大黄素抑制结肠癌转移的研究*
王旻晋,王元元,范继斌
1.四川大学华西医院 实验医学科 (成都 610041); 2.成都医学院 生物医学系(成都 610083);3.绵阳市梓潼县工人医院(梓潼 622150)
大黄素抑制结肠癌转移的研究*
王旻晋1,王元元2△,范继斌3
1.四川大学华西医院 实验医学科 (成都610041); 2.成都医学院 生物医学系(成都610083);3.绵阳市梓潼县工人医院(梓潼622150)
【摘要】目的研究大黄素对结肠癌细胞转移的抑制作用及其作用分子机制。方法通过MTT法确定大黄素有效作用浓度,采用细胞划痕实验、Transwell和基质胶实验检测大黄素对结肠癌细胞迁移、侵袭能力的影响。通过免疫印迹试验(Western blot)检测EMT事件标志性蛋白的变化及上游信号通路的标志性蛋白。结果MTT表明,大黄素对结肠癌细胞SW480有明显的抑制作用;细胞划痕、Transwell和基质胶实验表明,大黄素具有抑制结肠癌迁移和侵袭的能力;Western blot 结果表明,大黄素激活N-cadherin,抑制E-cadherin、Vimmentin、β-catenin的表达,同时抑制恶性基因VEGF、MMP-2、MMP-9的表达,抑制Akt/mTOR、STAT3 的磷酸化。结论大黄素通过抑制STAT3、PI3K-AKT信号通路进而抑制结肠癌转移,为其在临床上作为治疗结肠癌的辅助药物或直接作用药物提供理论依据。
【关键词】结肠癌;大黄素;转移;信号通路
结肠癌(colon cancer)是全球最常见的恶性肿瘤之一,位居恶性肿瘤死因的第2位,是我国高发癌症之一[1],其发生和发展与日常饮食习惯密切相关。结肠癌的发生与转移是一个十分复杂的生物学过程,很多分子参与其中。目前,结肠癌的治疗手段主要为放、化疗和手术,但放、化疗有很多的缺陷[2]。近年来日常饮食中的植物化学在肿瘤预防和治疗中得到广泛的认可,其化学成分单独或与其他药物共同起着对肿瘤的治疗作用[3]。大黄素作为从大黄根部提取的一种蒽醌类物质,在不同肿瘤细胞及动物模型中表现出抗炎、抗增殖、抗转移等作用[4-6]。研究[7]报道,大黄素能够抑制结肠癌、乳腺癌的迁移与浸润,但其作用分子机制不明确。本研究以结肠癌细胞SW480为研究对象,研究大黄素抑制结肠癌细胞转移的分子机制,以探讨大黄素的抗肿瘤药用价值。
1材料与方法
1.1材料
人结肠癌细胞SW480购自上海中科院细胞库,于-80 ℃冻存;DMEM培养基购自美国Gibco;胎牛血清购于杭州四季青生物公司;大黄素购自上海谱振生物科技有限公司;MTT、Transwell、基质胶购自美国Sigma 公司;蛋白质预染Marker购自立陶宛Fermentas公司;Tween-20购自北京中衫金桥生物技术有限公司;Vimentin、E-cadherin、N-cadherin、β-catenin、VEGF、STAT3、p-STAT3、AKT、p-AKT和β-Actin单克隆抗体均购自美国CST公司;PVDF 膜和 ECL 显影液购于美国Millipore 公司;X 光胶片购于美国Kodak 公司;其余化学试剂均为分析纯。
1.2方法
1.2.1细胞培养SW480在含有10% 胎牛血清的RPMI1640 培养基(含105U/L青霉素,100 mg/L链霉素)中于37 ℃,5% CO2培养箱中培养。
1.2.2MTT将100 μLSW480细胞悬液以50 000个/mL的密度接种于96孔板,在CO2孵箱中37 ℃培养孵育过夜。待细胞贴壁后,加入不同浓度(0、15、30、40、60、75和90 μM)的大黄素100 μL继续培养24、48和36 h。每组设4个复孔,另设不含细胞仅有培养基的空白孔为空白对照孔。药物处理结束后,加入MTT(5 mg/mL)试剂20 μL,37 ℃ 5% CO2孵育4 h,以空白孔调零,酶标仪检测590 nm波长下的吸光值。
1.2.3细胞划痕实验将生长良好的SW480细胞以6×104个/孔接种于6孔板中,培养24 h后,待密度达到90%以上时,用200 μL的枪头在6孔板中划痕,PBS洗2次,加入含大黄素的双无培养基,继续培养48 h后,照相观察划痕愈合情况。
1.2.4Transwell、基质胶实验参考文献[8]方法,将经大黄素处理48 h 后的细胞,PBS洗2次,用无血清培养液重悬。将200 μL细胞悬液(3×105/mL、4×105/mL)加入上室或含基质胶的小室,将含20%胎牛血清DMEM培养基540 μL加入24孔板下室,每组设3个复孔,培养48 h,取出小室,经 4%多聚甲醛固定后,结晶紫染色,用湿棉签擦去膜上面未穿过膜的细胞,自然风干后,在显微镜下照相,低倍镜下随机选取5个视野计数。最终以穿膜细胞的数目代表体外迁移能力、外侵袭能力。
1.2.5免疫印迹收集经药物处理后的细胞, 按1×106细胞浓度加入100 μL细胞裂解液,涡旋震荡,冰上放置1 h,将细胞裂解液 4 ℃ 13 000 rpm/min 离心15 min,取上清液加上样缓冲液,85 ℃加热变性10 min,样品中蛋白经BCA试剂盒定量,以确保蛋白上样量一致。将细胞总蛋白通过15% SDS-PAGE电泳分离后,转膜至PVDF膜上。分别加入一抗(一抗稀释比例均为1∶1 000),4 ℃孵育过夜。用TBST 洗膜后,辣根过氧化物酶标记二抗(1∶5 000)37 ℃ 孵育1 h,TBST 洗涤PVDF膜5次, 每次10 min,加入ECL显影剂后,通过X光胶片曝光。
1.3统计学方法
2结果
2.1大黄素抑制结肠癌细胞SW480的增殖
使用不同浓度(0、15、 30、 40、60、75和90 μM)的大黄素处理结肠癌细胞SW480 24、48和72 h 后,通过 MTT 实验检测细胞活力(图1)。结果表明,大黄素能促进细胞内毒性,显著抑制细胞增殖速率,并且抑制程度呈浓度依赖性。
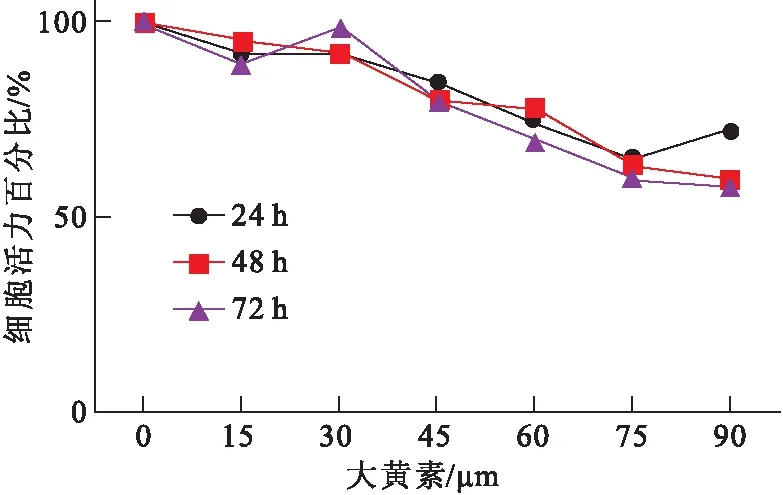
图1不同浓度大黄素处理SW480细胞24、48和36 h的细胞活力
2.2大黄素抑制结肠癌细胞迁移和浸润
采用45 μM大黄素处理结肠癌细胞SW480 48 h。通过划痕实验、Transwell和基质胶实验检测大黄素对结肠癌细胞迁移和浸润能力的影响。划痕实验结果表明,经大黄素处理后的细胞划痕处细胞愈合程度明显比对照低(图2)。Transwell 实验结果显示,经45 μM大黄素处理后的SW480穿过基底膜的细胞个数为(107.30±14.34),对照组穿过基底膜的细胞个数为(216.40±23.12),两组比较,差异有统计学意义(t=7.357,P< 0.001),表明大黄素抑制了结肠癌细胞的迁移能力(图3)。基质胶实验结果表明,经大黄素处理后SW480的浸润能力明显降低,穿过基底膜的细胞数为(205.00±17.24),对照组穿过的细胞数为(342.00±24.63),两组比较,差异有统计学意义(t=7.72,P<0.01) (图4)。以上实验结果说明,大黄素抑制了结肠癌细胞的迁移和浸润能力。

图2划痕实验检测大黄素对SW480的迁移能力改变

图3Transwell 实验检测大黄素对SW480迁移能力的影响

图4基质胶实验检测大黄素对SW480浸润能力的影响
2.3大黄素抑制EMT信号通路
将经大黄素处理后的结肠癌细胞SW480细胞裂解液进行蛋白质免疫印迹检测EMT相关基因的表达情况,western结果显示:大黄素促进了SW480细胞胞内表皮标志性蛋白E-Cadherin的表达,抑制了间质化细胞标志性蛋白N-Cadherin、vimentin的表达,同时抑制了胞内信号传导分子β-Cantein的表达(图5)。以上结果表明大黄素通过负调控EMT事件进而抑制了结肠癌细胞的转移。

图5免疫印迹检测EMT相关标志性蛋白
2.4大黄素抑制恶性基因的表达
结肠癌细胞SW480经45 μM大黄素处理48 h后,Western结果显示:SW480细胞胞内恶性基因MMP-9、MMP-2和VEGF的表达明显降低进而抑制了结肠癌细胞的转移。

图6免疫印迹检测恶性基因的表达
2.5大黄素抑制Akt/mTOR和 STAT-3 信号通路
用大黄素处理结肠癌细胞SW480 48 h后,进行免疫印迹检测。Western结果表明,大黄素抑制了AKT(S473)和mTOR(S2448)磷酸化水平,同时胞内STAT3(Tyr705)的磷酸化水平降低(图7)。以上实验结果表明,大黄素抑制了Akt/mTOR 和 STAT-3 信号通路。

图7免疫印迹分析AKT-mTOR和STAT3
3讨论
大黄素是一种传统中药,作为具有抗肿瘤作用的蒽醌类药品,主要用于抗菌、利尿、止咳等治疗[9]。1976首次提出大黄素具有抗肿瘤的作用[10]。后续研究[11-13]表明大黄素对前列腺癌、肺癌、乳腺癌均具有抗增殖作用。在体内实验中,大黄素对肿瘤细胞具有抑制作用,但对正常细胞或组织没有明显的毒性作用。癌症转移是癌症治疗过程中最为关键的因素[14]。大量文献[15-16]报道,大黄素通过阻断细胞周期和促凋亡进而抑制多种癌细胞。研究[17]表明,大黄素具有抗转移和浸润的作用。EMT是上皮细胞来源的恶性肿瘤细胞获得迁移和侵袭能力的重要生物学过程,表现为上皮标志蛋白E-Cadherin表达降低,间质化标志蛋白N-Cadherin和Vimentin表达上调[18]。在本研究中,大黄素抑制了EMT过程的发生,表现为E-Cadherin高表达,而N-Cadherin和Vimentin低表达。
随着研究的深入,EMT过程的发生受越来越多分子共同调控。文献[19]报道,基质金属蛋白酶(MMPS)在癌症细胞中调控EMT时间的发生。本研究检测了其中两个基质金属蛋白酶MMP-2、MMP-9。经大黄素处理后,MMP-2、MMP-9表达明显被抑制。进而检测调控该基质金属蛋白酶的上游Akt/mTOR 和 STAT-3 信号通路,实验结果表明,Akt/mTOR 和 STAT-3的磷酸化水平明显降低。血管生成是肿瘤转移过程中一个标志性事件,肿瘤细胞通过释放VEGF调控胞外基质进而激活下游信号促进肿瘤的恶化和癌症转移[20],本实验结果表明,大黄素能够显著抑制结肠癌细胞SW480胞内VEGF的表达。因此可推断出大黄素通过抑制Akt/mTOR 和 STAT-3 信号通路、调控MMP-2、MMP-9 酶活性和抑制VEGF的表达进而抑制结肠癌细胞的转移。
本研究结果解释了大黄素抑制结肠癌转移的作用机制,为其作为抗肿瘤药物提供了理论基础。研究表明,大黄素通过多个作用靶点影响多种癌细胞的生长、转移和增殖,但其作用机制不同[21-23],说明药物作用的直接靶点还不明确。笔者将在后续的研究中采用药物蛋白组学的方法对其药物直接作用靶点进一步验证与研究,为其在临床上更为广泛地运用提供理论基础。
参考文献
[1]Rasool S,Kadla SA,Rasool V,etal.A comparative overview of general risk factors associated with the incidence of colorectal cancer[J].Tumour Biol,2013,34(5): 2469-2476.
[2]Ahnen DJ,Wade SW,Jones WF,etal.The increasing incidence of young-onset colorectal cancer: a call to action[J].Mayo Clin Proc,2014,89(2): 216-224.
[3]Priyadarsini RV,Nagini S.Cancer chemoprevention by dietary phytochemicals: promises and pitfalls[J].Curr Pharm Biotechnol,2012,13(1): 125-136.
[4]Srinivas G,Babykutty S,Sathiadevan PP,etal.Molecular mechanism of emodin action: transition from laxative ingredient to an antitumor agent[J].Med Res Rev,2007,27(5): 591-608.
[5]Wei WT,Lin SZ,Liu DL,etal.The distinct mechanisms of the antitumor activity of emodin in different types of cancer (Review)[J].Oncol Rep,2013,30(6): 2555-2562.
[6]Damodharan U,Ganesan R,Radhakrishnan UC.Expression of MMP2 and MMP9 (gelatinases A and B) in human colon cancer cells[J].Appl Biochem Biotechnol,2011,165(5-6): 1245-1252.
[7]Lu Y,Zhang J,Qian J.The effect of emodin on VEGF receptors in human colon cancer cells[J].Cancer Biother Radiopharm,2008,23(2): 222-228.
[8]Yang J,Li TZ,Xu GH,etal.Low-concentration capsaicin promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by triggering ROS production and modulating Akt/mTOR and STAT-3 pathways[J].Neoplasma,2013,60(4): 364-372.
[9]Kupchan SM,Karim A.Tumor inhibitors.114.Aloe emodin: antileukemic principle isolated from Rhamnus frangula L[J].Lloydia,1976,39(4): 223-224.
[10] Acevedo-Duncan M,Russell C,Patel S,etal.Aloe-emodin modulates PKC isozymes,inhibits proliferation,and induces apoptosis in U-373MG glioma cells[J].Int Immunopharmacol,2004,4(14): 1775-1784.
[11] Guo J,Xiao B,Liu Q,etal.Suppression of C-myc expression associates with anti-proliferation of aloe-emodin on gastric cancer cells[J].Cancer Invest,2008,26(4): 369-374.
[12] Guo JM,Xiao BX,Liu Q,etal.Anticancer effect of aloe-emodin on cervical cancer cells involves G2/M arrest and induction of differentiation[J].Acta Pharmacol Sin,2007,28(12): 1991-1995.
[13] Yilmaz M,Christofori G.EMT,the cytoskeleton,and cancer cell invasion[J].Cancer Metastasis Rev,2009,28(1-2): 15-33.
[14] He TP,Yan WH,Mo LE,etal.Inhibitory effect of aloe-emodin on metastasis potential in HO-8910PM cell line[J].J Asian Nat Prod Res,2008,10(5-6): 383-390.
[15] Kuo PL,Lin TC,Lin CC.The antiproliferative activity of aloe-emodin is through p53-dependent and p21-dependent apoptotic pathway in human hepatoma cell lines[J].Life Sci,2002,71(16): 1879-1892.
[16] Lin ML,Lu YC,Chung JG,etal.Down-regulation of MMP-2 through the p38 MAPK-NF-kappaB-dependent pathway by aloe-emodin leads to inhibition of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell invasion[J].Mol Carcinog,2010,49(9): 783-797.
[17] Spaderna S,Schmalhofer O,Hlubek F,etal.Epithelial-mesenchymal and mesenchymal-epithelial transitions during cancer progression[J].Verh Dtsch Ges Pathol,2007,91: 21-28.
[18] Kessenbrock K,Plaks V,Werb Z.Matrix metalloproteinases: regulators of the tumor microenvironment[J].Cell,2010,141(1): 52-67.
[19] Zhang L,Kim S,Ding W,etal.Arsenic sulfide inhibits cell migration and invasion of gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo[J].Drug Des Devel Ther,2015,9: 5579-5590.
[20] Buchanan FG,DuBois RN.Connecting COX-2 and Wnt in cancer[J].Cancer Cell,2006,9(1): 6-8.
[21] Huang D,Du X.Crosstalk between tumor cells and microenvironment via Wnt pathway in colorectal cancer dissemination[J].World J Gastroenterol,2008,14(12): 1823-1827.
[22] Rao C,Lin SL,Wen H,etal.Crosstalk between canonical TGF-β/Smad and Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J].Journal of Zhejiang University Medical Sciences,2013,42(5): 591-596.
[23] Su YT,Chang HL,Shyue SK,etal.Emodin induces apoptosis in human lung adenocarcinoma cells through a reactive oxygen species-dependent mitochondrial signaling pathway[J].Biochem Pharmacol,2005,70(2): 229-241.
Emodin′s Suppression on Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer
WangMinjin1,WangYuanyuan2△,FanJibin3.
1.DepartmentofLaboratoryMedicine,WestChinaHospital,SichuanUniversity,Chengdu610041,China; 2.SchoolofBiomedicalSciences,ChengduMedicalCollege,Chengdu610083,China; 3.ZitongWorkers′HospitalinMianyang,Zitong622150,China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo study the suppression and its underlying molecular mechanism of emodin on the. MethodsMTT method was used to identify the effective working concentration of emodin. Scarification, Transwell and Matrigel assays were used to measure the influence of emodin on the metastasis of colorectal cancer cells. Western blot was used to detect the expression of proteins involved in EMT and marker proteins in upstream signaling pathway. Results MTT assay demonstrated that emodin significantly inhibited the proliferation of SW480. Scarification, Transwell and Matrigel assays showed that emodin suppressed the metastasis and invasion of colorectal cancer. Western blot showed that emodin promoted the expression of N-cadherin while inhibited the expression of E-cadherin, Vimmentin and β-catenin. Meanwhile, emodin decreased the expression levels of VEGF, MMP-2, MMP-9 and the phosphorylation of Akt/mTOR and STAT3. ConclusionEmodin suppressed STAT3 and Akt/mTOR signaling pathway, which further inhibited the metastasis of colorectal cancer. This study provides theoretical evidence that emodin functions as adjunct or direct drugs that targeting at colorectal cancer cells.
【Key words】Colorectal cancer; Emodin; Metastasis; Signal pathway
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1674-2257.2016.01.004
*基金项目:四川省教育厅基金项目(No:13ZB0225);四川省卫生厅基金项目(No:130303)
通信作者:△王元元, E-mail:vicky6936vicky@126.com
【中图分类号】R735.35
【文献标志码】A
网络出版地址:http://www.cnki.net/kcms/detail/51.1705.R.20160301.0944.006.html
·论著·

