mGluRs对铝致大鼠学习记忆障碍的影响
魏建宏 牛 侨
(山西医科大学汾阳学院,山西 汾阳 032200)
·基础研究·
mGluRs对铝致大鼠学习记忆障碍的影响
魏建宏牛侨1
(山西医科大学汾阳学院,山西汾阳032200)
〔摘要〕目的观察大鼠染铝后神经行为的改变以及海马区病理组织学的变化,研究代谢性谷氨酸受体(mGluRs)对铝致大鼠学习记忆障碍的影响。方法健康SD大鼠随机分为3组,经侧脑室分别注射生理盐水、0.75% Al3+和1.5% Al3+溶液3 μl,连续5 d,而后处死分离双侧海马,用免疫组化PAP法和Western印迹检测mGluR1、mGluR3、mGluR7的表达。结果镜下显示,随着染毒剂量的增加,大鼠海马区棕黄色阳性细胞增多;图像分析软件分析和Western印迹检测均可说明染铝组中mGluR3和mGluR7的表达明显升高(P<0.05),但mGluR1的表达没有明显变化。结论铝可致大鼠神经行为发生改变,导致学习和记忆能力障碍,且与mGluR3和mGluR7的表达升高有关。
〔关键词〕mGluRs;铝;学习记忆
铝可以多种途径进入人体,损伤神经系统,引起神经细胞凋亡;直接损伤突触可塑性,影响记忆过程。体内、外实验表明,铝可以抑制大鼠脑突触小体对谷氨酸的摄取,增强谷氨酸介导的兴奋性神经毒性。可见,铝神经毒性的重要原因之一可能是海马谷氨酸含量的改变〔1,2〕。有研究表明,代谢性谷氨酸受体(mGluRs)与神经细胞凋亡和学习记忆密切相关,神经递质与其受体之间相互调节,在小鼠的认知和学习记忆过程中可能有重要作用〔3,4〕。本实验拟探讨mGluRs对铝致大鼠学习记忆障碍的影响。
1材料与方法
1.1实验动物和取材山西医科大学动物实验中心提供健康SD大鼠。按体重随机分为3组,每组12只,连续5 d经侧脑室分别注射生理盐水、0.75% Al3+、1.5% Al3+液体各3 μl,从注射开始8 d后每组取一半大鼠脑组织的海马部位进行固定、石蜡包埋、切片,用于免疫组织化学PAP法检测mGluRs的表达;其余取脑后分离双侧海马,用Western印迹检测mGluR1、mGluR3、mGluR7在海马CA1区的表达。
1.2免疫组织化学PAP法各组大鼠选择保持一致的切片段面。按照试剂盒说明书步骤操作。鼠抗mGluR1、mGluR3、mGluR7抗体,4℃过夜。抗鼠或抗兔IgG,37℃20 min。HRP标记的链霉卵白素,37℃20 min。DAB显色。常规梯度酒精脱水,二甲苯透明,树胶封片。0.01 mol/L PBS代替一抗作阴性对照。免疫组化测定海马神经细胞中mGluRs表达的变化,图像分析系统进行密度扫描。
1.3Western印迹测定蛋白含量每组海马组织加入全细胞裂解液0.6 ml匀浆。按照试剂盒说明操作。一抗(1∶200),4℃过夜。二抗(1∶200),37℃ 2 h。DAB显色剂显色,至棕色条带清晰可见。凝胶图像分析系统扫描胶片,分析目标带的分子量和净光密度值。
2结果
2.1免疫组织化学PAP法观察不同剂量染铝组海马mGluRs的表达棕黄色阳性神经元分布于各组大鼠海马CA1区锥体细胞层,且随剂量增加,细胞连接逐渐松散,层次不清。图像分析软件显示,mGluR3和mGluR7的表达随着染毒剂量的增加而逐渐增加,见图1和表1。

图1 海马CA1区mGluRs阳性细胞的分布(PAP法,×400)
2.2Western印迹测定不同剂量染铝组海马CA1区mGluRs表达的变化mGluR1蛋白表达没有明显变化(P>0.05)。mGluR3和mGluR7蛋白高表达,随剂量的升高变化比较明显(P<0.05),见图2和表2。

表1 三组海马CA1区mGluRs阳性细胞
与对照组相比:1)P<0.05

图2 大鼠海马CA1区mGluRs的表达
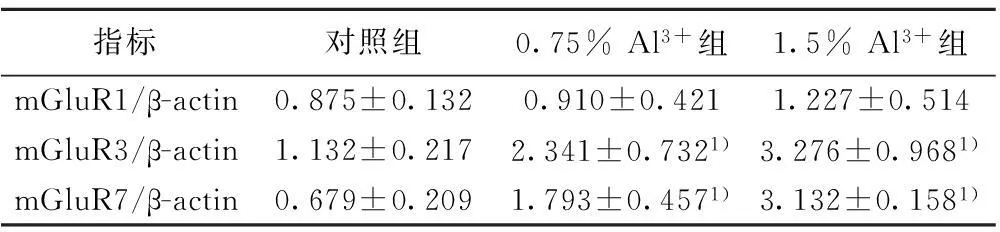
指标对照组0.75%Al3+组1.5%Al3+组mGluR1/β-actin0.875±0.1320.910±0.4211.227±0.514mGluR3/β-actin1.132±0.2172.341±0.7321)3.276±0.9681)mGluR7/β-actin0.679±0.2091.793±0.4571)3.132±0.1581)
与对照组相比:1)P<0.05
3讨论
铝是一种神经性毒物,长时间脑内蓄积可损害学习记忆功能。铝可引起脂质过氧化导致细胞内自由基增多,可影响LTP的形成和维持,影响学习记忆〔3〕。Untand等〔5〕认为mGluRs在学习记忆过程中有重要的作用,可能参与了LTP的产生与维持在神经系统的损害及疾病中扮演重要的角色〔4~6〕。
本实验结果表明mGluR3和mGluR7的表达随着染铝剂量的增加而升高,这与笔者以前研究结果一致〔7〕,表明mGluR3和mGluR7的表达升高可能是介导了铝的神经毒性过程。多数文献报道第Ⅱ、Ⅲ组mGluRs在脑的神经毒性中具有保护作用〔8~10〕;也有研究证明,Ⅱ、Ⅲ组mGluRs可抑制神经元内谷氨酸的过度释放,降低神经毒性作用〔11,12〕。由此可以说明mGluR3和mGluR7的表达升高可能是介导了铝的神经毒性,也可能是铝的神经毒性引起保护性的升高。
本实验从铝引起mGluRs表达改变来研究铝的神经毒性机制,对防治铝神经毒性实现早期干预具有重要的意义。
4参考文献
1Yang YX,Niu Q.Chronic aluminum contact different brain regions of rats the BCL-2 gene expression〔J〕.Environment Occupat Med,2002;19(4):209-12,218.
2Niu PY,He SC,Niu Q.Gastrodia elata on dye aluminum in the rat brain cortex SOD and MDA〔J〕.Influ Environment Occupat Med,2003;20(5):357-9.
3Grover LM,Yan C.Evidence for involvement of group Ⅱ/Ⅲ metabotropic glutamate receptors in NMDA receptor-independent long-term potentiation in area CA1 of rat hippocampus〔J〕.J Neurophysiol,1999;82(6):2956-69.
4Niu Q,Niu PY,He SC.Gastrodia elata on aluminum to affect learning and memory disorders in rats〔J〕.Health Res,2004;33(1):45-7.
5Untand D,Pampillo M,Caruso C,etal.Role of metabotropic gliutamate receptors in the control of neuroendocrine function〔J〕.Neuropharmacology,2008;55(4):577-83.
6Wang M,Chen JT,Ruan DY,etal.The influence of developmental period of aluminum exposure on synaptic plasticity in the adult rat dentate gyrus in vivo〔J〕.Neuroscience,2002;113(2):411-9.
7Wei JH.Metabolic glutamic acid receptor expression in aluminum to the damage of learning and memory in mice〔D〕.Master thesis of shanxi medical university,2008.
8Bruno V,Copani A,Bonanno L.Activation of group Ⅲ metabotropic glutamate receptors is neuroprotective in cortical cultures〔J〕.Eur J Pharmacol,1996;310(1):61-6.
9Kingston AE,O′Neill MJ,Lam A,etal.Neuroprotection bymetabotropic glutamate receptor glutamate receptor agonists:L Y354740,L Y379268 and L Y389795〔J〕.Eur J Pharmacol,1999;377(2):155-65.
10Bruno V,Battaglia G,Copani A,etal.Activation of class Ⅱ or Ⅲ metabotropic glutamate receptors protects cultured cortical neurons against excitotoxic degeneration〔J〕.Eur J Neurosci,1995;7:1906-13.
11Xi ZX,Shen H,Baker DA,etal.Inhibition of non-vesicular glutamate release by group Ⅲ metabotropic glutamate receptors in the nucleus accumbens〔J〕.Neurochem,2003;87(10):1204-12.
12Millan C,Lujan R,Shigemoto R,etal.Subtype-specific expression of group Ⅲ metabotropic glutamate receptors and Ca2+channels in single nerve terminals〔J〕.J Biol Chem,2002;277:47796-803.
〔2015-09-17修回〕
(编辑李相军)
Effect of mGluRs on learning and memory dysfunction in rats induced by aluminum
WEI Jian-Hong, NIU Qiao.
Fenyang College, Shanxi Medical University, Fenyang 032200, Shanxi, China
【Abstract】ObjectiveTo observe the effects of mice after dyed aluminum on nerve behavior and the pathological and histological changes of the hippocampus, and the effect of mGluRs on the disorder of learning and memory in mice.MethodsHealthy Kunming mice were randomly divided into 3 groups, with 10 mice in each group. Saline, 0.75% Al3+and 1.5% Al3+were respectively injected into lateral ventricle for five days. Then the mice were executed separation of bilateral hippocampus. The expressions of mGluRs1, mGluRs3 and mGluRs7 were detected by the immunohistochemistry PAP method and Western blot.ResultsThe microscopic showed that with the increasing of infected dose, the number of positive orange-brown hippocampus cells increased. Image analysis software analysis and Western blot detection all showed that the expressions of mGluRs3 and mGluRs7 in aluminum group were increased significantly (P<0.05), but there was no significant difference in the expression of mGluRs1. ConclusionsAluminum could cause the mice neural behavior change, learning and memory impairment, which associates with elevated expressions of mGluR3 and mGluR7.
【Key words】mGluRs;Aluminum; Learning and memory
〔中图分类号〕R3
〔文献标识码〕A
〔文章编号〕1005-9202(2016)05-1025-03;
doi:10.3969/j.issn.1005-9202.2016.05.001
基金项目:国家自然科学基金资助项目(30671777);山西省自然科学基金资助项目(2013011052-2)
1山西医科大学
第一作者:魏建宏(1972-),男,医学硕士,副教授,主要从事神经毒理学研究。

