曲伏前列素联合卡替洛尔对原发性闭角型青光眼患者术后高眼压的降压效果分析
张贵宁深圳市眼科医院药剂科,广东深圳 518040
曲伏前列素联合卡替洛尔对原发性闭角型青光眼患者术后高眼压的降压效果分析
张贵宁
深圳市眼科医院药剂科,广东深圳 518040
目的 研究曲伏前列素联合卡替洛尔对原发性闭角型青光眼(PAGG)患者术后高眼压的降压效果。方法 选择2012年4月~2013年4月在我院接受治疗的PACG患者64例(64只眼)作为研究对象。根据随机数字表法随机分成曲伏前列素组及卡替洛尔组两组,曲伏前列素组使用0.004%的曲伏前列素实施治疗,卡替洛尔组使用2%的卡替洛尔实施治疗,对比两组治疗前后的眼压变化情况,两组治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率,两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率。 结果 两组治疗后的眼压值均分别显著低于各组治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。但两组治疗前后的组间眼压值相比,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。曲伏前列素组治疗前后眼压差值与治疗后眼压下降的百分率均显著大于卡替洛尔组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。根据Spearman法分析相关性可知,治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率与前房角开放程度均无明显相关性。 结论 曲伏前列素与卡替洛尔均可用于降低PACG患者术后的高眼压,但曲伏前列素的药效更佳,值得在临床上推广应用。
曲伏前列素;卡替洛尔;原发性;闭角型青光眼;术后高眼压;降眼压作用
目前,使用激光周边虹膜切除手术或小梁切除术等方案治疗原发性闭角型青光眼(primary angleclosure glaucoma,PACG)在临床上已广泛应用,且疗效较好。但由于接受手术的部分患者术后可能有眼压升高的症状,形成残余型青光眼。需要接受药物再治疗,从而使患者的眼压维持在正常范围[1]。临床上,有诸多报道涉及使用前列腺素类药物对PACG的术后治疗情况[2],但关于曲伏前列素与卡替洛尔的疗效对比研究较少,本研究对此展开分析,以期寻找疗效更佳的药物。
1 资料与方法
1.1一般资料
选择2012年4月~2013年4月在我院接受治疗的PACG患者64例(64只眼)作为研究对象。男25例,女39例。年龄49~80岁,平均(64.3±2.5)岁。视力为0.12~1.2,平均(0.65±0.35)。纳入标准[3]:(1)手术后未经药物治疗或者经过药物的洗脱期后患者眼压>21mm Hg,同时≤35mm Hg者;(2)患者视力≥0.1者;(3)经裂隙灯检查显示角膜正常;(4)年龄≥40岁者。排除标准[4]:(1)PACG瞳孔阻滞未得到解除者;(2)激光周边虹膜切除手术后经前房角镜诊断显示患者未粘连前房角依旧狭窄,暗室超声活体显微镜显示有前房角的接触性关闭亦或是暗室试验呈阳性者;(3)有葡萄膜炎等其他类眼内病症者;(4)接受其他类内眼手术者;(5)含眼外伤病史者;(6)对研究药物发生过敏者;(7)严重的心血管系统等病症。根据随机数字表法随机分成曲伏前列素组及卡替洛尔组两组,每组各含32例(32只眼)。其中曲伏前列素组中含男13例,女19例。年龄49~76岁,平均(63.8±2.4)岁。视力为0.12~1.1,平均(0.63±0.21)。左眼18例,右眼14例。接受激光周边虹膜切除手术者16例,小梁切除术者16例。卡替洛尔组中含男12例,女20例。年龄50~80岁,平均(63.9±2.2)岁。视力为0.13~1.2,平均(0.64±0.25)。左眼15例,右眼17例。接受激光周边虹膜切除手术者18例,小梁切除术者14例。两组患者在性别、年龄、视力、患眼位置及手术类型等方面相比,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。具有可比性。
1.2研究方法
1.2.1前房角镜检查 依次对患者的上、下、鼻、颞等四个象限实施静态观察,选择Scheie分级法进行,将患者前房角分成宽角(W)及窄Ⅰ~Ⅳ级(N1~N4级)。而后根据动态检查技术,将可见巩膜突作为前房角是否开放的有关标准,对各方向的前房角开放情况及开放范围进行记录。
1.2.2药物治疗 曲伏前列素组使用0.004%的曲伏前列素实施治疗,1滴/次,1次/d,晚间用药。卡替洛尔组使用2%的卡替洛尔实施治疗,1滴/次,2次/d。分别在治疗前以及治疗1周后使用Goldmann眼压计测定患者的眼压,进行记录对比。
1.3观察指标
对比两组治疗前后的眼压变化情况,两组治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率,两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率。
1.4统计学方法
采用SPSS13.0统计软件进行统计学分析,计量资料以()表示,采用t检验,采用Spearman法分析相关性,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1两组治疗前后的眼压变化情况比较
两组治疗后的眼压值均分别显著低于各组治疗前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。但两组治疗前后的组间眼压值相比,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表1。
表1 两组治疗前后的眼压变化情况比较

表1 两组治疗前后的眼压变化情况比较
组别 n 治疗前 治疗后 t P曲伏前列素组 32 24.68±3.09 18.59±2.72 8.369 0.000卡替洛尔组 32 23.58±1.61 19.54±1.56 10.194 0.000 t 1.786 1.714 P 0.079 0.092
2.2两组治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率比较
曲伏前列素组的治疗前后眼压差值与治疗后眼压下降的百分率均显著大于卡替洛尔组,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。见表2。
表2 两组治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率比较
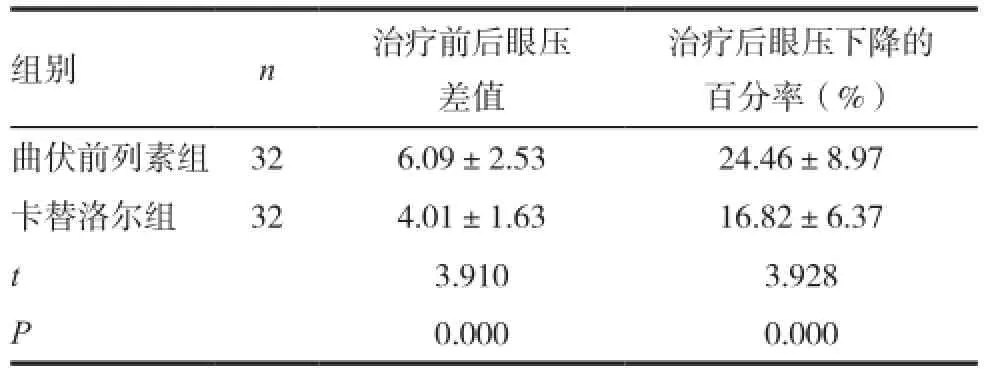
表2 两组治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率比较
治疗后眼压下降的百分率(%)曲伏前列素组 32 6.09±2.53 24.46±8.97卡替洛尔组 32 4.01±1.63 16.82±6.37 t 3.910 3.928 P 0.000 0.000组别 n 治疗前后眼压差值
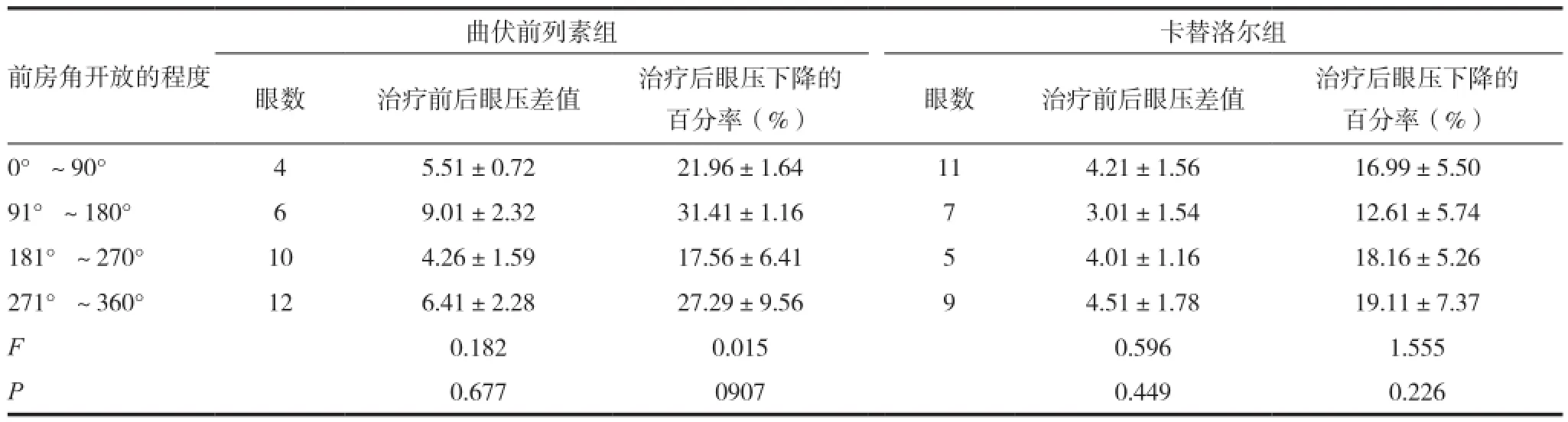
表3 两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率比较
2.3两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率比较
两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见表3。根据Spearman法分析相关性可知,治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率与前房角开放程度均无明显相关性(r=0.146,0.273,0.112,0.184;P=0.063,0.182,0.143,0.058)。
3 讨论
临床上,PACG患者一经确诊,则需尽快给予手术治疗,但手术后依然有部分患者会出现眼压上升的症状,给予此类患者药物治疗十分必要。关于前列腺素类药物治疗PACG手术后高眼压的报道,临床上较为多见[5]。但对于曲伏前列素以及卡替洛尔的对比治疗研究,则鲜有报道,本研究即通过对这两种药物在PACG术后高眼压的治疗效果进行对比分析,旨在选择更具疗效的临床治疗方案。
本研究发现,两组治疗后的眼压值均分别显著低于各组治疗前,但两组治疗前后的组间眼压值相比,差异均不显著。提示使用曲伏前列素或卡替洛尔治疗PACG术后高眼压,均可较好地降低眼压值,但单纯比较眼压值,无法区分二者间更具优势者。进一步研究发现,曲伏前列素组治疗前后眼压差值与治疗后眼压下降的百分率均显著大于对照组,这表明治疗前后利用眼压差值以及治疗后眼压下降的百分率,则可较好地判断曲伏前列素或卡替洛尔的疗效,本研究结果显示曲伏前列素的降眼压效果较卡替洛尔更佳,符合国外Yao等[6]的报道结果。究其原因,本研究认为这可能是因为曲伏前列素作为选择性的前列腺素FP型受体激动剂,在滴眼后,分子结构内α-与ω-碳链戊烯环能够协助其穿透患者的角膜,进而被酶分解成自由酸形式,使睫状肌及小梁网细胞内FP受体被激活,促进了基质金属蛋白酶的合成,此外,分解了睫状肌细胞外有关基质成分,增加其肌间隙,减少葡萄膜与巩膜有关房水外流主要途径的阻力,最终获得降压效果[7-9]。同时,曲伏前列素还可对小梁网细胞产生作用,增大患者压力敏感途径性房水流出,从而发挥降压效果。
本研究还发现,两组程度各异的前房角开放者治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率差异均不显著。且根据Spearman法分析相关性可知,治疗前后眼压差值及治疗后眼压下降的百分率与前房角开放程度均无明显相关性。表明前房角开放的程度对患者应用曲伏前列素或卡替洛尔治疗的疗效并无影响,满足国外Hong等[10-11]的报道结果,该报道指出,对实施手术治疗后的PACG患者,依照前房角的关闭程度,依次分成0~4个钟点,4~8个钟点,以及8~12个钟点进行关闭,在接受前列素眼液治疗后,患者眼压下降的百分率及眼压下降10%者的比例均无明显差异。原因可能在于手术后曲伏前列素作用在患者残余前房角开放处,而此区域只要获得一定程度的开放,即不会影响药效发挥[12]。亦或是药物经前房角以外处区域产生作用。但由于本研究样本量较少,这值得进一步大样本容量的深入研究。
综上所述,曲伏前列素与卡替洛尔均可用于降低PACG患者术后的高眼压,但曲伏前列素的药效更佳,值得在临床上推广应用。
[1] 张顺华,赵家良,刘小力,等.0.004%曲伏前列腺素滴眼液和2%毛果芸香碱滴眼液联合应用对正常兔降眼压效果的评价[J].中华实验眼科杂志,2012,30(9):774-778.
[2] Shin J,Jeon H,Byon IS,et al.Goniosynechialysis for secondary angle closure glaucoma in a pseudophakic patient after vitrectomy and silicone oil injection [J].Int J Ophthalmol,2014,7(5):914-916.
[3] Yan Y,Wu L,Wang X,et al.Appositional angle closure in Chinese with primary angle closure and primary angle closure glaucoma after laser peripheral iridotomy[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2014,16(1):426-427.
[4] Akal A,Kucuk A,Yalcin F,et al.Do we really need to panic in all acute vision loss in ICU?Acute angle-closure glaucoma[J].J Pak Med Assoc,2014,64(8):960-962.
[5] Prata Ts,Kanadani F,Simões R,et al.Angle-closure Glaucoma: treatment[J].Rev Assoc Med Bras,2014,60(4):295-297.
[6] Yao BQ,Pang YY,Li YX,et al.Effect of 0.004% travoprost and 2% carteolol on intraocular pressure in patients with ocular hypertension after laser peripheral iridotomy or trabeculectomy in primary angle-closure glaucoma[J]. Zhonghua Yan Ke Za Zhi,2013,49(4):340-344.
[7] 姚宝群,庞玉英,李祎馨,等.0.004%曲伏前列素与2%卡替洛尔对原发性闭角型青光眼术后高眼压的降眼压作用[J].中华眼科杂志,2013,49(4):340-344.
[8] Wu LL,Huang P,Gao YX,et al.A 12-week, doublemasked, parallel-group study of the safety and efficacy of travoprost 0.004% compared with pilocarpine 1% in Chinese patients with primary angle-closure and primary angleclosure glaucoma [J].J Glaucoma,2011,20(6):388-391.
[9] Brown RH,Zhong L,Whitman AL,et al.Reduced intraocular pressure after cataract surgery in patients with narrow angles and chronic angle-closure glaucoma[J].J Cataract Refract Surg,2014,40(10):1610-1614.
[10] Hong J,Yang Y,Wei A,et al.Schlemm's canal expands after trabeculectomy in patients with primary angleclosure glaucoma[J].Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci,2014,55(9):5637-5642.
[11] 朱研,杜立芳,邢怡桥,等.曲伏前列素治疗超声乳化术后的残余慢性闭角型青光眼[J].中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志,2010,10(4):227-228.
[12] Rajjoub LZ,Chadha N,Belyea DA,et al.Intermittent acute angle closure glaucoma and chronic angle closure following topiramate use with plateau iris configuration[J]. Clin Ophthalmol,2014,17(8):1351-1354.
Antihypertensive effect analysis of travoprost combined carteolol in the treatment of high intraocular pressure of primary angle closure glaucoma postoperative
ZHANG Guining
Pharmacy Department,Shenzhen Ophthalmic Hospital,Shenzhen 518040,China
Objective To investigate antihypertensive effect analysis of travoprost combined carteolol in the treatment of high intraocular pressure of primary angle closure glaucoma patients after operation. Methods 64 patients(64 eyes)with PACG from April 2012 to April 2013 to accept the treatment in our hospital as the research object.According to the figures were randomly divided into a travoprost group and a carteolol group,the travoprost group was used 0.004% travoprost for treatment,the carteolol group was used 2% carteolol for treatment,intraocular pressure changes before and after treatment,percentage between the two groups before and after treatment and after treatment of intraocular pressure difference of intraocular pressure drop,the percentage of two groups of varying degrees of anterior chamber angle open patients before and after intraocular pressure difference after treatment and intraocular pressure drop were compared. Results Intraocular pressure after the treatment in the two groups was significantly lower than the values of each group before treatment, the difference was statistically significant(P<0.05).But the two groups before and after treatment between the groups compared with intraocular pressure value,the differences were not statistically significant(P> 0.05).The percentage of travoprost group before and after treatment, intraocular pressure difference and intraocular pressure decreased after treatment were significantly higher than that in the control group,the difference was statistically significant(P< 0.05).The percentage difference between the two groups with different levels of anterior chamber angle open patients before and after intraocular pressure difference and intraocular pressure decreased after treatment had no statistical significance(P>0.05).According to correlation analysis showed that Spearman method,the percentage of anterior chamber intraocular pressure difference before and after treatment and after treatment and the degree of opening of the intraocular pressure decreased angle had no obvious correlation. Conclusion Travoprost and carteolol can be used to reduce the high intraocular pressure in patients with PACG after operation, but the travoprost effect is better,and it is worthy of clinical application.
Travoprost;Carteolol;Primary;Angle closure glaucoma;High intraocular pressure after surgery;Intraocular pressure lowering effect
R775.2
B
2095-0616(2015)11-54-04
广东省深圳市医疗卫生科研项目(201302082)。
(2015-03-03)

