滇池表层沉积物铵态氮吸附特征*
国家水体污染控制与治理科技重大专项(2012ZX07102)资助.2014-12-17收稿;2015-07-02
收修改稿. 邓伟明(1984~),男,硕士,助理工程师;E-mail:ming_605@163.com。
滇池表层沉积物铵态氮吸附特征*
*国家水体污染控制与治理科技重大专项(2012ZX07102)资助.2014-12-17收稿;2015-07-02
收修改稿. 邓伟明(1984~),男,硕士,助理工程师;E-mail:ming_605@163.com。
(昆明市环境科学研究院湖泊水库中心,昆明650032)
摘要:为研究滇池内源污染特征,2013年利用GIS软件针对滇池全湖布设36个采样点,采集表层沉积物,研究滇池表层沉积物铵态氮-N)吸附特征,同时分析沉积物的理化性质对-N吸附特性的影响.结果表明:滇池表层沉积物对-N的吸附量在前2 h之内呈增长趋势,吸附速率较大,之后沉积物对-N的吸附量不随时间变化而变化,基本达到平衡,最大吸附速率均发生在0~5 min内;不同区域表层沉积物-N最大吸附速率平均值表现为:外海南部>湖心区>外海北部>草海,最大吸附量平均值表现为:湖心区>外海南部>外海北部>草海,吸附效率平均值表现为:外海北部>草海>湖心区>外海南部;沉积物对-N的吸附量与-N的初始浓度大致呈线性关系,并且低浓度下表现出很好的吸附/解吸特征;滇池表层沉积物-N的吸附解吸平衡浓度(ENC0)高于上覆水中-N浓度,表明沉积物中-N有向上覆水中释放的风险,沉积物在很长一段时间内起到水体污染“源”的作用;ENC0与沉积物中总氮-N含量呈显著正相关,本底吸附量和有机质总量呈显著负相关,沉积物吸附-N主要受有机质的影响。
关键词:滇池;沉积物;铵态氮;吸附
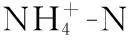

图1 滇池沉积物与水样监测点位Fig.1 Sediment and water monitoring sites of Lake Dianchi
1 材料与方法
1.1 研究区概况
滇池(24°28′~25°28′N,102°30′~103°0′E)位于昆明市南的西山脚下,是我国第6大淡水湖泊[7],呈南北向分布,东北部有一长4 km的天然沙堤,将滇池分为南北两部分,分别称为外海和草海;草海面积7.52 km2,湖容0.188×108m3,外海面积为287.10 km2,湖容约13.60×108m3,最大水深10.24 m,平均水深4.40 m[8]。
1.2 研究点位及采样方法
2013年在滇池全湖布设36个点位,包含常规监测点位、入滇河流入湖口监测点位和疏浚区监测点位,然后利用GPS定位进行采样,研究位点分布如图1所示。
利用彼得森采泥器采集滇池表层10 cm沉积物样品,样品装入塑料密封袋排出空气密封,及时送回实验室冷冻干燥,然后研磨过200目筛备用。
1.3 测定方法



实验数据分别采用Excel 2007、SPSS 16.0以及ArcGIS软件进行统计检验、多元回归和作图.
2 结果与分析
2.1 滇池表层沉积物中不同形态氮含量的分布特征
滇池表层沉积物总氮(TN)含量介于1596.25~5558.50 mg/kg之间,平均值为3307.26 mg/kg.长江中下游湖泊沉积物中TN含量在770.00~2630.00 mg/kg之间[10],洱海沉积物中TN含量在2084.40~6515.30 mg/kg之间[11],滇池沉积物TN含量与高原湖泊洱海相当,是长江中下游湖泊的2.5倍左右,表明其TN含量处于较高水平。

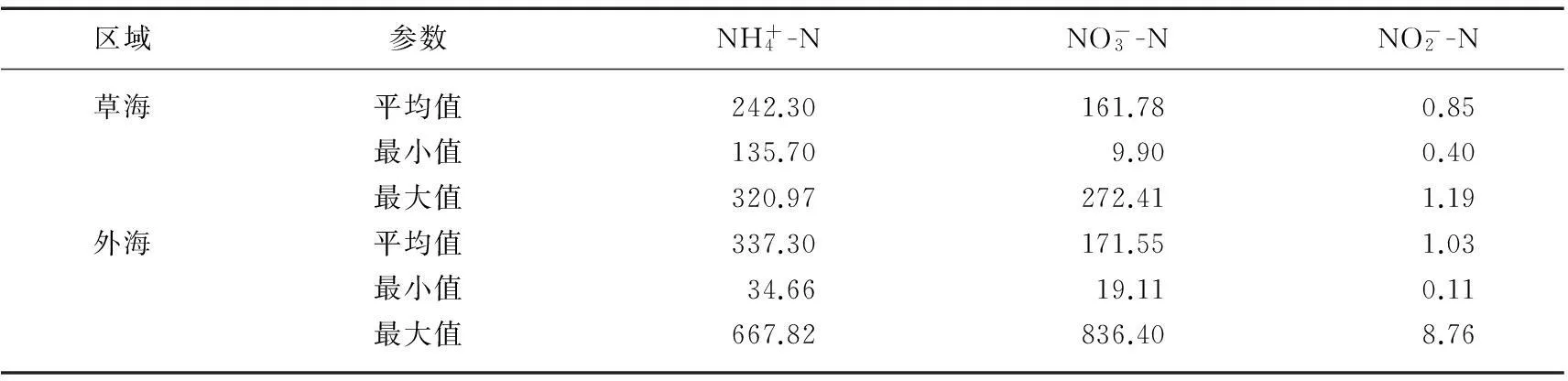
表1 2013年滇池沉积物中不同形态氮含量(mg/kg)

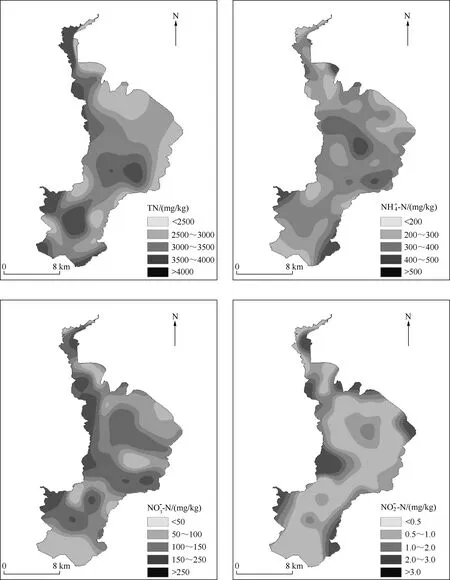
图2 滇池表层沉积物不同形态氮含量的空间分布Fig.2 The spatial distribution of different forms of nitrogen content in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi

图3 滇池表层沉积物-N吸附动力学曲线Fig.-N in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi

表2 不同时间段滇池表层沉积物对的吸附速率(mg/(kg·min))

图4 滇池表层沉积物对-N的最大吸附速率Fig.-N in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi

表3 滇池表层沉积物吸附-N
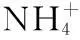
q=a+b·lnt
(1)


图5 滇池表层沉积物对-N的吸附-解吸特征曲线Fig.-N in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi
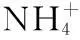
Q=NAN+Kd·ENC0
(2)
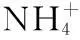

表4 滇池表层沉积物对-N的吸附-释放特征参数

表5 不同湖泊沉积物对-N的吸附/

湖泊(年份)NAN/(mg/kg)ENC0/(mg/L)滇池(2013年)500.134.39太湖(2003年)39.091.78鄱阳湖(2003年)21.541.20洪泽湖(2003年)31.861.22
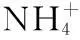

图6 滇池表层沉积物对-N的吸附等温线Fig.-N in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi
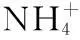
Q=Qmax·K·C/(1+K·C)
(3)
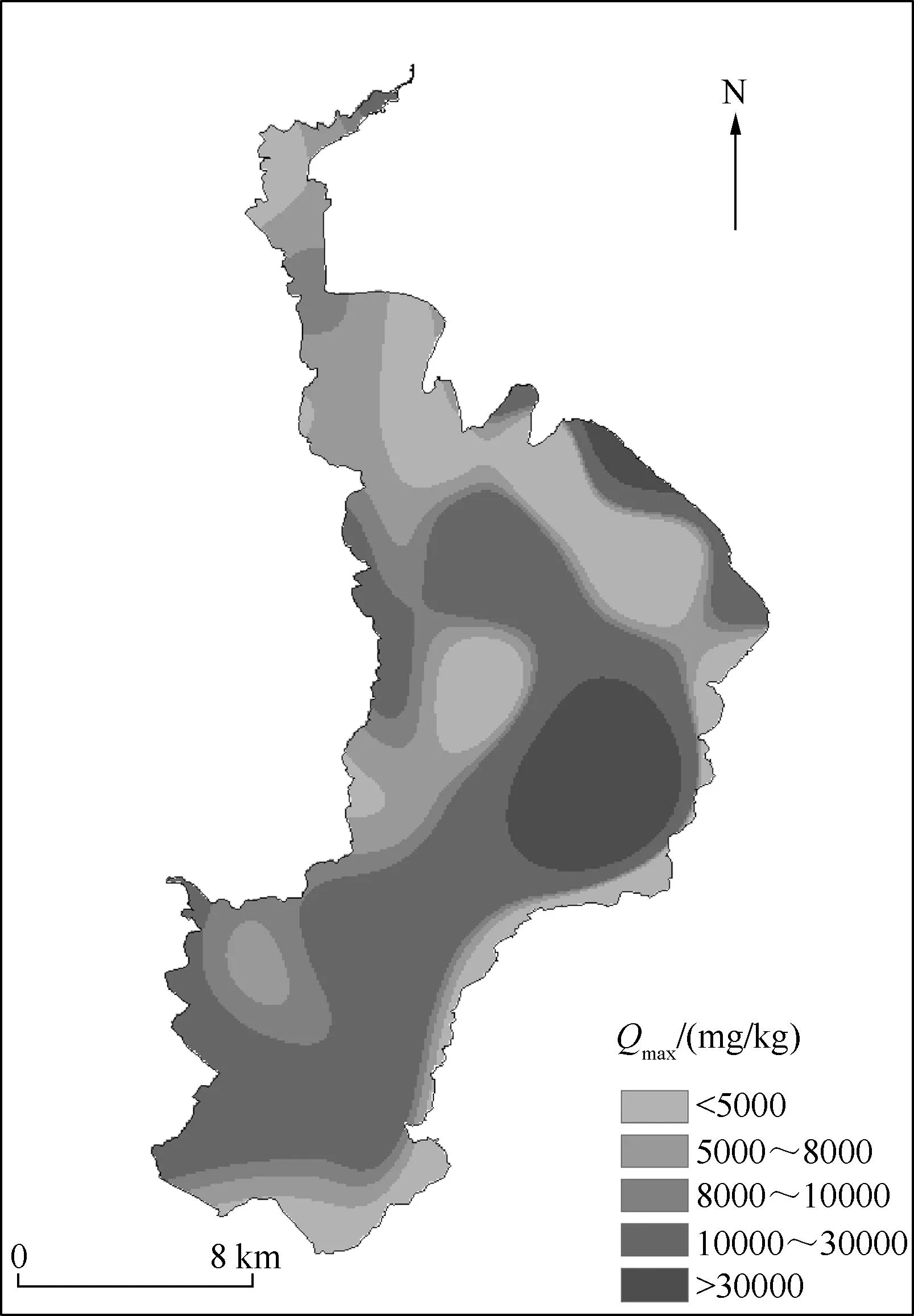
图7 滇池表层沉积物对-N的最大吸附量的分布Fig.7 The distribution of the maximum adsorption quantity -N in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi
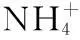

表6 滇池表层沉积物对-N的吸附等温线特征参数

表7 滇池表层沉积物-N的吸附特征参数与其理化指标的相关系数
*表示P<0.05。
3 结论

参考文献4
[1]Aller RC, Mckin JE, Ullman WJetal. Early chemical diagenesis, sediment-water solute exchange, and storage of reactive organic matter near the mouth of the Changjiang, East China Sea.ContinentalShelfResearch, 1985, 4(1/2): 227-251。
[2]王而力, 王雅迪, 王嗣淇. 西辽河不同粒级沉积物的氨氮吸附-解吸特征. 环境科学研究, 2012, 25(9): 1016-1023。
[3]Shen SY, Shu IT, Kemper WD. Equilibrium and kinetic study of ammonium adsorption and fixation in sodium-treated verniculite.SoilScienceSocietyofAmericanJournal, 1997, 61: 1611-1618。
[4]王娟, 王圣瑞, 金相灿等. 长江中下游浅水湖泊表层沉积物对氨氮的吸附特征. 农业环境科学学报, 2007, 26(4): 1224-1229。
[5]杨一光, 杨桂华. 滇池自然地理概要. 云南大学学报: 自然科学版, 1985, 7(增刊): 1-8。
[6]齐素华, 艾萍, 王趁义. 滇池的富营养化现状分析及防治对策. 江苏环境科技, 2000, 13(4): 27。
[7]Liu JL, Wang RM, Hu ABetal. Distribution and bioaccumulation of steroidal and phenolic endocrine disrupting chemicals in wild fish species from Dianchi Lake, China.EnvironmentalPollution, 2011, 159: 2815-2822。
[8]Wan X, Pan XJ, Wang Betal. Distributions, historical trends, and source investigation of polychlorinated biphenyls in Dianchi Lake, China.Chemosphere, 2011, 85: 361-367。
[9]鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析: 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000。
[10]王娟. 浅水湖泊中氮素分布特征与沉积物氨氮吸附释放机理研究[学位论文] . 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2007。
[11]王圣瑞, 何宗健等. 洱海表层沉积物中总氮含量及氨氮的释放特征. 环境科学研究, 2013, 26(3): 256-261。
[12]胡智瞍, 孙红文, 潭媛. 湖泊沉积物对N和P的吸附特性及影响因素研究. 农业环境科学学报, 2004, 23(6): 1212-1216。
[13]杨龙元, 蔡启铭, 秦伯强等. 太湖梅梁湾沉积物-水界面氮迁移特征初步研究. 湖泊科学, 1998, 10(4): 41-47. DOI 10. 18307/1998. 0406。
[14]姜霞, 王秋娟, 王书航等. 太湖沉积物氮磷吸附/解吸特征分析. 环境科学, 2011, 32(5): 1285-1291。
[15]Swift RS. The effect of adsorbed organic materials on the cation exchange of clay minerals. In: Banin A, Kafkafi U eds. Agrochemicals in soils, 1980: 123-129。
[16]Hedges JI, Keil RG. Sedimentary organic matter preservation: an assessment and speculative synthesis.MarineChemistry, 1995, 49: 81-115。
[17]Padmesha TVN, Vijayaraghavana K, Sekaranb Getal. Batch and column studies on biosorption of acid dyes on fresh water macro algaAzollafiliculoides.JournalofHazardousMaterials, 2005, 125( 1/2/3): 121-l29。
[18]Wang SR, Jin XC, Pang Yetal. The study on the effect of pH on phosphate sorption by different trophic Lake sediments.JournalofColloidandInterfaceScience, 2005, 285: 448-457。
[19]王圣瑞, 金相灿, 赵海朝等. 长江中下游浅水湖泊沉积物对磷的吸附特征. 环境科学, 2005, 26(3): 38-43。
[20]Jin X, Wang S, Pang Yetal. The adsorption of phosphate on different trophic lake sediments.ColloidsandSurfacesA:Physicochemical&EngineeringAspects, 2005, 254: 241-248。
[21]翟丽华, 刘鸿亮, 席北斗. 农业源头沟渠沉积物氮磷吸附特性研究. 农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(4): 1359-1363。
[22]杨洪美. 南四湖表层沉积物中氮形态及吸附释放研究[学位论文]. 北京: 中国矿业大学, 2007。
[23]金相灿, 刘鸿亮, 屠清瑛等. 中国湖泊富营养化. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 1990, 28(1): 121-133。
[24]王圣瑞. 湖泊沉积物-水界面过程. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012。
[25]姜桂华. 铵态氮在土壤中吸附性能探讨. 长安大学学报, 2004, 21(2): 32-38。
[26]Balci S. Nature of ammonium ion adsorption by sepiolite: analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherms.WaterResearch, 2004, 38: 1129-1138。
[27]陈永川, 汤利, 张德刚等. 滇池水体叶绿素a的时空变化及磷对藻类生长的影响. 农业环境科学学报, 2008, 27(4): 555-560。
[28]王雨春, 万国江, 尹澄清等. 红枫湖、百花湖沉积物全氮、可交换态氮和固定铵赋存特征. 湖泊科学, 2002, 14(4): 301-3091. DOI 10. 18307/2002. 0402。
[29]李震宇, 朱荫湄, 王进. 杭州西湖沉积物的若干物理和化学性状. 湖泊科学, 1998, 10(1): 79-84. DOI 10. 18307/1998. 0113。
[30]Raaphorst WV, Malschaert JFP. Ammonium adsorption in superficial North Sea sediments.ContinentalShelfResearch, 1996, 16(11): 1415-1435。
J.LakeSci.(湖泊科学), 2016, 28(1): 75-85
©2016 byJournalofLakeSciences
Sorption and desorption characteristics of ammonium in the surface sediments of Lake Dianchi
DENG Weiming, XU Xiaomei, CHEN Chunyu, HE Jia**, XU Di & WANG Li
(ResearchCenterofLakesandReservoirs,KunmingInstituteofEnvironmentalSciences,Kunming650032,P.R.China)
Abstract:In order to study the endogenous pollution characteristics of Lake Dianchi, 36 samples were set in whole Lake Dianchi using the GIS exploring in 2013. Through collecting the surface sediment samples, adsorption characteristics of ammonia on surface sediments were studied and the influence of physical and chemical properties of sediments on the adsorption characteristics of ammonia was also analyzed. The results showed that the adsorption quantity of ammonia nitrogen on surface sediments of the Lake Dianchi showed a growing trend in 2 h and the adsorption rate was relatively high. After 2 h, the adsorption quantity of ammonia on surface sediments did not change with time and attain the basic balance. The maximum adsorption rate appeared during 0-5 min. An order of the average maximum adsorption rate of ammonia on sediments of different sub-lake waters was: the south of Lake Waihai>the center of the lake>the south of Lake Waihai>Lake Caohai. An order of the average of maximum adsorbent quantity was: the center of the lake>the south of Lake Waihai>the north of Lake Waihai>Lake Caohai. A order of the average adsorption efficiency was: the north of Lake Waihai>Lake Caohai>the center of the lake>the south of Lake Waihai. The adsorption quantity of ammonia on sediments showed a rough linear relationship with the initial concentration of ammonia. Under a low concentration condition, a good adsorption/desorption characteristic occurred. Through comparing the concentration of adsorption/desorption of ammonia on sediments and the concentration between overlying water and sediments, the results showed that the ENC0of ammonia in sediments was higher than that in overlying water, indicating that the ammonia had the releasing risk from sediments to overlying water. These inferred that the sediments would play a role of the water pollution “source” in a long time. As ENC0had the positive correlation with total nitrogen and ammonium nitrogen in sediments and NAN had negative correlation with total organic matter, we recognized that the ammonia adsorbed by sediments was mainly influenced by organic matter。
Keywords:Lake Dianchi;sediments;ammonia nitrogen;adsorption
通信作者邓伟明,徐晓梅,陈春瑜,何佳*;E-mail:dcszxb@163.com.,许迪,王丽
DOI10.18307/2016.0109

