具有Holling Ⅳ型功能性反应的非自治脉冲捕食系统的动力学研究
张春花, 陈晓星, 张玉英
(福州大学数学与计算机科学学院, 福建 福州 350116)
具有Holling Ⅳ型功能性反应的非自治脉冲捕食系统的动力学研究
张春花, 陈晓星, 张玉英
(福州大学数学与计算机科学学院, 福建 福州350116)
摘要:讨论一类带有脉冲的Holling Ⅳ类功能性反应的非自治捕食系统,利用微分方程比较定理和构造Lyapunov函数等方法, 得到该类系统的持久生存、 灭绝以及全局渐近稳定的条件.
关键词:Holling Ⅳ捕食系统; 脉冲; 非自治; 持久生存; 灭绝; 渐近性
1引言
生态系统的持久生存以及全局渐近稳定一直是生态学研究的中心, 研究捕食系统特别是具有功能性反应的捕食系统的持久生存以及全局渐近稳定有着重要的现实意义, 已被许多学者广泛研究[1-3].但对于形式较复杂的Holling Ⅳ类功能性的捕食系统研究较少.
在文献[4]中作者讨论了Holling Ⅳ具有功能性反应的非自治捕食模型.
然而在现实生活中, 生态系统难免会受到一些外界的干扰.如: 种群的出生率、 死亡率以及种群间的相互关系往往受季节、 气候、 交配习惯等因素的干扰, 导致不能单一地采用差分或者微分方程表示其生物意义, 因为这些生物现象并非是一个连续的过程, 因而应将两者结合, 运用脉冲微分方程模型.这样, 在变系数的微分方程中加入脉冲更具有实际意义[5-7]. 本文将研究具有脉冲效应的Holling Ⅳ非自治捕食系统:
(1)
其中: x(t), y(t)分别表示食饵和捕食者种群的密度; a1(t)为定义在R+上的有界连续函数; a2(t), bi(t), ci(t)(i=1, 2,)为定义在R+上的正的有界连续函数; α(t)具有正的下界, hik>-1(i=1, 2)为常数以及假设存在正常数ωi和λi(i=1, 2),使得:
目的是寻求合理的条件, 使研究的系统仍然能够持久生存并且具有渐近稳定性.
2预备知识
对于单种群的非自治系统:
(2)
其中: a(t), b(t)为定义在t∈R+上的有界连续函数; b(t)≥0, hk≥-1为常数; 则有如下结论:
引理1[8]系统(2)中当初始条件x(0)>0时, x(t)的解恒为正.
引理2[9]假设存在正的常数ω和λ使得
1) 对于系统(2)的任一正解x(t), 存在正常数m和M使得:

引理3[10]假设存在正的常数ω和λ使得:
3系统的持久性

由比较定理知,对于任意的t≥0,有y(t)≥ν(t),其中ν(t)是如下系统
(3)



下面证明y(t)具有上界,对y(t)要分为以下三种情况讨论.
1)假设对于所有的t≥T′,y(t)≥η2, 则对任意的正整数l,有
显然,当l→+∞ 时,则y(T′+lω2)→0与假设矛盾.

取一个正整数l,使得t=ρn+lω2+ν2,其中0≤ν2<ω2,则:
3) 假设对于所有的t≥T′,y(t)≤η2,则y(t)≤η2≤η2exp(β2ω2+H2).
综上,对∀t≥T′,y(t)≤η2≤η2exp(β2ω2+H2).其中
由于δ2是任意的正数,当δ2→0时,取

所以当∀t≥T′时,A2≤y(t)≤B2
由定理1知,系统(1)的任意解z(t)=(x(t), y(t))中y(t)是有界.记


定理3在定理1和定理2的条件下,系统(1)持久生存.
4系统的绝灭性
定理4若(N1)~(N4)、 (N6)及(N7)满足,则系统(1)的半平凡解(0, y*(t))是全局吸引的.
证明由系统(1)可得
设μ(t)是如下系统

(4)
具有初始值为ω(T1)=y(T1; 0, y0)的解.由比较定理得
(5)
由(N2)知,对任意的ε都有
(6)
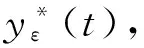
(7)
根据(N1)、 (N2)、 式(6)及引理2知,存在两个正的常数A和B,使得对于任意的t>T,有

由中值定理有

因为b2(t)为R+上正的连续有界函数,则有正的常数H和λ使得
定理5若条件(N1)、 (N3)、 (N4)以及(N6)~(N8)成立,则系统(1)是绝灭.

5系统的全局渐近稳定性

(8)
且对任意t>0,有

证明从定理2可知,存在两个正常数A和B,对于系统(1)任意解z1(t)=(x1(t), y1(t)), z2(t)=(x2(t), y2(t)), 存在T, 使得对任意t>T,有A≤x1(t), x2(t)≤B. 根据微分中值定理,有
则
同理

则V(t)是定义在正实数上的连续函数.
由于
则对任意的t>T,有
参考文献:
[1] DU P, DUAN C X, LIAO X Y. Dynamics behaviors of a reaction-diffusion predator-prey system with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response and delay[J]. Applied Mathematics, 2014, 5(6): 843-851.
[2] SU H, DAI B X, CHEN Y M,etal. Dynamic complexities of a predator-prey model with generalized Holling type Ⅲ functional response and impulsive effects[J]. Computers & Mathematics with Applications, 2008, 56(7): 1 715-1 725.
[3] WANG Q, DAI B X, CHEN Y M. Multiple periodic solutions of an impulsive predator-prey model with Holling type IV functional response[J]. Mathematical and Computer Modelling, 2009, 49(9/10): 1 829-1 836.
[4] 余长春, 李培峦, 曾宪武. 具有IV类功能反应的非自治捕食系统的持续性和周期解[J]. 数学杂志, 2006, 26(6): 619-622.
[5] LIU X X.Impulsive periodic oscillation for a predator-prey model with Hassell-Varley-Holling fuctional response[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2014, 38(4): 1 482-1 494.
[6] DU Z J, FENG Z S. Periodic solutions of a neutral impulsive predator-prey model with Beddington-DeAngelis functional response with delays[J]. Journal of Computational and Applied Mathematics, 2014, 258(1): 87-98.
[7] KAN M F, ZHOU Y, WANG J R, On the concept and existence of solution for impulsive fractional differential equations[J]. Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2012, 17(7): 3 050-3 060.
[8] HU H X, TENG Z D, JIANG H J. On the permanence in nonautonomous Lotka-Volterra competitive system with pure-delays and feedback controls[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2009, 10(3): 1 803-1 815.
[9] HUO J, LIU H H. Permanence and asymptotic behavior of the nonautonomous Lotka-Valterra competitive system with impulses[J]. Journal of Biomathematics, 2009, 24(2): 213-221.
[10] HUO J, TENG Z D, GAO S J. Permanence and global stability for nonautonomous N-species Lotka Valterra competitive system with impulses[J]. Nonlinear Analysis: Real World Applications, 2010, 11(3): 1 882-1 896.
(责任编辑: 蒋培玉)
The permanence extinction and asymptotic behavior of anonautonomous Holling Ⅳ predator-prey system with impulses
ZHANG Chunhua, CHEN Xiaoxing, ZHANG Yuying
(College of Mathematics and Computer Science, Fuzhou University, Fuzhou, Fujian 350116, China)
Abstract:The paper studies a Holling Ⅳ nonautonomous predator-prey system with impulses. Sufficient conditions for the permanence extinction and global asymptotical stability behavior to the system are established by the methods of differential comparison theorem and Lyapunov functions.
Keywords:Holling Ⅳ predator-prey system; impulse; nonautonomous; permanence; extinction; asymptotic behavior
DOI:10.7631/issn.1000-2243.2016.03.0325
文章编号:1000-2243(2016)03-0325-06
收稿日期:2014-06-11
通讯作者:陈晓星(1963-), 教授, 主要从事微分方程及其应用方面的研究, cxxing79@163.com
基金项目:福建省自然科学基金资助项目(2013J01011)
中图分类号:O175.14
文献标识码:A

