Effect of Low Temperature and Sparse Light Conditions on Cold Tolerance of Different Rice Lines at Seedling Stage
Zengfeng MA, Chi LIU, Yuexiong ZHANG, Dahui HUANG
Rice Research Institute, Guangxi Academy of Agricultural Sciences/Nanning Sub-center of National Center for Rice Improvement,Nanning 530007, China
Rice is thermophilic crop,and is very sensitive to low tempera ture[1-2]. Suitable growth temperature of rice seedling is between 25 and 35 ℃, and 10-20 ℃of low temperature could severely hinder the growth of rice seedling[2]. Nishiyama pointed out that indica at seedling stage was hurt when temperature was lower than 18 ℃[3].Chilling injury of rice is a worldwide problem,and is particularly prominent in Japan,South Korea,America and China[4]. Due to chilling injury,3×109-5×109kg of paddy is lost every year in China, which is equivalent to 1% of crop yield[5]. In Guangxi,chilling injury also severely affects rice production, which mainly shows as seedling rot and death when “unusually cold spell in early spring” cold weather appears in sowing, seedling and transplanting stages[6].Later seedling and transplanting induced by low temperature is also one of factors for rice yield reduction[7].To overcome adverse influences on rice brought by low temperature and increase and stabilize yield, besides taking other agricultural measures, it is the most economic and effective measure for reducing chilling injury to select cold resistant variety. In recent years, the researches about identification,screening and utilization of rice cold tolerance were conducted successively by many scholars at home and abroad. Liu Guanglin et al. identified 458 high-quality rice germplasm resources, and screened 6 high-quality rice germplasm resources which all showed strong or extremely strong cold tolerance during each growth stage under natural low temperature condition, and could be used for germplasm innovation and genetic improvement[8].Zhang Jianhua et al.car-ried out cold tolerance evaluation on 690 rice germplasm resources at bud and seedling stages provided by China and Japan under temperature control condition. They screened out 25 extremely strong (level 0) cold resistant resources and 89 strong (level 1-2)cold resistant resources at bud stage;14 extremely strong cold resistant resources and 8 strong cold resistant resources at seedling stage. Among them, 29 resources had stronger cold tolerance at bud and seedling stages[9].Chen Dazhou et al. took Dongxiang wild rice as backbone parent, and used “double” low-temperature pressuring screening method to conduct genetic improvement on cold tolerance of japonica, which obtained good effect. The cultivated 4913-1 japonica was not hurt after processed for 48 h at 0 ℃ during seedling stage, and could winter and regenerate for 3 years under natural condition in Nanchang[10].In addition,rainy weather often occurs in rice growth period of Guangxi. Photosynthesis is fundamental basis of rice matter production,and light energy utilization is the key of rice production.When rice plant is under weak illumination environment at varying degrees, not only is its growth and development affected at varying degrees, but also yield will decline[11].In recent years,chilling injury occurring frequently brings large negative influence on China’s rice production, and causes large-area yield reduction of rice in China,which severely threatens national crop safety.Therefore,it is imperative to strengthen research about cold tolerance of rice,identify and analyze the breeding materials,and breed cold resistant variety.During January-March, 2014, Guangxi successively suffered four times of cold wave and frost.Under such continuous low temperature and rainy condition, cold tolerance characters of 36 parents and offspring from 68 hybrid groups at seedling stage were verified and analyzed. We aimed to screen out highquality resource with strong cold tolerance at seedling stage, accumulate material for studying and using cold tolerance of rice, and provide good parent for cold resistant breeding of rice.
Materials and Methods
Materials
Test materials were 36 parents(Table 1) and 423 rice lines from 68 hybrid groups.

Table 1 The cold tolerance of different rice cultivars
Methods
Meteorological data Meteorological data of natural low temperature were from meteorological observation station near test field, and were provided by Nanning Municipal Meteorological Bureau.Average temperature of whole seedling period from March 1 to 30,2014 was only 17 ℃, especially daily average temperature from March 2 to 17 was only 12.5-17.0 ℃, which was typical low temperature and sparse light weather. Temperature change was shown as Fig.1.
Cold tolerance identification at seedling stage Using natural low temperature and sparse light weather in early spring of 2014(Fig.1),cold tolerance at seedling stage was identified. Under the situation of thin film cover, cold tolerance of seedlings which have sprouted was identified. It was sown on March 1, 2014, and removed film after 28 days, and cold tolerance result statistics was conducted on the 30thday. Referring to the method of Han Longzhi et al.[12], cold tolerance at seedling stage was identified. The identification standard was:level 1, all leaves were close to green,with extremely strong cold tolerance,which was marked as RR; level 3,leaves bleached little or were yellow,with strong cold tolerance, which was marked as R; level 5, leaves mostly yellowed, with moderate cold tolerance,which was marked as M;level 7,leaves withered, and some seedlings died, with weak cold tolerance, which was marked as S; level 9, most or all seedlings died, with extremely weak cold tolerance, which was marked as SS.
Results and Analysis
Cold tolerance of parent
Generally, the optimal growth temperature of rice seedling is between 20 and 25 ℃. Seen from temperature change chart, during whole test stage from March 1 to 30,average temperature was only 17 ℃,especially in prior period of seedling growth from March 2 to 17,daily average temperature did not exceed 17 ℃. Long-time low temperature and sparse light weather affected seedling growth at large degree, which could identify cold tolerance of the material. As shown in Table 1, there were 10 parents reaching level one of cold tolerance, in which 3 parents were wild rice DP3,DP17, DP20, while 3 parents were japonica BaiR54, BaiR55 and BaiR56,and 3 parents were indica Dalihui,Shuhui527 and 3550R. Another one cold resistant material Y1-4 was hybrid offspring of japonica and indica.Other levels 3 -9 of cold resistant materials were all indica rice, in which both maintainer line XianB and restorer 998R had better cold tolerance,and reached level three of cold tolerance (Table 1). Strong restorer line Gui99 and MH63 which were used widely in combination were level five of cold resistant materials(Table 1).

Table 2 The cold tolerance of offspring derived from wild rice
Cold tolerance of derived progeny from wild rice
In 252 derived progeny of common wild rice from 24 groups, there were 33 level one of cold resistant materials,which accounted for 13.1%;20 level three of cold resistant materials,which accounted for 7.9%;68 level five of cold resistant materials, which accounted for 27.0%;97 level seven of cold resistant materials, which accounted for 38.5%;34 level nine of not cold resistant materials, which accounted for 13.5%(Table 2).In all level one of cold resistant materials, the proportion of 93-11/DP3 combination was the most, and there were 12 materials, followed by 10 materials from BaiR10//93-11/DP17 combination.
Cold tolerance of IRBB5 derived progeny
IRBB5 is the variety of IRRI, and shows as level five of cold tolerance.There were 22 combinations by IRBB5 and 93 derived progeny materials joining in test.As shown in Table 3, under low temperature and sparse light condition, there were 15 materials showing as level one of cold tolerance,which accounted for 16.1%; 13 materials showing as level three of cold tolerance, which accounted for 14.0%;24 materials showing as level five of cold tolerance, which accounted for 25.8%; 25 materials showing as level seven of cold tolerance, which accounted for 26.9%;16 materials showing as level nine of cold tolerance,which accounted for 17.2%.In all combinations, 649R/IRBB5 had the most level one of cold resistant material,and there were 6 materials, followed by Fuhui838/IRBB5, and there were 5 materials (Table 3).In the two combinations, IRBB5 was level five of cold resistant material,while both Fuhui838 and 649R were level seven of cold resistant materials.However,super parent offspring with cold tolerance could be screened out from their hybrid offspring. It illustrated that these combinations had very good super parent advantage, and it was hopeful to screen cold resistant high quality plant from offspring of these combinations.
Cold tolerance of BPHR96 derived progeny
BPHR96 is stable parent resisting to brown planthopper,is very sensitive to low temperature and sparse light weather, and shows as level nine of not cold tolerance (Table 1). There were 12 BPHR96 combinations and 52 derived progeny materials. As shown in Table 4, only Fuhui838/BPHR96 combination had 3 level one of cold resistant materials, which accounted for 5.8%. There were 3 level three of cold resistant materials; 14 level five of cold resistant materials,which accounted for 26.9%; 23 level seven of cold resistant materials,which accounted for 44.2%; 9 level nine of cold resistant materials, which accounted for 17.3%.
Cold tolerance of other materials
Parents of other combinations mainly included Y1-4 containing japonica consanguinity, African new rice Z3 and Z4 and some maintaining systems,such as GuiB,MeiB,MengB,TianB and TeB,etc. (Table 5). Under low temperature and sparse light conditions, these parents mostly showed as level 7-9 of not cold tolerance (Table 1). These combinations did not have super parent advantage generating posterity with strong cold tolerance like 649R/IRBB5 and Fuhui838/IRBB5, and did not have level one of cold resistant progeny plant (Table 5). There was one level three of cold resistant material, 7 level five of cold resistant materials,15 levelseven of cold resistant materials and 3 level nine of not cold resistant materials (Table 5).Here,3 level nine of not cold resistant materials were all from the combinations containing African new rice consanguinity.

Table 3 The cold tolerance of offspring derived from IRBB5
Discussion
Cold tolerance difference of different parent materials
Generally,cold tolerance of japonica is stronger than that of indica, and japonica and indica can suffer chilling injury at 15 and 18 ℃respectively. 3 japonica materials in the research all showed as level one of strong cold tolerance, while in 29 indica materials,there were only 3 level one of strong cold resistant materials. It was clear that the occurrence frequency of cold resistant material in japonica was higher than indica. As ancestor of cultivated rice, common wild rice showed good tolerance to chilling injury. In the research, 3 common wild rice materials all showed as level one of cold tolerance. Wild rice could survive under extremely low temperature. For example, Dongxiang wild rice could survive under extremely low temperature (-12.8 ℃)[11]because of strong cold resistant gene.
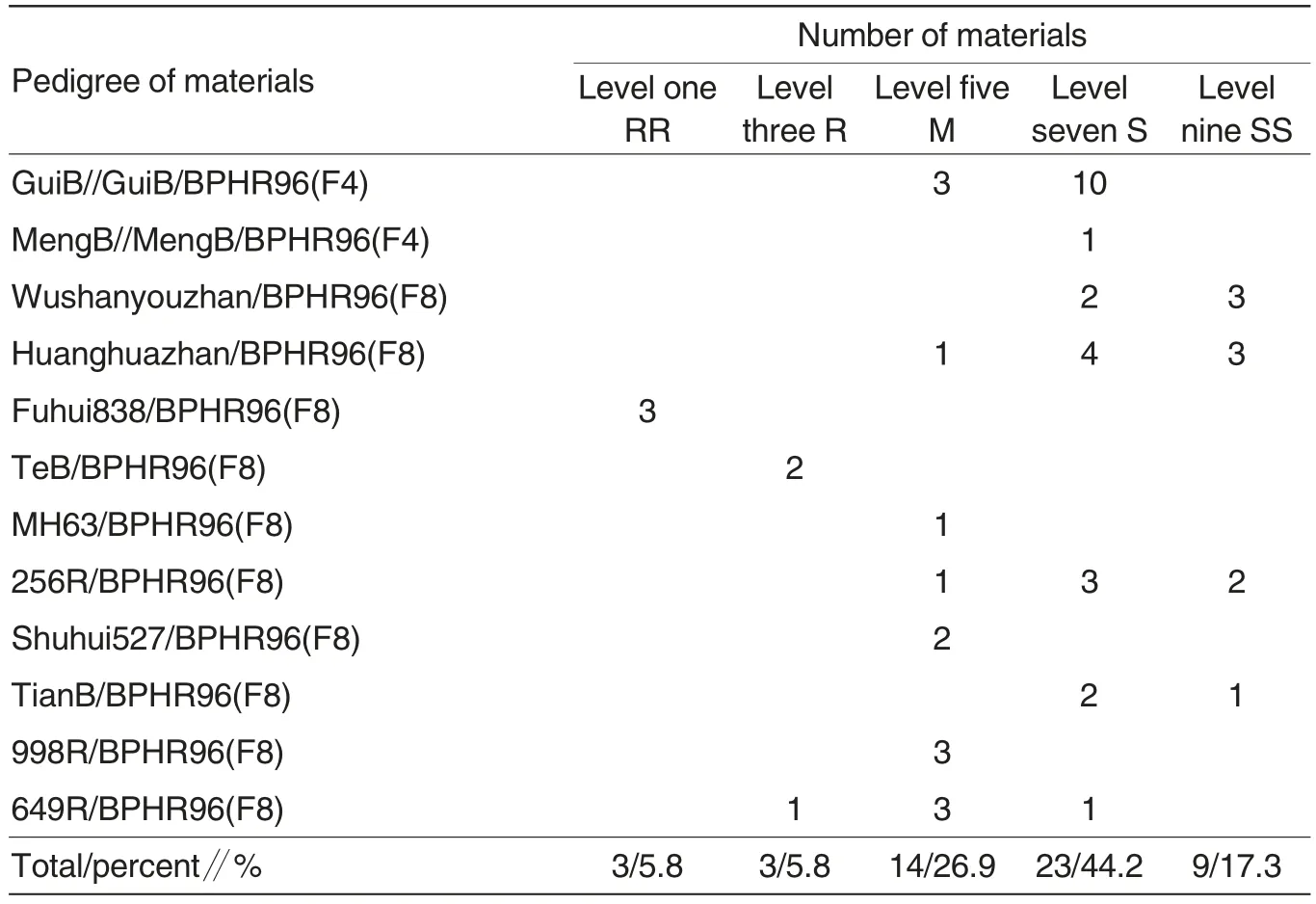
Table 4 The cold tolerance of offspring derived from BPHR96
Cold tolerance of derived progeny from different hybrid combinations
Some researches show that cold tolerance of rice is controlled by 4-7 couples of genes, which all belong to dominant genes.Cold tolerance of derived progeny from different parent hybrid combinations is depended on comprehensive effect of additive and interaction effect of cold resistant genes from parent[1]. The research result showed that occurrence rate of strong cold resistant plant from derived posterity of wild rice was higher. In 24 posterity materials containing wild rice consanguinity, 8 combinations all had level one of strong cold resistant posterity plant,33 materials in total (Table 2). It is one of channels breeding cold resistant rice to use common wild rice with strong cold tolerance hybridizing with japonica and indica with cold tolerance.
It was worthy to think why hybrid combination whose cold tolerance was not very strong could breed strong cold resistant material.In the research,hybrid posterity of parent IRBB5 whose cold tolerance was not very strong and strong recovery systems Gui99,Fuhui838,998R and 649R whose cold tolerance was not strong had level one of strong cold resistant material,which showed super parent phenomenon(Table 3). Maybe cold resistant gene from different parents gathered at pos-terity, thereby making that these offspring materials showed stable strong cold tolerance via multi-generation self crossing. Therefore, in breeding practice, besides wild rice, japonica and indica with good cold tolerance, we should also value strong recovery materials, such as Gui99, Fuhui 838 and 998R. Hybrid posterity of these materials often showed strong cold tolerance.
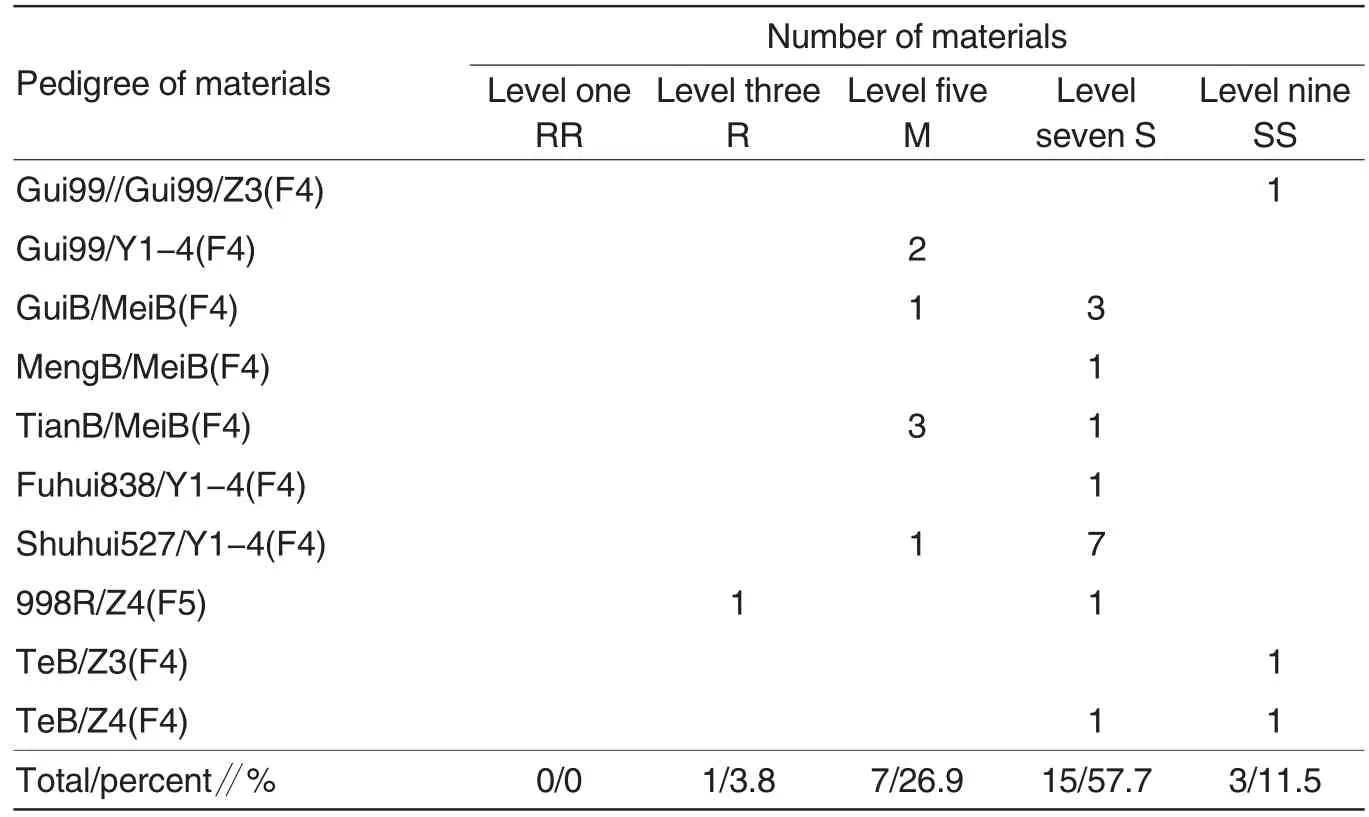
Table 5 The cold tolerance of the other lines
Advantage and disadvantage of cold tolerance at seedling stage identified under natural condition
It is a kind of economic and effective method conducting field identification and evaluation on cold tolerance of rice germplasm resources under natural condition.Using natural low temperature condition, cold tolerance of a large number of germplasm resources at different periods especially heading and flowering periods could be identified, which consumes little and saves time and power. Especially under rare extremely natural weather,cold tolerance of rice germplasm resources could be tested. But because occurrence intensity and time of natural low temperature have differences in different years, and it is not accurate enough to evaluate cold tolerance of germplasm according to an identified site and an identified result,the initially screened germplasm material with strong or extremely strong cold tolerance also needs multi identifications under artificial control.
Influence of weak light environment on rice seedling growth
Rice is a kind of light-loving crop.Weak light often causes insufficient sunlight, and photosynthetic productivity declines, which severely affects the formation of rice yield. Abnormal change of global climate causes that rainy and sparse light weather increases in some areas during rice growth period, and solar radiation decreases.Weak light could form adverse impact on rice growth. Each aspect of rice vegetative growth is affected by weak light, including plant height, tiller, root system, leaf and its stoma and chlorophyll.It is the most important that weak light affects accumulation and distribution of dry matter via photosynthesis,thereby causing that rice yield and quality decline[11]. Seen from the angle of yield, illumination condition has the smallest influence on vegetative growth stage, followed by latter period of young seedling development, and has the most influence on heading and seed setting periods. Even if vegetative growth is affected by adverse condition, and growth is bad, only if light condition at middle and latter periods of growth is good, certain high yield can also be obtained when reasonably using fertilizer and water, and sufficiently playing the role of illumination condition promoting spikelet per unit of area.
Conclusion
Using natural low temperature condition to conduct cold tolerance identification and evaluation of highquality rice germplasm resources, it could significantly distinguish highquality rice germplasm resources showing strong and weak cold tolerance at different growth periods.Identification method of cold tolerance under natural low temperature is especially suitable for cold tolerance screening and identification of a large number of rice germplasm resources or breeding materials[12]. The identified 10 parent materials with extremely strong cold tolerance could be used as donor of cold resistant gene in hybrid breeding of rice. For hybrid materials with strong cold tolerance, on one hand, they can be used as cold resistant breeding materials. On the other hand, they could be used to establish positioning group and find new cold resistant genes under control condition. Research results thought that cold resistant gene of japonica at seedling period was richer than that of indica. It is one of channels breeding cold resistant rice variety to use hybridization of wild rice resource with strong cold tolerance with indica and japonica.
[1]FU TL(傅泰露),MA J(马均),LI M(李敏),et al. Comprehensive evaluation and screening identification indexes of cold tolerance at seedling stage in rice (杂交水稻苗期耐冷性综合评价及其鉴定指标的筛选)[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences (西南农业学报),2009,22(3):608-614.
[2]YANG SM(杨树明),ZENG YW(曾亚文),DU J (杜娟),et al.Analysis on cold tolerance at seedling stage of the backcross hybrids of Indica with core collection for rice landrace in Yunnan (云南籼稻核心种质回交后代苗期耐冷性研究)[J]. Ecology and Environment (生态环境),2007,16(6):1754-1758.
[3]NISHIYAMA I.Effects of temperature on the vegetative growth of rice plants[C]//Proceedings of the symposium on climate and rice.Manila:IRRI,1976:159-185.
[4]LUO SY(罗世友),LIU HA(刘红安),WU WC (邬文昌),et al. Research advance in tolerance to cold of rice at seedling stage(水稻苗期耐冷性研究进展)[J].Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi (江西农业学报),2006,18(1):91-93.
[5]Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences(中国农业科学院). Chinese rice science(中国稻作学)[M].Beijing:Beijing Agricultural Press (北京: 北京农业出版社),1991.
[6]HE Y(何燕),GAO YZ(高永珍).Analysis of major agricultural meteorological dis-asters in Guangxi and disaster prevention and reduction countermeasures(广西主要农业气象灾害分析及防灾减灾对策)[J].Guangxi Agricultural Science (广西农业科学),1998(5):254-257.
[7]LIU XG (刘献刚).Influence of low temperature and chilling injury on rice yield and response measures(低温冷害对水稻产量的影响及应对措施)[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology(现代农业科技),2013(1):69-70.
[8]LIU GL (刘广林), CHEN CH (陈传华),LUO QC (罗群昌), et al. Preliminary identification and evaluation of high quality rice germplasm resources for cold tolerance under natural low temperatures during 2009 (自2009 年自然低温下优质稻种质资源耐冷性初步鉴定评价)[J]. Journal of Southern Agriculture(南方农业学报), 2012, 43(4): 407-412.
[9]ZHANG JH(张建华),LIAO XH(廖新华),DAI LY (戴陆园), et al. Evaluation on rice resources for cold tolerance at both budding stage and seedling stage(稻种资源芽期和苗期的耐冷性评价)[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin (中国农学通报),1996(5):10-13.
[10]CHEN DZ(陈大洲),XIAO YQ(肖叶青),PI YH(皮勇华),et al.The improvement of cold tolerance in Japonica rice(东乡野生稻耐冷性的遗传改良初步研究)[J].Acta Agriculturae Universitis Jiangxiensis (江西农业大学学报), 2003, 25(1):8-11.
[11]DU YX(杜彦修),JI X(季新),ZHANG J(张静),et al.Research progress on the impacts of low light intensity on rice growth and development (弱光对水稻生长发育影响研究进展)[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture(中国生态农业学报),2013,21(11):1307-1317.
[12]HAN LZ(韩龙植),ZHANG SY(张三元).Methods of characterization and evaluation of cold tolerance in rice(水稻耐冷性鉴定评价方法)[J].Journal of Plant Genetic Resources (植物遗传资源学报),2004,5(1):75-80.
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年10期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- Research Advances in Gene Regulation and Genetic Improvement of Fish Feeding
- Instrucions for Authors
- Cambridge Scientific Abstracts (CSA)
- Overview of Pharmaceutical Research on the Poria with Hostwood of Traditional Chinese Medicine
- Molecular Marker Assisted Selection for Fusarium Wilt Resistance Breeding in Watermelon(Citrullus lanatus)
- Study on Relative Soil and Water Conservation Benefits of Ridge Tillage in Different Terrain Conditions in the Black Soil Area of Northeast China
