三疣梭子蟹细胞周期蛋白H基因克隆及其在卵巢发育中的表达分析❋
贾复龙, 孟宪亮, 刘 萍❋❋, 李 健, 高保全, 高天翔, 宋 娜
(1. 中国海洋大学水产学院,山东 青岛 266003;2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所农业部海洋渔业可持续发展重点实验室,山东 青岛 266071;3. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室,山东 青岛 266071)
三疣梭子蟹细胞周期蛋白H基因克隆及其在卵巢发育中的表达分析❋
贾复龙1,2,3, 孟宪亮2,3, 刘萍2,3❋❋, 李健2,3, 高保全2,3, 高天翔1, 宋娜1
(1. 中国海洋大学水产学院,山东 青岛 266003;2. 中国水产科学研究院黄海水产研究所农业部海洋渔业可持续发展重点实验室,山东 青岛 266071;3. 青岛海洋科学与技术国家实验室海洋渔业科学与食物产出过程功能实验室,山东 青岛 266071)
摘要:Cyclin H作为细胞周期调控活动中的关键因子,通过与相应的细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶(Cdks)结合来调控细胞周期中的各个环节,而三疣梭子蟹(Portunus trituberculatus)卵巢发育过程中存在旺盛细胞分裂活动的阶段,关于其卵巢发育的分子机制研究依旧较少。本实验通过SMART RACE方法,获得三疣梭子蟹cyclin H基因cDNA序列全长。并通过实时荧光定量PCR对其进行三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育相关的表达分析。结果发现,基因全长1 077 bp,开放阅读框(ORF)、5’及3’非编码区(UTR)长度分别为999、31和46 bp。预测编码一个包含332个氨基酸,分子量、等电点分别为38.89和 6.20kDa的蛋白质,蛋白序列包含一个周期蛋白盒保守结构域。同源分析表明,三疣梭子蟹Cyclin H蛋白序列其他甲壳动物有着较高的同源性,与拟穴青蟹(Scylla paramamosain)和斑节对虾(Penaeus monodon)的同源性分别为95%和80%。表达分析后结果显示,cyclin H基因在卵巢中的表达量最高且在Ⅰ期和Ⅱ期卵巢中的表达量显著高于其他卵巢发育时期,去眼柄后该基因在卵巢中的表达量于第4天达到最大值且显著高于对照组,呈现先升高后降低的趋势(P<0.05)。研究结果为深入开展三疣梭子蟹和其他甲壳动物性腺发育调控研究提供了重要信息。
关键词:三疣梭子蟹; cyclin H; 基因克隆; 去眼柄; 基因表达; 卵巢
引用格式:贾复龙, 孟宪亮, 刘萍, 等. 三疣梭子蟹细胞周期蛋白H基因克隆及其在卵巢发育中的表达分析[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 46(7): 62-69.
JIA Fu-Long, MENG Xian-Liang, LIU Ping, et al. Clong and expression in the ovarian development ofcyclinHgene ofPortunustrituberculatus[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2016, 46(7): 62-69.
三疣梭子蟹(Portunustrituberculatus)隶属于节肢动物门(Arthropoda)甲壳纲(Crustacea)十足目(Decapoda)梭子蟹科(Portunidae)梭子蟹属(Portunus),广泛分布于中国、日本、韩国等近海水域,是中国沿海的重要经济蟹类[1]。近年来,三疣梭子蟹的繁殖生物学研究已经取得了很大的进步。吴旭干等通过对东海三疣梭子蟹第一次卵巢发育期间卵巢外部特征及组织学变化等研究后将三疣梭子蟹第一次卵巢发育分为6期[2]。贾磊等在对越冬和抱卵期间三疣梭子蟹的卵巢发育进行研究后发现,亲蟹在越冬期间卵巢发育不显著,而抱卵期间发育显著[3]。谢熙在对三疣梭子蟹FAMeT和MIH基因研究后发现,FAMeT基因与三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育密切相关,MIH基因表达量与卵巢发育呈显著负相关[4]。而有关甲壳动物卵巢发育的分子机制研究依然很少[2,5-6]
1980年代初,Tim Hunt等在对海胆进行早期胚胎发育的研究中发现,细胞中存在一种随细胞周期变化而改变的蛋白,这就是细胞周期蛋白(Cyclins)。而Cyclin H作为CAK的调节亚基,可以通过和Cdk7结合后磷酸化Cdks[7],从而激活真核细胞周期调控的关键因子——成熟促进因子(Maturation or M-phase promoting factor, MPF)[8]。细胞周期蛋白都含有一段长约为100个氨基酸的高度保守同源序列,称为周期蛋白盒,凭此结构域与Cdks的PSTAIRE区结合,用于激活MPF。此外,有研究表明Cyclin H也是TFⅡH的亚基之一而TFⅡH也在细胞周期调控、DNA修复和转录中发挥着重要的作用[9]。韩坤煌在对拟穴青蟹cyclinH基因在卵巢各个不用发育阶段的荧光定量PCR研究发现,其表达呈现一定上升趋势,且在Ⅵ期卵巢中表达量最高[10]。斑节对虾cyclinH基因在卵巢发育Ⅱ期表达量呈现峰值且显著高于其他时期[11]。Cyclin B、cdc2作为MPF的组成部分在甲壳动物中已有一些研究,在有着旺盛细胞分裂活动的卵巢组织中,中华绒螯蟹(Eriocheirsinensis)、锯缘青蟹(Scyllaserrata)、斑节对虾cyclin B和cdc2基因都有着很高的表达量[12-14],并在不同卵巢发育时期表达量也有显著差异[14-16]。而cyclin H作为MPF激活过程必不可少的部分,随卵巢发育是否也会有相似的表达量的改变,值得研究。
本实验使用SMARTTMRACE的方法,获得了三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因的cDNA序列全长,并通过qRT-PCR技术分析了该基因在三疣梭子蟹各组织以及卵巢发育不同时期的差异表达状况;同时还通过去除眼柄探究该基因在去除眼柄后卵巢组织中表达量改变。研究结果将为三疣梭子蟹以及其他甲壳动物性腺发育调控机制研究提供帮助。
1 材料与方法
1.1 材料
实验所用三疣梭子蟹取自本实验室昌邑市养殖基地户外养殖池,于周转箱(560 mm×360 mm×280 mm)中暂养7 d(周转箱通过使用3块中间相通的PVC板分隔,每个周转箱6个小格每隔一只)。水温(20±2)℃、盐度33,pH 8.2,使用充气泵充氧,每天上午及傍晚投喂蛤蜊肉,每天下午清除箱底排泄物及食物残渣并换去周转箱原水量的1/3。
Trizol Reagen试剂、SMARTTMRACE Amplification Kit试剂盒、DNA胶回收试剂盒、SYBR PremixExTaqTMⅡ荧光定量试剂盒、PrimeScript RT reagent Kit、PMD18-T载体和Dh1α感受态细胞分别购自Invitrogen公司、Clontech公司、生工生物工程(上海)股份有限公司、TaKaRa公司。
不同卵巢发育时期样品采集通过于2014年7月至2015年3月每月一次在海丰水产养殖责任有限公司进行连续取样,参照吴旭干等对三疣梭子蟹卵巢的分期方法[2],首先通过对卵巢外部特征进行初步分期,初步分期后进行切片HE染色后显微镜下观察各样品组织学特征,从而进行最终卵巢时期的确定从中随机选取各发育时期5个样品。
1.2 三疣梭子蟹总RNA提取及cDNA 的合成
通过Trizol试剂参照说明书分别提取卵巢,精巢,肝胰腺,鳃,肌肉,心脏,脑神经节,胸神经节,眼柄,血淋巴,胃和肠组织的总RNA,用紫外分光光度计与琼脂糖凝胶电泳等方式对提取总RNA的质量进行检测。选取质量及完整性较好的精巢、卵巢组织总RNA等量均匀混合,按照SMARTTMRACE Amplification Kit说明书的方法合成3’和5’RACE的cDNA第一链。
1.3 三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因全长cDNA的克隆及测序
依据三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因的EST序列,使用Primer Premier 5.0软件设计3’和5’RACE引物(表1)后由公司合成。3’和5’末端扩增使用Advantange 2 PCR Kit进行,参照RACE说明书,引物CyclinH-3’-1 和CyclinH-5’-1分别和引物UPM配对,进行cyclinH基因cDNA 3’及5’末端扩增。PCR反应程序:94 ℃ 30 s,60 ℃ 30 s,72 ℃ 2 min,30个循环(见表1)。

表1 本实验过程中所用到的引物序列
扩增产物参照核酸凝胶回收试剂盒经1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后切胶回收目的片段,将得到的目的片段参照PMD18-T说明书与PMD18-T连接,之后将连接产物转入Dh1α,经涂板过夜培养后,将通过蓝白斑筛选的菌落挑出于AMP液体培养基中培养6 h后经菌液PCR及琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后送去测序。
1.4cyclinH基因的生物信息学分析
利用VecScreen(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/tools/vecscreen/)在线去掉载体留下目的片段序列,然后使用ContigExpress Project软件与三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因EST序列拼接后得到三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因cDNA序列全长。通过使用EditSeq预测开放阅读框(ORF),并对其进行氨基酸序列翻译。将得到的三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因EditSeq翻译得到的氨基酸序列通过BLAST(http://blast.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Blast.cgi)进行同源性比对。利用ExPASy(http://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/)进行分子量及等电点的预测,利用InterproScan(http://www.ebi.ac.uk/interpro/scan.html)进行蛋白质功能结构域分析,利用NetPhos 2.0 Server(http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetPhos/)进行蛋白质磷酸化位点分析,采用PSIPRED Protein StructurePredictionServer(http://bioinf.cs.ucl.ac.uk/psipred/)进行二级结构预测,将Genbank中下载其他物种Cyclin H氨基酸序列和三疣梭子蟹Cyclin H氨基酸序列一起使用DNAMAN软件进行氨基酸序列比对,利用MEGA 5.0软件对cyclinH基因构建NJ的系统进化树。
1.5 去眼柄实验
将暂养7 d交配后雌蟹随机分为3组:对照组、去单侧眼柄组、去双侧眼柄组,每组40只。去眼柄方法采用烧红的镊子紧捏三疣梭子蟹眼柄庞大处基部3s,之后放入单独的小格中,防止打斗。于去眼柄后1、4、7和10 d每组分别取5只三疣梭子蟹卵巢,立即放入液氮中保存,用于RNA提取。
1.6 三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因的表达分析
每个卵巢发育时期取5只健康三疣梭子蟹的卵巢组织作为平行,另取5只健康三疣梭子蟹分别取卵巢,精巢,鳃,胃,肠,肝胰腺,胸神经节,脑神经节,血淋巴,眼柄,心脏,肌肉等组织,于液氮中冷冻保存,用于RNA的提取。Trizol试剂提取各组织总RNA,并使用PrimeScript RT reagent Kit 反转录合成cDNA。
根据三疣梭子蟹cyclinH和β-actin基因开放阅读框cDNA序列,由公司分别设计合成1对荧光定量引物(β-actin-F和β-actin-R、Cyclin H-F和Cyclin H-R)(见表1),参照SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ说明书对三疣梭子蟹不同卵巢发育时期的卵巢组织,及三疣梭子蟹鳃,胃,肠,肝胰腺,胸神经节,脑神经节,血淋巴,眼柄,心脏,肌肉等组织中cyclinH基因的相对表达量进行分析。参照SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ说明书的方法于ABI7500仪器上样分析,反应完成后结果采用2-ΔΔCt法计算,并对结果利用SPSS19.0软件进行差异显著性等统计学分析(P<0.05表示差异显著,用小写字母a、b、c、d、e、f、g标记,存在相同字母表示差异不显著,字母完全相同表示差异显著)。
2 结果
2.1 三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因的获得及其序列分析
将抽提得到的总RNA,经紫外分光光度计分析后发现其OD260nm/OD280nm均在1.9~2.0之间;在进行1.0%琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后发现, 28S和18S rRNA条带清晰完整,这两部分结果能够说明实验所用总RNA质量较好,可用于RACE模板合成。参照SMARTTMRACE Amplification Kit说明书方法合成的3’和5’RACE的cDNA第一链为模板,使用特异性引物CDK7-5’-1和CDK7-3’-1分别于通用引物UPM配对进行5’和3’末端RACE扩增,实验重复5次,所得产物经测序以及拼接后得到三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因cDNA全长序列,GenBank登录号KT025877。该基因cDNA全长1 077 bp,包含开放阅读框99bp、5’端非编码区(UTR)31bp和3’非编码区46bp。3’末端有多聚腺苷酸(PolyA)尾,未发现多聚腺苷酸加尾信号(见图1)。

图1 三疣梭子蟹cyclin H基因核苷酸序列及其推导的氨基酸序列
经氨基酸序列分析得知,三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因编码一个由332个氨基酸组成的蛋白质;预测分子量为38.89 kDa,理论等电点为6.20;理论磷酸化位点14个,其中丝氨酸(Ser)12个,苏氨酸(Thr12)1个,酪氨酸(Tyr125)1个;BLAST比对发现其氨基酸序列中包含保守周期蛋白盒(aa56-143);理论糖基化位点2个(N-202,N-299)(见图2)。


图2 三疣梭子蟹Cyclin H 蛋白二级结构的预测
2.2 三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因同源性分析
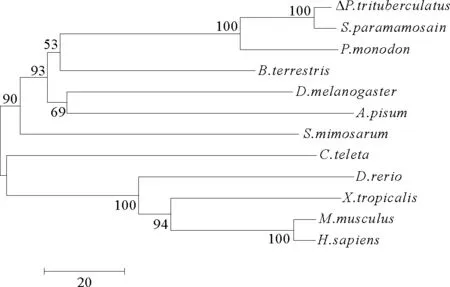
通过BLAST比对三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因编码的氨基酸序列,发现该序列与拟穴青蟹cyclinH基因的同源性最高,为95%;与其他物种如、熊蜂(Bombusterrestris)、隆头蛛(Stegodyphusmimosarum)、长牡蛎(Crassostreagigas)和小家鼠(Musmusculus)的同源性分别为80%、55%、48%、43%和42%。将三疣梭子蟹CyclinH基因与拟穴青蟹、斑节对虾、小家鼠、海蠕虫(Capitellateleta)、熊蜂、斑马鱼(Daniorerio)、隆头蛛、智人(Homosapiens)、黑腹果蝇(Drosophilamelanogaster)和非洲爪蟾(Xenopustropicalis)的Cyclin H氨基酸序列比对发现Cyclin H的氨基酸序列物种间相对保守,特别是周期蛋白盒具有很高的保守性(见图3)。利用MEGA5.0软件,采用邻位相接法(Neighbor Joining)将三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因与其他物种cyclinH基因构建系统进化树,进化树分为2大类群,分别为脊椎动物和无脊椎动物,三疣梭子蟹和拟穴青蟹紧密聚合为一枝,之后和斑节对虾聚为一枝,然后和昆虫纲的熊蜂聚为一枝,最后和蛛形纲的隆头蛛聚为无脊椎动物的一枝(见图4)。
2.3 三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因表达分析
利用Real-time PCR分析了三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因在不同组织的表达分布特征,结果显示,cyclinH基因在鳃,胃,肠,肝胰腺,胸神经节,脑神经节,血淋巴,眼柄,心脏和肌肉等多组织中均有表达,其中性腺(卵巢、精巢)中的表达量显著高于其他组织,血淋巴中表达量最少(见图5)。在对三疣梭子蟹6个卵巢发育时期的卵巢组织中cyclinH基因表达特征分析后发现,cyclinH基因在Ⅱ期卵巢中表达量显著高于其他时期,其次是Ⅰ期卵巢,且Ⅲ~Ⅴ期表达水平呈下降趋势(见图6)。在对去眼柄后三疣梭子蟹卵巢组织中cyclinH基因表达分析后发现,去眼柄后第1、4天去眼柄组都显著高于对照组;第10天cyclinH表达量去双侧眼柄组显著低于去单侧眼柄组,显著高于对照组(见图7)(P<0.05)。

(周期蛋白盒用粗线框标出。各物种Cyclin H序列登录号:拟穴青蟹(ACL81559.1)、斑节对虾(AGP03382.1)、熊蜂(XP_003400032.1)、黑腹果蝇(NP_524207.1)。The Cyclin box was marked with thick box. GenBank accession numbers of each species Cyclin H gene were as follows:S.paramamosain(ACL81559.1),P.monodon(AGP03382.1),Bombusterrestris(XP_003400032.1),Drosophilamelanogaster(NP_524207.1).)
图3三疣梭子蟹Cyclin H基因推导氨基酸序列与其他物种Cyclin H氨基酸序列比对
Fig.3Multiple alignments ofP.trituberculatusCyclin H gene with Cyclin H in other species
(各物种Cyclin H氨基酸序列GenBank登录号:拟穴青蟹(ACL81559.1)、斑节对虾(AGP03382.1)、熊蜂(XP_003400032.1)、黑腹果蝇(NP_524207.1)、隆头蛛(KFM58496.1)、斑马鱼(ABB97083.1)、非洲爪蟾(NP_001016256.1)、小鼠(NP_075732.1)、人(AAA57006.1)。GenBank accession numbers of each speciescyclinHgene were as follows:S.paramamosain(ACL81559.1),P.monodon(AGP03382.1),Bombusterrestris(XP_003400032.1),Drosophilamelanogaster(NP_524207.1),Stegodyphusmimosarum(KFM58496.1),Daniorerio(ABB97083.1),Xenopus(Silurana)tropicalis(NP_001016256.1),Musmusculus(NP_075732.1),Homosapiens(AAA57006.1).)
图4基于Cyclin H氨基酸序列的NJ进化树
Fig.4NJ tree based on Cyclin H amino acids
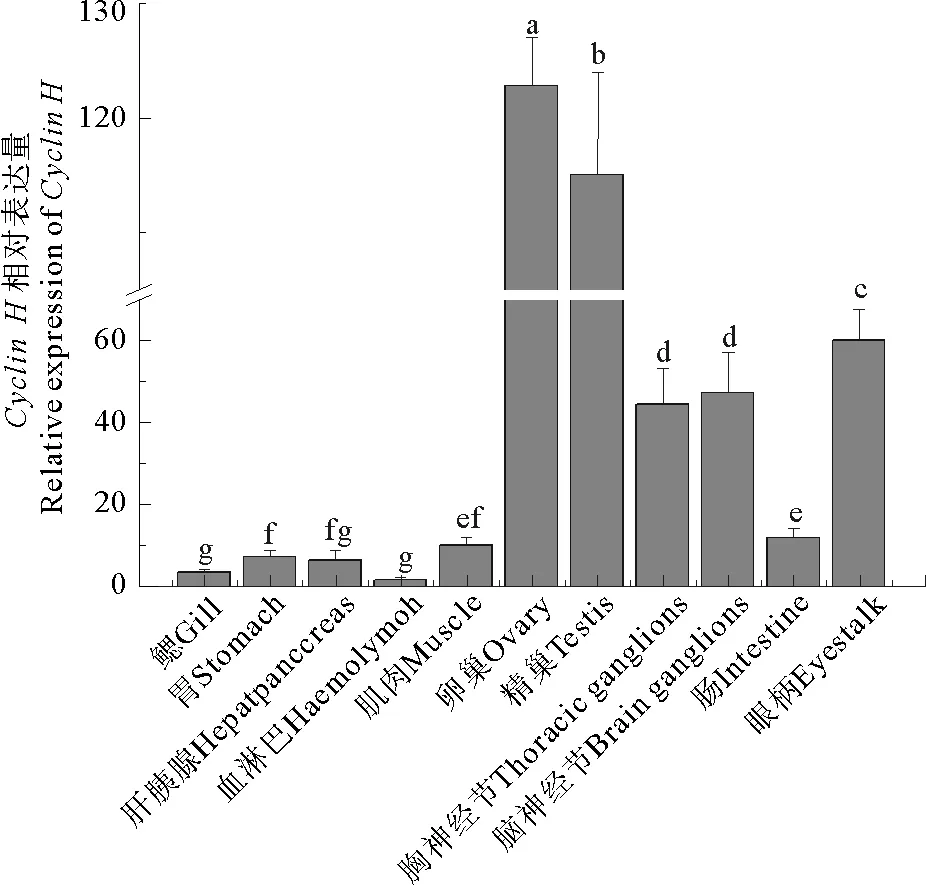
图5 三疣梭子蟹cyclin H基因在不同组织中的表达分布状况

图6 Cyclin H基因在三疣梭子蟹不同发育时期卵巢组织中的表达
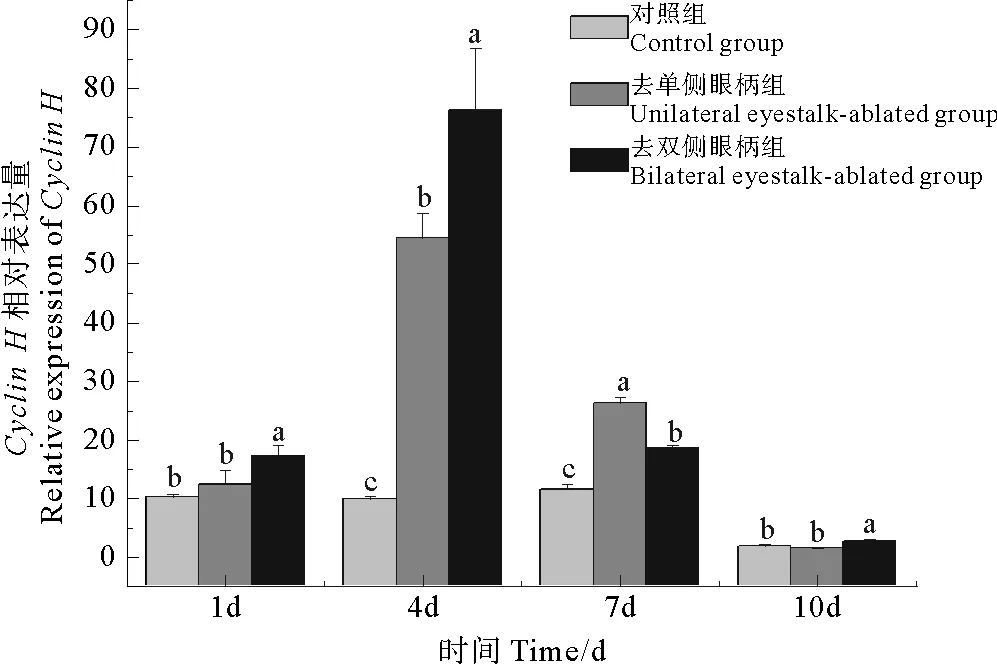
图7 去眼柄后三疣梭子蟹卵巢中cyclin H基因的表达情况
3 讨论
Cyclin H作为CAK的调节亚基,通过结合Cdk7,磷酸化Cdks,从而调节细胞周期[8]。cyclinH基因在其他物种中已有较多研究,而在甲壳动物中的研究依然很少。本研究通过克隆得到的三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因与其他物种细胞周期蛋白相同都含有一段约100个氨基酸的保守序列,称之为周期蛋白盒,参与和Cdks的PSTAIRE区结合,同时也是周期蛋白的标志[14]。有研究表明CAK的活性不仅能通过Cdk7的自身磷酸化和去磷酸化来调节活性,同时Cyclins是磷蛋白,可以通过磷酸化和去磷酸化作用来调节CAK的活性[15]。蛋白激酶Ck2可以通过磷酸化Cyclin H的相应苏氨酸磷酸化位点,从而激活CAK[16]。本研究通过在线预测发现三疣梭子蟹Cyclin H包含一个苏氨酸磷酸化位点(Thr12),而Thr12是否是蛋白激酶Ck2的识别位点还有待进一步研究。对三疣梭子蟹Cyclin H二级结构及空间结构进行预测结果显示其主要由α-螺旋和无规则卷曲组成,这与拟穴青蟹[10]和人类的Cyclin H[17]结构相似。
Cyclin H作为细胞周期调控的关键因子在细胞分裂较活跃的组织中应有较高的表达量。本研究通过对三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因进行RT-PCR后发现,cyclinH基因在三疣梭子蟹卵巢,精巢中表达显著高于其他组织,而性腺正是三疣梭子蟹成熟过程中细胞分裂最旺盛的组织,这也印证了cyclinH基因在细胞周期中具有十分重要的作用。
在对三疣梭子蟹卵巢不同发育阶段卵巢组织进行RT-PCR分析后发现,Ⅰ、Ⅱ期卵巢的表达量显著高于其他时期,与斑节对虾表达模式类似[18]。参照吴旭干等对三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育分期方法,Ⅰ、Ⅱ期卵巢发育以有丝分裂为主来增加卵母细胞数量。Ⅲ期,Ⅳ期以卵黄积累为主,细胞分裂活动减弱。从我们的结果中可以看出,Ⅲ期,Ⅳ期卵巢组织中cyclinH基因表达量逐步降低。而Ⅵ期卵巢组织正为第二次卵巢发育作准备,与Ⅰ、Ⅱ期卵巢组织相似,存在旺盛的细胞分裂活动,cyclinH基因的高表达也进一步印证了cyclinH在卵巢发育过程中扮演重要角色。由卵巢不同时期cyclinH基因表达模式可以看出,三疣梭子蟹cyclinH参与了卵巢发育过程中细胞分裂活动,并在卵巢发育过程中占有十分重要的地位。
去眼柄作为一种诱导甲壳动物卵巢发育的常用方式,已经有较多研究[19-24]。但是去眼柄诱导卵巢发育的分子机制依然研究较少。Okumura等报道称,在去除单侧眼柄导致日本囊对虾(Penaeusjaponocus)的卵黄蛋白原mRNA水平上升[25],Visudtiphole等检测到去除单侧眼柄后斑节对虾卵黄发生期cyclinA基因表达水平下调而cyclinB基因表达水平没有显著变化[26]。Preechaphol等报道称,去除单侧眼柄促使斑节对虾卵母细胞膜上孕酮胞膜受体组件1和孕酮胞内受体相关蛋白p23的表达水平上调[27]。本研究通过对比对照组,去单侧眼柄组和去双侧眼柄组三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因的表达量差异,发现在去眼柄后第四天去单侧眼柄组和去双侧眼柄组cyclinH基因表达量显著高于对照组,而去双侧眼柄组表达量显著高于去单侧眼柄组,此外,Cyclin H可以通过激活MPF来促进卵母细胞成熟分裂,这可以说明去眼柄诱导卵巢发育的分子机制中可能包含MPF对卵母细胞成熟分裂的促进作用。
4 结语
本研究成功克隆获得了三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因cDNA序列全长,分析了其在三疣梭子蟹不同组织及不同卵巢发育时期的表达差异,并通过分析去眼柄后三疣梭子蟹cyclinH基因的表达差异,证明了其参与了三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育调控,研究结果为进一步开展三疣梭子蟹卵母细胞成熟分裂的分子机制提供了理论依据。
参考文献:
[1]Sakai T. Crabs of Japan and Adjacent Seas[M]. Tokyo: Kodansha Ltd., 1976: 773.
[2]吴旭干, 姚桂桂, 杨筱珍, 等. 东海三疣梭子蟹第一次卵巢发育规律的研究[J]. 海洋学报(中文版), 2007, 29(4): 120-127.
Wu Xu-gan, YAO Gui-gui, YANG Xiao-zhen, et al. A study on the ovarian development ofPortunustrituberculatusin East China Sea during the first reproductive cycle[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2007, 29(4): 120-127.
[3]贾磊, 马甡. 三疣梭子蟹雌蟹在越冬和抱卵期间的卵巢发育[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版), 2007, 37(S2): 55-60.
JIA Lei, MA Shen. The ovarian development ofPortunustrituberculatusduring overwintering and spawning periods[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China, 2007, 37(S2): 55-60.
[4]谢熙. 三疣梭子蟹卵巢发育过程中FAMeT和MIH基因表达变化[D]. 宁波: 宁波大学, 2013.
XIE Xi. The Gene Expression ofMIHandFAMeTin the Ovarian Development ofPortunustrituberculatus[D]. Ningbo: Ningbo University, 2013.
[5]贾磊. 三疣梭子蟹(Portunustrituberculatus)卵巢发育的初步研究[D]. 青岛: 中国海洋大学, 2008.
JIA Lei. Preliminary Study on the Ovary Development of the CrabPortunustrituberculatus[D]. Qingdao: Ocean University of China, 2008.
[6]姚桂桂, 吴旭干, 杨筱珍, 等. 三疣梭子蟹的第二次卵巢发育规律[J]. 动物学研究, 2007, 28(4): 423-429.
YAO Gui-gui, WU Xu-gan, YANG Xiao-zhen, et al. The second ovarian development of swimming crabPortunustrituberculatus[J]. Zoological Research, 2007, 28(4): 423-429.
[7]储琳, 钱旻, 严缘昌. 细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶活化激酶(CAK)的研究进展[J]. 生命科学, 2006, 18(2): 127-132.
CHU Lin, QIAN Min, YAN Yuan-chang. Advances in the studies of cyclin development kinase-activating kinase (CAK)[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Life Sciences, 2006, 18(2): 127-132.
[8]Yoshida N, Mita K, Yamashita M. Comparative study of the molecular mechanisms of oocyte maturation in amphibians[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol B Biochem Mol Biol, 2000, 126(2): 189-197.
[9]Nagaraj S, Ziske C, Schmidt-Wolf I G. Human cytokine-induced killer cells have enhanced in vitro cytolytic activity via non-viral interleukin-2 gene transfer[J]. Genet Vaccines Ther, 2004, 2(1): 12-17.
[10]韩坤煌. 拟穴青蟹细胞周期及泛素系统若干基因参与性腺发育的研究[D]. 厦门: 集美大学, 2010.
HAN Kun-huang. The Study of Cell-Cycle and UPP Related Genes in the Goand Development of Mud Crab,Scyllaparamamosain[D]. Xiamen: Jimei University, 2010.
[11]Yang Y, Hu Y, Gu H Y, et al. Oroxylin A induces G2/M phase cell-cycle arrest via inhibiting Cdk7-mediated expression of Cdc2/p34 in human gastric carcinoma BGC-823 cells[J]. J Pharm Pharmacol, 2008, 60(11): 1459-1463.
[12]Fang J, Qiu G. Molecular cloning ofcyclinBtranscript with an unusually long 3’ untranslation region and its expression analysis during oogenesis in the Chinese mitten crab,Eriocheirsinensis[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2009, 36(6): 1521-1529.
[13]Qiu L, Jiang S, Zhou F, et al. Molecular cloning and characterization of acyclinBgene on the ovarian maturation stage of black tiger shrimp (Penaeusmonodon)[J]. Molecular Biology Reports, 2007: 1-8.
[14]Han K, Dai Y, Zou Z, et al. Molecular characterization and expression profiles of cdc2 and cyclin B during oogenesis and spermatogenesis in green mud crab (Scyllaparamamosain)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2012, 163(3-4): 292-302.
[15]Krempler A, Kartarius s, Gunther J, et al.CyclinHis targeted to the nucleus by C-terminal nuclear localization sequences [J]. Cell Mol Life Sci, 2005, 12(62): 1379-1387.
[16]Qiu G, Liu P. On the role of Cdc2 kinase during meiotic maturation of oocyte in the Chinese mitten crab,Eriocheirsinensis[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part B: Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, 2009, 152(3): 243-248.
[17]Andersen G, Poterszman A, Egly J M, et al. The crystal structure of human cyclin H[J]. FEBS Lett, 1996, 397(1): 65-69.
[18]赵超. 斑节对虾细胞周期蛋白家族部分基因的分子克隆及表达分析[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2014.
ZHAO Chao. Molecular Cloning and Expression Analysis of Some Cell Cyclin Genes from Black Riger Shrimp (Penaeusmonodon)[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2014.
[19]Sroyraya M, Chotwiwatthanakun C, Stewart M J, et al. Bilateral eyestalk ablation of the blue swimmer crab,Portunuspelagicus, produces hypertrophy of the androgenic gland and an increase of cells producing insulin-like androgenic gland hormone[J]. Tissue Cell, 2010, 42(5): 293-300.
[20]Bai H, Qiao H, Li F, et al. Molecular characterization and developmental expression of vitellogenin in the oriental river prawnMacrobrachiumnipponenseand the effects of RNA interference and eyestalk ablation on ovarian maturation[J]. Gene, 2014, 562(1): 22-31.
[21]Kang B J, Okutsu T, Tsutsui N, et al. Dynamics of vitellogenin and vitellogenesis-inhibiting hormone levels in adult and subadult whiteleg shrimp,Litopenaeusvannamei: relation to molting and eyestalk ablation[J]. Biol Reprod, 2014, 90(1): 12.
[22]Shen H, Hu Y, Zhou X. Sex-lethal gene of the Chinese mitten crabEriocheirsinensis: cDNA cloning, induction by eyestalk ablation, and expression of two splice variants in males and females[J]. Dev Genes Evol, 2014, 224(2): 97-105.
[23]Sun Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, et al. Changes in the organics metabolism in the hepatopancreas induced by eyestalk ablation of the Chinese mitten crabEriocheirsinensisdetermined via transcriptome and DGE analysis[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(4): e95827.
[24]Uawisetwathana U, Leelatanawit R, Klanchui A, et al. Insights into eyestalk ablation mechanism to induce ovarian maturation in the black tiger shrimp[J]. PLoS ONE, 2011, 6(9): e24427.
[25]Okumura T, Kim Y K, Kawazoe I, et al. Expression of vitellogenin and cortical rod proteins during induced ovarian development by eyestalk ablation in the kuruma prawn,Marsupenaeusjaponicus[J]. Comp Biochem Physiol A Mol Integr Physiol, 2006, 143(2): 246-253.
[26]Visudtiphole V, Klinbunga S, Kirtikara K. Molecular characterization and expression profiles of cyclin A and cyclin B during ovarian development of the giant tiger shrimpPenaeusmonodon[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Molecular & Integrative Physiology, 2009, 152(4): 535-543.
[27]Preechaphol R, Klinbunga S, Yamano K, et al. Molecular cloning and expression of progestin membrane receptor component 1 (Pgmrc1) of the giant tiger shrimpPenaeusmonodon[J]. Gen Comp Endocrinol, 2010, 168(3): 440-449.
责任编辑高蓓
基金项目:❋ 国家自然科学基金项目(41576147;41306178)资助
收稿日期:2015-10-28;
修订日期:2015-12-30
作者简介:贾复龙(1989-),男,硕士生,研究方向为海水养殖生物种质资源与工程育种。E-mail: 1360639373@qq.com ❋❋通讯作者:E-mail: liuping@yshri.ac.cn
中图法分类号:Q953.1;S917.4
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-5174(2016)07-062-08
DOI:10.16441/j.cnki.hdxb.20150365
Clong and Expression in the Ovarian Development ofCyclinHGene ofPortunustrituberculatus
JIA Fu-Long1,2,3, MENG Xian-Liang2,3, LIU Ping2,3,LI Jian2,3, GAO Bao-Quan2,3, GAO Tian-Xiang1, SONG Na1
(1.College of Fisheries. Ocean Unversity of China, Qingdao 266003, China; 2.The Key Laboratory of Sustainable Development of Marine Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, P.R.China, Yellow Sea Fisheries Research Institute, Chinese Academy of Fishery Sciences; 3.Function Laboratory for Marine Fisheries Science and Food Production Processes, Qingdao National Laboratory for Marine Science and Technology, Qingdao 266071, China)
Abstract:The swimming crab (Portunus trituberculatus) is the most important economic crbs in China and widely distributed in the coastal of China, Japan and Korea. At present, the problem of ovarian hypoplasis and brooding poor quality in process of the swimming crab aquaculture is widespread. And cell devision of gonads is very strong. Besides, Cyclin H is a key factor in cell cycle regulation activities. It controls multiple link of cell cycle through corresponding Cyclin dependent kinase (Cdks), then active Cdks through phosphorylate corresponding phosphorylation site. And the maturation or M-phase promoting factor was activated. In addition to these key roles in cell cycle progression, Cyclin H is a component of the general transcription factot TFIIH. So, the researching about cyclin H gene of the swimming crab is important to solve these problem. The cyclin H gene of the swimming crab was cloned using rapid amplification of its cDNA ends (RACE) based on the EST sequence. Then analysed the complete sequence using VecScreen、ContigExpress Project、EditSeq、BLAST、ExPASy、InterproScan、NetPhos and DNAman et, al. The sample ovary different stages and different tissue of the swimming crab were collected from Chang Yi, Shan Dong. And we analysed the expression of ovarian development of the swimming crab cyclin H gene using SYBR Premix Ex TaqTM. Then put it to the ABI7500 machine. After the completion of the reaction, we analysised the relative expression by the method of 2-ΔΔCt. The complete cDNA sequence of this gene is 1077bp in length, which contains an open reading frame (ORF) of 999bp, a 5’untranslated region(5’UTR) of 31bp and a 3’unteranslated region(3’UTR) of 46bp. The ORF encodes 332 amnio caid polypepteds. Molecular mass and the estimated isoelectric point (pI) of this protein are 38.89kDa and 6.20. Protein sequence contains a conservative domain structure named cyclin box. GenBank accession number is KT025877. Homology analysis revealed that the swimming crab cyclin H gene have high homology with other crustaceans. And the identities were 95% and 80% compared with Scylla paramamosain and Penaeus monodon. We found a threonine phosphorylation site (Thr12) from this gene by online prediction. Protein kinase Ck2 active Cyclin H through phosphorylate corresponding threonine phosphorylation site of Cyclin H. It needs further research for Ck2 recognition site in Cyclin H. The relative expression level of cyclin H gene analysised by quantitative Real-time PCR showed that the highest expression level of cyclin H gene was in ovary, especially in the first and second stage of ovary. The characteristics of high expression level of this gene in gonads consistent with its important role in cell division regulation. The activity of oogonium proliferation is vigorousness in the early ovarian development phase. These may suggest that cyclin H gene participate in the process of cell division in the activities of the ovarian development. After eyestalk ablation, the expression level of cyclin H in ovary was up-regulated significantly firstly, reached the peak on the fourth day, and then decreased. And we suggest that eyestalk ablation may promote the development of ovary. Also, this may be associated with MPF activated which cyclin H gene participated in (P<0.05). Our results suggested that Cyclin H might play important roles in ovarian development especially oogenesis of the swimming crab. And it would provide more usdful information for the research of gonadal development regulation in crustaceans.
Key words:Portunus trituberculatus; cyclin H; gene cloning; eyestalk ablation; gene expression; ovary
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (41576147;41306178)

