基于吡啶基苯甲酸盐的两个银(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、晶体结构及荧光性质
马 雁 毕凯伦 崔洋哲刘 敏 李中峰 金琼花(首都师范大学化学系,北京 00048)(北京工业大学材料科学与工程学院,北京 004)
基于吡啶基苯甲酸盐的两个银(Ⅱ)配合物的合成、晶体结构及荧光性质
马雁1毕凯伦1崔洋哲1刘敏2李中峰1金琼花*,1
(1首都师范大学化学系,北京100048)
(2北京工业大学材料科学与工程学院,北京100124)
摘要:合成了2个含有吡啶基苯甲酸盐的银(Ⅱ)配合物,即[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,4-pybz)2(H2O)2]n(1)和[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,3-pybz)2]·2CH3OH(2)(PPh3=三苯基膦,4,4-pybz=4-吡啶-4-基-苯甲酸根,4,3-pybz=4-吡啶-3-基-苯甲酸根),并通过红外光谱、元素分析和荧光光谱进行分析和表征,它们的结构由X射线单晶衍射测定。在不同的溶剂下,2个配合物由AgBF4、PPh3和不同的吡啶苯甲酸在氨水作用下,以1∶1∶1的比例反应而成。在配合物1中,所有的银原子由吡啶基苯甲酸桥连形成一维链状结构。在配合物2中,2个银原子通过2个4-吡啶-3-基-苯甲酸根配体形成双核结构。在荧光光谱中,在发射状态下所有的峰均来源于配体的π-π*跃迁。
关键词:银;三苯基膦;4-吡啶-3-基-苯甲酸;4-吡啶-4-基-苯甲酸
0 Introduction
In recent year,the research of coordination polymers have been of considerable interests due to important applications in gas storage[1-2],heterogeneous catalysis[3-4],sensing[5-6],high photosensitivity material[7]
国家自然科学基金(No.21171119,81573832)、863国家高技术研究发展计划(No.2012AA063201)、北京教育委员会基金(No.KM201210028020)、北京市优秀人才项目(No.2010D005016000002)和北京市自然科学基金(No.7122015)资助。
*通信联系人。E-mail:jinqh@cnu.edu.cn;会员登记号:S06N3669M1105。andmagneticmaterial[8].Thepreparationof coordination polymers or complexes can be controlled by many factors,including temperature,solution,and concentration.Closed-shell d10metal(Cu,Ag,Au)irons used for the construction of compound have also attracted attention on their coordination geometry,especiallyAg(Ⅱ)ions.Owingtotheirvariable coordinationnumberandflexiblegeometryand properties,they have been widely used[9].
Pyridylbenzoateligandisausefulkindof bridging ligand because it contains unsymmetrical bifunctional groups.In view of this character,it has a chance of generating chiral coordination polymers[10]. 4-pyridin-4-yl-benzoic acid(4,4-Hpybz)and 4-pyridin-3-yl-benzoic acid(4,3-Hpybz)are two rigid linear kinds of ligands,which have the O and N donors on the opposite sides.In the previous studies,a numbe of group 11 or heterometallic organic frameworks with 1D,2D and 3D have reported[11-14].
Basedontheseconsiderations,wechoos pyridylbenzoate ligand and report in this paper tw coordinationcomplexesderivedfrom triphenylphosphineligandandpyridylbenzoat ligands,namely[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,4-pybz)2(H2O)2]n(1)and [Ag2(PPh3)2(4,3-pybz)2]·CH3OH(2) (4,4-pybz=4 pyridin-4-yl-benzoate,4,3-pybz=4-pyridin-3-yl benzoate).They were synthesized and characterized by IR,elemental analysis and fluorescence spectrum,and their structures were elucidated by single-crystal X ray diffraction.
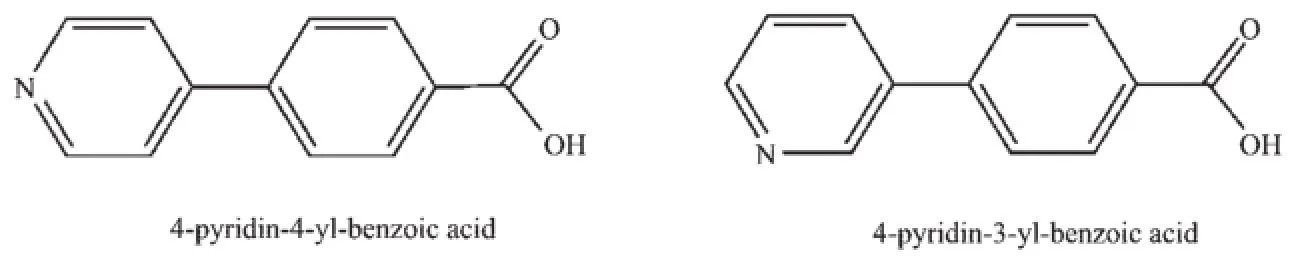
Scheme 1 Ligands used in the present work

Scheme 2 Routine of synthesis for complexes 1 and 2
1 Experimental
1.1Materials and measurement
All chemical reagents are commercially available and used without furthermore treatment.FTIR spectra (KBrpellets)weremeasuredonaPerkin-Elmer Infrared spectrometer.C,H and N elemental analysis were carried out on an ElementarVario MICRO CUBE (Germany)elemental analyzer.
1.2Synthesis of[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,4-pybz)2(H2O)2]n(1)
A mixture of AgBF4(0.2 mmol,0.038 6 g),triphenylphosphine(PPh3)(0.2 mmol,0.052 2 g)and 4-pyridin-4-yl-benzoic acid(4,4-Hpybz,0.2 mmol, 0.040 0 g)with a little ammonia water were dissolved in a mixture of CH3CN(5 mL)and H2O(5 mL),stirred for 6 h and filtered.Colorless crystal 1 was obtained from the filtrate after standing at the room temperature for several days.Yield:54%.Element analysis Calcd for C60H50Ag2N2O6P2(%):C,61.40;H,4.26;N,2.39 Found(%):C,59.59;H,4.16;N,2.57.IR data(cm-1KBr pellets):3 647w,3 356m,3 048m,1 669w,1 593s 1558s,1478m,1434m,1375s,1228w,1181w,1 096w 1 067w,1 027w,997w,870w,832m,781s,753s,694s 561w,520m,506m,477m.
1.3Synthesisof[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,3-pybz)2]·2CH3OH(2)
Complex 2 was prepared in a manner similar tthat described for 1,using AgBF4(0.2 mmol,0.039 2 g),PPh3(0.2 mmol,0.052 4 g)and 4-pyridin-3-ylbenzoic acid(4,3-Hpybz,0.2 mmol,0.039 8 g)with a little ammonia water as starting materials in a mixture of CH3OH (5mL)and CH2Cl2(5 mL).Yield:49%. Element analysis Calcd.for C62H54Ag2N2O6P2(%):C,61.96;H,4.50;N,2.33.Found(%):C,62.14;H,4.45;N,2.21.IRdata(cm-1,KBrpellets):3324w,3053w,2 918w,2 811w,1 585m,1 535m,1 477m,1 433m,1388s,1332w,1309w,1179w,1152w,1095m,1068w,1 040m,1 007w,870w,844w,813w,786m,747s,695s,559w,520m,507m,495m,463w.
1.4Structure determination
Singlecrystalsofthetitlecomplexeswere mounted on a Bruker Smart 1000 CCD diffractometer equipped with a graphite-monochromated Mo Kα(λ= 0.071 073 nm)radiation at 298 K.Semi-empirical absorption corrections were applied using SADABS program[15a].All the structures were solved by direct methods using SHELXS program of the SHELXS-97 package and refined with SHELXL-97[15b].Metal atom centers were located from the E-maps and other nonhydrogen atoms were located in successive difference Fourier syntheses.The final refinements were performed by full matrix least-squares methods with anisotropic thermal parameters for non-hydrogen atoms on F2.The hydrogen atoms were generated geometrically and refined with displacement parameters riding on the concerned atoms.
Crystallographic data and experimental details for structural analysis are summarized in Table 1,and selected bond lengths and angles of complexes 1~2 are summarized in Table 2.The hydrogen bonds of complexes 1~2 are listed in Table 3.
CCDC:890642,1;890650,2.

Table 1 Crystallographic data for complexes 1~2

Table 2 Selected bond distances(nm)and bond angles(°)for complexes 1~2

Table 3 Hydrogen bonds of complexes 1~2
2 Results and discussion
2.1Synthesis of the complex
As is known to all,ligand and solvent are factors of influencing the structures of the compounds.In the preparation of title complexes,the ligands 4-pyridin-4-yl-benzoic acid(4,4-Hpybz)and 4-pyridin-3-yl-benzoic acid(4,3-Hpybz)influence the coordination modes of the silver atom.Complex 1 is obtained by the reaction of AgBF4,PPh3and 4,4-Hpybz with ammonia water in 1∶1∶1 molar ratio in mixed solvent(CH3CN/H2O)generating an infinite chain structure.Complex 2 is obtained by the reaction of AgBF4,PPh3and 4,3-Hpybz with ammonia water in 1∶1∶1 molar ratio in mixed solvent(CH3OH/CH2Cl2)generating a binuclear structure.In the synthesis process,NH3·H2O is used as a critical material of deprotonation,which makes 4,4-Hpybz and 4,3-Hpybz transformed into 4,4-pybz and 4,3-pybz.
2.2Infrared spectroscopy
The infrared spectra of complex 1~2 show the absorptions around 1 434 cm-1are due to C-C stretch vibrationofthephenylringsandthemiddle absorptions around 3 048 cm-1are caused by C-H vibration of the phenyl rings.The absorptions of the COO-stretch vibration are around 1 388 cm-1.
2.3Description of the crystal structure
Single-crystal X-ray diffraction analysis reveals that 1 crystallizes in the Orthorhombic system with space group P212121.The asymmetric unit(Fig.1)is comprised of two Ag(Ⅱ) ions,two PPh3ligands,two water ligands and two 4-pyridin-4-yl-benzoate(4,4-pybz)ligands,which is further linked by 4,4-pybz to generate a 1D coordination polymer(Fig.2).The metal whichadoptsfour-coordinatedmode,isuniquely bonded to one of oxygen atoms of a carboxyl fragment and a N atom from the pyridine ring fragment of the 4,4-pybz ligand establishing a distorted tetrahedral geometry about the metal,just as in the complex{[Ag(PPh3)2(bpp)](BF4)}n[16].Ag-N(0.2325(3),0.2253(3)nm)and Ag-P bond lengths(0.2368 6(10),0.235 99(9)nm)are typical Ag(Ⅱ)-Npyand Ag(Ⅱ)-P distances,respectively[17].Ag(Ⅱ)-Npybond distances are longer than that observed in[Ag(pycz)(H2O)]·3H2O(pycz=4-(4-pyridyl)benzonate)(0.214 5(3)nm)[18].Moreover,the intramolecular O-H…O hydrogen bond is observed(O …O 0.267 5(4)nm,O-H…O 137.8°)in the complex 1.
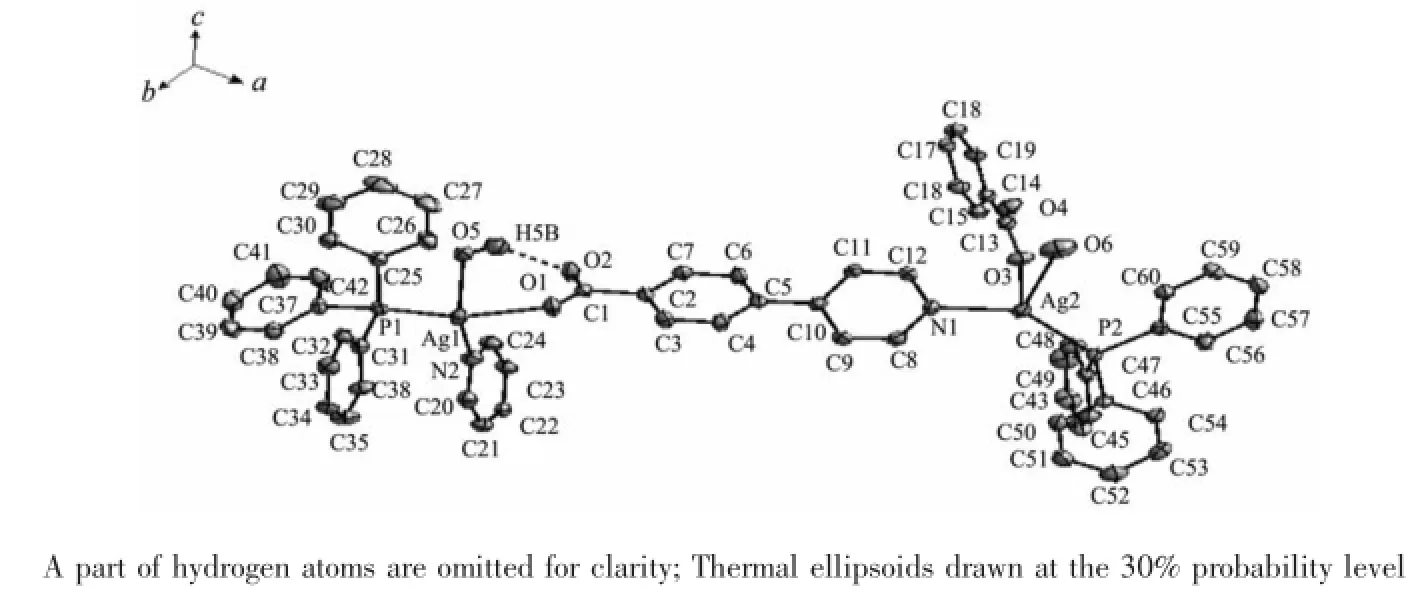
Fig.1 Perspective view of complex 1

Fig.2 Linear chain of 1

Fig.3 Asymmetric unit of complex 2
Complex 2 is a binuclear heteroleptic complex formed with distinctly soft Ag(Ⅱ),PPh3and 4,3-pybz in 1∶1∶1 molar ratio.Each Ag is four-coordinated,surrounded by a P atom from a PPh3ligands and two chelating O atoms and a N atom from two 4,3-pybz ligands(Fig.3).The ligand 4,3-pybz acts as a typical multiple dentate ligand to join Ag(Ⅱ)atoms,just as in the complex[La2Cu2(ox)2L6]·4HL(HL=4-pyridin-4-ylbenzoic acid)[19].The angles around Ag(Ⅱ) ranging from 88.70(8)°to 136.69(6)°indicate that the geometry around Ag atom is distortedly tetrahedral.In complex 2,Ag(Ⅱ)-Npy bond distance(0.234 2(2)nm)is longer than those in the complex[Ag3(CH3CN)3(L1)2Cl](BF4)2·3CH3CN(0.218 7(18)and 0.232 0(5)nm)[20].The main structure of 2 links free CH3OH by hydrogen bonding interactions.The O-H…O hydrogen bond to link freeCH3OH is observed(O…O 0.270 2(5)nm,O-H…O 168.6°)in the complex 2.

Fig.4 Solid-state excitation and emission spectra of 1~2 at 298 K
2.4FluorescenceSpectrum
The luminescent excitation and emission spectra of complexes 1~2 and 4,4-Hpybz,4,3-Hpybz ligand in the solid state at room temperature are obtained.The emission peak of PPh3is at 402 nm(λex=372 nm)[21].In the fluorescence emission spectra of 4,4-Hpybz ligand,the emission peaks are found at 395 nm(λex=322 nm). The 4,3-Hpybz ligand exhibits fluorescence signal centered at 417 nm with an excitation maximum at 341 nm.When excited at 354 nm,a fluorescence emission peak of complex 1 is found at 424 nm.The complex 2 exhibits fluorescence signal centered at 356 nm with an excitation maximum at 425 nm(Fig.4). The red-shift of emission peaks of 1~2 are derived from ligand-centered π-π*transition.
3 Conclusions
Two new Ag(Ⅱ)complexes of phosphine-containing ligands,namely[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,4-pybz)2(H2O)2]n(1)and [Ag2(PPh3)2(4,3-pybz)2]·2CH3OH(2),have been synthesized and characterized by elemental analysis,IR,X-raydiffractionandfluorescencespectra. Structureanalyses show that,theAg atomsare bridged by pyridylbenzoate-containing ligand to form infinite chain structure in 1.Two Ag atoms are bridged by two 4-pyridin-3-yl-benzoate ligands to form binuclear complex in 2.The luminescent spectra show that the origin of these emissions all involves emissive state derived from ligand centered π-π*transition We hope our results could offer new strategy for the characterization and design of coordination polymers.
References:
[1]Duan J G,Jin W Q,Krishna R.Inorg.Chem.,2015,54 4279-4284
[2]Zhang J,Xue Y S,Liang L L,et al.Inorg.Chem.,2010,49 7685-7691
[3]Tanabe K K.,Cohen S M.Angew.Chem.Int.Ed.,2009,48 7424-7427
[4]Yoon M,Srirambalaji R,Kim K.Chem.Rev.,2012,112 1196-1231.
[5]Zhang S,Echegoyen L.J.Am.Chem.Soc.,2005,127:2006 2011
[6]DemasJN,GraffBA.Coord.Chem.Rev.,2001,211:317-351
[7]Rajput G,Yadav M K,Drew M G B,et al.Inorg.Chem. 2015,54:2572-2579
[8]Coronado E,Espallargas G M.Chem.Soc.Rev.,2013,42 1525-1539
[9]Katagiri K,Sakai T,Hishikawa M,et al.Cryst.Growth Des. 2014,14:199-206
[10]Ayyappan P,Evans O R,Cui Y,et al.Inorg.Chem. 2002,41:4978-4980
[11]Fang W H,Yang G Y.J.Solid State Chem.,2014,212:249 257
[12]Jia X L,Zhou J,Zheng S T,et al.J.Cluster Sci.,2009,20 555-563
[13]Wang Z L,Fang W H,Yang G Y.Chem.Commun.2010,46,8216-8218
[14]He Y P,Tan Y X,Zhang J.CrystEngComm,2012,14:6359-6361
[15](a)Sheldrick G M.SADABS,Program for Empirical Absorption Correction of Area Detector Data,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997. (b)SheldrickGM.SHELXS-97 and SHELXL-97,University of Göttingen,Germany,1997.
[16]Huang X,Li Z F,Jin Q H,et al.Polyhedron,2013,65:129-135
[17]Carlucci L,Ciani G,Proserpio D M,et al.CrystEngComm,2002,4:121-129
[18]Ou G C,Gu J Z,Lu T B,et al.J.Mol.Struct.,2005,740: 143-146
[19]Fang W H,Yang G Y.CrystEngComm,2014,16:4091-4094
[20]Ronson T K,Hardie M J.CrystEngComm,2008,10:1731-1734
[21]Lobana T S,Sultana R,Butcher R J,et al.Z.Anorg.Allg. Chem.,2014,640:1688-1695
中图分类号:O614.122
文献标识码:A
文章编号:1001-4861(2016)05-0884-07
DOI:10.11862/CJIC.2016.100
收稿日期:2015-12-25。收修改稿日期:2015-03-02。
Syntheses,Crystal Structures and Fluorescence Properties of Two Silver(Ⅱ)Complexes Derived from Pyridylbenzoate Ligands
MA Yan1BI Kai-Lun1CUI Yang-Zhe1LIU Min2LI Zhong-Feng1JIN Qiong-Hua*,1
(1Department of Chemistry,Capital Normal University,Beijing 100048,China)
(2The College of Materials Science and Engineering,Beijing University of Technology,Beijing 100124,China)
Abstract:Two silver(Ⅱ) complexes with pyridylbenzoate ligands,namely[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,4-pybz)2(H2O)2]n(1),[Ag2(PPh3)2(4,3-pybz)2]·2CH3OH(2)(PPh3=triphenylphosphine,4,4-pybz=4-pyridin-4-yl-benzoate,4,3-pybz=4-pyridin-3-yl-benzoate)were synthesized and characterized by IR,elemental analysis and fluorescence spectra,and their structures were elucidated by single-crystal X-ray diffraction.They have been made by reacting AgBF4,PPh3,different pyridylbenzoic acids in 1∶1∶1 molar ratio with ammonia water under different mixed solution conditions. In 1,the Ag atoms are bridged by pyridylbenzoate-containing ligand to form infinite chain structure.In 2,two Ag atoms are bridged by two 4-pyridin-3-yl-benzoate ligands to form binuclear complex.In fluorescence spectra,these emission peaks indicate that the origin of these emissions all involves emissive state derived from ligandcentered π-π*transition.
Keywords:silver;triphenylphosphine;4-pyridin-3-yl-benzoic acid;4-pyridin-4-yl-benzoic acid

