Accounting information quality,governance efficiency and capital investment choice
aSchool of Public Finance,Central University of Finance and Economics,China
bSchool of Accounting,Central University of Finance and Economics,China
Accounting information quality,governance efficiency and capital investment choice
Jinbu Zhaia,Yutao Wangb,*
aSchool of Public Finance,Central University of Finance and Economics,China
bSchool of Accounting,Central University of Finance and Economics,China
ARTICLEINFO
Article history:
Received 22 May 2013
Accepted 4 August 2016
Available online 6 September 2016
Accounting information quality Governance efficiency Capital investment choice
This paper examines the relationship between accounting information quality and capital investment choice from the perspective of accounting information’s governance function.Measuring capital investment choice as the correlation of growth of operating income between company and industry,this paper investigates whether and to what extent companies focus on their core business.The results show that the higher the quality of publicly listed firms’accounting information,the stronger that correlation,particularly when the corporate governance of the listed company is poor.The findings imply that accounting information quality can thus optimize the capital investment choice,which complements and strengthens the functioning of corporate governance.Hence, regulators should pay more attention to the market’s power to supervise the behavior of listed firms,improve the governance functions of accounting information and increase the efficiency of capital allocation.
©2016 Sun Yat-sen University.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).
1.Introduction
China’s stock market has developed rapidly since 1990,when the capital market was set up.The number of listed companies increased from 10 in 1990 to 2063 in 2010.In the 1990–2010 period,about 5253.7 billion yuan in outside capital f l owed into listed companies by initial public of f erings,seasoned equity of f erings or corporate bonds(China Statistical Yearbook,2011).Whether companies allocated the capital into their own core businesses has become a very important issue,which more and more market participants are focusing on.However,this paper finds that in the 2000–2011 period,about 63.7%of capital was allocated to non-core operating activities,against their original investment plans.There are an average of 53 million yuan for each change,the average 6.7 months of change frequency,and the average 3.6 times change for every f i rm.Moreover,almost 69.6%of all the changes are inefficient.The frequent changes of the capital investment directions have become a notable problem in China,which severely harms capital allocation efficiency.Many scholars pay attention to this issue and research on it from the views of implementing laws and regulations or improving corporate governance,but the ef f ect of these suggestions is not good to date.Based on this important issue, this paper examines the governance function of accounting information and whether high accounting information quality can form an enforcement mechanism to push management to make capital investment more efficiently.
Since China’s Accounting Law was implemented in 1985,the Chinese government has devoted ef f ort to complete the accounting principles system and related rules to improve accounting information quality.In 2006,the Chinese Ministry of Finance issued new accounting principles comprising one basic accounting standard,38 specif i c standards and application guides that have been applied to publicly listed companies since 2007.The goal of these standards is to ensure the firms to provide useful accounting information and to help investors make good investment decisions.These accounting standards are created to reduce the information asymmetry between investors and listed companies,helping investors better understand those companies’risks and thus make more rational investment decisions.However,in China’s current special institutional background,can accounting information also serve a governance function to influence managements’capital investment choice?
There are several objective external forces that enhance the governance function of accounting information in China’s capital market.By the end of 2010,the country’s number of securities investment funds had reached 704,with 2.4228 trillion yuan in total assets(China Statistical Yearbook,2011).Institutional investors also play an important role in China to dig up and transfer the information disclosed by listed firms,compared with other investors.More importantly,institutional investors can also respond more quickly to abnormal accounting information,‘‘vote by foot”,and f i nally improve the market efficiency.We believe that in the long term,high-quality accounting information can help these investors to identify inefficient investments,and in turn incur the pressure on stock price by investors’voting by foot.In an efficient market,the potential decrease in stock prices will further push management to make good investments.Meanwhile,other market forces,such as individual investors and the media,have also begun to pay more attention to interpreting accounting information,and thus f i nally constrain and supervise the managements’investment behavior. Hence,accounting information has become increasingly important in China to optimize corporate capital investments.
This paper examines whether and how accounting information quality has an ef f ect on corporate investment choices,based on the governance function of accounting information.This issue is very important to government,market participants,current and latent investors,and listed firms.Addressing this issue will help them(such as market participants)better understand the governance function of accounting formations,so as to help them make good decisions.
2.Literature review
Many researchers,both Chinese and foreign,have explored the role played by accounting information quality and information transparency in market efficiency.For example,Zhou and Chen(2008)investigate the influence of the transparency of industry accounting information on industry-level capital allocation based on data from all A-share listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges from 1999 to 2004.They measured capital allocation efficiency as the allotment of shares and amount of newly raised funds,focusing on whether external capital f l ows to the best industries.Zhou and Chen(2008)find industry accounting information transparency to exert a signif i cant ef f ect on resource allocation,such that the more transparent that information is,the higher the efficiency of resource allocation.
Based on 3600 f i rm-year observations of A-share listed companies on the Shanghai and Shenzhen exchanges from 2004 to 2006,Li(2009)examines the influence of accounting information quality on the under-and over-investment of listed companies.His results show that high-quality accounting informationreduces the risks of moral hazard and adverse selection and inhibits both under-investment and overinvestment by ameliorating contracts and supervision,thereby improving capital allocation efficiency at the company level.
Bhattacharya et al.(2003)investigate the influence of accounting opacity on the cost of equity capital in 34 countries,finding that the lower a country’s degree of accounting information transparency,the higher its overall cost of equity capital and the smaller the trading scale of stocks.Hence,it appears that accounting information transparency also has an influence on capital allocation efficiency at the country level.Using the same 34 countries,Biddle and Hilary(2006)survey the effects of accounting information quality on capital investment efficiency(measured by the sensitivity of the amount of capital investment to net cash f l ows in operating activities,with the greater the sensitivity,the lower the degree of investment efficiency)at both the country and company levels.Their results indicate that high-quality accounting information reduces information asymmetry between managers and external capital providers,and therefore increase capital investment efficiency at both levels.Drawing on these studies,Biddle et al.(2009)research company-level capital investment efficiency in depth from both the over-and under-investment perspectives,which focus on the relationship between such efficiency and high-quality accounting information.
Using a sample of listed companies that had been examined by the U.S.Securities and Exchange Commission(SEC)or sued by shareholders because of accounting information distortions or restated f i nancial statements,McNichols and Stubben(2008)investigate the role of accounting information in internal decisionmaking efficiency.Their results suggest that companies engage in over-investment during the periods of illegal accounting activity,but exhibit higher investment efficiency after that activity has been investigated.Hence,it appears that accounting information quality affects companies’internal decisions.
Based on 37 countries and 37 manufacturing industries for each country,Francis et al.(2009)examine the ef f ect of country-level information transparency,rather than just accounting information quality,on resource allocation efficiency.They use the growth rate correlations between manufacturing industries and countries to measure resource allocations.The results show that the higher a matched country’s degree of information transparency,the stronger the correlation of growth rate between industries and countries.Therefore,in countries with better information transparency environments,resources f l ow more smoothly to better-developed industries,resulting in more efficient industry-level resource allocation.
Chen et al.(2011)investigate the association between accounting information quality and the investment efficiency of private enterprises in emerging markets.They find that even when accounting information is of poor quality,it still exerts a positive influence on investment efficiency.Because private enterprises are dependent primarily on bank financing,the association is more obvious than in other scenarios.
The prior literature above examines not only the effects of accounting information quality or transparency on capital allocation efficiency at the country and industry levels,but also on company-level decision-making and investment efficiency from the over-and under-investment perspectives.Based on the analysis of this paper,listed companies frequently change the direction of their capital flows on a large scale.Hence,whether fi rms invest capital in their main businesses is a major factor in evaluating capital allocation efficiency.However,few studies focus on this issue.This paper thus makes two important contributions to the prior literature. First,it explores the relationship between accounting information quality and a company’s choice of capital investment in depth,with a focus on whether it invested capital in its core business.Second,it also examines that relationship from the perspective of the market forces from which the governance function and efficiency of accounting information arise.
3.Theoretical analysis and hypothesis development
Beaver(1989)argues that the major objective of accounting information was to help its users make informed decisions.The quality of accounting information can be assessed in two ways.The first is valuation usefulness,which means that the information is useful to investors looking to make valuation decisions.It reflects the pricing function of accounting information.The second is contract validity,which means that the accounting information benefits contracts,particularly those between investors and administrators.It reflects the governance function of such information.Accordingly,accounting information has two basic functions:pricing and governance.First,accounting information implements its pricing function by inf l uencingcapital costs and stock prices.High-quality information can alleviate information asymmetry,thereby reducing the capital cost of external fi nancing(Myers and Majluf,1984;Easley and O’Hara,2004;Zeng and Lu, 2006).The pricing function can also be realized by in fl uencing stock prices.To some extent,a listed company’s stock price re fl ects special information about it.Higher quality,more transparent accounting information allows growth opportunities to be incorporated into the stock price,thereby attracting new investors.Second, by alleviating the ex-post information asymmetry among the interested parties to a contract,accounting information can reduce the imperfections of the contract and restrain and monitor the opportunistic behavior of management.In this way,accounting information serves a governance function.In the case of obtaining external capital,that governance function of accounting information helps listed fi rms to make rational decisions to focus on their main business and allocate the capital more efficiently.
Bushman and Smith(2003) finds that high-quality information disclosures are bene fi cial to investors by monitoring management,encouraging them to make investment decisions efficiently and e ff ectively,and finally improving capital allocation efficiency and gaining more returns to investors.Ball and Shivakumar (2005)believe that high-quality accounting information strengthens investors’supervision of management, by placing restrictions on managerial pay for their own or others’interests and by optimizing investment decision-making.In addition,high-quality accounting information can also inform investors in a timely manner about the orientation of the f i rm’s capital investments and help them to supervise managerial activities. Similarly,Biddle et al.(2009)argue that high-quality accounting information inhibits management from building‘‘an empire,”discourages unwise investments and improves the ability of investors to monitor the efficiency of managers’investment decisions.Fig.1 shows how the two major functions of accounting information affect a company’s capital investment choice.
On the other hand,the aim of accounting disclosures was to provide external stakeholders with useful information.The quantity and quality of accounting information will affect an investor’s judgment on the intrinsic value of the company.If the company’s share price or earnings declines,investors will seek to avoid losses through such actions as‘‘exercising their decision-making right to vote”and/or‘‘voting with their feet.”Hence,accounting data constitute an essential information resource in determining whether a company’s stock price is over-or underestimated.Ohlson(2005)builds a model that reflects the relationship between accounting information and f i rm value.Many scholars have demonstrated the usefulness of such information by showing how investors use it to make decisions(Beaver,1968;Ball and Brown,1968).Investors are concerned with the quality of accounting information because it helps them to better understand the company’s operating situation and other fundamentals.High-quality accounting information af f ords external stakeholders a comprehensive understanding of f i rm fundamentals and allows them to take action to supervise management behavior.Once managements’activities are not aimed at maximizing the interests of stockholders,major shareholders can seek to alter it by voting for changes on the board of directors and taking part in shareholder meetings.Although minority shareholders are unable to influence management directly,they can influence the stock price by voting with their feet.Institutional investors(and other strategic investors)can also ef f ect managerial changes both through their right to vote for board directors and by voting with their feet.High-quality accounting information thus helps external stakeholders,who can interfere with management either directly or indirectly,to gain a better understanding of a company’s capital use and business performance,thereby affecting its choice of capital investment.Hence,the first hypothesis of this paper is developed as following.
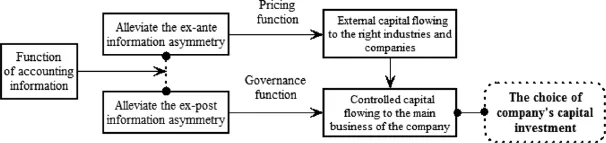
Figure 1.Theoretical analysis framework.
H1.Companies with higher quality accounting information are more likely to invest more capital in their core business.
Most of the listed companies were established during the country’s planned economy era.Hence,they have close relationships with the government that were complicated by the f i scal decentralization reforms that began at the end of the 1970s.Local governments’pursuit of economic and political objectives is heavily dependent on the listed companies under their control,state-owned enterprises(SOEs)in particular.Meanwhile,the legal environment governing Chinese listed companies is in urgent need of improvement.The incomplete nature of the regulatory system results in the companies not abiding by the law and the law not being strictly enforced.It also remains difficult for shareholders to f i le successful legal appeals,and thus ef f ectively constrain or exert pressure on management.
Although listed firms in China have formally established boards of directors,in reality there are still a number of challenges to those boards’independence.First,the majority of board members are also managers,particularly in SOEs,which result in serious internal control problems.The State-owned Assets Management Department commonly appoints managers,which exacerbates these problems.Second,the role of independent directors is questionable in China because their appointment is intended to meet the requirements of regulators rather than to strengthen corporate governance.Finally,independent directors are normally nominated or appointed by the board chair,and thus constitute an extension of the chair’s relationship with and control by the majority shareholders.
The scarcity of board independence and the complex external governance environment make it difficult for corporate governance mechanisms to exert any real ef f ect.Investors,in contrast,can exercise real external supervision by voting with their feet in the case of unreasonable investments,thus placing management under the threat of potential stock price revaluations and promoting the efficient resource allocation.High-quality accounting information can help investors to identify inefficient investments,thereby leading to a potential share price revaluation and putting pressure on the board of directors,which in turn push management to focus on the company’s core business and improve the efficiency of capital allocation.Therefore,when a company’s internal and external governance environment is weak,the ef f ect of high-quality accounting information on capital investment choice is more pronounced.Hence,we posit the second hypothesis.
H2.The influence of high-quality accounting information on management capital investment choices is more pronounced when the external governance environment is poor.
4.Research design
4.1.Measurement of accounting information quality
The prior literature measures accounting information quality by two approaches.The first is measured as earnings characteristics,such as accruals quality and earnings persistence,predictability,smoothing,aggressiveness and loss avoidance,mainly based on the f i nancial statements.The second method is to use a company’s stock price to measure the quality of accounting information,such as earnings value relevance, earnings timeliness and earnings conservatism.This approach reflects investors’recognition of accounting information quality,which is affected by factors such as the degree of capital market development and the knowledge of individual professionals.Due to weak or not efficient capital market in China,this paper measures accounting information quality as earnings-related characteristics based on f i nancial statement data.We develop four measures to proxy for accounting information quality,such as Accruals Quality,Earnings Persistence,Earnings Predictability and Earnings Smoothing.Meanwhile,for robustness,this paper also constructs a comprehensive measurement by ranking the four variables above.
4.1.1.Accruals quality
The Jones model and modif i ed Jones model are frequently used to assess companies’earnings management. However,it is difficult to measure the normal and abnormal components of accruals objectively and precisely. Therefore,Dechow and Dichev(2002)devise another method to measure accruals quality that is based onwhether a company’s accruals correspond to its cash holdings in the past,present or future.The more(less) closely the company’s past,present and future cash correspond to its accruals,the higher(lower)its accruals quality is.This paper calculates accrual quality based on the DD model.It takes into account how well the company’s accruals in the current period(year t)match its cash in the previous period(year t-1),current period(year t)and next period(year t+1):
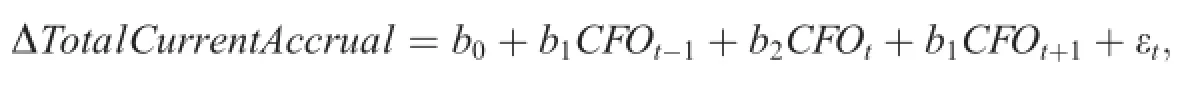
where ΔTotalCurrentAccrual stands for the company’s accruals in year t,which equals the current assets change in year t minus current liability changes,minus the changes of cash and cash equivalent changes in year t,plus change of short-term liability with interests in year t.CFO refers to the operating cash fl ow.
The regression residual means unrealized cash fl ow,which is relative to the company’s expected accruals. The standard deviation(σ(residuals))of all observation residuals is used to measure a company’s accrual quality.A greater standard deviation means both lower accrual and accounting information quality.We calculate accrual quality by using these variables during the past 10 years for each fi rm.
4.1.2.Earnings persistence
Using time-series data,the persistence of a company’s earnings is measured by regressing its current ROAton its previous ROAt-1(Lev,1983;Ali and Zarowin,1992).The model is as follows.
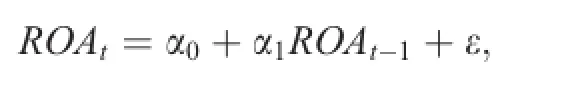
where ROAtrepresents the return on assets in period t.Regression coefficient α1indicates the level of earnings persistence,with a larger α1indicating a higher earnings persistence.For ease of explanation,we take negative value of earnings persistence,which implies a larger-α1is poorer quality accounting information.We calculate this measure by using data during the past 10 years for each f i rm.
4.1.3.Earnings predictability
Earnings predictability describes the ability of a company’s current earnings to predict its future earnings.It is measured by the same model as that for earnings persistence,i.e.,
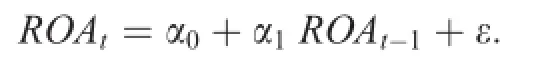
The standard deviation of the residuals(σ(residuals))obtained from the regression can be used to measure the prediction error in company earnings,with larger σ(residuals)indicating poorer earnings predictability or accounting information quality.We calculate this measure by using data during the past 10 years for each fi rm.
4.1.4.Earnings smoothing
Our measure of earnings smoothing is based primarily on the shift between accruals and cash in net income, which can be measured by the ratio of the standard deviation of net income to operating cash f l ow or by the correlation between changed accruals and operating cash f l ow in the current period.As the principles of the two methods are both based on the shift between accruals and cash in net income,they should produce the same results.
Here,we use the ratio of the standard deviation of net income to operating cash f l ow,that is,σ(net income)/ σ(operating cash f l ow),where a larger ratio suggests a greater degree of artif i cial earnings smoothing and lower degree of accounting information quality.We calculate this measure by using data during the past 10 years for each f i rm.
4.1.5.Comprehensive index of accounting information quality
As we are unable to ascertain which measurement of accounting information quality above is the most important,we construct a comprehensive variable of accounting information quality according to the approach used in the prior literature(Bhattacharya et al.,2003;Biddle and Hilary,2006).We calculate each unique measurement of accounting information quality for all f i rm-year observations,and then sort them bydecile ranks by year(with each variable falling between 0 and 9).Finally,we sum up the rank values of every measurement to obtain the comprehensive index of accounting information quality.The smaller the rank value,the better the comprehensive quality of the accounting information.
4.2.Capital investment choice
A company’s capital investment choice refers simply to whether the capital it controls f l ows to its core business.Properly describing and measuring capital investment choice,however,is very complicated. Francis et al.(2009)measure resource allocation efficiency as the correlation between the growth rate of the manufacturing industry to which a focal company belongs and that of a matched sample of companies in the same industry to determine whether capital f l ows to the most efficient industries at the national level.If a company’s capital f l ows to its main business or main industry,there should be a high degree of correlation and consistency between the firms’operating prof i ts growth and that of the industry as a whole.Therefore,referring to Francis et al.(2009),this paper measures capital investment choice as the correlation between the growth rate of its own operating income and that of the industry as a whole based on the data during the past 10 years.The higher this correlation,the more capital that f l ows into the company’s core business.In calculations,we take the average of the operating income growth of all companies apart from the focal company as the industry-level value.The variable growth_corrtrepresents the correlation between a company’s operating income growth and that of the industry in year t. Industries are divided into 13 types in accordance with the industry classif i cations released by the China Securities Regulatory Commission(CSRC).In robustness tests,we also use both the correlation of the growth of a company’s sales with that of the industry and synchronicity to measure capital investment choice.
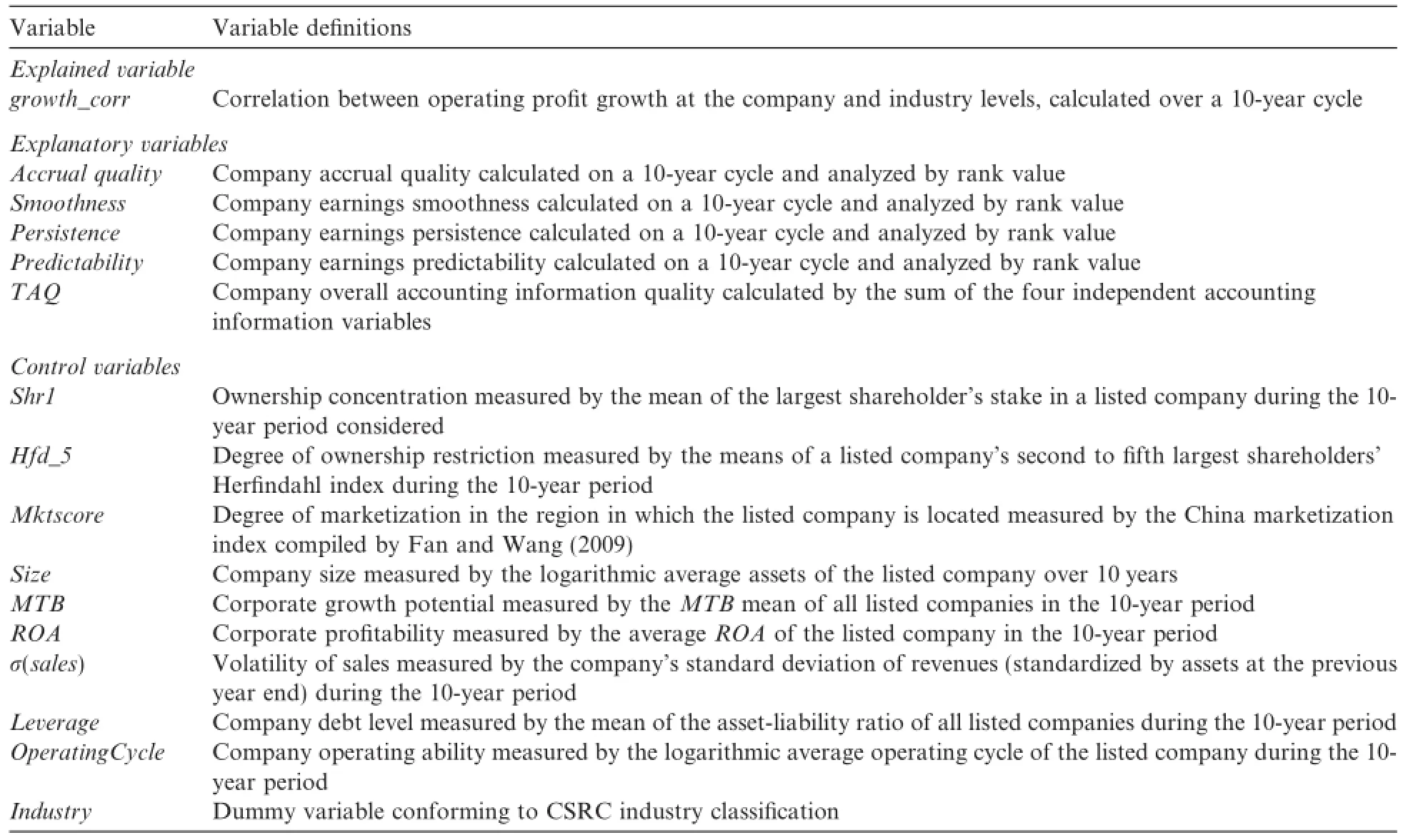
Table 1Variable def i nitions.
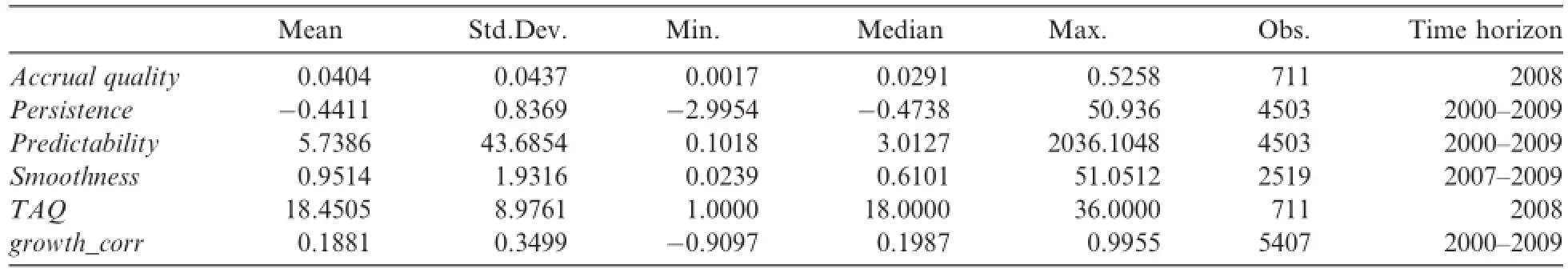
Table 2Descriptive statistics.
4.3.Control variables
The control variables in this paper are f i rm size,f i rm growth,prof i tability,operational volatility,debt ratio, operating cycle and industry f i xed effects.The def i nitions of these control variables are listed in Table 1.
4.4.Model specif i cation
Regression models(1)and(2)are used to test H1and H2,respectively:
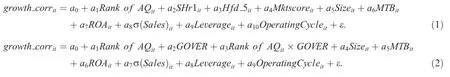
In model(1),growth_corrtrepresents the correlation between the company and industry operating income growth rates from years t-9 to t.Rank of AQit(accounting quality)represents the accounting information quality,including accruals quality,earnings persistence,predictability and smoothness,and total accounting quality(TAQt).Due to big standard deviation of actual value of these variables,this paper takes the ranking value in decile level.The smaller the rank value of these measures,the higher is the accounting information quality.Total accounting quality(TAQt)is the sum of all four single variables’rank values in year t.
In model(2),growth_corrtis the same as in model(1),but total accounting quality(TAQt)is used as a substitute for Rank of AQit.1This article also analyzes the rank values of the four single variables:accruals and earnings persistence,predictability and smoothness. The overall result is consistent with that based on total accounting quality(TAQt).Owing to space limitations,these results are omitted.GOVOR represents the corporate governance mechanism,such as Shr1,Hfd_5 and Mktscore.Due to the highly correlations among the corporate governance variables,we test each variable separately to address potential multicollinearity in the model.The coefficient of AQt×GOVER allows us to infer whether the effects of accounting information quality on the capital investment choice are more pronounced with better corporate governance.
5.Data and empirical findings
5.1.Sample and data
All data and all variables come from the Wind Database.With 10 years adopted as the calculation cycle and data of operating cash f l ow disclosed from 1998 onward,this paper calculates the measurements of accounting information quality and capital investment choices based on different time horizons.The descrip-tive statistics for the key variables at the different time horizons based f i nal samples with excluding missing values are listed in Table 2.
We know that the smaller the value of the f i ve accounting information quality variables,the better the quality of the accounting information.In Table 2,earnings predictability has a mean value of 5.74 with a standard deviation of 43.69%,which indicates that it is easier to distinguish accounting information quality than the other four variables.Earnings persistence has a mean value of-0.44 and a standard deviation of 0.84.The comprehensive index of accounting quality,TAQ has a mean value of 18.45,and its minimum value and maximum values are 1 and 36,respectively.The maximum value of growth_corr is 1 and its minimum value is-0.91,which demonstrates that there are considerable inter-company dif f erences in capital investment choice.
Table 3 reports the correlation matrix for the key variables.
Table 3 results(for both the Pearson and Spearman coefficients)show that the four independent measures of accounting information quality are strongly correlated with one another at the 1%signif i cance level,which indicates that all four are important measures.At the same time,the comprehensive accounting information quality variable is signif i cantly correlated with all of the independent variables(at the 1%signif i cance level). More importantly,the results of both the Pearson and Spearman coefficients show that TAQ has a signif icantly negative correlation with growth_corr at the 1%signif i cance level,which suggests that the higher the level of comprehensive accounting information quality,the higher the governance efficiency,and the higher likelihood the firms focus on its core business.
The measurements of accounting information quality,such as accrual quality,persistence,predictability and smoothness have a negative correlation with growth_corr,signif i cantly in Spearman index(at the 1%signif icance level),but not in Pearson index.This univariate tests show that the higher the quality of the accounting information the higher likelihood the company will focus on its core business.
5.2.Univariate analysis
For each independent variable,all of the sample firms are sorted by decile ranks in ascending order,and divided into groups 1–10,with the smaller the group number,the higher the quality of accounting information.Then,taking the median and mean of growth_corr in each group,we map the relationship between accounting information quality and capital investment choice,as shown in Fig.2.
The direction of the curves in Fig.2 depends on whether the independent variables or comprehensive variable are used in the calculation.The lower the level of accounting information quality,the smaller the medianor mean of growth_corr,which indicates that there is a signif i cant relationship between whether a company invests its capital primarily in its main business and the quality of its accounting information,thus of f ering further evidence for this article’s main assumption.
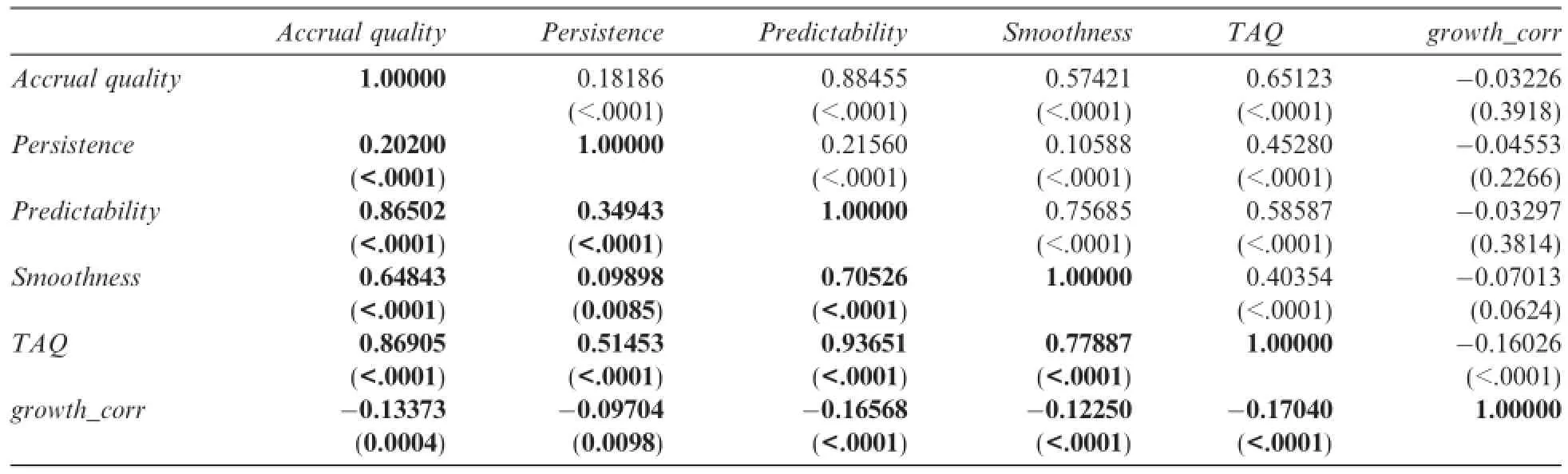
Table 3Correlation matrix for key variables.
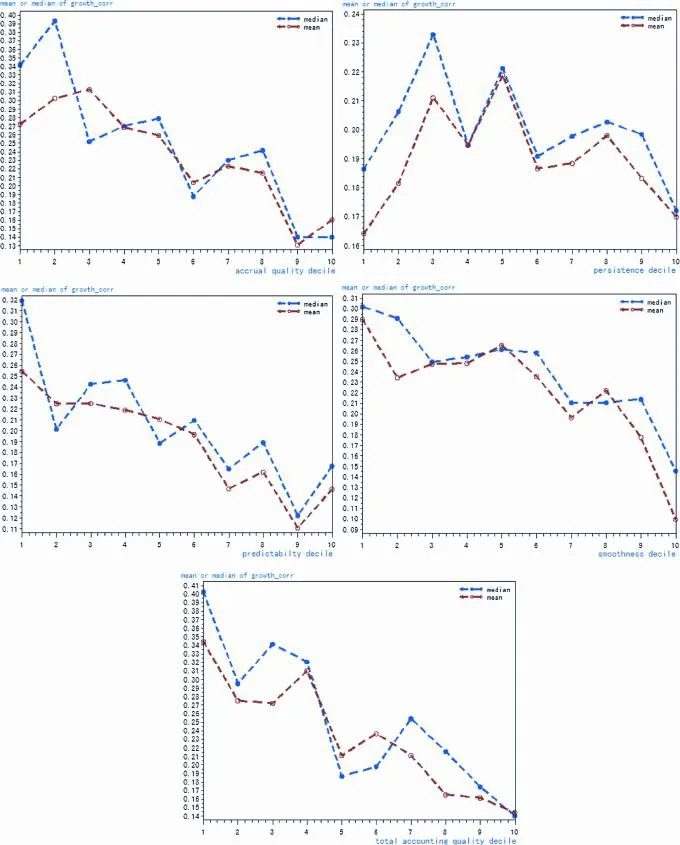
Figure 2.Relationship between growth_corr and accounting information quality.
For examining the correlation between accounting information quality and capital investment choices,we classify the full sample into two groups based on two different methods.The first is to sort all sample firms by decile rank from smallest to largest into 10 groups,with the top and bottom 10%of firms constituting the high-and low-quality information groups,respectively.The second is to divide the sample into two groups by the median of accounting information quality,with the top 50%of the sample def i ned as the highquality group,and the bottom 50%def i ned as the low-quality group.Table 4 reports the dif f erence of investment choice between high and low quality of accounting information.
Table 4 shows that there are signif i cant dif f erences in the mean of growth_corr between the higher and lower quality groups based on two different classif i cation methods,except for persistence.For example,the mean of growth_corr in the higher quality group is 0.1902,signif i cantly higher(at the 1%signif i cance level)than 0.0707 in the lower quality group for smoothness.These univariate results support our prediction,that is,accounting information quality has a signif i cant influence on the choice of capital investment.
5.3.Multivariate analysis
Based on the regression model(1),Table 5 reports the multivariate results.
Table 5 shows all the results based on different measurements of accounting information quality.Except for persistence in model(2),all other measurements have a signif i cant ef f ect on capital investment choice,which support H1.The results imply that higher quality accounting information makes a f i rm more inclined to invest its capital in its core business.
For testing H2,Table 6 reports the results of the joint influence of corporate governance and accounting information quality on capital investment choice.Taking the comprehensive measure of accounting information quality(Rank of AQ)as main variable,columns(1)–(3)of Table 6 show different cross-sectional results based on the different measures of corporate governance,such as biggest shareholders ownership(Shrl),the Herfindahl index of second to f i fth largest shareholders’ownership(Hfd_5)and market index(Mktscore)from Fan and Wang(2009).Column(4)shows the results when the three measures of corporate governance are included in one regression model.Table 6 shows that the coefficients on Rank of AQ are all signif i cantlynegative,inconsistent with Table 5.The interactive coefficients of corporate governance and accounting information quality in column(1)–(3)are positive for Rank of AQ×Shrl,negative for Rank of AQ×Hfd_5 and negative for Rank of AQ×Mktscore,all signif i cant at the 5%level,suggesting that accounting information quality plays a more important role in guiding a company to choose the right investment when the corporate governance environment is inefficient.In other words,the results imply that there is a complementary relationship between such quality and the corporate governance mechanisms.
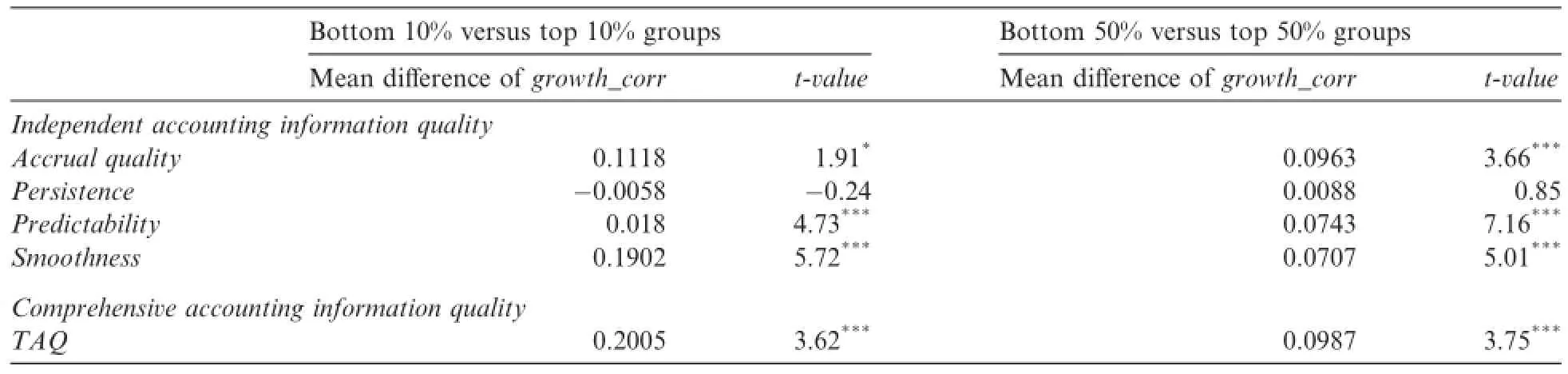
Table 4Dif f erences in capital investment choices between the high-and low-quality accounting information groups.
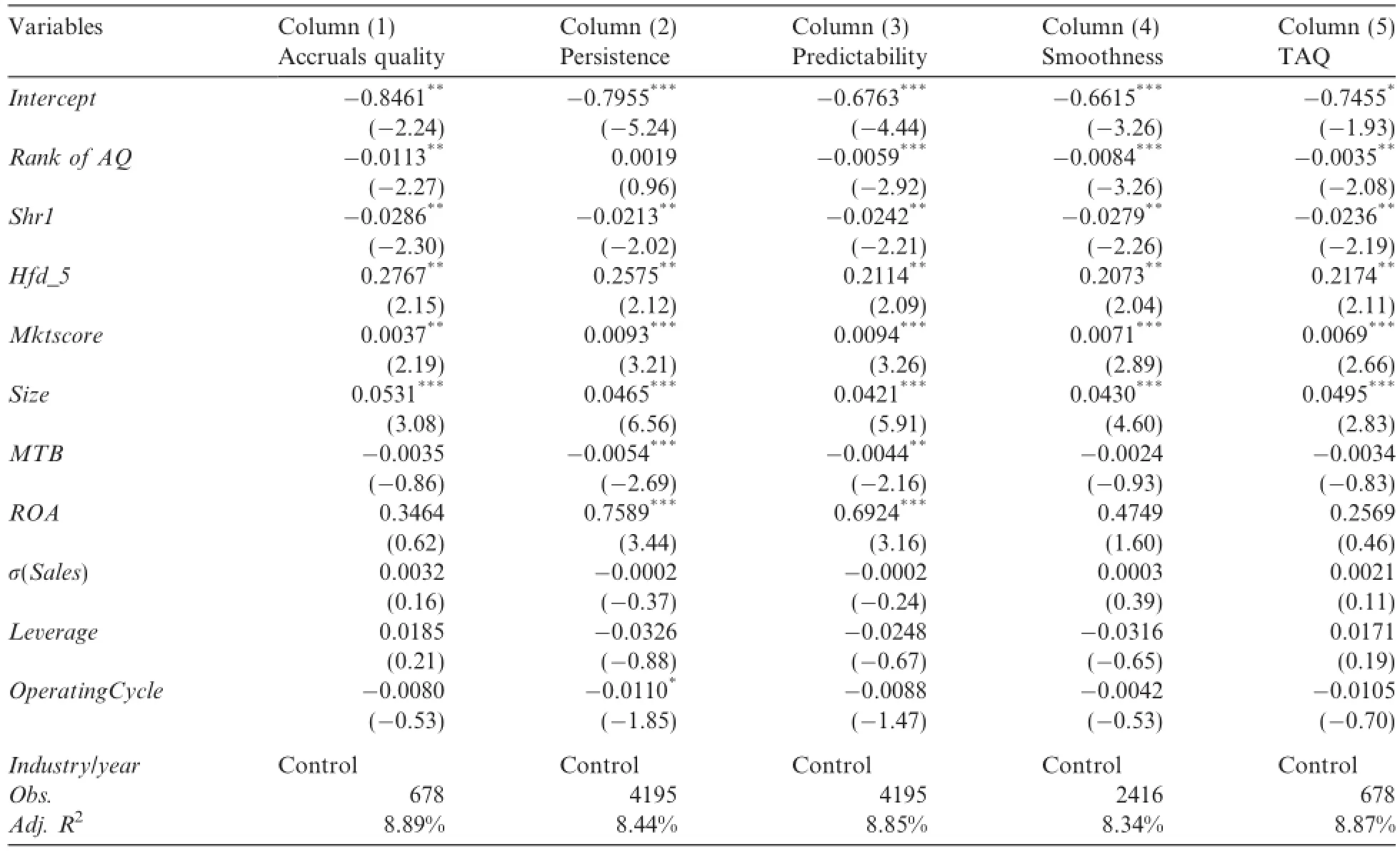
Table 5Ef f ect of accounting information quality on the choice of capital investment.
6.Robustness tests
For robustness,we also perform the following tests.
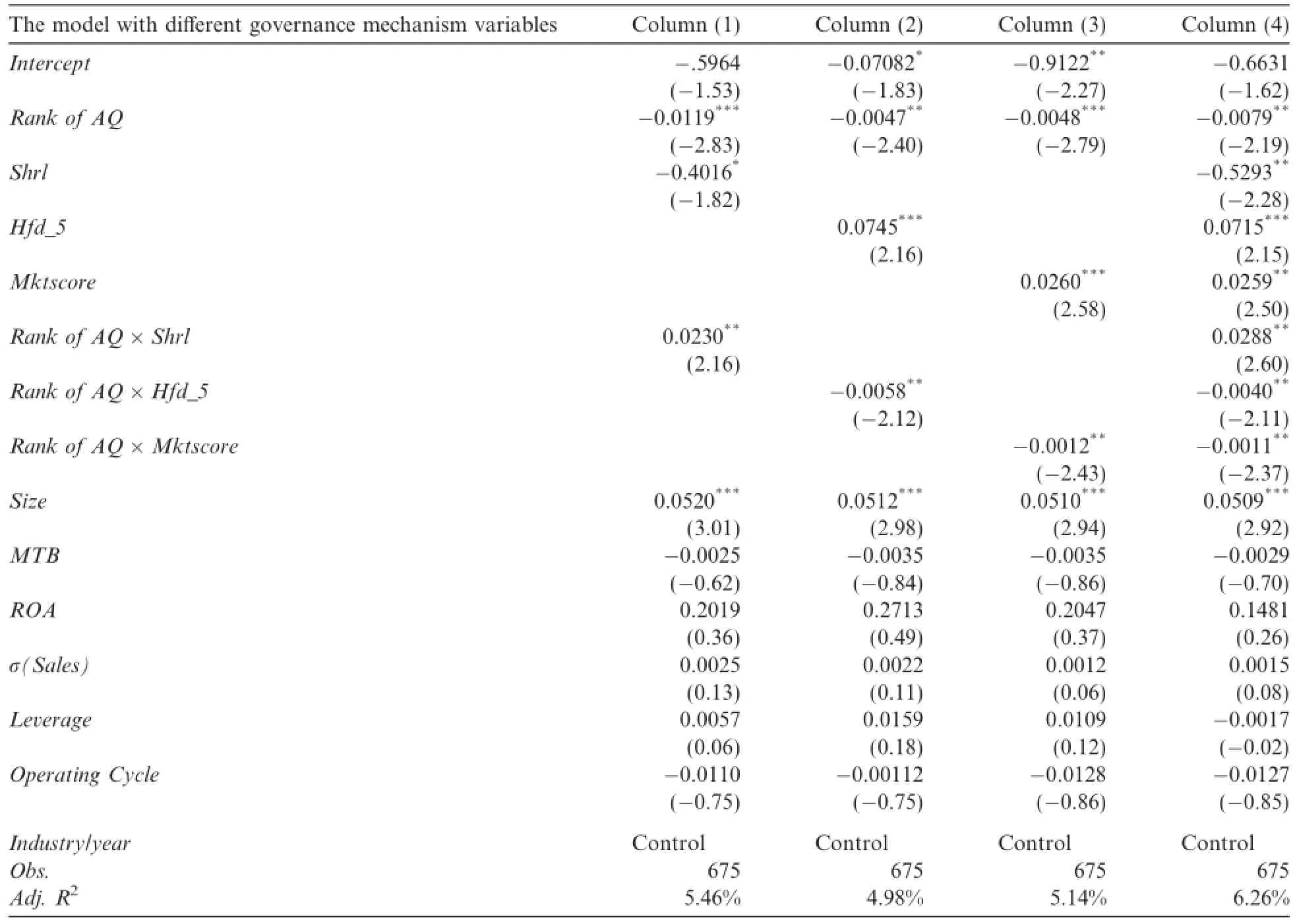
Table 6Cross-sectional analysis of the ef f ect of accounting information quality on the choice of capital investment.
6.1.The ef f ect of other unobservable information and endogeneity
The main analysis and variables above in this paper are based on a relatively long time period(i.e., 10 years),which unavoidably result in the problem:are the results above driven by other unobservable information?Meanwhile,the endogeneity problem also arises,as a company’s choice of capital investment is likely to affect accounting information quality.To address these issues and problems,we control for growth_corr in t-1 period(growth_corrt-1)in regression model(1),and the results are presented in Table 7.
Table 7 shows that after controlling for growth_corrt-1,the coefficients of accounting information quality are still signif i cantly negative at least the 10%level(except for persistence).Thus,the results are consistent with Table 5.
6.2.Measurement of the capital investment choice
For robustness,this paper f i nally refers to the ideas of Morck et al.(2000)about stock price synchronicity, and uses the synchronicity of operating income growth between industry and f i rm level as an alternative measurement of capital investment choice.This new measurement is based on the following model.
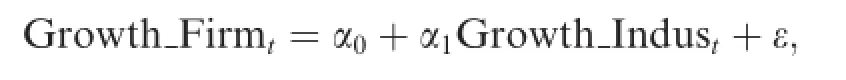
where Growth_Firmtis the operating income growth of a given company in year t,and Growth_Industis that of the industry to which the company belongs(using the median of other companies’operating income growth in the same industry).We obtain the R-square(R2)from the regression model above,which reflects the degree to which the industry’s growth rate explains that of the company.A higher R2indicates greater synchronicity between the operating income growth rates of the company and industry.Based on this new measurement,the new results are consistent with those reported(untabulated due to space limitations).
7.Conclusion
This paper examines whether and how high-quality accounting information can push management to optimize the capital investment choice of listed firms.This is a very important issue.Addressing this issue can help researchers to realize the governance functions of accounting information.The empirical results show that the higher the accounting information quality is,the higher the correlation and synchronicity of operating income growth between the listed f i rm and its industry.Moreover,the relationship between accounting information quality and capital investment choice is more pronounced when the corporate governance environment is poor.These results imply that high-quality accounting information serves an important governance role, which can supervise and push management to optimize capital investment choices,and f i nally maximize stockholders’interests.
This paper has several important contributions.First,this paper provides new empirical evidence in a developing capital market.Second,this conclusion implies that regulators need to build a transparent and reliable information environment to allow accounting information to play an ef f ective role to push listed firms to focus on their core business,optimize firms’capital investment choices,and f i nally increase resource allocation efficiency.Finally,this paper can also help researchers to better understand and realize the governance role of accounting information,and push them to investigate the other role of accounting information deeply and broadly.
One limitation of this paper is that we assume that a company’s investment choice is ef f ective only when it invests capital in its core business.It is of course possible that a better choice for some companies would be to change their current business(rather than increasing the level of investment in their core business),particularly in the case of an industry recession or excess capacity.Therefore,the relationship between accounting information quality and capital investment choice may dif f er with the different development stage of the industry. Maybe this issue is an important topic for future research.
Acknowledgments
This paper was supported by Zhongcai-Pengyuan Local Finance Investment and Funding Research Institute,Program for Innovation Research in Central University of Finance and Economics,the National Natural Science Foundation of China(Project No.71102124)and Beijing Municipal Commission of Education‘‘Pilot Reform of Accounting Discipline Clustering”.
Ali,A.,Zarowin,P.,1992.The role of earnings levels in annual earnings-returns studies.J.Account.Res.30,286–296.
Ball,R.,Brown,P.,1968.An empirical evaluation of accounting income numbers.J.Account.Res.6(2),159–178.
Ball,R.,Shivakumar,L.,2005.Earnings quality in UK private firms:comparative loss recognition timeliness.J.Account.Econ.39,83–128.
Beaver,W.H.,1968.The information content of annual earnings announcements.J.Account.Res.6(3),67–92.
Beaver,W.H.,1989.An accounting revolution,second ed.Prentice Hall,Englewood Clif f s,NJ.
Bhattacharya,U.,Daouk,H.,Welker,M.,2003.The world price of earnings opacity.Account.Rev.78(3),641–678.
Biddle,G.,Hilary,G.,2006.Accounting quality and f i rm-level capital investment.Account.Rev.81(5),963–982.
Biddle,G.,Hilary,G.,Verdi,R.,2009.How does f i nancial reporting quality relate to investment efficiency?J.Account.Econ.48,112–131.
Bushman,R.,Smith,A.,2003.Transparency,f i nancial accounting information and corporate governance.FRBNY Econ.Policy Rev.9, 65–87.
Chen,F.,Hope,O.K.,Li,Q.Y.,Wang,X.,2011.Financial reporting quality and investment efficiency of private firms in emerging markets.Account.Rev.86(4),1255–1288.
China Statistical Yearbook,2011.National Bureau of Statistics of China,pp.730–731.
Dechow,P.M.,Dichev,I.D.,2002.The quality of accruals and earnings:the role of accrual estimation errors.Account.Rev.(Suppl),35–59.
Easley,D.,O’Hara,M.,2004.Information and the cost of capital.J.Finance 59,1553–1583.
Francis,J.R.,Huang,S.,Khurana,I.K.,Pereira,R.,2009.Does corporate transparency contribute to efficient resource allocation?J. Account.Res.47,943–989.
Fan,G.,Wang,X.,2009.China Market Index.Enconomic Science Press,Beijing.
Lev,B.,1983.Some economic determinants of the time-series properties of earnings.J.Account.Econ.5,31–38.
Li,Q.,2009.Accounting information quality and capital allocation efficiency:empirical evidence of Chinese listed corporations.Nankai Business Rev.12,115–124.
McNichols,M.F.,Stubben,S.R.,2008.Does earnings management affect firms’investment decisions?Account.Rev.83(6),1571–1603.
Morck,R.,Yeung,B.,Yu,W.,2000.The information content of stock markets:why do emerging markets have synchronous stock price movements?J.Financial Econ.58,215–260.
Myers,S.C.,Majluf,N.,1984.Corporate financing and investment decisions when firms have information that investors do not have.J. Financial Econ.13,187–221.
Ohlson,J.,2005.On accounting-based valuation formulae.Rev.Acc.Stud.10(2),323–347.
Zeng,Y.,Lu,Z.,2006.The relationship between disclosure quality and cost of equity capital of listed companies in China.J.Econ.Res. China 2,69–76.
Zhou,Z.,Chen,H.,2008.Accounting information transparency and resources allocation efficiency:theory and empirical evidence. Account.Res.2,53–62.
*Corresponding author.
E-mail address:wangyutao@cufe.edu.cn(Y.Wang).
http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.cjar.2016.08.001
1755-3091/©2016 Sun Yat-sen University.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.
This is an open access article under the CC BY-NC-ND license(http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc-nd/4.0/).

