比,虽然收敛过程中超调量更大,但是在0.11 s即收敛到稳定值,稳态误差为0.01 A,体现了UKF算法对频率突变良好的适应性。UKF算法提取直流偏移量曲线如图1(c)所示,估计曲线经过振荡后在0.11 s收敛到稳态值,稳态误差为0.004 A。UKF算法提取基波频率曲线如图1(d)所示,估计曲线在0.12 s收敛到稳态值,稳态误差为0.1 Hz。分析图1(c)和1(d)可知,UKF能够实现对直流偏移量和基波频率比较快速准确地跟踪。
3.2 直流偏移量突变
本算例是仿真比较电力信号直流偏移量突变对全波Fourier算法和UKF算法的影响。设置电流测试信号的直流偏移量在时由0.2 A变化为A,仿真结果如图2所示。
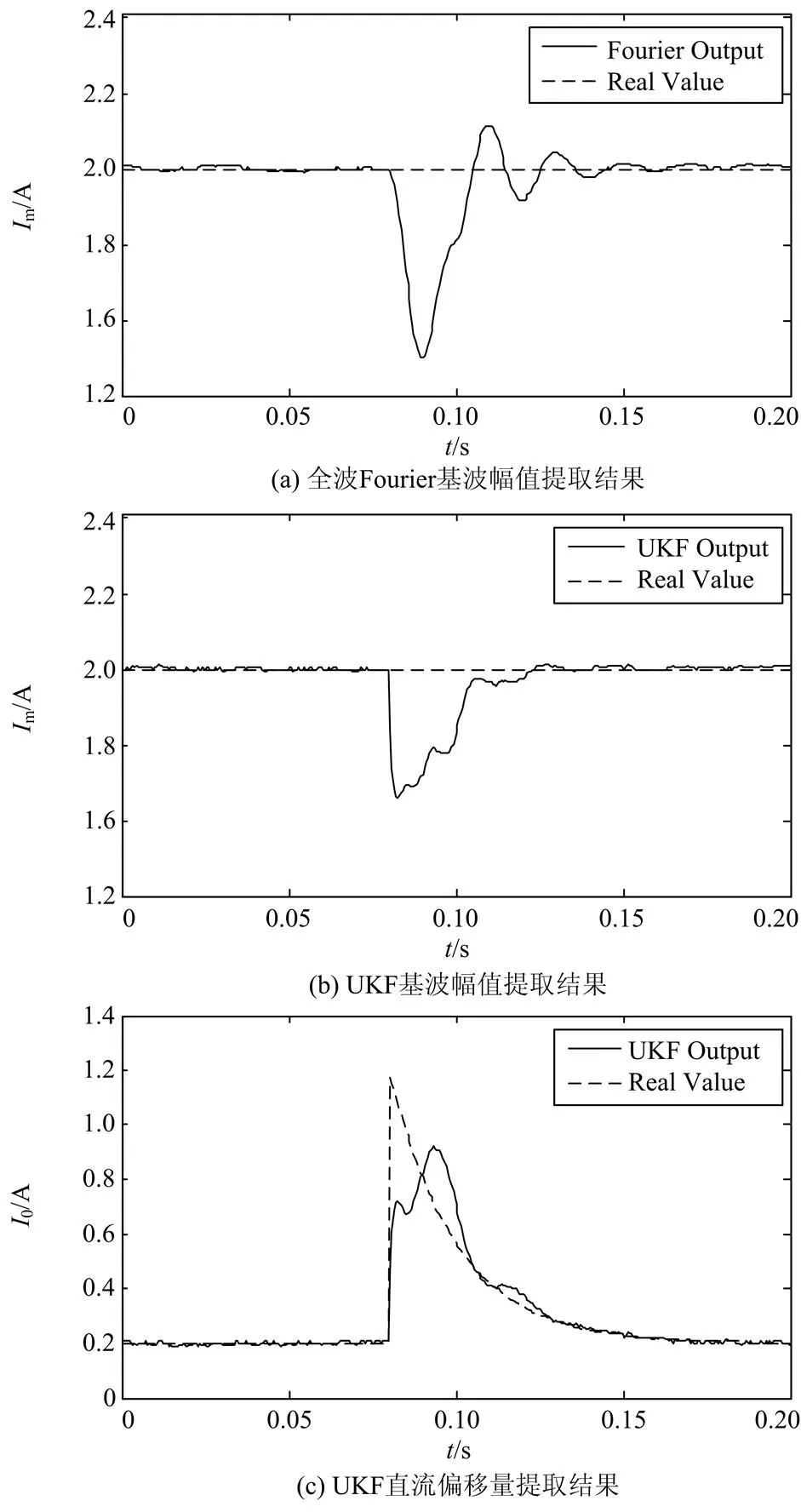
对比图2(a)和图2(b)可知,直流偏移量突变后,全波Fourier经过多次振荡在0.16 s左右收敛到稳态值,稳态误差为0.02 A,而UKF和全波Fourier算法相比,收敛曲线超调量小,振荡次数少,在0.13 s左右即收敛到稳态值,稳态误差为0.008 A,体现了UKF对直流偏移量突变良好的适应性。UKF提取信号直流偏移量和基波频率曲线分别如图2(c)和2(d)所示,从图中可知,发生突变后,估计曲线都是经过振荡后分别在0.13 s和0.14 s左右收敛到稳态值,稳态误差分别为0.005 A和0.02 Hz,体现了UKF算法对直流偏移量和基波频率良好的跟踪性能。
3.3 故障实例仿真
本算例仿真对比全波Fourier算法和UKF算法对输电线路故障信号基波分量的提取效果。在Matlab/Simulink仿真环境下搭建如图3所示的双端电源系统输电线路故障仿真模型,仿真模型参数为:
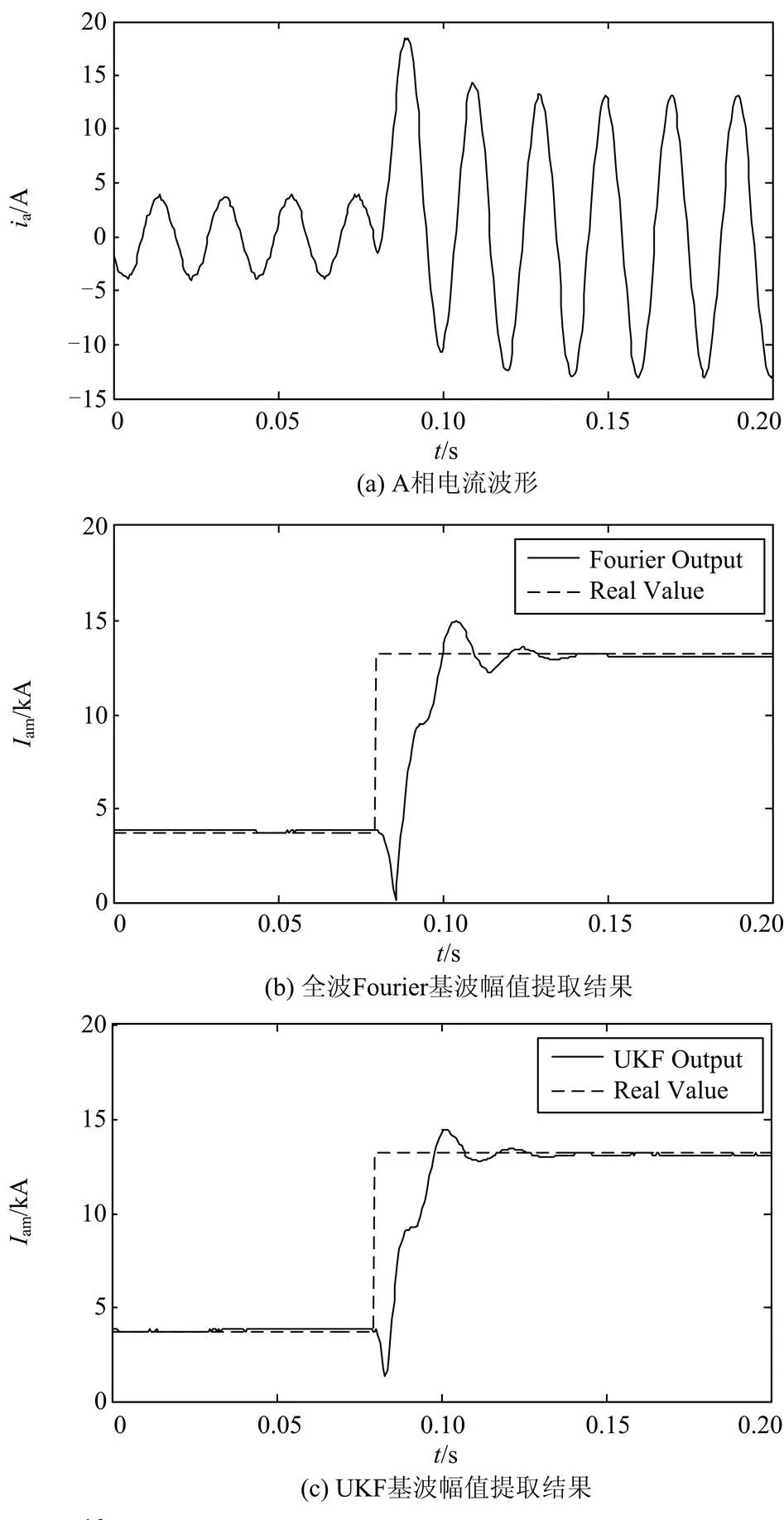
0.08 s时刻在F处设置AB两相接地短路故障,从母线M处保护装置采集A相电流如图4(a)所示。从图中可知,故障发生后的短路电流的幅值远大于正常状态下的电流幅值,并且含有衰减的直流分量。采用全波Fourier算法对故障电流的基波幅值进行估计得到的结果如图4(b)所示,利用UKF算法提取的基波幅值如图4(c)所示。首先对算法的收敛精度进行分析,从图中可知,两种算法的收敛精度都比较高,稳态误差在0.05 kA左右。然后对算法的收敛速度进行分析,受到各次谐波、衰减直流分量等暂态噪声的影响,全波Fourier算法经过多次振荡才在0.145 s左右收敛到稳态值。而UKF算法和全波Fourier算法相比,振荡次数少,超调量小,在0.125 s左右即达到稳态值,具有较快的响应速度。此外,在故障发生后,两种算法输出都存在反向突变量,和全波Fourier算法相比,UKF算法输出的突变量较小,体现了其良好的滤波性能。UKF实时估计出故障信号的直流偏移量和频率,仿真结果分别如图4(d)和4(e)所示,估计曲线能够较好地反映信号的变化趋势。
4 结论
本文采用无迹Kalman滤波在建立的信号非线性模型基础上,提取出信号的基波分量、直流偏移量以及基波频率。多个算例仿真结果表明,滤波算法抗噪声能力强,对频率突变、直流偏移量突变具有良好的适应性,在信号突变后滤波器的估计曲线能够比较快速、平滑地收敛到稳态值,具有较快的收敛速度和较高的收敛精度。
[1] 张斌, 张东来. 电力系统自适应基波提取与频率跟踪算法[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2011, 31(25): 81-88.
ZHANG Bin, ZHANG Donglai. Adaptive fundamental component extraction and frequency tracking algorithm for power systems[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2011, 31(25): 81-88.
[2] 梁远升, 王钢, 李海锋. 消除暂态过程影响的滤波算法及其在故障测距中的应用[J]. 电力系统自动化, 2007, 31(22): 77-82.
LIANG Yuansheng, WANG Gang, LI Haifeng. A filtering algorithm for eliminating effect of transient component and its application on fault location[J]. Automation of Electric Power Systems, 2007, 31(22): 77-82.
[3] 梅永, 王柏林. 降阶快速傅里叶变换算法在电力系统谐波分析中的应用[J]. 电网技术, 2010, 34(11): 117-120.
MEI Yong, WANG Bolin. Application of order-reducing Fourier transform algorithm in power system harmonics analysis[J]. Power System Technology, 2010, 34(11): 117-120.
[4] 于九祥. 利用卡尔曼滤波技术滤取工频分量的方法[J]. 电网技术, 1993, 17(6): 44-50.
YU Jiuxiang. Method of obtaining fundamental frequency components with Kalman filtering technique[J]. Power System Technology, 1993, 17(6): 44-50.
[5] 吴晓波, 赵仁德, 马帅. 电网畸变条件下基于滑动平均-自陷波滤波器的基波相位提取[J]. 电网技术, 2013, 37(12): 3528-3533.
WU Xiaobo, ZHAO Rende, MA Shuai. Fundamental phase extraction based on moving average-adaptive notch filter under distorted grid conditions[J]. Power System Technology, 2013, 37(12): 3528-3533.
[6] 江辉, 邹崇杰, 谢兴, 等. 基于集合Kalman 滤波的暂态电压扰动检测[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(17): 38-44.
JIANG Hui, ZOU Chongjie, XIE Xing, et al. Transient voltage disturbances detection based on Ensemble-Kalman filtering[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(17): 38-44.
[7] 翟明岳, 苏岭东.基于EMD-TFPF算法的电力线通信噪声消除技术研究[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(7): 51-56.
ZHAI Mingyue, SU Lingdong. A noise mitigation method based on EMD-TFPF in powerline communication system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(7): 51-56.
[8] 黄世年, 佟为明, 郭志忠, 等. 直接提取基频分量瞬时值的快速滤波算法[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2013, 41(3): 44-49.
HUANG Shinian, TONG Weiming, GUO Zhizhong, et al. A fast filtering algorithm for extracting fundamental instantaneous value[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2013, 41(3): 44-49.
[9] 胡志坚, 张承学, 陈允平, 等. 滤除衰减非周期分量的微机保护算法研究[J]. 电网技术, 2001, 25(3): 7-11.
HU Zhijian, ZHANG Chengxue, CHEN Yunping, et al. Study on protective algorithm for elimination of decaying aperiodic component[J]. Power System Technology, 2001, 25(3): 7-11.
[10] 吕思颖, 裴旵, 秦昕, 等.基于小波多尺度分析和 Kalman滤波的微机保护算法[J].电力系统保护与控制, 2015, 43(21): 54-59.
LÜ Siying, PEI Chan, QIN Xin, et al. Microprocessor- based protection algorithm based on wavelet multi-scale analysis and Kalman filter[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2015, 43(21): 54-59.
[11] 张举, 董杰. 数字保护中两种算法的比较研究[J]. 华北电力大学学报, 2003, 30(4): 6-10.
ZHANG Ju, DONG Jie. Comparison of two algorithms in digital protection[J]. Journal of North China Electric Power University, 2003, 30(4): 6-10.
[12] GIRGIS A A, BROWN R G. Application of Kalman filtering in computer relaying[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and System, 1981, 100(7): 3387-3395.
[13] GIRGIS A A. A new Kalman filtering based digital distance relay[J]. IEEE Transactions on Power Apparatus and System, 1982, 101(9): 3471-3380.
[14] 李江, 王义伟, 魏超, 等. 卡尔曼滤波理论在电力系统中的应用综述[J]. 电力系统保护与控制, 2014, 42(6): 135-144.
LI Jiang, WANG Yiwei, WEI Chao, et al. A survey on the application of Kalman filtering method in power system[J]. Power System Protection and Control, 2014, 42(6): 135-144.
[15] 马帅, 赵仁德, 吴晓波. 基于强跟踪滤波器的单相电压基波相位实时提取[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2004, 24(7): 68-73.
MA Shuai, ZHAO Rende, WU Xiaobo. Strong tracking filter based fundamental phase real-time extraction for single-phase voltage[J]. Proceedings of the CSEE, 2004, 24(7): 68-73.
[16] JULIER S J, UHLMANN J K. Unscented filtering and nonlinear estimation[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2004, 92(3): 401-422.
[17] 潘泉, 杨峰, 叶亮, 等. 一类非线性滤波器-UKF综述[J]. 控制与决策, 2005, 20(5): 481-490.
PAN Quan, YANG Feng, YE Liang, et al. Survey of a kind of nonlinear filters-UKF[J]. Control and Decision, 2005, 20(5): 481-490.
(编辑 张爱琴)
Fundamental component extraction based on unscented Kalman filter
LÜ Siying, LI Dan, YAO Hang, PEI Chan
(School of Electrical Engineering, Guangxi University, Nanning 530004, China)
Aiming at the full-wave Fourier and Kalman filter algorithms’ shortcomings of sensitive to frequency changes and poor ability of DC offset component reduction in the extraction of the fundamental component, a new fundamental component extraction algorithm is presented. First of all, this paper defines the DC offset component, fundamental angular frequency, fundamental component of the fault signal as state variables, and establishes the nonlinear state space model. Then, the Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF) is adopted to estimate the fundamental component based on the nonlinear model of signal. In addition, the filter algorithm is able to estimate the DC offset component and fundamental frequency in real-time. Several numerical simulations are carried out to testify the proposed algorithm and the results validate the algorithm's feasibility and effectiveness. The simulation results show that the algorithm is adaptive to the sudden changes of frequency and DC offset component, and it can extract the fundamental component quickly and accurately.
fundamental component extraction; DC offset component; fundamental angular frequency; nonlinear state space model; UKF
10.7667/PSPC151333
广西研究生教育创新计划项目(YCSZ2014041)
2015-07-31;
2015-09-13
吕思颖(1989-),女,通信作者,硕士研究生,研究方向为电力系统继电保护、高压直流输电;E-mail: 369347928@ qq.com 黎 丹(1991-),女,硕士研究生,研究方向为工业自动化、信号处理分析。E-mail: 631628690@qq.com

