常压室温等离子体诱变扭脱甲基杆菌AM1高产吡咯喹啉醌
李慧芝,康振,李江华,周景文,堵国成
1 江南大学 工业生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 2141222 江南大学 生物工程学院,江苏 无锡 214122
生物育种与工艺优化
常压室温等离子体诱变扭脱甲基杆菌AM1高产吡咯喹啉醌
李慧芝1,2,康振1,2,李江华1,2,周景文1,2,堵国成1,2
1 江南大学 工业生物技术教育部重点实验室,江苏 无锡 214122
2 江南大学 生物工程学院,江苏 无锡 214122
李慧芝, 康振, 李江华, 等. 常压室温等离子体诱变扭脱甲基杆菌 AM1高产吡咯喹啉醌. 生物工程学报, 2016, 32(8): 1145-1149.
Li HZ, Kang Z, Li JH, et al. Heterologous expression and characterization of Klebsiella oxytoca lysine decarboxylase. Chin J Biotech, 2016, 32(8): 1145-1149.
吡咯喹啉醌 (Pyrroloquinoline quinone,PQQ) 作为一种新型的氧化还原酶辅酶,在医药和食品等领域有广阔的应用前景。为改善扭脱甲基杆菌Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 PQQ生产性能,采用常压室温等离子体 (Atmospheric and room temperature plasma, ARTP) 进行诱变,结合高通量快速筛选方法,得到以PQQ产量为指标的正向突变株。ARTP诱变的菌株正突变率为31.6%,筛选得到的较优正突变株M. extorquens AM1 (E-F3),PQQ产量达到54.0 mg/L,是出发菌株的近3倍。系统的高通量方法筛选ARTP诱变菌为后续进一步提高M. extorquens AM1菌株PQQ的产量奠定了基础,亦为改善菌株生产性能提供了新思路。
常压室温等离子体,吡咯喹啉醌,高通量筛选,正向突变
吡咯喹啉醌 (Pyrroloquinoline quinone,PQQ)是继烟酰胺核苷酸和黄素核苷酸之后发现的第 3类氧化还原酶的辅酶[1-2],能通过参与蛋白转运来调节酶的活性[3]。PQQ是高水溶性、热稳定性分子,具有强大的抗氧化活性[4],是当今科学界的研究热点。
诱变育种是菌种改良的重要手段[5],针对传统诱变方法的低突变率和操作安全性不足等问题[6],研究人员发展了新型常压室温等离子体(Atmospheric and room temperature plasma, ARTP)诱变技术[7]。目前ARTP诱变技术已成功应用于40多种微生物,包括细菌、真菌及微藻等[8-9]。
扭脱甲基杆菌M. extorquens AM 1的PQQ合成能力强[10],且具备已知的全基因组序列信息,对于菌株PQQ合成的代谢工程研究具有重要意义。目前生物发酵法是PQQ合成的主要研究方向[11],因此筛选PQQ高产菌株是实现PQQ工业化发酵生产的前提。本研究以M. extorquens AM 1为研究对象,结合高通量筛选手段,建立快速筛选PQQ高产诱变株的方法,为今后逐步实现发酵法工业化生产PQQ奠定基础。
1 材料与方法
1.1材料
1.1.1菌种
扭脱甲基杆菌M. extorquens AM 1为本研究的出发菌株;M. extorquens AM 1 (E-F3) 为本研究获得的诱变株。
1.1.2培养基
Mex培养基:KH2PO41.0 g/L,K2HPO42.12 g/L,Methylamine·HCl 6.75 g/L,MgSO4·7H2O 0.1 g/L,CaCl2·2H2O 10 mg/L,FeSO4·7H2O 10 mg/L,MnSO4·7H2O 0.5 mg/L,Na2MoO4·2H2O 0.5 mg/L。
改良LB培养基:在LB培养基中按照Mex培养基添加相同浓度 MgSO4·7H2O、CaCl2·2H2O、 FeSO4·7H2O、MnSO4·7H2O、Na2MoO4·2H2O。
1.1.3主要试剂和仪器
Methylamine·HCl购自Sigma A ldrich公司;其他化学试剂购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
本研究所用仪器主要有:ARTP诱变育种仪(无锡源清天木生物科技有限公司);QPix 420微生物筛选系统 (Molecular Devices公司);BioTek Cytation 3酶标仪 (美国BioTek公司)。
1.2培养方法
种子培养条件:M. extorquens AM 1进行菌种活化后挑取单菌落接种于Mex培养基中,30 ℃、220 r/min培养72 h。
摇瓶发酵条件:取种子培养物接种于Mex培养基中,接种量为 10% (V/V),30 ℃、220 r/m in发酵培养6-7 d。
发酵罐发酵条件:3 L发酵罐装液量1.5 L,接种量10% (V/V),搅拌转速600 r/m in,通气比1 vvm,30 ℃发酵7-8 d。
1.3ARTP诱变方法
诱变菌液制备和预处理方法见参考文献[5]。
1.4高通量筛选
将诱变单菌落转移到96孔深孔板中的Mex培养基中,900 r/m in、30 ℃培养72 h;再以10%接种量转接到48孔深孔板中,900 r/min、30 ℃发酵培养4-5 d。
1.5分析方法
1.5.1菌体生长情况测定
取1 m L发酵液,测定吸光值OD600。
1.5.2胞外PQQ测定
检测方法见参考文献[12]。
1.5.3诱变致死率和突变率计算
致死率及突变率计算方法见参考文献[5]和[8]。
1.5.4遗传稳定性分析
为分析正向突变株的遗传稳定性,分别进行4代和6代传代培养,并分析正突变株的菌体生长情况和PQQ产量变化。
2 结果与分析
2.1ARTP诱变致死率曲线测定
如图1所示,ARTP处理85 s后致死率趋于稳定达到100%,但处理65 s出现致死率下降的折点。故本研究在避开折点的前提下选择致死率在 95%以上的处理时间,即80-95 s处理菌株,以方便后续的高通量筛选。
2.2高通量快速初筛突变株
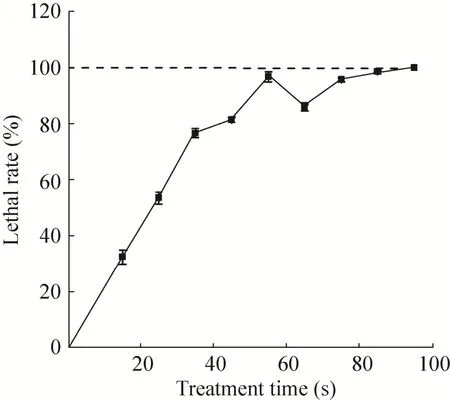
图1 扭脱甲基杆菌的致死率曲线Fig. 1 The lethal rate curve of the M. extorquens AM 1.

图2 基于48孔板的高通量筛选结果 (*A1为野生菌,图中字母A-I分别编码48孔深孔板初筛结果的热图,每个小图中字母A-H为孔板竖排编号,数字1-6为孔板横排编号)Fig. 2 Results of high-throughput prelim inary screening.

表1 较优正突变株初筛结果Table 1 Prelim inary screening results of excellent positive mutant strains
初筛结果如图2所示,其中较优正突变株初筛结果见表1。以PQQ产量为指标,对近500株诱变菌的初筛结果进行统计,得到菌株突变率为49.8%,其中正突变率为31.6%。可见ARTP诱变方法得到的菌株正突变率较高。由表 1可知,对M. extorquens AM 1首次尝试ARTP诱变初筛效果良好,较优菌株PQQ产量提高在120%以上。根据图2选择PQQ产量提高较明显的7株突变株进行后续复筛实验验证。
2.3较优正突变株摇瓶复筛
诱变菌株的摇瓶复筛结果如图3所示。由图可知,正突变株PQQ产量均比出发菌株高,其中E-F3 的 PQQ产量提高最明显,PQQ摇瓶产量达到6.3 mg/L,比出发菌株提高142.3%。
2.4遗传稳定性分析
为分析正突变株的遗传稳定性,选择上述得到的较优正突变株E-E2和E-F3进行传代发酵 (表2)。从表2可知,从菌体生长情况看,上述两株诱变菌进入生长对数中期的时间较野生菌长,可能是ARTP诱变的不定向性,引起的负面影响。以PQQ产量为评价指标,经诱变得到的M. extorquens AM 1突变株PQQ产量波动幅度较小,能保持良好的遗传稳定性。
2.5正突变株E-F3分批发酵
M. extorquens AM 1野生菌和正突变株E-F3发酵结果分别如图4A和图4B所示。
比较图4A和图4B,发现M. extorquens AM 1出发菌株在发酵156 h,发酵液中PQQ积累量达到最大值,约为18.0 mg/L;E-F3发酵168 h达到最大值,约为54.0 mg/L,是出发菌株的3倍。可见,经ARTP诱变后,PQQ产量有明显提高。
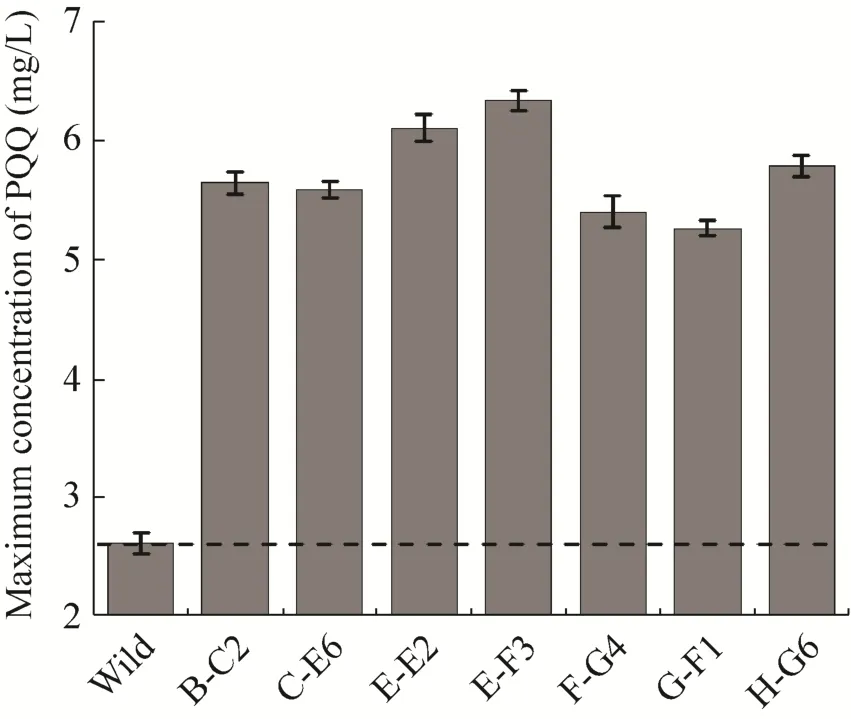
图3 较优正突变株复筛结果 (*虚线代表野生菌产量值)Fig. 3 PQQ yield of excellent positive mutant strains.
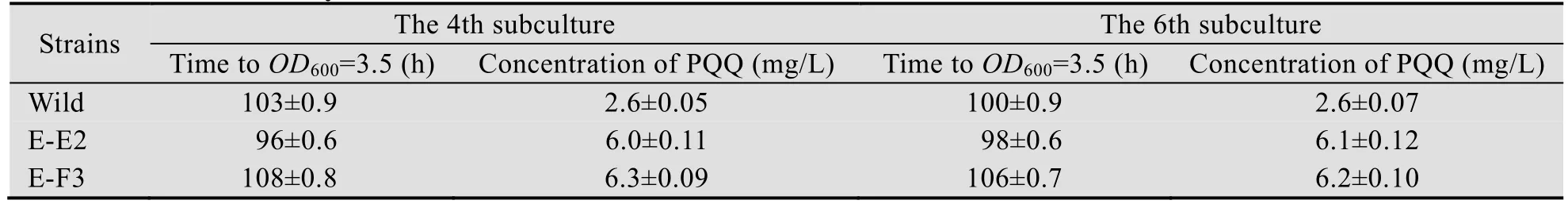
表2 突变菌的遗传稳定性Table 2 Genetic stability of mutant strains
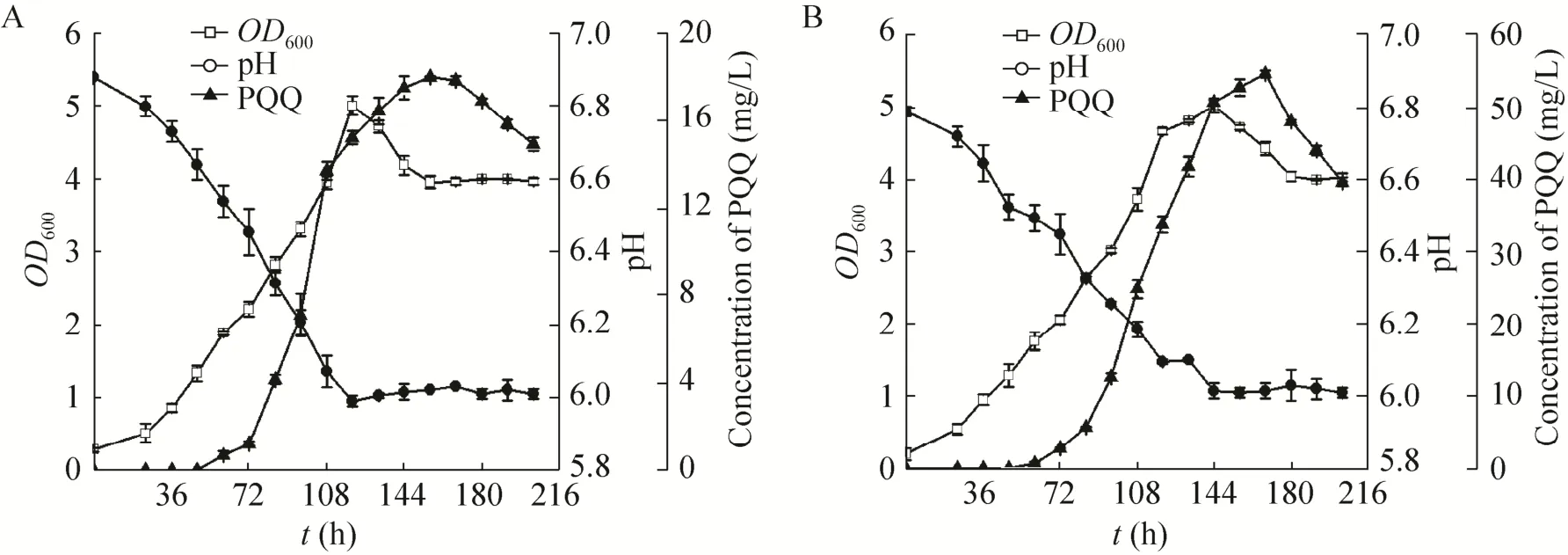
图4 M. extorquens AM 1野生菌 (A) 和正突变株E-F3 (B) 的分批发酵结果Fig. 4 Batch fermentation of M. extorquens AM 1 (A) and E-F3 (B).
3 讨论
据报道食甲基营养菌Methylovorus sp. MP688[11]、生丝微菌TH205[13]和假单胞杆菌Pseudomonas sp. 0813[14]产PQQ最高水平分别可达到 15 mg/L、26.6 mg/L和 448 mg/L。可见,M. extorquens AM 1菌株在PQQ产量提升方面还有很大进步空间。首先,可以尝试从多次累积诱变或者发酵工艺优化方面来进一步提高 PQQ产量。其次,研究表明,在氧化葡萄糖酸杆菌Gluconobacter oxydans 621H中 过 量 表 达pqq ABCDE基因簇,PQQ产量提高了近30倍[15]。由此启发我们,可以尝试调节PQQ基因簇中某个基因的比例或过量表达PQQ合成基因簇来进一步提高PQQ产量。最后,结合基因组学和蛋白质组学技术,可以尝试将PQQ高产诱变菌中基因的改变,与PQQ生物合成途径相关联,以进一步促进PQQ的合成。
REFERENCES
[1] Duine JA. Cofactor diversity in biological oxidations: implications and applications. Chem Rec, 2001, 1(1): 74-83.
[2] Matsushita K, Toyama H, Yamada M, et al. Quinoproteins: structure, functions and biotechnological applications. Appl M icrobiol Biotechnol, 2002, 58(1): 13-22.
[3] Kasahara T, Kato T. Nutritional biochemistry: a new redox-cofactor vitamin for mammals. Nature, 2003, 422(6934): 832.
[4] Pandey S, Singh A, Kumar P, et al. Probiotic Escherichia coli CFR 16 producing pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ)ameliorates 1,2-dimethylhydrazine-induced oxidative damage in colon and liver of rats. Appl Biochem Biotechnol, 2014,173(3): 775-786.
[5] Wang FF, Sun PY, Yin HJ, et al. Mutation of alcohol-producing yeast using atmospheric room temperature plasma and the mutant strain characteristic. China Brew, 2013, 32(10): 117-119 (in Chinese).
王方方, 孙沛勇, 银会娟, 等. 常压室温等离子体快速诱变酒精酵母及其突变株的特性研究. 中国酿造, 2013, 32(10): 117-119.
[6] Kurowska M, Labocha-Pawłowska A, Gnizda D, et al. Molecular analysis of point mutations in a barley genome exposed to MNU and gamma rays. Mutat Res, 2012, 738-739: 52-70.
[7] Wang LY, Huang ZL, Li G, et al. Novel mutation breeding method for Streptomyces avermitil is using an atmospheric pressure glow discharge plasma. J Appl M icrobiol, 2010,108(3): 851-858.
[8] Jin LH, Fang MY, Zhang C, et al. Operating conditions for the rapid mutation of the oleaginous yeast by atmospheric and room temperature plasmas and the characteristics of the mutants. Chin J Biotech, 2011, 27(3): 461-467 (in Chinese).
金丽华, 方明月, 张翀, 等. 常压室温等离子体快速诱变产油酵母的条件及其突变株的特性. 生物工程学报, 2011,27(3): 461-467.
[9] Zhang X, Zhang XF, Li HP, et al. Atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP) as a new powerful mutagenesis tool. Appl M icrobiol Biotechnol, 2014, 98(12): 5387-5396.
[10] Stoddard SF. Bacterial strains for the production of pyrroloquinoline quinone: US, 6511820. 2003-01-28.
[11] Zhong SS, Liu H, Ge XZ, et al. Optimization of fermentation conditions for pyrroloquinoline quinone expression by Pseudomonas 0813. J Beijing Univ Chem Technol: Nat Sci,2013, 40(5): 88-92 (in Chinese).
钟杉杉, 刘辉, 葛喜珍, 等. 吡咯喹啉醌生产菌的发酵条件优化. 北京化工大学学报: 自然科学版, 2013, 40(5): 88-92.
[12] Gao LL, Du GC, Zhou JW, et al. Characterization of a group of pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent dehydrogenases that are involved in the conversion of L-sorbose to 2-keto-L-gulonic acid in Ketogulonicigenium vulgare WSH-001. Biotechnol Progr, 2013, 29(6): 1398-1404.
[13] Xiong XH, Zhi JJ, Yang L, et al. Complete genome sequence of the bacterium Methylovorus sp. strain MP688, a high-level producer of pyrroloquinolone quinone. J Bacteriol, 2011,193(4): 1012-1013.
[14] Yin F, Lu B, Chen GH, et al. Study on the production of pyrroloquinoline quinone by using methanol-utilizing bacteria. J East China Univ Sci Technol, 2004, 30(2): 227-229, 233 (in Chinese).
尹芳, 陆兵, 陈国豪, 等. 甲醇利用型细菌发酵生产吡咯喹啉醌的培养条件. 华东理工大学学报, 2004, 30(2): 227-229,233.
[15] Höelscher T, Göerisch H. Knockout and overexpression of pyrroloquinoline quinone biosynthetic genes in Gluconobacter o xydans 621H. J Bacteriol, 2006, 188(21): 7668-7676.
(本文责编 郝丽芳)
Mutagenesis of Methylobacterium extorquens AM1 for increasing pyrroloquinoline quinone production by atmospheric and room temperature plasma
Huizhi Li1,2, Zhen Kang1,2, Jianghua Li1,2, Jingwen Zhou1,2, and Guocheng Du1,2
1 Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu, China
2 School of Biotechnology, Jiangnan University, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu, China
As a novel cofactor of oxidoreductase, pyrroloquinoline quinone (PQQ) has a great potential of application in medicine, food industries. In order to improve the efficiency of the PQQ production by Methylobacterium extorquens AM1,the strain was treated by atmospheric and room temperature plasma (ARTP). Positive mutants with changes in PQQ yield were obtained based on a high-throughput screening approach. After ARTP treatment, analysis data show that the positivemutation rate was 31.6%. Furthermore, we obtained an excellent positive mutant M. extorquens AM 1 (E-F3) w ith the yield of 54.0 mg/L PQQ, which was approximately 3 times as much compared w ith that of the w ild-type strain. The robust high-throughput screening method for mutagenesis by ARTP improves PQQ production. In addition, this method also provides a new strategy for further strain improvement.
December 9, 2015; Accepted: March 24, 2016
Guocheng Du. Tel: +86-510-85918309; E-mail: gcdu@jiangnan.edu.cn
atmospheric and room temperature plasma, pyrroloquinoline quinone, high-throughput screening, positive mutation
Supported by: National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program) (No. 2012AA022103), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2014CB745100), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University (No. NCET-12-0876).
国家高技术研究发展计划 (863计划) (No. 2012AA022103),国家重点基础研究发展计划 (973计划) (No. 2014CB745100),新世纪优秀人才支持计划 (No. NCET-12-0876)资助。

