新鲜电解锰渣和长期堆存渣的矿物成分和毒性特征的差异分析
陈红亮
(安顺学院 化学化工学院,贵州 安顺 561000)
新鲜电解锰渣和长期堆存渣的矿物成分和毒性特征的差异分析
陈红亮
(安顺学院 化学化工学院,贵州 安顺561000)
摘要:以电解锰渣为研究对象,对比分析了新鲜电解锰渣和长期堆存渣的重金属含量、矿物成分、浸出毒性等的特征和差异。结果表明:新鲜渣中Mn的含量高于堆存渣。两种渣的矿物成分主要包括SiO2、含不同结晶水的硫酸钙以及铵盐、锰盐等。堆存渣与新鲜渣的矿物成分相比,不含FeS2、MnSO4·H2O、(NH4)2SO4等矿物;电解锰渣浸出液中毒性污染物主要是Mn和-N。堆存渣中Mn和-N的含量、浸出量均低于新鲜渣,说明在电解锰渣堆存过程中,-N不断从渣中溶出。电解锰渣渗滤液中Mn和-N的含量分别为1 776.8mg/L、1 225.8mg/L,分别是污水排放标准GB8978-2002的355倍、49倍。该研究为电解锰渣无害化处置提供参考。
关键词:电解锰渣;矿物成分;锰;氨氮;渗滤液
0引言
电解金属锰(简称电解锰)是冶金、航天、化工等工业部门的关键基础材料。我国在“十一五”期间就将锰列入了国家战略资源。目前我国已成为全球最大的电解锰生产国、消费国和出口国。2013年我国生产电解锰110万t,占世界金属锰产量的98%以上[1]。目前,每生产1t电解锰要排放10~12t电解锰渣,中国每年排放约200万t电解锰渣[2]。电解锰渣是碳酸锰矿经酸浸、中和、压滤工序后产生的废渣。随着碳酸锰矿资源的日益消耗,锰矿主流品位越来越低,将排放越来越多的电解锰渣,进一步加重电解锰渣处置的压力[3,4]。当前,针对电解锰渣的处置和利用,研究人员开展了相关研究。Zhou等[5]以电解锰渣、胶结剂、集料等原材料制备蒸压转,研究了成型压力、蒸气条件和电解锰渣掺量对蒸压转性能的影响;Wang等[6]研究了以电解锰渣为激发剂,混合高炉矿渣制备水泥,分析了电解锰渣、氢氧化钙、炉渣之间的掺量比对水泥强度和凝结性能的影响;Qian等[7]研究了玻璃基材掺入电解锰渣制备微晶玻璃的结晶过程和结晶活化能;Xin等[8]采用硫氧化细菌和黄铁矿细菌联合浸出电解锰渣中的锰达98.1%;Tao等[9]采用水洗-二次沉淀法回收电解锰渣中金属锰和氨氮,回收率分别为99.5%和94.5%。综合相关文献发现,电解锰渣的处置和利用等方面的研究主要是在实验室中进行,未见应用于实际生产的报道。
我国电解锰渣主要采取渣库堆存的处置方式,渣中含有大量有害成分[7,10],因降雨形成渗滤液,严重污染周边环境。因此,研究电解锰渣在堆存过程中矿物成分和浸出毒性的变化规律,对电解锰渣的污染治理具有指导意义。通过对比分析新鲜电解锰渣和长期堆存的电解锰渣中的化学成分含量、矿物相特征以及毒性成分的浸出量,并结合我国污水排放标准GB8978-2002,探究电解锰渣在堆存过程中矿物成分和浸出毒性的变化规律,为电解锰渣无害化处置和二次利用提供参考。
1材料与方法
1.1实验样品和试剂
电解锰渣取自重庆某电解锰厂,渣样分为2类,一类是经压滤后产生的新鲜电解锰渣(新鲜渣),另一类是在渣库中堆存两年以上的电解锰渣(堆存渣)。渣样在渣库中随机取样,均匀混合后于105℃烘干至恒重,球磨机研磨,过80目筛备用。电解锰渣浸出实验在回旋式振荡仪上进行。实验所用氯化铵为优级纯,碘化钾、碘化汞、氢氧化钠、酒石酸钾钠均为分析纯。
1.2 实验方法

2结果与讨论
2.1矿物成分差异
电解锰渣为颗粒细小、黑色、泥糊状粉末物质。新鲜渣和堆存渣的电镜照片发现,电解锰渣是由无规则颗粒和柱状、片状颗粒交替堆积,中间有絮状物(图1)。新鲜渣和堆存渣的主要化学成分有O、Si、S、Ca、Al、Fe、Mn、K等(见表1),新鲜渣中Mn的含量高于堆存渣。

表1 电解锰渣化学成分
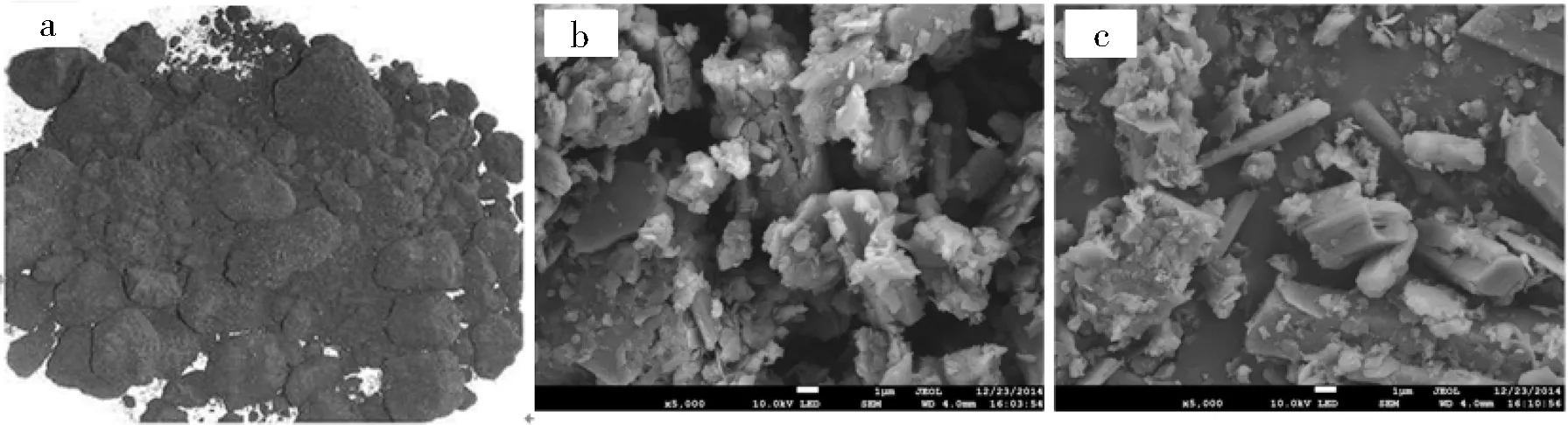

图1 电解锰渣外观图和SEM照片(a电解锰渣外观图;b新鲜渣SEM照片;c堆存渣SEM照片)Fig.1 The appearance and SEM photographs of EMR (a the appearance photograph; b the SEM photograph of the fresh residue; c the SEM photograph of the stockpiling residue)
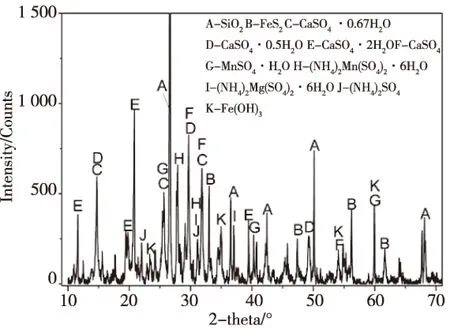
图2 新鲜渣的物相XRD图谱Fig.2 XRD patterns of the fresh residue
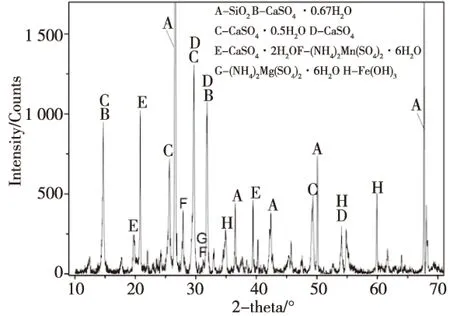
图3 堆存渣的物相XRD图谱Fig.3 XRD patterns of the stockpiling residue
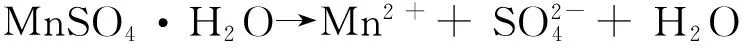
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Fe3++OH-→Fe(OH)3↓
(5)
蒋小花、张强等[18,19]认为电解锰渣中硫酸钙主要以二水石膏形式存在。实际电解锰渣中硫酸钙存在形式比较复杂,且晶体类型在电解锰渣堆存过程中不断变化。表1中出示电解锰渣中O、S、Ca等含量较高,结合电解锰渣矿物成分分析(图2和图3),电解锰渣中O、S、Ca主要以含不同结晶水的硫酸钙形式存在。以石膏(CaSO4·2H2O)形式计算,新鲜渣和堆存渣中含量分别高达40%、51%,表明电解锰渣属于高硫酸钙工业废弃物。
2.2浸出毒性差异

表2 电解锰渣化学成分浸出情况

表3 电解锰渣中金属的浸出率

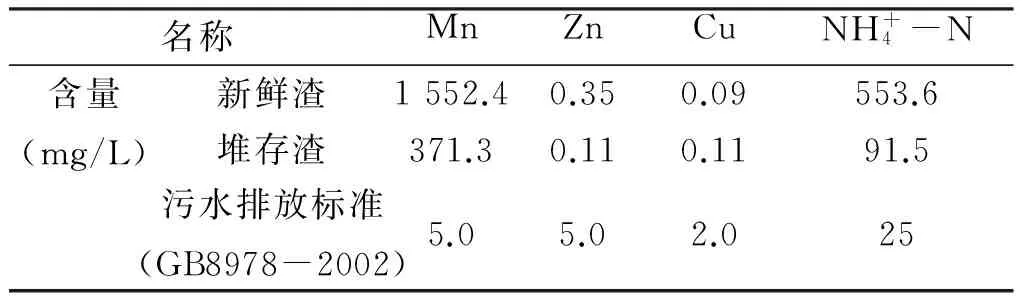
表4 电解锰渣浸出液中毒性污染物的含量
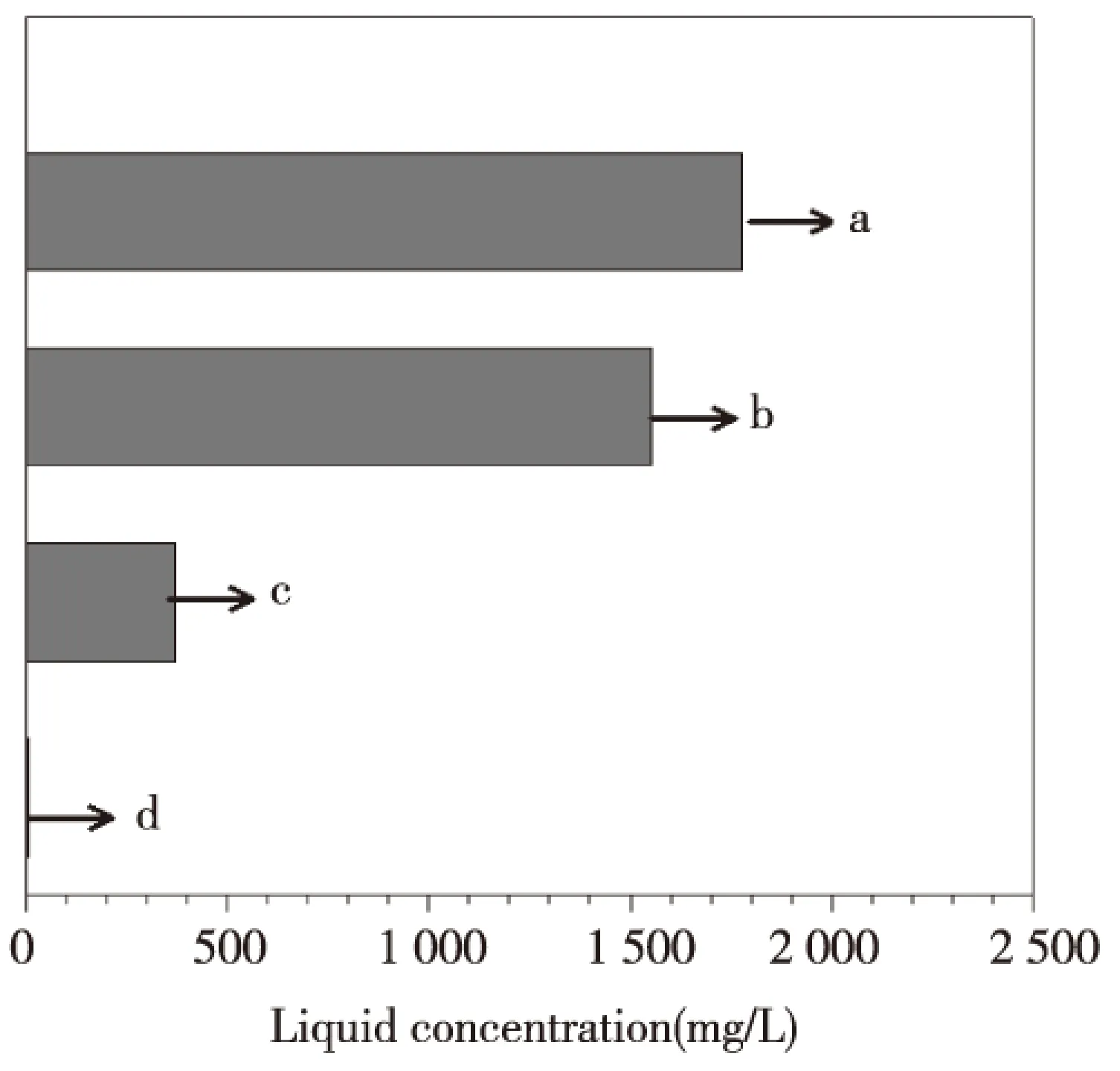
图4 电解锰渣浸出液和渗滤液中Mn的含量(a渗滤液;b新鲜渣浸出液;c堆存渣浸出液;d污水排放标准)Fig.4 The Mn concentrations from the leaching solution and the percolating water of EMR (a the percolating water; b the leaching solution of the fresh residue; c the leaching solution of the stockpiling residue; d the sewage discharge standard)
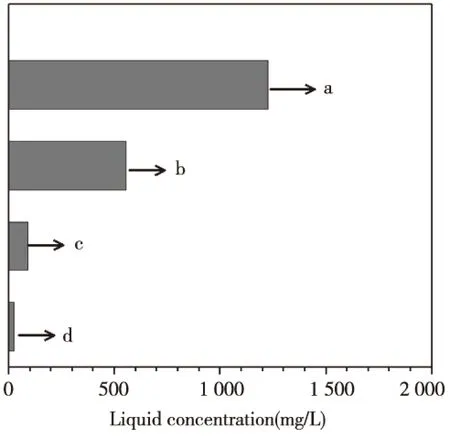
图5 电解锰渣浸出液和渗滤液中-N的含量(a渗滤液;b新鲜渣浸出液;c堆存渣浸出液;d污水排放标准)Fig.5 The -N concentrations from the leaching solution and the percolating water of EMR (a the percolating water; b the leaching solution of the fresh residue; c the leaching solution of the stockpiling residue; d the sewage discharge standard)
3结论
电解锰渣由无规则颗粒、絮状物和柱状、片状颗粒交替堆积而成。新鲜渣中Mn的含量高于堆存渣,两种渣的矿物成分主要包括SiO2,含不同结晶水的硫酸钙以及铵盐、锰盐等。堆存渣与新鲜渣中矿物成分相比,不含FeS2、MnSO4·H2O、(NH4)2SO4等矿物。
参考文献:
[1] 曾湘波.中国电解金属锰行业的发展趋势[J].中国锰业,2014,32(1):1-4.
[2] DUAN N,FAN W,CHANGBO Z,et al.Analysis of pollution materials generated from electrolytic manganese industries in China [J].Resources, Conservation and Recycling,2010,54(8):506-511.
[3] DUAN N,DAN Z,WANG F,et al.Electrolytic manganese metal industry experience based China’s new modelfor cleaner production promotion [J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2011,19(17):2082-2087.
[4] LI H,ZHANG Z,TANG S,et al.Ultrasonically assisted acid extraction of manganese from slag [J].Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2008,15(4):339-343.
[5] ZHOU C,DU B,WANG N,et al.Preparation and strength property of autoclaved bricks from electrolytic manganese residue [J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2014,84:707-714.
[6] WANG J,PENG B,CHAI L,et al.Preparation of electrolytic manganese residue-ground granulated blastfurnace slag cement [J].Powder Technology,2013,241: 12-18.
[7] QIAN J,HOU P,WANG Z,et al.Crystallization characteristic of glass-ceramic made from electrolytic manganese residue [J].Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater Sci Ed,2012,27(1):45-49.
[8] XIN B,CHEN B,DUAN N,et al.Extraction of manganese from electrolytic manganese residue by bioleaching [J].Bioresource Technology,2011,102(2):1683-1687.
[9] TAO C,LI M,LIU Z,et al.Composition and recovery method for electrolytic manganese residue [J].中南大学学报(英文版),2009,16(s1):309-312.
[10]LI Z,PENG X,OUYANG Y.Conditions for leaching manganese from electrolytic manganese waste residue [J].Journal-Jishou University Natural Science,2006,27(2):110-113.
[11]环境保护部科技标准司.固体废物浸出毒性浸出方法水平振荡法:HJ 557-2010[S/OL].北京:环境保护部,2010:2-3[2015-12-20].http://wenku.baidu.com/view/3949118e84868762caaed533.html?from=search.
[12]国家环境保护部.水质氨氮的测定纳氏试剂分光光度法:HJ535-2009[S/OL].北京:环境保护部,2009:2-5[2015-12-20].http://wenku.baidu.com/view/74adc59
3f61fb7360b4c65d4.html###.
[13]黎铉海,纪旦旦,粟海锋,等.高温结晶法生产硫酸锰工艺研究[J].无机盐工业,2010,42(12):16-19.
[14]宋力,胡付欣,李苹,等.硫酸锰铵结晶水的测定及热分析[J].武汉大学学报(理学版),2003, 49(6):685-688.
[15]何强,王韧超,柴宏祥,等.化学沉淀/混凝沉淀工艺序批式处理电解锰废水[J].中国给水排水,2007, 23(10):62-64.
[16]蒋磊,周怀阳,彭晓彤.氧化亚铁硫杆菌对黄铁矿?黄铜矿和磁黄铁矿的生物氧化作用研究[J].科学通报,2007, 52(15):1802-1813.
[17]李红,胡兆吉,董庆珍,等.响应曲面法优化氧化亚铁硫杆菌氧化Fe2+工艺条件试验研究[J].湿法冶金.2011,30(1):14-19.
[18]蒋小花,王智,侯鹏坤,等.用电解锰渣制备免烧砖的试验研究[J].非金属矿,2010, 33(1):14-17.
[19]张强,彭兵,柴立元,等.电解锰渣体系中硫酸钙特性的研究[J].矿冶工程,2010,30(5):70-73.
[20]国家环境保护总局科技标准司.城镇污水处理厂污染物排放标准:GB18918-2002[S/OL].北京:国家环境保护局,2002:2[2015-12-20].http://wenku.baidu.com/view/5eee62747fd5360cba1adb50.html?from=search.
Differences analysis of minerals compositions and toxicity characteristics between the fresh electrolytic manganese residue and the stockpiling residue
CHEN Hongliang
(College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Anshun University, Anshun, Guizhou 561000, China)
Abstract:The objective of this work was to analyze and compare the contents of heavy metals, minerals compositions and leached toxic substances from the fresh electrolytic manganese residue and the stockpiling residue. The results indicated that the content of Mn from the fresh residue was greater than from the stockpiling residue. The both residues mainly contained SiO2, calcium sulfates embodying different crystal waters, ammonium salts and manganese salts, etc. The minerals forFeS2, MnSO4·H2O, (NH4)2SO4 disappeared in the stockpiling residue. The toxic pollutants were Mn and -N in the leaching solutions of the both residues. The contents and leaching amounts of Mn and -N in the stockpiling residue were lesser than in the fresh residue, which revealed that the dissolutions of Mn and -N occurred at the stockpiling process of the electrolytic manganese residue (EMR). The contents of Mn and -N in the EMR percolating water were 1 776.8mg/L, 1 225.8mg/L, respectively, and 355 times, 49 times as many as the requirement values of the GB8978-2002 standard. This study could provide a reference for the harmless treatment of EMR.
Key words:electrolytic manganese residue; minerals compositions; manganese; ammonia nitrogen;percolating water
文章编号:1004—5570(2016)02-0032-05
收稿日期:2016-01-14
基金项目:贵州省教育厅自然科学研究项目(黔教合KY字[2013]202号)
作者简介:陈红亮(1982-),男,副教授,研究方向:资源化工和环境科学,E-mail:278631830@qq.com.
中图分类号:P618.32;TF042;X753
文献标识码:A

