miR-21 miR-205联合检测对非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值
陈弘磊 王伟⋆ 李芳琼 刘琴 赵桂枝
miR-21 miR-205联合检测对非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值
陈弘磊 王伟⋆ 李芳琼 刘琴 赵桂枝
目的 探讨联合检测血液中microRNA-205(miR-205)和microRNA-21(miR-21)对非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值。方法 收集27例非小细胞肺癌患者术前及术后血清,并收集29例健康志愿者血清作为对照。应用实时荧光定量PCR 法检测以上标本中miR-205和miR-21 的表达水平,并分析其与临床病理特征的相关性,评估miR-205和miR-21联合检测对非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值。结果 非小细胞肺癌患者术前血清中miR-205和miR-21的表达水平均高于健康人群(P< 0.05),其中23例非小细胞肺癌患者术后血清中miR-205的表达水平较术前明显降低(P<0.01),术前与术后miR-21表达水平无显著性差异(P>0.05)。而术前血浆中miR-205和miR-21的表达水平与患者淋巴结转移及Dukes分期存在相关性(P<0.05)。miR-205和miR-21 的受试者(ROC)曲线下面积为0.968,非小细胞肺癌患者和健康人群的敏感度和特异度分别为96.3%和89.7%。结论 血清miR-205和miR-21作为新的生物学指标,两者联合检测对非小细胞肺癌的诊断和预后监测有一定价值。
非小细胞肺癌 miR-21 miR-205 联合检测
肺癌是一种全球范围内常见的癌症,出现临床表现时已经是晚期,故有较高的致死率[1]。约75%的肺癌患者在确诊时已经是晚期或癌细胞已经转移,因此肺癌患者5年生存率<15%[2]。miRNA在血清/血浆中可以稳定存在,表达量不受各种保存条件、保存时间的影响;且miRNA的表达无年龄、性别差异,具有肿瘤特异性[3]。因此,血清/血浆中miRNAs可能成为一种新的非侵入性肿瘤标志物。2013年10月至2015年至5月作者通过实验研究,探讨联合检测血液中miR-205、miR-21对非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样本 采集EDTA抗凝血浆样本,健康对照组29例,男15例,女14例;年龄(46.3±11.2)岁。肺癌组27例,男16例,女11例;年龄(49.6±9.7)岁。病理诊断均为非小细胞肺癌,术前均未进行过化疗、放疗,1例术后脱落。肺癌患者术前、术后3d分别采集血浆。
1.2 试剂及仪器 血浆miRNA提取采用miRcute miRNA Isolation Kit。反转录试剂盒采用TaqMan® MicroRNA Reverse Transcription Kit。探针由自行设计并合成;反转录茎环引物、PCR扩增引物由自行设计合成。cel-miR-39购自QIAGEN。BioRad CFX实时荧光定量PCR仪。
1.3 血浆miRNA的提取及cDNA制备 使用miRcute miRNA Isolation Kit提取血浆miRNA,使用TaqMan® MicroRNA Reverse Transcription Kit反转录成cDNA。
1.4 PCR反应 miRNA反转录为cDNA后,按照下面组分进行PCR反应。循环参数设置:95℃10min预变性,然后95℃15s 和60℃1min退火延伸40个循环。荧光通道检测选择FAM。单点荧光检测在60℃。反应体系为20μl,包括检测试剂混合液(18.5μl)、DSC-Taq DNA聚合酶(0.2μl)、cDNA(1.3μl)。
1.5 统计学方法 采用SPSS软件。计算术前术后ΔmiR-21、ΔmiR-205的差值xi=Ct(术后ΔmiRNA)-Ct(术前ΔmiRNA),然后计算差值的平均数和标准差,并计算T0,并查表得t0.05。若T0<t0.05,则术前术后无显著差异;若T0>t0.05,则术前术后差异显著。
2 结果
2.1 肺癌组术前与术后miR-21、miR-205检测结果比较 miR-21术后与术前比较差异无统计学意义,miR-205术后与术前比较差异有统计学意义。见图1、图2、表1。
2.2 两组术前、术后miR-21、miR-205比较 两组术前比较,差异有统计学意义(P< 0.01),可用于肺癌的判定;而两组术后比较,miR-21差异有统计学意义,miR-205差异无统计学意义。见表2。

图1 miR-21在术前与术后的表达差异
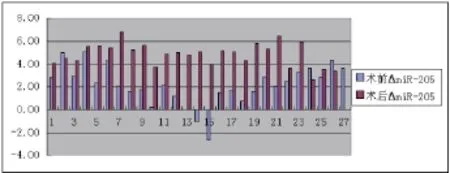
图2 miR-205在术前与术后的表达差异
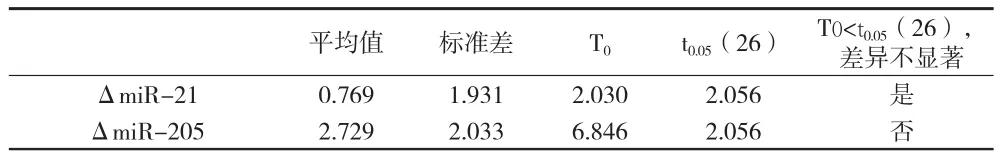
表1 肺癌组术前与术后miR-21、miR-205比较
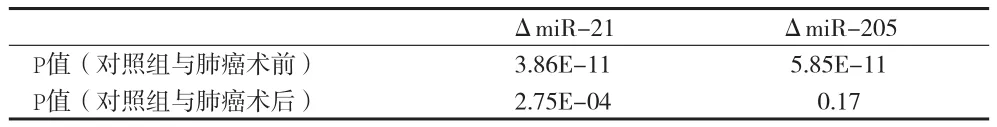
表2 miR-21、miR-205与正常健康组t-test结果比较
2.3 ROC曲线和cut-off值 从图3及表3中可知,曲线下面积为0.968,表明miR-21和miR-205联检对肺癌的判别有意义(P<0.001)。根据ROC曲线坐标,选择敏感度+特异性最大值-1.435作为cut-off值,此时灵敏度为0.963,特异性为0.897。比较Ct计算公式为:Ct(-ΔmiR-21)×0.578 + Ct(-ΔmiR-205)×0.550,若比较Ct > -1.435,则为肺癌;比较Ct < -1.435,则为健康。
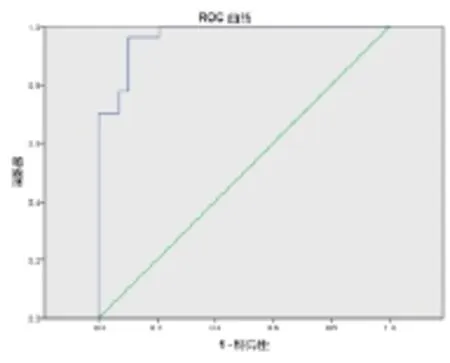
图3 ΔmiR-21、-ΔmiR-205ROC曲线

表3 曲线下面积
3 讨论
微小RNA(miRNAs)是一类核苷酸序列高度保守、长度为21~23nt的非编码单链RNA,主要参与转录后水平的基因调控,介导基因沉默。人类miRNA编码基因有700多个结合位点,而将近1/3基因的表达调控均有miRNA的参与,涉及细胞分化、增殖与凋亡等生命活动的多个进程。miRNA的表达异常能够引发多种疾病,甚至导致肿瘤的发生[4]。研究表明,大量的miRNA位于与肿瘤相关的基因区、杂合性丢失区与扩增区[5],且在较多恶性肿瘤(如肺癌、肝癌、结肠癌、卵巢癌等)组织中均有异常表达,提示肿瘤发生可能与miRNA有密切关联[6]。
miR-21是miRNA家族中成员之一,成熟的miR-21主要通过与靶mRNA的3'UTP完全或不完全的特异性配对从而影响mRNA的降解,或通过与靶mRNA序列互不配对结合而阻断其翻译过程,最终在转录后水平上调控基因表达[7]。进而调节一系列机体重要的生理过程,包括细胞的增殖、分化与凋亡等。近年来对miR-21与肿瘤的大量研究表明,miR-21在多种肿瘤组织中均有异常表达,典型的有肺癌、胃癌、前列腺癌、乳腺癌等[8];研究显示miR-21拥有抗凋亡作用,相当于癌基因功能。有研究表明,在非小细胞肺癌患者的血清中,miR-146b、miR-221、let-7a、miR-155、miR-17-5p、miR-27a、miR-106a的表达量显著下降,而miR-29c的表达量则显著升高[9]。miR-21、miR-210在NSCLC表达谱中通常表现为显著下调[10]。Wang 等[11]认为,与健康组比较,非小细胞肺癌患者血清中的miR-21显著提高。miR-21的高表达水平和淋巴结转移及淋巴结分期相关。
miR-205是miRNA家族中与肿瘤发生密切相关的另一成员,核苷酸序列高度保守,位于人第一号染色体LOC642587位点第二内含子中[12]。miR-205在各种肿瘤中的表达水平并不一致,有研究报道,在前列腺癌和乳腺癌等肿瘤组织中miR-205表达明显下降[13],而在肺癌组织中表达显著上调。Markou等应用PCR技术对非小细胞肺癌患者研究中,检测到肿瘤细胞中miR-205高表达,但表达量与生存率无关[14]。
本资料结果表明,非小细胞肺癌患者术前miR-21、miR-205均明显升高,采用ROC曲线评估,当cut-off值取-1.435时,灵敏度为96.3%,特异性为89.7%,具有极其良好的对临床非小细胞肺癌的诊断价值。 肺癌患者术前与术后血浆miR-21差异无统计学意义,而miR-205差异有统计学意义,肺癌患者术前与术后miR-21与对照组比较差异有统计学意义,而miR-205术前差异有统计学意义,术后差异无统计学意义。表明血浆miR-21在肺癌术后3d并未立即下降,而miR-205则会立即下降至正常水平,因此miR-205可能为非小细胞肺癌的一个相关的肿瘤指标,可能比其他miR更加灵敏地反映肿瘤的变化。综上所述,联合检测miR-21、miR205能更有效提高非小细胞肺癌的检出率,为术后的治疗效果提供更可靠的依据,有望为肿瘤诊断、治疗及预后过程提供一种新方法。
1 Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, et al. Cancer statistics,2010. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians, 2010, 60(5): 277~300.
2 Aberle DR, Berg CD, Black WC, et al. The National Lung Screening Trial: overview and study design. Radiology ,2011,258:243~253.
3 Heegaard N H H, Schetter A J, Welsh J A, et al. Circulating micro-RNA expression profiles in early stage nonsmall cell lung cancer. International Journal of Cancer, 2012, 130(6): 1378~1386.
4 SM H. MicroRNAs as oncogenes. Current Opinion in Genetics & Development, 2006, 16:103~105.
5 Calin G A.Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and genomic regions involved in cancers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2004,101(9): 2999~3004.
6 Chen X, Ba Y, Ma L, et al. Characterization of microRNAs in serum: a novel class of biomarkers for diagnosis of cancer and other diseases.Cell research,2008,18(10): 997~1006.
7 Volinia S. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2006,103(7): 2257~2261.
8 Lui W O. Patterns of known and novel small RNAS in human cervical cancer. Cancer Research, 2010,67:671~675.
9 Yu L, Todd N W, Xing L, et al. Early detection of lung adenocarcinoma in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. International Journal of Cancer, 2010, 127(12): 2870~2878.
10 Chen X, Hu Z, Wang W, et al. Identification of ten serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as novel noninvasive biomarkers for nonsmall cell lung cancer diagnosis. International Journal of Cancer, 2012, 130(7): 1620~1628.
11 Wang Z X, Bian H B, Wang J R, et al. Prognostic significance of serum miRNA-21 expression in human non-small cell lung cancer. Journal of surgical oncology, 2011, 104(7): 847~851.
12 Landgraf P. A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell, 2007,129(7): 1401~1414.
13 Majid S.MicroRNA-205-directed transcriptional activation of tumor suppressor genes in prostate cancer. Cancer, 2010,116(24):5637~5649.
14 Athina Markou, Emily GTsaroucha, Loukas Kaklamanis,et al.Prognostic value of mature microRNA-21 and microRNA-205 overexpression in non-small cell lung cancer by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. Clinical Chemistry, 2008, 54(10): 1696~1704.
Objective To explore the diagnostic value of plasma microRNA-205(miR-205)and microRNA-21(miR-21) in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Methods The preoperative plasma specimens from 29 patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer and their postoperative (at day 7 after operation) plasma specimens (only 26 cases among them) were collected. At the same time,the plasma specimens from 33 healthy volunteers were used as the controls. The expression of miR-205 and miR-21 in these samples was measured by real-time fl uorescence quantitative-PCR,and its relationship with the clinical characteristics of patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer was analyzed. Results The expression level of miR-205 and miR-21 in preoperative plasma from the patients with Non-small Cell Lung Cancer was higher than that from healthy volunteers (P<0.05). As compared with the preoperative plasma,the expression of miR-205 in postoperative plasma from 23 cases was decreased remarkably (P<0.01).however,the expression level of miR-21 in postoperative plasma group and preoperative plasma group didn't signifi cantly differ (P>0.05). The expression of miR-205 and miR-21 in preoperative plasma had a signifi cant impact on lymphatic metastasis and Duke's stage (P<0.05). For discriminating Non-small Cell Lung Cancer patients from healthy volunteers,the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve was 0.968,and the sensitivity and specifi city were 96.3% and 89.7%,respectively. Conclusion Plasma miR-205 and miR-21,as new biomarkers,the combined detection of them may help the diagnosis of non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Non-small Cell Lung Cancer MicroRNAs Diagnosis Plasma MicroRNA-205 MicroRNA-21
·基础研究·
浙江省公益技术研究社会发展项目(2013C33199)
310000 浙江中医药大学(陈弘磊)
310012 浙江省立同德医院(王伟 李芳琼 刘琴赵桂枝)

