柔性神经网络滑模主动控制技术*
杨庆超,杨理华,朱石坚,楼京俊
(1. 海军工程大学 科研部, 湖北 武汉 430033; 2. 海军潜艇学院 动力操纵系, 山东 青岛 266042)
柔性神经网络滑模主动控制技术*
杨庆超1,杨理华2,朱石坚1,楼京俊1
(1. 海军工程大学 科研部, 湖北 武汉430033; 2. 海军潜艇学院 动力操纵系, 山东 青岛266042)
针对复杂激励条件下的振动控制,对Jiles-atherton模型的磁致伸缩作动器在双层隔振系统中的主动控制进行了研究。以传统滑模控制为基础,提出一种柔性神经网络滑模控制算法。用正则化方法设计控制器的切换矩阵,建立神经网络权值和柔性映射参数更新学习公式,并将该控制策略应用于双层隔振系统的振动主动控制中。通过单频、多频及随机信号激励进行仿真研究,结果表明:柔性神经网络滑模控制器具有较强的鲁棒性,具有较好的控制效果。
双层隔振;磁致伸缩作动器;滑模控制;柔性神经网络;主动控制
目前,诸多隔振控制仅研究振源设备或基础振动,即抑制设备传递至基础振动以减小对外辐射噪声或隔离基础传递至设备振动以减小对设备的影响。实际上,设备和基础上都会存在外界激励,然而对这种复杂激励下的振动控制的研究还相对较少。双层隔振作为一种有效的隔振方式已被广泛应用,其可大幅降低机械设备振动与基础的振动传递,是隔离振动和结构噪声的有效措施,对其进行主动控制一直是国内外研究重点[1-4]。随着智能材料的发展,智能型作动器也应运而生,如磁流变作动器、记忆合金作动器、磁致伸缩作动器等,这些智能型执行机构对主动控制产生了巨大的推动作用[5-6]。
磁致伸缩作动器(Magnetostrictive Actuator, MA)具有定位精度高、响应快、频带宽、输出力大等优点,在振动控制、精密定位等领域有广阔应用前景[7-10]。张天飞等建立了超磁致伸缩作动器动力学方程,并研究了比例-积分-微分(Proportion Integration Differentiation, PID)算法的主动控制,结果表明该作动器能有效降低低频振动,但系统自适应能力较弱[11]。Francesco等分析了作动器幅频特性,并对单自由度隔振系统进行了主动控制研究,仿真表明磁致伸缩作动器可明显减小传递至基础的力[12]。王社良等设计出一种磁致伸缩作动杆,并用线性二次型调节器(Linear Quadratic Regulator, LQR)算法研究了系统结构主动振动,结果表明磁致伸缩材料作动杆可有效地减小结构的加速度和位移响应[13]。
目前,针对主动控制,较为常用的控制策略主要有PID控制[14]、鲁棒控制[15]、模糊控制[16]、最优控制[17]、自适应控制[18]、滑模控制[19]及神经网络控制[20]等。这些控制策略各有优缺点,因此可将其进行交叉融合设计复合控制器以求更好的控制效果。滑模控制在系统处于滑动模态时与系统参数摄动及外部扰动无关,鲁棒性较强,但传统滑模控制存在抖振现象,对系统稳定性有一定影响[21]。柔性神经网络采用带有可调参数的映射函数,在学习过程中能同时调整权值和映射函数参数,大大增加了神经网络灵活性和自学习能力[22-23]。结合两种算法优点,可设计一种鲁棒性能更好的柔性神经网络滑模控制算法,这也为复杂激励条件下的双层隔振主动控制提供了一种新的控制思路。
1 双层隔振系统描述
1.1隔振系统动力学模型

(1)
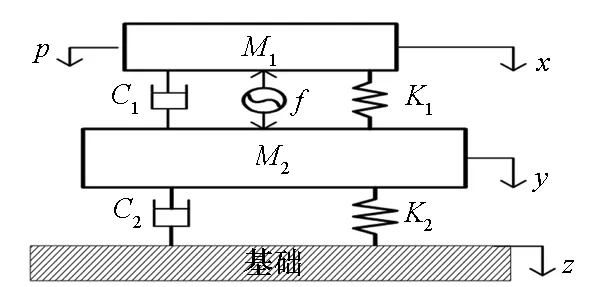
图1 双层隔振系统主动控制模型Fig.1 Active control model of double-layer vibration isolation system
1.2隔振系统状态空间
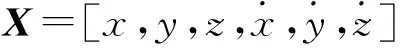
(2)
式中,
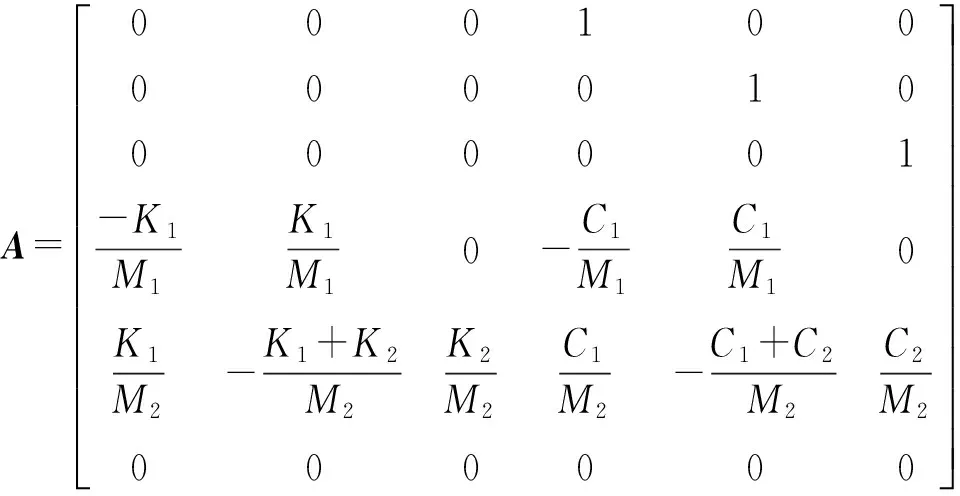
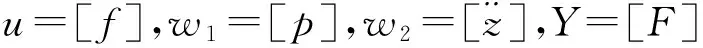
2 磁致伸缩作动器模型
MA结构及原理如图2、图3所示,主要由磁致伸缩棒(Giant Magnetostrictive Material, GMM)、驱动线圈、偏置磁场及输出顶杆等组成。
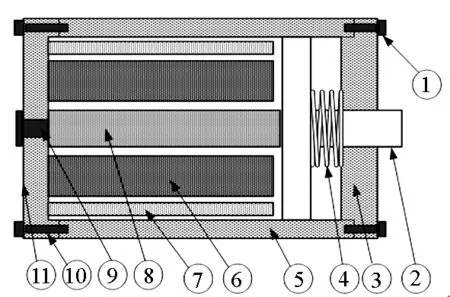
①顶端盖螺钉;②输出顶杆;③顶端盖;④预紧弹簧;⑤外套;⑥驱动线圈;⑦偏置线圈;⑧GMM⑨预紧螺钉;⑩底端盖螺钉底端盖图2 磁致伸缩作动器结构Fig.2 MA structure diagram
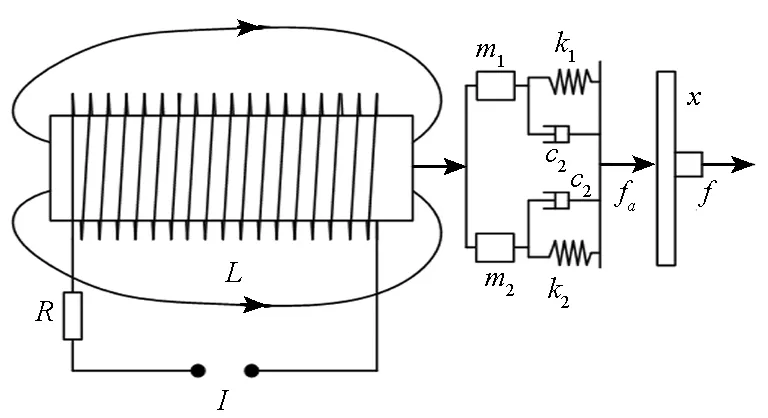
图3 磁致伸缩作动器原理Fig.3 MA schematic
以Jiles-atherton理论为基础,研究磁致伸缩作动器的非线性磁滞特征,通过优化结构、合理配置参数可使理论仿真和实验精确吻合并使作动器具有较高线性度。依据磁畴理论、压磁理论[24-25]建立磁致伸缩作动器磁化过程偏微分方程及动力学方程,如式(3)~(10)所示:
(3)
Man=Ms[coth(He/a)-a/He]
(4)
(5)
Mrev=b(Man-Mirr)
(6)
M=Mirr+Mrev
(7)
(8)
(9)
(10)
3 控制器的设计及分析
3.1系统描述
将设备和基础扰动均看作外界激励,令ΔB2=B1-1B2,方程式(2)可表示为:
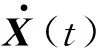
=AX(t)+BU(t)
(11)

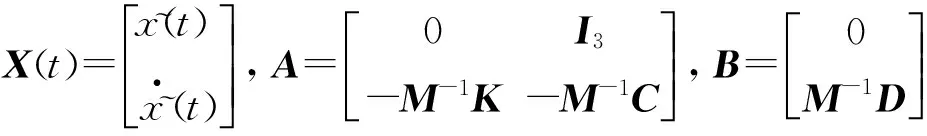
3.2滑模控制设计
滑模控制使系统从任意初始状态趋近滑模面后以全状态反馈为基础用跃变方式实现滑模运动。因此,合理设计滑模面对系统动态特性至关重要。假定系统切换函数有如式(12)所示形式[26-27]:
S(t)=ΘX
(12)

Z(t)=ΓX(t)
(13)
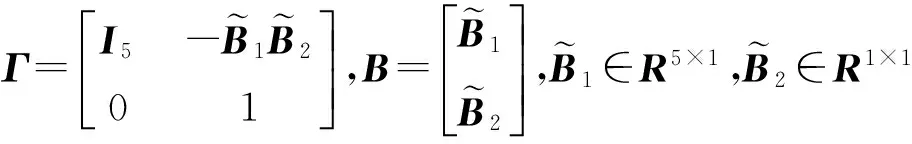
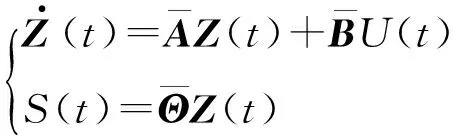
(14)

(15)
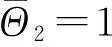
(16)
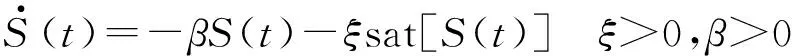
(17)
式中,β为趋近系数,ξ为切换面趋近速率,其值越大系统抖振也越强烈,sat为饱和函数,联合式(11)、式(12)、式(17)并忽略外界扰动可得滑模控制律为:
u=-(ΘB)-1{ΘAX(t)+βS(t)+ξsat[S(t)]}
(18)
3.3柔性神经网络滑模控制器设计
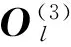

图4 柔性神经网络模型Fig.4 Flexible neural network model

(19)
那么,隐含层和输出层的输入、输出可表示为:
(20)
(21)
以中层平台位移为调整指标,如式(22)所示:
(22)
应用梯度下降法,柔性神经网络输出层网络权值调整算法为:
(23)
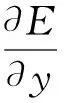
(24)
同理,可得输出层映射函数参数调整为:
(25)
柔性神经网络隐含层网络权值调整算法为:
(26)
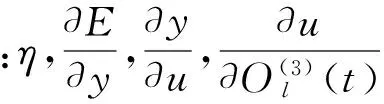
(27)
(28)
输出层、隐含层网络权值及参数更新算法为:
(29)
其中,学习速率为η∈(0,1),惯性量系数为α∈(0,1)。柔性神经网络滑模控制器通过以上算法可自适应改变连接权值和Sigmoid函数参数,从而实现滑模参数β和ξ自动调节,柔性神经网络滑模控制律可表示为:
(30)
4 数值算例
本节通过数值仿真对上述理论进行验证,中低频条件下以中层筏架平台位移为评价指标,将不同控制策略的主动控制与被动隔振进行对比,相关参数如下:
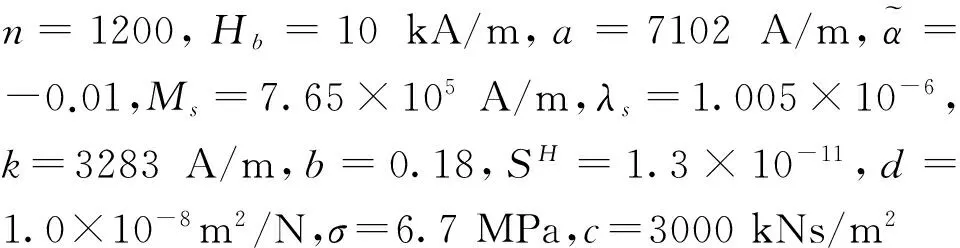
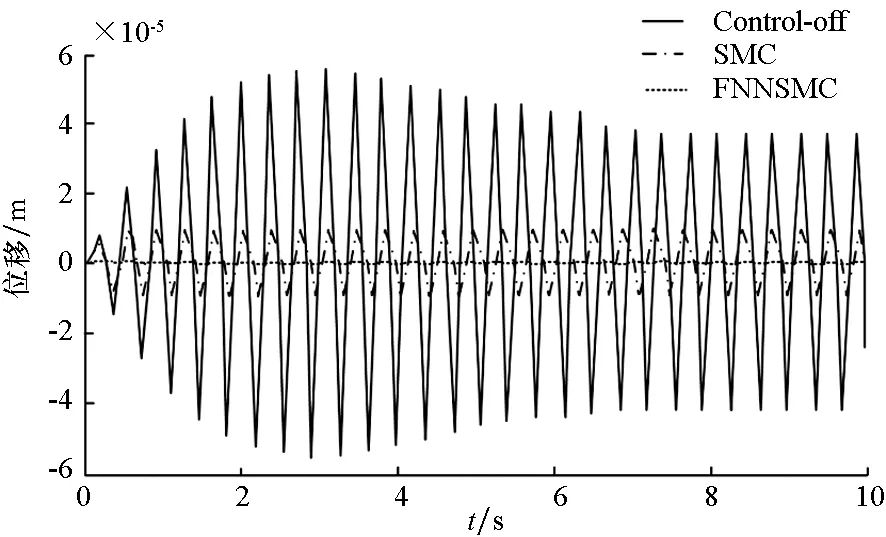
图5 单频f1激励中层位移历程图Fig.5 Time history of middle-layer displacement with f1 excitation

图6 单频f2激励中层位移历程图Fig.6 Time history of middle-layer displacement with f2excitation

图7 多频激励中层位移历程图Fig.7 Time history of middle-layer displacement with
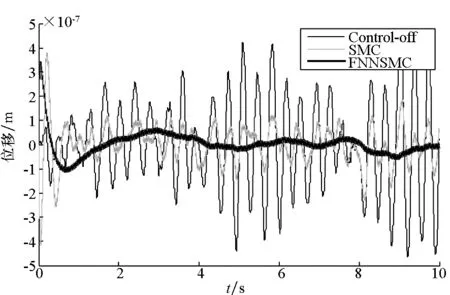
图8 随机激励中层位移历程图Fig.8 Time history of middle-layer displacement with random excitation
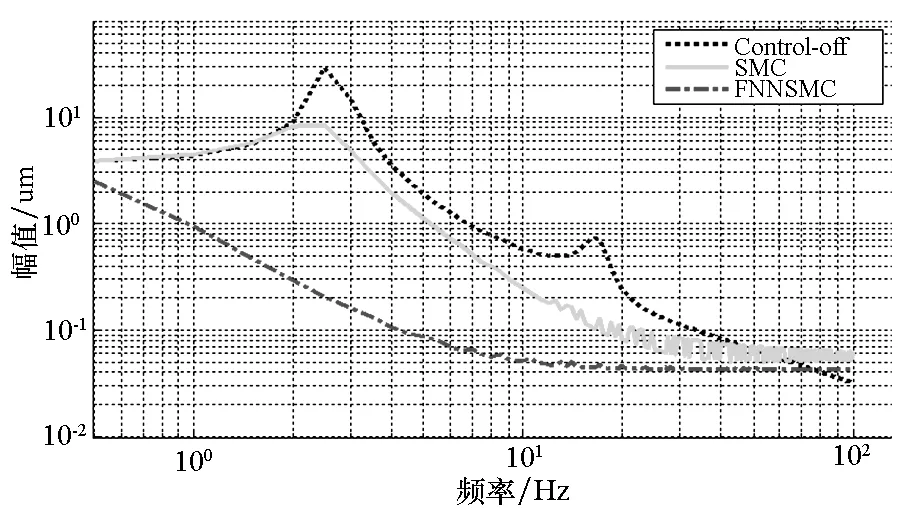
图9 中层位移幅频曲线Fig.9 Amplitude frequency curves of middle-layer displacement
图中,control-off,SMC及FNNSMC分别表示被动隔振、滑模算法及柔性神经网络滑模的主动控制。由图5~8可知,两种控制算法的主动控制均可有效抑制复杂条件下的外界激励,但相对SMC算法而言,FNNSMC明显具有更好的隔振效果和响应速度。由表1可知,相对于被动隔振,SMC和FNNSMC在单频、多频及随机激励时筏架位移分别减小了约81.08%,78.22%,81.13%,55.34%及99.46%,93.17%,96.25%,73.57%。因此,FNNSMC比SMC具有明显的优越性和良好的控制效果。
由图9可知,被动隔振系统的两个峰值所对应的固有频率与有限元软件计算的固有频率完全吻合,通过主动控制可以改变系统模态,消除系统一阶和二阶共振峰,从而达到隔振目的。由图可知,在复杂激励条件下,SMC算法主动控制在2 Hz之前隔振效果较差,随着激励频率增加控制效果存在一定振荡。而FNNSMC算法则在较宽频段内都有良好的控制效果,特别是10 Hz以内隔振效果特别明显。但是,主动控制和被动隔振的幅频曲线始终有交叉点,这也说明主动控制比较适合于中低频振动控制,可以弥补被动隔振的不足,能有效抑制振动传递并拓宽系统隔振频段,这对研究复杂激励条件下的振动控制有重要意义。
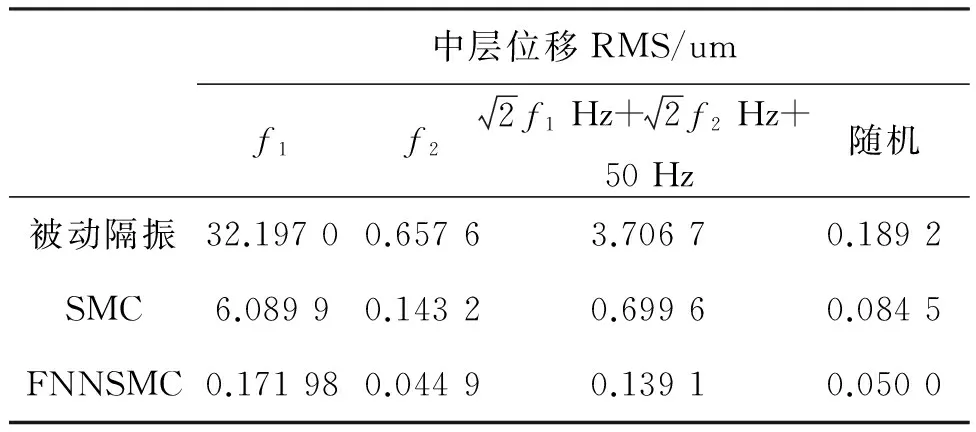
表1 各激励中层位移均方根值
5 结论
针对复杂激励条件下的振动控制,建立了双层隔振系统动力学方程,以磁致伸缩作动器为执行机构,结合滑模和神经网络理论,提出了柔性神经网络滑模控制器的设计方法,并研究其在主动控制中的应用。结果表明:在单频、多频及随机激励条件下,滑模算法及柔性神经网络滑模算法的主动控制效果均优于被动隔振;柔性神经网络滑模算法的主动控制具有更好的隔振效果和更宽的隔振频段,能有效提高响应速度并抑制振动传递;主动控制有一定的隔振范围,超出该有效频段隔振效果有所恶化。本文对研究复杂激励条件下隔振系统的设计、控制及工程应用具有实际意义。
References)
[1]高宏伟, 罗军, 贾建援. 双层隔振系统主动控制的建模与仿真[J].机械科学与技术, 2005, 24(11): 1340-1344.
GAO Hongwei, LUO Jun, JIA Jianyuan. Modeling and simulation of active control of two-layer vibration isolation system[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology, 2005, 24(11): 1340-1344. (in Chinese)
[2]杨铁军, 顾仲权, 刘志刚, 等. 双层隔振系统耦合振动主动控制试验研究[J].振动工程学报, 2003, 16(2): 25-27.
YANG Tiejun, GU Zhongquan, LIU Zhigang,et al. Experimental research on active control of coupled vibration for a two-stage isolation system [J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2003, 16(2): 25-27. (in Chinese)
[3]张克国, 杜清府.复杂激励下双层隔振系统的主动控制研究[J].中国机械工程, 2006, 17(2): 134-136.ZHANG Keguo, DU Qingfu. Study on active control of vibration in two-layer isolation system with multiple excitations[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2006, 17(2): 134-136. (in Chinese)
[4]何琳, 徐伟.舰船隔振装置技术及其进展[J].声学报, 2013, 38(2): 128-135.
HE Lin, XU Wei. Naval vessel machinery mounting technology and its resent advances[J].Acta Acustica, 2013, 38(2): 128-135. (in Chinese)
[5]王云峰, 程伟.小型航天器微振动主动控制平台建模与仿真[J].振动与冲击, 2013, 32(22): 140-145.WANG Yunfeng, CHENG Wei. Modeling and simulation of a mini micro-vibration active control platform for spacecrafts[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(22): 140-145. (in Chinese)
[6]权渭锋, 毛剑琴, 李超.智能结构与智能控制在振动主动控制中的应用[J].信息与电子工程, 2004, 2(3): 232-237.
QUAN Weifeng, MAO Jianqin, LI Chao. Application of intelligent structure and intelligent control in active vibration control [J].Information and Electronic Engineering, 2004, 2(3): 232-237. (in Chinese)
[7]Sathishkumar R,Vimalajuliet A, Prasath J S. Terfenol-D:a high power giant magnetostrictive material for submarine mapping[J].International Journal of Engineering Science and Technology, 2010, 2(12): 7165-7170.
[8]陶孟仑, 陈定方, 卢全国, 等.超磁致伸缩材料动态涡流损耗模型及试验分析[J].机械工程学报, 2012, 48(13): 146-151.
TAO Menglun, CHEN Dingfang, LU Quanguo, et al. Eddy current losses of giant magnetostrictors: modeling and experimental analysis[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 48(13): 146-151. (in Chinese)
[9]胡世峰, 朱石坚.基于CMAC小脑神经网络的超磁致伸缩作动器高精度控制的仿真研究[J].振动与冲击, 2009, 28(3): 68-72.
HU Shifeng, ZHU Shijian. High-precision control of giant magnetostrictive actuator based on CMAC neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2009, 28(3): 68-72. (in Chinese)
[10]Lau H Y, Liu K P. Feasibility of using GMM based actuators in active control of journal bearing system [C]//Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, 2009.
[11]张天飞, 汪鸿振, 孙曜.超磁致伸缩作动器用于振动主动控制中的仿真研究[J].振动与冲击, 2006, 25(1): 61-65.
ZHANG Tianfei, WANG Hongzhen, SUN Yao. Simulation on active vibration control [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2006, 25(1): 61-65. (in Chinese)
[12]Francesco C D, Simone C. A model of magnetostrictive actuators for active vibration control[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Electronics, 2011.
[13]王社良, 纪庆波, 代建波, 等.基于超磁致伸缩作动杆的结构振动主动控制研究[J].噪声与振动控制, 2010, 30(6): 23-26.
WANG Sheliang,JI Qingbo, DAI Jianbo,et al. Study on active vibration control of the structure using giant magnetostrictive actuator [J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2010, 30(6): 23-26. (in Chinese)
[14]李斌, 董万元, 王小兵.一种气动/电磁联合作动的主动隔振器设计与仿真[J].西北工业大学学报, 2013, 31(6): 871-877.
LI Bin,DONG Wanyuan,WANG Xiaobin. Design and simulation of an active vibration isolator based on pneumatic electromagnetic hybrid driving [J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University,2013, 31(6): 871-877. (in Chinese)
[15]郝慧荣, 白鸿柏, 张慧杰.六自由度主被动一体隔振平台鲁棒控制[J].振动与冲击, 2012, 31(7): 122-127.
HAO Huirong, BAI Hongbai, ZHANG Huijie. Robust control of a 6-DOF active-passive vibration isolation platform [J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(7): 122-127. (in Chinese)
[16]赫晓光.双层隔振系统模糊振动主动控制技术[J].噪声与振动控制, 2010, 30(2): 38-42.
HE Xiaoguang. Fuzzy logic control of double stage vibration isolation system[J]. Noise and Vibration Control, 2010, 30(2): 38-42. (in Chinese)
[17]高新科, 邵鹊.智能阻尼双层隔振系统的半主动最优控制[J].振动与冲击, 2012, 31(19): 128-133.
GAO Xinke, SHAO Que. Semi-active optimal control of intelligent damping double vibration isolation system [J].Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2012, 31(19): 128-133. (in Chinese)
[18]李以农, 张锋, 王雷.次级通道在线辨识的齿轮啮合振动主动控制[J].振动与冲击, 2013, 32(16): 7-12
LI Yinong, ZHANG Feng, WANG Lei.Active vibration control of gear meshing based on online secondary path identification algorithm[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2013, 32(16): 7-12. (in Chinese)
[19]胡庆雷, 马广富, 姜野.三轴稳定挠性卫星姿态机动时变滑模变结构和主动振动控制[J].控制理论与应用, 2009, 26(2): 122-126.
HU Qinglei, MA Guangfu, JIANG Ye. Variable structure control with time varying sliding mode and vibration control for flexible satellite [J].Control Theory and Applications, 2009, 26(2): 122-126. (in Chinese)
[20]朱熹育, 王社良, 朱军强.基于Sugeno型模糊神经网络的空间杆系结构的压电驱动器主动控制[J].工程力学, 2013, 30(8): 272-277.
ZHU Xiyu, WANG Sheliang, ZHU Junqiang. Sugeno-type fuzzy neural network active control of space frame structure based on piezoelectric actuator[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2013, 30(8): 272-277. (in Chinese)
[21]Lan K J, Yen J Y, Kramar J A. Sliding mode control for active vibration isolation of a long range scanning tunneling microscope[J]. Review of Scientific Instruments, 2004, 75(11): 4367-4373.
[22]Chen Y H,Yang B,Dong J W. Evolving flexible neural networks using ant programming and PSO algorithm[J].Advances in Neural Networks, 2004, 3173: 211-216.
[23]葛宝明, 林飞, 李国国.先进控制理论及其应用[M].北京:机械工业出版社, 2007.
GE Baoming, LIN Fei, LI Guoguo. Advanced control theory and its application[M]. Beijing: Mechanical Industry Press, 2007. (in Chinese)
[24]Won J K, Ali S. A novel low-power linear magnetostrictive actuator with local three-phase excitation[J]. IEEE/ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2010, 15(2): 299-307.
[25]王博文, 曹淑瑛, 黄美文.磁致伸缩材料与器件[M].北京:冶金工业出版社, 2008.
WANG Bowen, CAO Shuying, HUANG Meiwen. Magnetostrictive materials and devices [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2008. (in Chinese)
[26]Young K D, Utkin V I, Ozguner U.A control engineer′s guide to sliding mode control[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 1999, 7(3): 328-342.
[27]Ricardo C L, Maurício C O, Pedro L D. Convergent LMI relaxations for robust analysis of uncertain linear systems using lifted polynomial parameter-dependent lyapunov functions[J].Systems & Control Letters, 2008, 57(8): 680-689.
[28]郑凯, 陈杰, 杨义勇.压电自适应桁架结构智能振动控制[J].控制理论与应用, 2010, 27(7): 943-947.
ZHENG Kai, CHEN Jie, YANG Yiyong. Intelligent vibration control of adaptive piezoelectric truss structure [J]. Control Theory & Applications, 2010, 27(7):943-947. (in Chinese)
Active control technology using flexible neural network sliding mode algorithm
YANG Qingchao1, YANG Lihua2, ZHU Shijian1, LOU Jingjun1
(1. Office of Research & Development, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China; 2. Power Control Department, Navy Submarine Academy, Qingdao 266042, China)
For solving the vibration control problem in complex excitation, the active control of magnetostrictive actuator of Jiles-atherton model in double-layer vibration isolation system was researched. Based on the traditional sliding mode control, a flexible neural network sliding mode control algorithm was proposed and the controller switching matrix was designed by the regularization method, then the updating formulas of the neural network weights and flexible mapping parameter were also established. Furthermore the control strategy was used for the active vibration control in double-layer vibration isolation system. Finally, the single frequency, multi frequency and random signal excitation were simulated and the results show that the flexible neural network sliding mode controller has a strong robustness and a good control effect.
double-layer vibration isolation; magnetostrictive actuator; sliding mode control; flexible neural network; active control
10.11887/j.cn.201604020http://journal.nudt.edu.cn
2015-03-21
国家自然科学基金资助项目(51179197,51579242);国家自然科学基金青年基金资助项目(51509253)
杨庆超(1985—),男,河南许昌人,讲师,博士,E-mail:yangsuper1987@126.com
O328
A
1001-2486(2016)04-125-07

