冰蓄冷低温送风空调系统损因素分析
周学丽,李念平,邹杰
(1.湖南大学 土木工程学院 长沙 410082;2.广州黄岩机电科技有限公司 广州 510000)

周学丽1,李念平1,邹杰2
(1.湖南大学 土木工程学院 长沙 410082;2.广州黄岩机电科技有限公司 广州 510000)
摘要:低温送风空调系统引进新型冰蓄冷设备,采用正丁烷作为制冷剂,制冷剂与水直接接触,换热更强烈且稳定。为了研究该系统相应损因素条件下的节能薄弱环节,实现系统性能优化,基于该系统及各表冷器分析模型,分析了热湿比、新风比、送风温差等损因素对系统效率和各表冷器损率的影响。结果表明:当热湿比变化时,处理二次混风的表冷器损率随之呈正比变化,其他表冷器损率及系统效率随之呈反比变化;当新风比变化时,处理新风的两级表冷器损率随之呈正比变化,其他表冷器损率及系统效率随之呈反比变化;当送风温差变化时,处理一次回风的表冷器损率随之呈正比变化,其他表冷器损率及系统效率随之呈反比变化。
关键词:低温送风空调系统;分析模型;损率;效率;冰蓄冷
自从20世纪推广使用冰蓄冷技术以来[1],冰蓄冷技术以“移峰填谷”的优势,成为暖通空调领域炙手可热的“宠儿”[1-2]。传统的冰蓄冷设备采用乙烯乙二醇溶液为制冷剂,制冷剂不与冰水直接接触,传热热阻高,传热效率低;为了满足制冷要求,需要配备大面积换热管,运行效率较低[3]。邹杰[3]研发了一种新型动态冰蓄冷设备,采用正丁烷作为制冷剂,制冷剂与冰水直接接触,制冰过程中制冷剂带走热量将冷水制成冰,融冰过程中依靠冰融化向空调系统供冷;为了更好地将水与制冷剂混合,在冰蓄冷设备中设置移动床等传动装置,换热更加强烈,运行效率更高,控制更加可靠[4]。笔者介绍的低温送风空调系统引进该新型动态冰蓄冷设备,夜晚利用冷水机组制冰,白天利用冷水机组和冰蓄冷设备分别向空调机组提供7/12 ℃和0/7 ℃的冷冻水,高效实现低温送风和负荷转移[5]。但是相关研究发现该系统能量利用效率受到诸如热湿比、新风比、送风温差等运行参数的影响,因此,笔者基于能量利用效率进行研究,为优化系统性能及提高系统节能性奠定理论基础。

(1)
式中:T0为环境空气温度,K;Ta为进出口对数平均温度,K。
(2)

(3)

(4)

(5)

冰蓄冷低温送风空调系统空气处理流程如图1所示[5],空气处理过程焓湿图如图2所示[5],由图1和图2可知,表冷器1是处理新风(状态点1)的一级表冷器,冷冻水供回水温度为7/12 ℃,由冷水机组提供;处理新风的二级表冷器是表冷器2,由冰蓄冷系统提供冷冻水,供回水温度为0/7 ℃,它能够将表冷器1处理后的新风(状态点1′)处理到温度T=3.8 ℃,相对湿度φ=95%,含湿量d=4.76 g/kg的低温风(状态点1″);一次回风(状态点2)由变频风机控制流量,由表冷器3(供回水温度为0/7 ℃)处理到温度T=3.8 ℃,相对湿度φ=95%,含湿量d=4.76 g/kg的低温风(状态点2′),最终与两级表冷处理过的新风混合为一次混风,一次混风和二次回风(状态点2″)混合为二次混风(状态点3);二次混风由表冷器4(供回水温度为7/12 ℃)在干工况下处理到达送风状态(状态点4),最终由送风机将送风(状态点5)送入室内用于消除房间热湿负荷。

图1 冰蓄冷低温送风空调系统空气处理流程图Fig.1 Flow diagram of the ice storage system with cold

图2 冰蓄冷低温送风空调系统空气处理焓湿图fig.2 Air conditioning process of the ice storage system with cold air
(6)

(7)

(8)

(9)


(10)


(11)



图3 各设备损失率随热湿比变化曲线Fig.3 Different exergy loss rate values of the surface air coolers under different heat and humidity
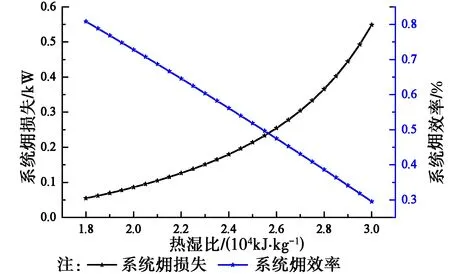
图4 系统损失和效率随热湿比变化曲线Fig.4 Different exergy loss values and exergy efficiency values of the system under different heat and humidity
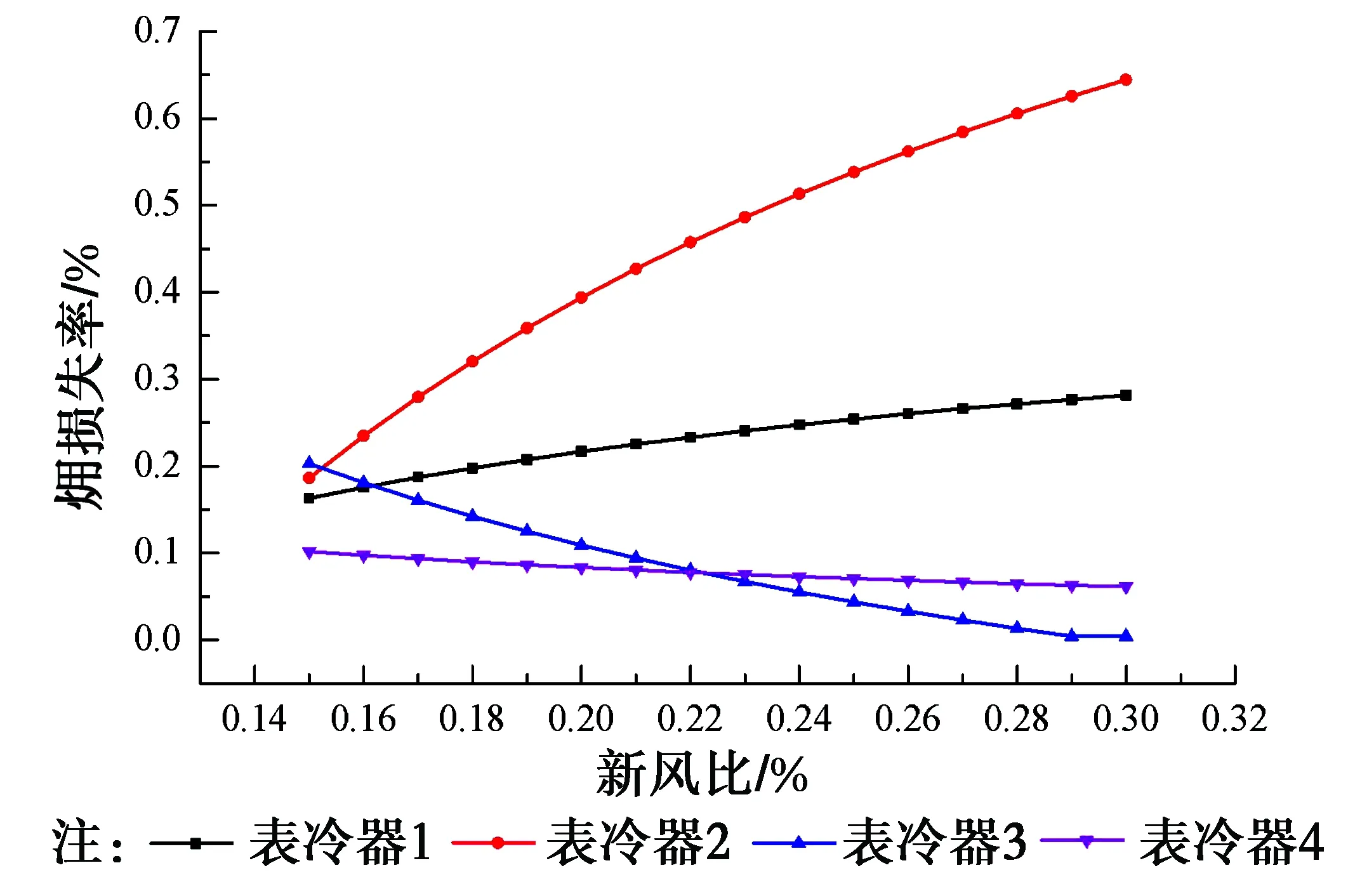
图5 各设备损失率随新风比变化曲线Fig.5 Different exergy loss rate values of the surface air coolers under different fresh air

图6 系统损失和效率随新风比变化曲线Fig.6 Different exergy loss values and exergy efficiency values of the system under different fresh air ratio


图7 各设备损失率随送风温差变化曲线Fig.7 Different exergy loss rate values of the surface coolers under different temperature difference between supply air and indoor

图8 系统损失和效率随送风温差变化曲线Fig.8 Different exergy loss values and exergy efficiency values of the system under different temperature difference between supply air and indoor
4结论与展望

5)笔者的分析计算依据来源于冰蓄冷低温送风空调系统设计工况,对于非设计工况的系统性能优化具有指导意义,而与非设计工况的对比研究有待开展。
参考文献:
[1] 李蕾,魏兵. 低温变风量空调系统的能耗分析[J]. 低温与超导,2014(9): 64-68.
LI L.WEI B. Energy consumption analysis of cold air distribution VAV system [J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2014(9): 64-68. (in Chinese)
[2] LI X W,ZHANG X S, SHUO Q. Evaporative supercooling method for ice production [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2012, 37(1): 120-128.
[3] 邹杰.一种动态冰蓄冷设备:200720058204.6 [P]. 2008-10-1.
ZOU J. A dynamic ice storage equipment: 200720058204.6 [P]. 2008-10-1. (in Chinese)
[4] 邹杰.一种蓄冷设备: 201310047656.4 [P]. 2013-05-09.
ZOU J. A dynamic ice storage equipment: 201310047656.4 [P]. 2013-05-09. (in Chinese)
[5] ZHOU X L, LI N P. Research on Energy-saving of new type low-temperature air flow dehumidification system based on exergy analysis method [C]// Proceedings of ISHVAC-COBEE conference, Tianjin, July 12-15, 2015.
[6] 李念平,孙剑,汤广发. 低温送风空调系统对室内空气环境的影响及技术经济初析[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版),1999(S1):56-61.
LI N P, SUN J, TANG G F. Effects of cold air distribution on indoor air environment and analysis of its technology economic [J]. Journal of Hunan University(Natural Science Edition),1999(S1):56-61. (in Chinese)
[7] 梁坤峰,王林,张林泉,等. 冰蓄冷辐射空调系统方案设计与能耗分析 [J]. 低温与超导,2014(2):85-91.
LIANG K F, WANG L, ZHANG L Q, et al. Design and energy consumption analysis of a new air-conditioning system[J]. Cryogenics & Superconductivity, 2014(2): 85-91.(in Chinese)
[8] 梁坤峰,任岘乐,贾雪迎,等. 冰蓄冷辐射空调系统运行优化与能耗分析[J]. 制冷技术,2014(6):68-74.
LIANG K F, REN X L, JIA X Y, et al. Operation optimization and energy consumption analysis of radiation air conditioning system with ice storage [J]. Refrigeration Technology, 2014(2): 85-91. (in Chinese)
[9] 殷平.空调大温差研究(3):空调送风大温差经济分析 [J]. 暖通空调,2000(6):75-76.
YIN P. Resrarch of large temperature difference in air conditioning(3):An economical analysis [J]. Journal of HVAC,2000(6): 75-76. (in Chinese)
WANG L. Thermodynamics analysis of HVAC systems based on exergy method [D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2012. (in Chinese)
[11] 颜志猛,连之伟,王文.一次回风空调系统的分析[J]. 流体机械,2002(11):58-60.
YAN Z M, LIAN Z W, WANG W. Analysis on exergy of air conditioning system with primary return air [J].Fluid Machinery, 2002(11):58-60. (in Chinese)
[12] HURDOGAN E, BUYUKALACA O, HEPBASLI A. Exergetic modeling and experimental performance assessment of a novel desiccant cooling system [J]. Energy and Buildings, 2011,43(6): 1489-1498.
[13] AHMADI P,DINCER I. Thermodynamic and exergoenvironmental analyses, and multi-objective optimization of a gas turbine power plant [J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2011, 32(14/15): 2529-2540.
[14] BALTA M T, DINCER I, HEPBASLI A. Exergoeconomic analysis of a hybrid copper-chlorine cycle driven by geothermal energy for hydrogen production [J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36(17): 11300-11308.
[15] CHEN L G, FENG H J, SUN F R. Exergoeconomic performance optimization for a combined cooling,heating and power generation plant with an endoreversible closed Brayton cycle [J]. Mathematical and Computer Modeling, 2011, 54(11/12): 2785-2801.
[16] OZGENER L. A review on the experimental and analysis of earth to air heat exchange (EAHE) systems in Turkey [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15(9): 4483-4490.
[17] AHAMED J U, SAIDUR R, MASJUKI H H. A review on exergy analysis of vapor compression refrigeration system [J]. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2011, 15(3): 1593-1600.
[18] HEPBASLI A. A comparative investigation of various greenhouse heating options using exergy analysis methos [J]. Applied Energy, 2011, 88(12): 4411-4423.
[19] MOROSUK T, TSATSARONIS G. Comparative evaluation of LNG-based cogeneration systems using advanced exergetic analysis [J]. Energy, 2011, 36(6): 3771-3778.
[20] 卓金武. MATLAB在数学建模中的应用[M]. 北京:北京航空航天大学出版社,2011.
ZHUO J W. The application of MATLAB in mathematical modeling [M]. Beijing: Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011. (in Chinese)
(编辑胡英奎)
Analysis on exergy loss factors of a novel ice storage system with cold air distribution
Zhou Xueli1, Li Nianping1, Zou Jie2
(1.College of Civil Engineering, Hunan University, Changsha 410082, P. R. China;2.Guangzhou Huangyan Mechanical and Electrical Technology Co., Guangzhou 510000, P. R. China)
Abstract:An exergy analysis model was developed for a novel ice storage system with cold air distribution and its main surface air coolers. Based on this model, the influence of heat and humidity ratio, fresh air ratio and temperature difference between supply air and indoor air on the exergy efficiency of the system and the exergy loss rate of its surface air coolers was studied. Finally the important parameters for system optimization were identified. The simulation results show that the exergy loss rate of the surface air cooler for secondary mixed air is positively proportional to the variation of heat and humidity ratio, while it is inverse for the other; the exergy loss rate of the surface air coolers for fresh air is positively proportional to the variation of fresh air ratio, while it is opposite for the other; the exergy loss rate of the surface air cooler for primary mixed air is positively proportional to the variation of temperature difference between supply air and indoor air, while it is inverse for the other.
Keywords:cold air distribution system; exergy analysis model; exergy loss rate; exergy efficiency; ice storage.
doi:10.11835/j.issn.1674-4764.2016.02.018
收稿日期:2015-08-12
基金项目:国家自然科学基金(51578220)
作者简介:周学丽(1991-),女,主要从事建筑节能技术研究,(E-mail)18229945449@163.com。
中图分类号:TU831.3
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1674-4764(2016)02-0132-06
李念平(通信作者),男,教授,博士生导师,(E-mail)linianping@126.com。
Received:2015-08-12
Foundation item:National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51578220)
Author brief:Zhou Xueli (1991- ), main research interest:building energy-saving technology,(E-mail) 18229945449@163.com.
Li Nianping(corresponding author), professor, doctor supervisor, (E-mail) linianping@126.com.

