采用粒片状肥料实现夏玉米一次施肥的可行性研究
王宜伦, 白由路, 谭金芳, 刘 举, 卢艳丽, 韩燕来*
(1中国农业科学院农业资源与农业区划研究所, 农业部植物营养与肥料重点实验室, 北京 100081;2河南农业大学资源与环境学院, 河南粮食作物协同创新中心, 郑州 450002)
采用粒片状肥料实现夏玉米一次施肥的可行性研究
王宜伦1,2, 白由路1*, 谭金芳2, 刘 举2, 卢艳丽1, 韩燕来2*
(1中国农业科学院农业资源与农业区划研究所, 农业部植物营养与肥料重点实验室, 北京 100081;2河南农业大学资源与环境学院, 河南粮食作物协同创新中心, 郑州 450002)

夏玉米; 定量施肥; 粒片状肥料
玉米作为中国主要粮食作物,是食品、 饲料和工业等产业的重要原料,自2007年以来,玉米成为中国播种面积最大的作物。夏玉米生育期内吸肥能力强,需肥量大,科学施肥是提高玉米产量的关键技术措施[1-3]。随着生产的发展,各种养分配比的复混肥料、 功能型复混肥、 缓/控释肥料及玉米专用肥等化肥品种日渐增多,各类化肥性质和效果各异[4-9]; 另一方面,农村劳动力转移,迫切需要一次性简化生产技术,有针对性研制和推广高效、 适合机械化操作的玉米专用配方肥对于提高夏玉米产量和增加农民收入具有重要意义。

根据夏玉米需肥特性,研制开发大小一致的新型压缩片状肥料,每片肥料含有等量的氮磷钾养分,将片状肥料施在玉米植株适宜的位置,可使每株玉米均匀等量吸收养分,实现单株定量精准施肥; 另一方面,大片肥料具有一定的缓释效果,亦适宜机械化操作。目前,有关片状肥料在夏玉米上的单株定量施肥效应未见报道。本研究通过田间试验研究了专用片状肥料对夏玉米产量、 氮代谢、 养分吸收积累及肥料利用效率的影响,明确单株定量施肥在夏玉米上的效果,探求夏玉米高效一次性施肥技术,为夏玉米科学施肥提供技术依据。
1 材料与方法
1.1试验点概况

表1 试验地土壤农化性状
1.2试验设计
试验共设4个处理: T1, 定量施肥(在夏玉米苗期两株玉米中间两边间隔15 cm各施一粒7.02 g片肥,每2片含N 4.00 g、 P2O51.72 g、 K2O 1.43 g,施肥深度10 cm 左右,一次施肥); T2, 常规施肥(在夏玉米苗期,距植株15 cm左右开沟施肥施入50%氮肥和全部磷钾肥,吐丝期在两株玉米中间采用穴施50%氮肥,施肥深度10 cm左右, 2次施肥,养分量同T1); T3, 缓释肥(苗期距植株15 cm左右开沟施入,缓释氮比例为52%,缓释氮为硫磺、 树脂“双膜双控”包膜尿素,土壤中的释放期约90天。一次施肥,养分量同T1); T4, 不施氮肥(在夏玉米苗期,距植株15 cm左右开沟施肥施入全部磷钾肥。一次施肥,磷钾肥用量同T1)。施肥位置及方式见图1。

图1 不同施肥方式示意图Fig.1 Schematic diagram of different fertilization methods
鹤壁试验点种植密度75000 plant/hm2,小区面积32 m2,总施肥量为N 300 kg/hm2、 P2O5129 kg/hm2、 K2O 107 kg/hm2。菏泽试验点种植密度67500 plant/hm2,小区面积40 m2,总施肥量为N 270 kg/hm2、 P2O5116 kg/hm2、 K2O 96 kg/hm2。均为3次重复,随机区组排列,供试品种均为浚单29,分别按照当地习惯进行栽培管理。
1.3样品采集与分析
播前和收获后采集0—20 cm混合土壤样品,过筛处理混合均匀后保留约500 g有代表性的土壤样品,用于常规养分分析。采用重铬酸钾容量法-外加热法(GB 7857-87)测定土壤有机质,碱解-扩散法测定土壤碱解氮(GB 7849-87),0.5 mol/L碳酸氢钠浸提—钼蓝比色法测定土壤速效磷; 乙酸铵浸提—火焰光度法测定土壤速效钾。
收获时每个小区采集有代表性的植株样品3株,分器官烘干称重,在105℃下杀青15 min,再在65℃下烘干至恒重,粉碎后分析植株各器官养分含量。采用浓H2SO4-H2O2消煮—蒸馏定氮法测定植株全氮,钼黄比色法测定植株全磷,火焰光度计法测定植株全钾[19]。

1.4计产与考种
每个小区随机收获30穗玉米,装入尼龙网袋,晒干称重,以含水量14%折算作为小区产量,另取10穗玉米进行考种,调查穗粒数和百粒重等。
用Excel 2003和DPS 7.05软件进行数据处理和统计分析。
2 结果与分析
2.1单株定量施肥对夏玉米产量及其构成因素的影响


表2 不同处理对夏玉米产量及其构成因子的影响
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters within a column mean significant at 5% level among treatments.
2.2单株定量施肥对夏玉米干物质积累量的影响

2.3单株定量施肥对夏玉米叶片硝酸还原酶(NR)和谷氨酰胺合成酶(GS)活性的影响
从图3可以看出,大喇叭口期和吐丝期T1、 T2、 T3处理的夏玉米叶片NR活性均比T4处理显著增强,大喇叭口期T3处理 叶片NR活性最强,较T2处理高11.51%, T1较T2处理高7.45%; 吐丝期T1处理叶片NR活性最强,较T2高5.57%。可见, 施用氮肥促进了夏玉米叶片硝酸还原酶活性的增强,单株定量一次性施肥叶片硝酸还原酶活性与习惯2次施肥无差异。夏玉米叶片GS活性均比T4处理显著增强。大喇叭口期T1处理叶片GS活性较T2处理提高了9.88%,T3处理较T2处理高5.96%; 吐丝期T1处理和T3处理叶片GS活性分别较T2处理高6.18%和4.92%,三者无显著性差异。施用氮肥显著提高了夏玉米叶片谷氨酰胺合成酶活性,单株定量一次性施肥与习惯2次施肥的夏玉米叶片谷氨酰胺合成酶活性相同。

图2 不同处理对夏玉米干物质积累量的影响Fig.2 Effect of different treatments on dry matter accumulation of summer maize[注(Note): 柱上不同字母表示处理间在5%水平差异显著 Different letters above the bars indicate a significant differnece among treatments at 5% level.]
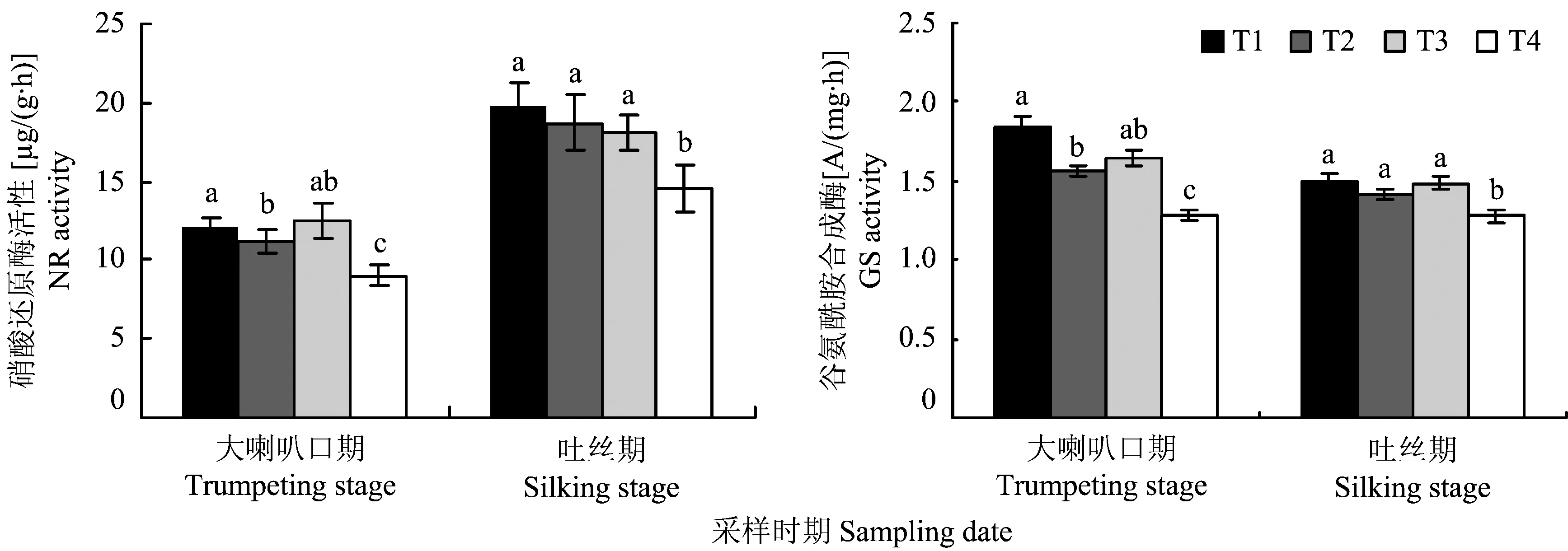
图3 不同处理对夏玉米叶片硝酸还原酶和谷氨酰胺合成酶活性的影响(鹤壁)Fig.3 Effects of different fertilizer treatments on NR and GS activity of leaves of summer maize in Hebi[注(Note): 柱上不同字母表示处理间在5%水平差异显著 Different letters above the bars indicate a significant differnece among treatments at 5% level.]
2.4单株定量施肥对夏玉米植株养分积累量的影响


表3 不同处理夏玉米植株氮磷钾积累量 (kg/hm2)
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters within a column mean significant at 5% level among treatments.
2.5单株定量施肥对夏玉米氮肥利用效率的影响
表4表明,鹤壁和菏泽T1、 T3处理的氮肥农学效率均略高于T2处理,T1处理较T2处理分别增加1.07 kg/kg和1.42 kg/kg,平均为1.24 kg/kg。鹤壁和菏泽T1处理氮肥利用率均最高,较T2处理分别高出3.02和3.80个百分点,平均为3.41个百分点; T1处理较T3处理分别高出3.52和1.09个百分点,平均为2.30个百分点。单株定量一次性施肥的肥料利用率较常规2次施肥略有提高。

表4 不同处理对夏玉米氮肥利用率的影响
注(Note): 同列数据后不同字母表示处理间差异达5%显著水平 Values followed by different letters within a column mean significant at 5% level among treatments.
3 讨论
充足的养分供应是作物高产的基础,科学的养分管理措施是将合适的肥料品种和适宜的用量在合适的施肥时期施在恰当的位置,并与最佳农艺管理措施相结合,实现作物的高产优质和高效生产[22]。夏玉米通常为麦茬直播,出苗后再追肥,习惯上多采用一边开沟施肥,使得肥料只能被玉米一侧的根系容易吸收,且肥料量不能保证均衡充足供应,影响玉米对养分的吸收利用。本研究结合玉米养分吸收特性,合理配比氮磷钾肥,通过压缩成型技术精准到每株玉米的养分需要量; 将等养分量的片状复混肥料在苗期一次性施在两株玉米中间两边间隔15 cm处,使每株夏玉米四边有养分供应,有利于夏玉米对氮磷钾养分的吸收利用,产量略有增加,实现了一次性施肥的目标。
缓/控释肥可根据作物对养分的需求控制其养分释放模式,使养分释放与作物养分吸收相同步,施用缓/控释掺混肥能促进玉米生长发育,增产效果和经济效益明显,提高了肥料利用率,一次性施肥可满足当前农村劳动力转移、 简化生产的需求[23-25]。本研究的等养分量片状复混肥料颗粒较大,且施入土壤10 cm深左右,具有一定的缓释效果,氮素挥发损失减少,有利于保持土壤中的养分持续供应。本试验表明,采用片状复混肥料一次性单株定量精准施肥与缓释肥一次性施用的产量无显著差异,而氮肥当季利用率较高,单株定量精准施肥具有与缓释肥同样的效果,结合机械化施肥亦能满足当前玉米简化施肥的需求。
硝酸还原酶是高等植物氮素同化的限速酶,谷氨酰胺合成酶是氨基酸合成和代谢的关键酶,对植物生长发育、 产量形成有重要作用,两者保持较高活性,有助于硝态氮的转化吸收[26-27]。已有研究报道,玉米生育后期追施氮肥比例大或施用控释肥,能有效协调玉米生育后期植株体碳、 氮代谢,叶片硝酸还原酶和谷氨酰胺合成酶活性较高,保障了生育后期碳氮代谢的高效进行[29-30]。本研究表明,夏玉米单株定量精准施肥叶片硝酸还原酶和谷氨酰胺合成酶活性较习惯两次施肥有所提高,能较好地协调生育后期的碳氮代谢,促进夏玉米对养分的吸收利用。
随着农业生产的发展,玉米机械化和简化施肥将逐渐应用和推广,本研究的单株定量精准施肥亦适合机械化施肥。研制配套的施肥机械,因地制宜研发玉米专用单株定量片状肥料,实现种、 肥同播对于玉米科学和简化施肥具有重要意义。
[1]郭庆法, 王庆成, 汪黎明, 等. 中国玉米栽培学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2004. 1-5.
Guo Q F, Wang Q C, Wang L M. Maize cultivation science of China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2004. 1-5.
[2]中华人民共和国国家统计局. 中国统计年鉴2013[M]. 北京: 中国统计出版社, 2013.
National Bureau of Statistics of China. Chinese statistics yearbook in 2013[M]. Beijing: China Statistics Press, 2013.
[3]朱兆良, 金继运. 保障我国粮食安全的肥料问题[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2013, 19(2): 259-273.
Zhu Z L, Jin J Y. Fertilizer use and food security in China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2013, 19(2): 259-273.
[4]何萍, 金继运. 不同专用肥对玉米养分吸收和产量的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2007, 15(5): 117-120.
He P, Jin J Y. Nutrient uptake and yield responses to maize specific fertilizers[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2007, 15(5): 117-120.
[5]易镇邪, 王璞, 陈平平, 等.氮肥类型对夏玉米氮素吸收和利用的影响[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(3): 472-478.
Yi Z X, Wang P, Chen P P, et al. Effect of different types of nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen absorption and utilization of summer maize(ZeamaysL.)[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008, 14(3): 472-478.
[6]李伟, 李絮花, 唐慎欣, 等.控释掺混肥对夏玉米产量及土壤硝态氮和铵态氮分布的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2011, 25(6): 68-71.
Li W, Li X H, Tang S X,etal. Effect of controlled-release urea combined with common urea on the grain yields of summer maize and distribution of soil ammonium and nitrate content[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2011, 25(6): 68-71.
[7]张春梅, 秦嘉海, 王爱勤, 等. 多功能专用肥对土壤理化性质和制种玉米增产效果的影响[J].草业科学, 2013(4): 610-615.
Zhang C M, Qin J H, Wang A Q,etal. Effects of applying optimized multi-functional fertilizer on soil physical, chemical properties and yield of maize in Hexi Irrigation Areas[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2013(4): 610-615.
[8]卢艳丽, 白由路, 王磊,等.华北小麦-玉米轮作区缓控释肥应用效果分析[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(1): 209-215.
Lu Y L, Bai Y L, Wang L,etal. Efficiency analysis of slow/controlled release fertilizer on wheat-maize in North China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(1): 209-215.
[9]王小明, 谢迎新, 张亚楠, 等. 新型肥料施用对玉米季土壤硝态氮累积的影响[J].水土保持学报, 2009, 23(5): 222-236.
Wang X M, Xie Y X, Zhang Y N,etal. Effect of new type fertilizers application on accumulation of soil nitrate nitrogen in the maize season[J]. Journal of Soil and Water Conservation, 2009, 23(5): 222-236.
[10]王宜伦, 李潮海, 何萍, 等. 超高产夏玉米养分限制因子及养分吸收积累规律研究[J].植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 559-566.
Wang Y L, Li C H, He P,etal. Nutrient restrictive factors and accumulation of super-high-yield summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(3): 559-566.
[11]赵营, 同延安, 赵护兵. 不同供氮水平对夏玉米养分累积、 转运及产量的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2006, 12(5): 622-627.
Zhao Y, Tong Y A, Zhao H B. Effects of different N rates on nutrients accumulation, transformation and yield of summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2006, 12(5): 622-627.
[12]吕丽华, 陶洪斌, 王璞, 等. 施氮量对夏玉米碳、 氮代谢和氮利用效率的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2008, 14(4): 630-637.
Lü L H, Tao H B, Wang P,etal. The effect of nitrogen application rate on carbon and nitrogen metabolism and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2008, 14(4): 630-637.
[13]吕鹏, 张吉旺, 刘伟, 等. 施氮量对超高产夏玉米产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(4): 852-860.
Lü P, Zhang J W, Liu W,etal. Effects of nitrogen application on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize under super-high yield conditions[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(4): 852-860.
[14]吕鹏, 张吉旺, 刘伟, 等. 施氮时期对超高产夏玉米产量及氮素吸收利用的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2011, 17(5): 1099-1107.
Lü P, Zhang J W, Liu W,etal. Effects of nitrogen application dates on yield and nitrogen use efficiency of summer maize in super-high yield conditions[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2011, 17(5): 1099-1107.
[15]王宜伦, 李潮海, 谭金芳, 等. 氮肥后移对超高产夏玉米产量及氮素吸收和利用的影响[J]. 作物学报, 2011, 37(2): 339-347.
Wang Y L, Li C H, Tan J F,etal. Effect of postponing N application on yield, nitrogen absorption and utilization in super-high-yield summer maize[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica, 2011, 37(2): 339-347.
[16]王宜伦, 李潮海, 谭金芳, 等. 超高产夏玉米植株氮素积累特征及一次性施肥效果研究[J]. 中国农业科学, 2010, 43(15): 3151-3158.
Wang Y L, Li C H, Tan J F,etal. Studies on plant nitrogen accumulation characteristics and the effect of single application of base fertilizer on super-high-yield summer maize[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2010, 43(15): 3151-3158.
[17]王宜伦, 卢艳丽, 刘举, 等. 专用缓释肥对夏玉米产量及养分吸收利用的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2015, (1): 29-32.
Wang Y L, Lu Y L, Liu J,etal. Effects of special slow-release fertilizer on yield and nutrient absorption and utilization of summer maize[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2015, (1): 29-32.
[18]中国科学院南京土壤所长效肥组.碳酸氢铵粒肥的肥效和机械造粒[J]. 土壤, 1974, (3): 91-96.
Long effect fertilizer group, Institute of Soil Science, Chinese Academy of Sciences. Effects of granular ammonium bicarbonate fertilizer and mechanical granulation[J]. Soils, 1974, (3): 91-96.
[19]鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析(第3版)[M].北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
Bao S D. Soil agro-chemistry analysis (3rd edition)[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
[20]邹琦. 植物生理学实验指导[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.
Zou Q. Guide in plant physiology testing[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
[21]高俊凤.植物生理学实验指导[M].北京: 高等教育出版社,2005: 142-143.
Gao J F.Guide in plant physiology testing[M].Beijing: High Education Press, 2005: 142-143.
[22]Bruulsema T W, Witt C, García F,etal. Global framework for fertilizer BMPs[J]. Better Crops with Plant Food, 2008, (2): 13-15.
[23]樊小林, 刘芳, 廖照源, 等. 我国控释肥料研究的现状和展望[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2009, 15(2): 463-473.
Fan X L, Liu F, Liao Z Y,etal. The status and outlook for the study of controlled-release fertilizers in China[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2009, 15(2): 463-473.
[24]阎湘, 金继运, 何萍, 等.提高肥料利用率技术研究进展[J].中国农业科学, 2008, 41(6): 450-459.
Yan X, Jin J Y, He P,etal. Recent advances in technology of increasing fertilizer use efficiency[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2008, 41(6): 450-459.
[25]王宜伦, 李潮海, 王瑾, 等.缓/控释肥在玉米生产中的应用与展望[J].中国农学通报, 2009, 25(24): 254-257.
Wang Y L, Li C H, Wang J,etal. Application and prospect of slow/controlled release fertilizers in maize production[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(24): 254-257.
[26]李洪岐, 蔺海明, 梁书荣, 等. 密度和种植方式对夏玉米酶活性和产量的影响[J].生态学报, 2012, 32(20): 6584-6590.
Li H Q, Lin H M, Liang S R,etal. Effects of planting densities and modes on activities of some enzymes and yield in summer maize[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2012, 32(20): 6584-6590.
[27]田华, 段美洋, 王兰. 植物硝酸还原酶功能的研究进展[J]. 中国农学通报, 2009, 25(10): 96-99.
Tian H, Duan M Y, Wang L. Research progress on nitrate reductase functions in plants[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin, 2009, 25(10): 96-99.
[28]赵洪祥, 尚东辉, 边少锋, 等. 氮肥不同比例分期施用对玉米硝酸还原酶活性的影响[J]. 玉米科学, 2009, 17(6): 97-100.
Zhao H X, Shang D H, Bian S F,etal. Effect of nitrogen fertilizer application by stages in different proportion on nitrate reductase activity of maize[J]. Journal of Maize Sciences, 2009, 17(6): 97-100.
[29]Wang Y L, Wang Q, Han D,etal. Effects of postponing N application on metabolism, nitrogen absorption and utilization of summer maize in super-high yield region[J]. Agricultural Science & Technology, 2013, 14(1): 131-134, 185.
[30]卫丽, 马超, 黄晓书, 等. 控释肥对夏玉米碳、 氮代谢的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2010, 16(3): 773-776.
Wei L, Ma C, Huang X S,etal. Effects of controlled-release nitrogen fertilizer on carbon and nitrogen metabolism of summer maize[J]. Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science, 2010, 16(3): 773-776.
Availability study of once quantitative fertilization in summer maize using fertilizer tablets
WANG Yi-lun1,2, BAI You-lu1*, TAN Jin-fang2, LIU Ju2, LU Yan-li1, HAN Yan-lai2*
(1InstituteofAgriculturalResourcesandRegionalPlanning,ChineseAcademyofAgriculturalSciences/KeyLaboratoryofPlantNutritionandFertilizer,MinistryofAgriculture,Beijing100081,China; 2CollegeofResourceandEnvironment,HenanAgriculturalUniversity/CollaborativeInnovationCenterofHenanGrainCrops,Zhengzhou450002,China)
【Objectives】 Single fertilization has been approached for decreasing the cost of fertilization in crop production by choosing the form of fertilizers. The availability of flaky fertilizer tablets containing a certain amount of NPK nutrients was tested for the purpose. 【Methods】 According to nutrient requirement of summer maize under a target yield, urea, mono-ammonium phosphate and potassium chloride were mixed in rational proportion and compressed into flaky tablets weighted 7.0 g each. Two pieces of the flaky fertilizer tablets contained the demanded nutrient amount for one summer maize plant. At the seedling stage of summer maize, two pieces of the flake fertilizer were buried 10 cm deep in between two plants with 15 cm apart, thus, the fertilizers were applied around every plant. Field experiments were conducted in Shandong and Henan provinces, the effect of flaky fertilizer (T1: two fertilizer tablets containing N 4.00 g, P2O51.72 g and K2O 1.43 g, were placed at seeding stage in between two plants and 15 cm apart from each other) was compared with conventional fertilization (T2: with the same nutrient imput, one top dressing at seedling stage, the other one in bumpet stage), slowly-release fertilizer(T3: containing 52% of slow-realse nitrogen double coated with sulfur and resin, same nutrient amounts with the flaky fertilizer and once top dressed inside ditches 15cm apart from plants) and no N fertilizer (T4: no N fertilizer but all the P and K top dressed like T3) in grain yield, dry matter accumulation, nitrogen metabolism, N, P and K nutrient accumulation of summer maize.【Results】 The results show that the yields are increased by 15.1%-19.5% and 13.8%-16.1% respectively by applying the N fertilizer in Hebi and Heze areas. Compared with the conventional fertilizer application, the precision fertilization improves leaf nitrate reductase activities by 7.45% and 5.57% respectively at the trumpeting and silking stages, and the glutamine synthetase activities are improved by 9.88% and 6.18%. The N, P and K nutrient accumulation amounts of summer maize plants are increased by 3.4%-4.1%, 3.7%-7.0% and 2.7%-3.9%, the N agronomy efficiency and N fertilizer use efficiency are increased by 1.24 kg/kg and 3.41 percentage points respectively, and the average yield is increased by 2.5%. 【Conclusions】 The precision fertilization improves leaf nitrate reductase and glutamine synthetase activities of summer maize at the trumpeting and silking stages, promotes the N, P and K nutrient absorption and utilization, and increases the yield and nitrogen use efficiency to some extent. These results are the same as the slow-release fertilizer by single application as base fertilizer, and the precision fertilization realizes the aim of single application, high yield and high fertilization efficiency of summer maize.
summer maize; quantitative fertilization; fertilizer tablet
2015-01-21接受日期: 2015-06-08
河南省科技成果转化基金项目(142201110025); 郑州市科技创新团队项目(131PCXTD610); 国家“十二五”粮食丰产科技工程(2011BAD16B15-2)资助。
王宜伦(1976—),男,山东郓城人,副教授,博士后,从事植物营养与施肥研究。Tel: 0371-63558290; wangyilunr1@163.com
E-mail: baiyoulu@caas.cn; E-mail: hyanlai@126.com
S143.5; S513.06
A
1008-505X(2016)04-1126-07

