血管内超声表现不同的冠状动脉斑块临床特点比较
白延平,徐 凯,董 海,荆全民,韩雅玲
血管内超声表现不同的冠状动脉斑块临床特点比较
白延平1,2,徐 凯1*,董 海1,荆全民1,韩雅玲1
(1沈阳军区总医院心内科,沈阳 110016;2延安大学附属医院心内科,延安 716000)
采用血管内超声(IVUS)分析冠心病患者冠状动脉内斑块的临床特点。入选2010年1月至2013年12月在沈阳军区总医院心内科住院并经冠状动脉造影证实的冠心病患者220例,根据IVUS斑块回声强弱分为3组:衰减斑块组(=42),钙化斑块组(=63)和纤维斑块组(=115)。对此220例患者的基线资料和斑块特点进行比较分析。根据IVUS检查结果,确定需行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(PCI)术的患者有140例(全部成功),其中衰减斑块组26例(PCI比率62%),钙化斑块组41例(PCI比率65%)、纤维斑块组73例(PCI比率63%)。对此140例患者的斑块特点、PCI术特点以及随访情况进行比较分析。钙化斑块组患者年龄较其余两组大(<0.05),总胆固醇(TC)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(LDL-C)均显著低于其余两组(<0.05);衰减斑块组患者的既往心肌梗死或冠状动脉搭桥术(CABG)以及吸烟史均显著高于其余两组(<0.05)。钙化斑块组的最小管腔面积和病变血管直径显著低于其余两组(<0.05);与其他两组患者相比,衰减斑块组患者的斑块负荷较重、病变血管面积较大(<0.05)。在行PCI术的患者中:与其他两组患者相比,衰减斑块组患者的斑块负荷较重(<0.05)。行PCI术的各组患者在1年内发生死亡、心肌梗死和再次血运重建的概率间无统计学差异(>0.05)。吸烟、既往心肌梗死或CABG史与衰减斑块的发生有关;与钙化斑块组及纤维斑块组相比,衰减斑块组具有较大的斑块负荷;PCI对IVUS证实的不稳定斑块具有较好的治疗效果。
冠状动脉;血管内超声;斑块
血管内超声(intravascular ultrasound,IVUS)是近年新诞生的一种冠状动脉内影像诊断方法,可根据斑块的性质指导介入治疗,并对冠状动脉介入治疗进行实时评价,大大提高了冠心病(coronary heart disease,CHD)诊断的准确率及疗效。近年来,随着IVUS器械技术的发展,人们对于冠状动脉斑块的认识更加深入,依据不同斑块回声的强弱和分布可分为:衰减斑块、纤维化斑块和钙化斑块[1]。既往研究发现[2],衰减斑块可作为急性心血管事件的预测因素,主要存在于不稳定的冠状动脉病变中,如急性冠脉综合征(acute coronary syndrome,ACS)。目前,关于冠状动脉不同类型斑块比较的临床报道甚少,本文通过对不同斑块的临床特点进行统计分析,以期提高临床医师对CHD中不同类型斑块的认识。
1 对象与方法
1.1 研究对象
入选2010年1月至2013年12月在沈阳军区总医院心内科住院并经冠状动脉造影证实的CHD患者220例,其中男性167例,女性53例,年龄(60.48±8.90)岁。所有患者在禁食12h后于次日晨取外周血,进行常规及生化检测。冠状动脉造影术中均行IVUS检查,根据IVUS斑块回声强弱分为3组:衰减斑块组(=42),钙化斑块组(=63)和纤维斑块组(=115),所有患者均签署了知情同意书。对此220例患者的基线资料和斑块特点进行比较分析。
根据IVUS检查结果,确定需行经皮冠状动脉介入治疗(percutaneous coronary intervention,PCI)术的患者有140例,手术全部成功。其中衰减斑块组26例、PCI比率62%,钙化斑块组41例、PCI比率65%,纤维斑块组73例、PCI比率63%,对此140例患者的斑块特点、PCI术特点以及随访情况进行比较分析。
1.2 冠状动脉造影术
冠状动脉造影术是指依靠二维成像技术通过改变投射体位来完善术者对冠状动脉血管病变部位及狭窄程度的观察及判断。操作时选取右侧桡动脉或股动脉作为穿刺血管,穿刺成功后选用合适的造影导管至左右冠状动脉口,注入造影剂,使冠状动脉显影[3]。
1.3 IVUS检查方法
采用经桡动脉或股动脉置入6F的指引导管至冠状动脉口,送入经皮冠状动脉腔内血管成形术(percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty,PTCA)导丝至冠状动脉远端,将超声导管沿此导丝送至病变的远端,然后以0.5mm/s速度自动回撤超声导管,同时进行超声检测[4]。IVUS常用的定量测量指标如下。(1)最小管腔面积:冠状动脉内最狭窄处的管腔面积。(2)参考面积:最小管腔面积近端10mm以内最大管腔面积。(3)血管面积:冠状动脉外膜以内的面积。(4)斑块面积:血管面积减去管腔面积。(5)斑块负荷:斑块面积占血管面积的百分比。采用Boston Scientific iReview软件分析患者IVUS检测的斑块特点,参考2001年美国心脏病学会(American College of Cardiology,ACC)和美国心脏协会(American Heart Association,AHA)的IVUS专家共识,根据回声强弱分为:衰减斑块(低回声)、钙化斑块(高回声)、纤维斑块(等回声)。典型斑块IVUS图像如图1所示。
1.4 PCI术
行PCI术标准:(1)斑块面积狭窄程度>70%;(2)冠状动脉血管最小管腔面积≤4mm2;(3)斑块面积狭窄程度介于50%~70%,且合并斑块破裂及夹层。PCI术1年后通过电话随访患者发生死亡、心肌梗死和再次血运重建等情况。
1.5 统计学处理
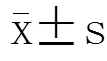
2 结 果
2.1 一般资料比较
结果表明,钙化斑块组患者年龄较衰减斑块组和纤维斑块组大,差异有统计学意义(<0.05);衰减斑块组患者的既往心肌梗死或冠状动脉搭桥术(coronary artery bypass surgery,CABG)以及吸烟史均显著高于其余两组(<0.05)。生化指标对比发现,钙化斑块组患者的总胆固醇(total cholesterol,TC)和低密度脂蛋白胆固醇(low-density lipoprotein cholesterol,LDL-C)均显著低于其余两组,差异有统计学意义(<0.05;表1)。
2.2 各组患者斑块特点比较
钙化斑块组的最小管腔面积和病变血管直径显著低于其余两组(<0.05);与其他两组患者相比,衰减斑块组患者的斑块负荷较重、病变血管面积较大,差异均具有统计学意义(<0.05;表2)。
2.3 各组中行PCI术患者的斑块特点和PCI术特点比较
在行PCI术的患者中:与其他两组患者相比,衰减斑块组患者的斑块负荷较重,差异均具有统计学意义(<0.05);各组患者在PCI术中所使用支架的长度和直径均无显著性差异(>0.05;表3)。
2.4 各组中行PCI术患者的随访结果比较
各组中行PCI术的患者,在1年内均无死亡和发生心肌梗死的病例,3组患者发生再次血运重建的例数分别为:衰减斑块组2例(7.7%);钙化斑块组2例(4.9%);纤维斑块组3例(4.1%)。结果表明,行PCI术的各组患者在1年内发生死亡、心肌梗死和再次血运重建的概率间无统计学差异(>0.05)。
3 讨 论
IVUS显示不稳定性斑块为低回声的“软斑块”:由大的低回声暗区(脂核)伴高回声区(纤维帽)组成。稳定性斑块则表现为高回声的“硬斑块”:由回声近于或高于外膜组织的回声伴或不伴声影组成。纤维型斑块和钙化型斑块多为稳定性斑块。IVUS研究发现,在稳定型心绞痛患者中,有75%的狭窄性病变合并钙化斑块及纤维化斑块,而在ACS患者中,上述斑块不太常见[5−7]。回声衰减是斑块不稳定的一种表现,病理本质大多提示为晚期的、成熟的、富含胆固醇结晶和/或坏死组织的粥样硬化斑块,回声衰减发生的主要机制在于胆固醇结晶及其含的微小钙化对超声的折射和吸收。通过对IVUS图像的分析,认为低回声斑块和正性冠状动脉重构与ACS的发生有关[8−10],所以不难理解,既往有坏死组织的粥样硬化斑块、高脂血症尤其高胆固醇血症的患者血管中易产生衰减斑块。
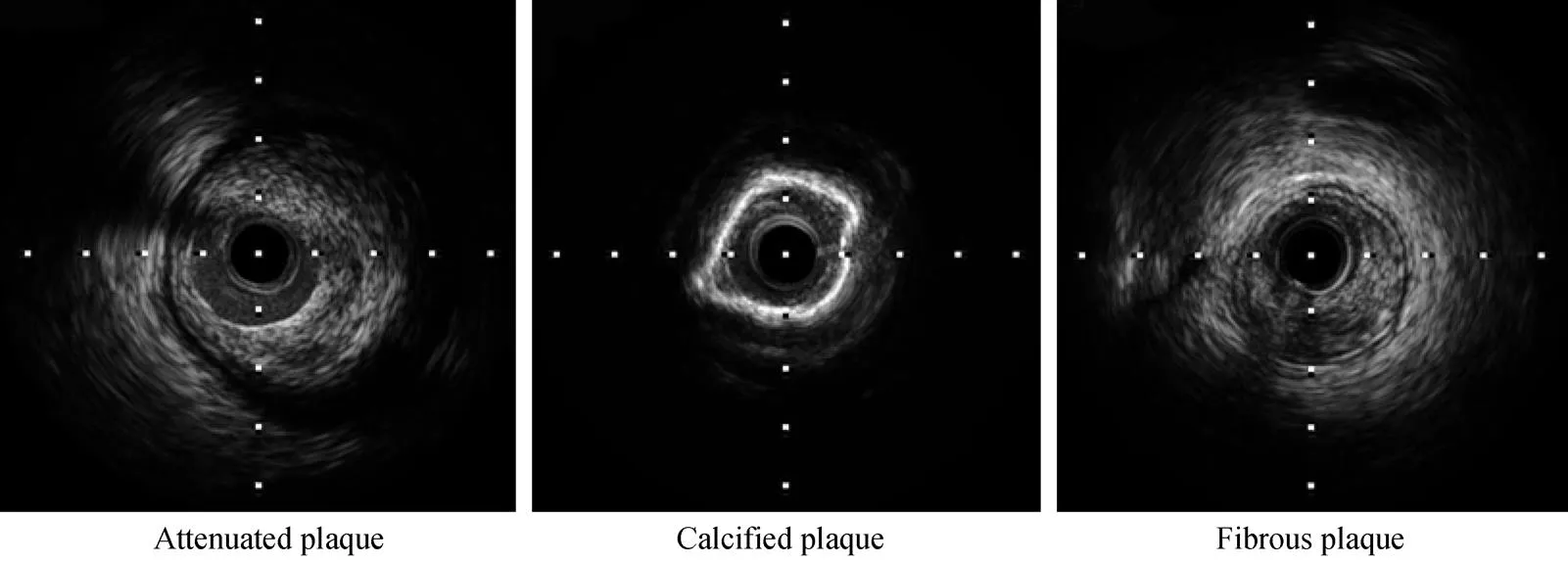
图1 典型斑块IVUS图像
Figure 1 IVUS images of typical plaques IVUS: intravascular ultrasound

表1 各组患者基线资料比较
CHD: coronary heart disease; PMI: previous myocardial infarction; CABG: coronary artery bypass surgery; SAP: stable angina pectoris; UAP: unstable angina pectoris; NSTEMI: non-ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; STEMI: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction; TC: total cholesterol; TG: triglycerides; LDL-C: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol; HDL-C: high-density lipoprotein cholesterol; Hb: hemoglobin

表2 各组斑块特点比较
RCA: right coronary artery; LAD: left anterior descending; LCX: left circumflex artery; MLA: minimal lumen area; LVA: lesion vessel area; MLD: minimal lumen diameter; LVD: lesion vessel diameter
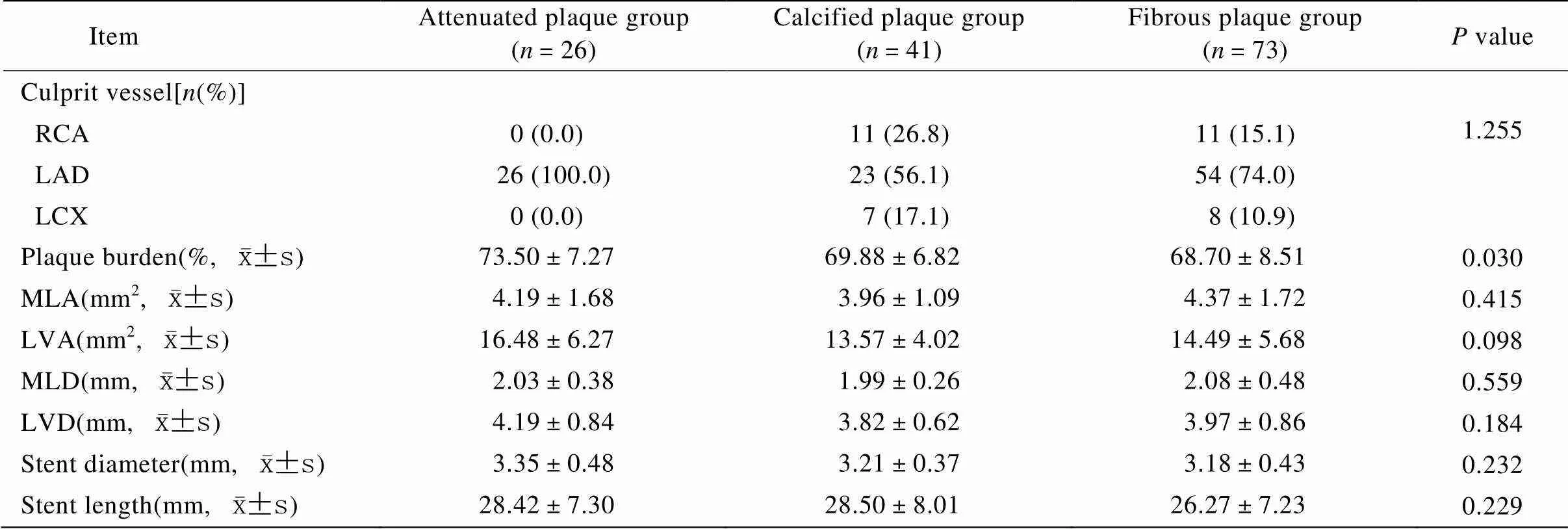
表3 各组中行PCI术患者的斑块特点和PCI术特点比较
RCA: right coronary artery; LAD: left anterior descending; LCX: left circumflex artery; MLA: minimal lumen area; LVA: lesion vessel area; MLD: minimal lumen diameter; LVD: lesion vessel diameter
本研究显示:衰减斑块组的患者既往心肌梗死或CABG史为13例(31.0%),相比钙化斑块组9例(14.3%)和纤维斑块组14例(12.2%),差异有统计学意义(<0.05);衰减斑块组患者的吸烟比例也显著高于其余两组(<0.05)。这与既往国外研究结果一致[5]。吸烟可直接损伤内皮细胞,增加其通透性,表现为炎症因子水平增高,炎症细胞黏附性增强,而且干扰凝血纤溶过程,使凝血因子表达增加,血小板增多,血栓更易形成[11]。
动脉重构是指动脉管腔大小、形态在动脉粥样硬化发生、发展过程中的变化,是血管对血流动力学阻力、动脉损伤及细胞增殖的代偿反应。在动脉粥样硬化早期,虽然斑块很小,但已经存在血管重构,且主要表现为正性重构,因此冠脉造影虽示正常,但IVUS可显示冠状动脉内粥样硬化斑块的存在。血管外膜代偿是有限度的,负性重构是动脉粥样硬化病变进展过程中逐渐出现的代偿失调,可表现为斑块增大、管腔减少。正性重构的血管,血栓和斑块破裂较负性重构的血管多见,因为正性重构的血管多见于动脉粥样硬化病变的早期,此时的病变多由富含脂质的脂质性斑块组成,会产生更多的血管活性物质扩张血管。随着粥样硬化病变进展,斑块被纤维成份替代,并有钙盐沉积,这时病变相对稳定,但管腔失去代偿,更多为负性重构[12]。本研究显示,与其他两组患者相比,衰减斑块组患者的斑块负荷较重、病变血管面积较大;钙化斑块组的最小管腔面积和病变血管直径显著低于其余两组。这一结果与Lee等[13]的研究报道一致。本研究显示,衰减斑块组患者的斑块负荷较重,其可能原因为衰减斑块多见于正性重构血管,往往会合并斑块破裂的情况。
Qiu等[14]认为除了围手术期心肌梗死,衰减斑块并不与长期恶化临床结果相关联。本研究随访1年结果也显示,各组中行PCI术患者发生死亡、心肌梗死和再次血运重建的概率间无统计学差异。表明衰减斑块患者成功实施PCI后,其1年预后与其他两组患者相比无差异,提示PCI对IVUS证实的不稳定斑块具有较好的治疗效果。
本研究检测到衰减斑块的易发因素有吸烟、既往心肌梗死或CABG病史,且IVUS显示衰减斑块的斑块负荷较重。本研究存在一定的局限性,研究例数较少,在以后的工作中,需要搜集更多的例数分析不同类型斑块的临床特征。
[1] Kubo T, Matsuo Y, Ino Y,. Optical coherence tomography analysis of attenuated plaques detected by intravascular ultrasound in patients with acute coronary syndromes[J]. Cardiol Res Pract, 2011, 2011: 687515.
[2] Pu J, Mintz GS, Biro S,. Insights into echo-attenuated plaques, echolucent plaques, and plaques with spotty calcification: novel findings from comparisons among intravascular ultrasound, near-infrared spectroscopy, and pathological histology in 2294 human coronary artery segments[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2014, 63(21): 2220−2233.
[3] Qiao SB. Cardiovascular Interventional Treatment for Advanced Training Course[M]. Beijing: People’s Medical Publishing House, 2011: 22−23. [乔树宾. 心血管介入治疗高级培训教程[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2011: 22−23.]
[4] Zhao RP, Meng XD. The diagnostic value of significance of intermediate coronary stenosis with intravascular ultrasound[J]. Chin J Cardiovas Res, 2011, 9(8): 607−609. [赵瑞平, 孟显达. 血管内超声对冠脉造影临界病变的诊断价值[J]. 中国心血管病研究, 2011, 9(8): 607−609.]
[5] Zhang M, Zhang Y, Zhang PF,. Diagnosis of structure and elastic properties of atherosclerotic plaque: a review[C]. Proceedings of the 9th National Conference on Echocardiography, 2007: 39−40. [张 梅, 张 运, 张鹏飞, 等. 动脉粥样硬化斑块结构和弹性特性的诊断进展[C]. 第九届全国超声心动图学术会议论文集, 2007: 39−40.]
[6] Bech GJ, De Bruyne B, Bonnier HJ,. Long-term follow-up after deferral of percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty of intermediate stenosis on the basis of coronary pressure measurement[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1998, 31(4): 841−847.
[7] Yanagisawa H, Chikamor T, Tanaka N,. Application of pressure-derived myocardial fractional flow reserve in assessing the functional severity of coronary artery stenosis in patients with diabetes mellitus[J]. Circ J, 2004, 68(11): 993−998.
[8] Pasterkamp G, Schoneveld AH, van der Wal AC,. Relation of arterial geometry to luminal narrowing and histologic markers for plaque vulnerability: the remodeling paradox[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 1998, 32(3): 655−662.
[9] Schoenhagen P, Ziada KM, Kapadia SR,. Extent and direction of arterial remodeling in stableunstable coronary syndromes: an intravascular ultrasound study[J]. Circulation, 2000, 101(6): 598−603.
[10] Yamagishi M, Terashima M, Awano K,. Morphology of vulnerable coronary plaque:insights from follow-up of patients examined by intravascular ultrasound before an acute coronary syndrome[J]. J Am Coll Cardiol, 2000, 35(1): 106−111.
[11] Wu QH, Lv AK, Shen WF. Biochemical and molecular mechanisms of tobacco-related coronary heart disease[J]. Int J Cardiovas Dis, 2010, 37(5): 283−285. [吴祁红, 吕安康, 沈卫峰. 与烟草相关冠心病的生化及其分子机制[J]. 国际心血管病杂志, 2010, 37(5): 283−285. ]
[12] Heagery AM, Allqener C, Pund SJ,. Small artery structure in hypertension. Dual processes of remodeling and growth[J]. Hypertension, 1993, 21(4): 391−397.
[13] Lee T, Kakuta T, Yonetsu T,. Assessment of echo-attenuated plaque by optical coherence tomography and its impact on post-procedural creatine kinase-myocardial band elevation in elective stent implantation[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2011, 4(5): 483−491.
[14] Wu X, Mintz GS, Xu K,. The relationship between attenuated plaque identified by intravascular ultrasound and no-reflow after stenting in acute myocardial infarction: the HORIZONS-AMI (Harmonizing Outcomes with Revascularization and Stents in Acute Myocardial Infarction) trial[J]. JACC Cardiovasc Interv, 2011, 4(5): 495−502.
(编辑: 吕青远)
Clinical characteristics of coronary plaques differentiated by intravascular ultrasound
BAI Yan-Ping1,2, XU Kai1*, DONG Hai1, JING Quan-Min1, HAN Ya-Ling1
(1Department of Cardiology, General Hospital of Shenyang Military Command, Shenyang 110016, China;2Department of Cardiology, Affiliated Hospital of Yan’an University, Yan’an 716000, China)
To investigate the clinical characteristics of different plaques detected by intravascular ultrasound (IVUS).From January 2010 to December 2013, 220 patients with coronary heart diseases confirmed by coronary angiography in our department were enrolled in this study. The patients were divided into 3 groups according to the ultrasound echo intensities of plaques in IVUS findings, that is, attenuated plaque group (=42), calcified plaque group (=63), and fibrous plaque group (=115). Their clinical baseline data and IVUS data were analyzed and compared. According to the results of IVUS findings, there were 140 case needing to undergo percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), including 26, 41 and 73 cases respectively from the attenuated, calcified and fibrous plaque groups, with the ratio of PCI 62%, 65% and 63% in the three groups respectively. All were successful. The plaque types, PCI features and follow-up data were also analyzed in these 140 patients.The patients from the calcified plaque group had older age and lower levels of total cholesterol (TC) and low density lipoprotein-cholesterol (LDL-C) when compared with those from the other groups (all<0.05). The attenuated plaque group had higher ratios in past histories of smoking, myocardial infarction, and coronary artery bypass surgery (CABG), and larger plaque burden and lesion vessel area when compared with the other 2 groups (all<0.05). Minimal lumen area and lesion vessel diameter were obviously smaller in the calcified plaque group than in the other 2 groups (all<0.05). For the 140 patients undergoing PCI, those from the attenuated plaque group had higher plaque burden than that from the other 2 groups (<0.05), and there were no significant differences in 1-year mortality, incidence of myocardial infarction and ratio of target vessel revascularization from the 3 groups (>0.05).Past histories of smoking, myocardial infarction and CABG are correlated with the incidence of attenuated plaques. The patients with attenuated plaques have larger plaque burden than those with calcified or fibrous plaques. PCI has satisfactory therapentic effect on unstable plaques detected by IVUS.
coronary artery; intravascular ultrasound; plaque
R445.1
A
10.11915/j.issn.1671-5403.2016.02.025
2015−11−19;
2015−12−16
徐 凯, E-mail: xukai2001@sina.com

