复发性膀胱尿路上皮癌中IMP3和CD44蛋白表达*
李沐寒邢添瑛贺慧颖
·临床研究与应用·
复发性膀胱尿路上皮癌中IMP3和CD44蛋白表达*
李沐寒①邢添瑛②贺慧颖①
目的:评价IMP3和CD44蛋白在复发性膀胱癌中表达及二者的相关性。方法:收集2002年1月至2012年12月经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术诊断为尿路上皮癌(UC)的病例,其中筛选出6个月内短期复发组25例和3年以上较长期首次复发组29例。应用半定量免疫组织化学法检测短期复发组和较长期首次复发组UC病例中IMP3和CD44蛋白表达情况。结果:6个月内UC复发为25例,6例表达IMP3,且均为高级别UC。3年以上较长期首次UC复发为29例,仅有1例低级别UC表达IMP3。在短期复发组中IMP3阳性率为24%(6/25),表达强度为弱阳性16%(4/25)和强阳性8%(2/25),明显高于较长期首次复发组中阳性率3.45%(1/29)以及表达强度中的弱阳性3.45%(1/29)和强阳性0(0/29)。CD44蛋白表达在两组之间差异无统计学意义。IMP3表达与UC复发患者的肿瘤分期、分级呈正相关,而CD44表达与肿瘤的分级呈负相关。IMP3表达与CD44表达之间无明显相关性。结论:IMP3在UC短期复发组中的表达明显高于较长期首次复发组。IMP3可作为新的指标,并联合肿瘤病理分期、分级等因素对膀胱UC患者经尿道肿瘤电切术后短期复发的高危性进行预测。
膀胱尿路上皮癌 复发 IMP3 CD44 免疫组织化学法
膀胱癌是泌尿系统中最常见的恶性肿瘤,其中90%以上为尿路上皮癌(urothelial carcinoma,UC)。2015年美国预测新发膀胱癌患者74 000例,死亡16 000例。男性癌症发病率中膀胱癌已上升至第4
位,死亡率为第8位[1]。在我国,2008年全国肿瘤登记地区膀胱癌发病率为7.49/10万,居中国恶性肿瘤发病率第8位,并呈逐年增长趋势,10年间的年均增长率为4.60%[2]。膀胱UC的显著特点是初发多为非浸润性且复发率高,越早发生复发的肿瘤越易进展,预后较差。目前预测膀胱UC复发的指征包括肿瘤的病理分期、分级、是否为多发肿瘤、肿瘤大小、手术方式、联合化疗药物等[3-4],但这些都有其局限性,不能准确的预测个体复发情况。因此对参与膀胱UC复发的相关分子的研究具有重要临床意义,能够为临床综合判断预后及个体化治疗提供依据。
胰岛素样生长因子ⅡmRNA结合蛋白(insulinlike growth factorⅡmessenger RNA binding proteins,IMPs)是一类mRNA结合蛋白,能影响靶基因mRNA的定位、转运和稳定性,包括IMP1、IMP2和IMP3。近年来的研究发现IMP3在众多类型的肿瘤组织中高表达,而在成人良性组织中低表达或不表达,因此被称为癌胚蛋白[5],提示IMP3参与多种肿瘤的发生和发展。已有研究显示IMP3可以作为膀胱UC一个独立的不良预后指标[6],但IMP3在复发性膀胱UC中的表达尚不清楚。CD44作为一种重要的细胞黏附分子,同时也是IMP3重要的靶分子之一,在膀胱癌中的报道不一,在我国复发性膀胱UC中的表达水平如何鲜有报道。因此本研究对IMP3和CD44在复发性膀胱UC的表达情况及二者之间有无相关性进行探讨。
1 材料与方法
1.1研究材料
选取北京大学第三医院病理科2002年1月至2012年12月期间经尿道膀胱肿瘤电切术中诊断为短期内复发(<6个月)和较长期首次复发(>3年以上)UC病例。由1位泌尿病理医生重新阅片并进行组织学评级,为避免肿瘤分期不准确,标本中未见固有肌的病例均去除。6个月内短期复发组25例,3年以上较长期首次复发组29例列入本研究。54例复发性膀胱UC中男性42例,女性12例;年龄39~84岁,平均年龄65.7岁。组织切片标本根据世界卫生组织/国际泌尿病理学会(2004年)最新pT分期,其中Ta为30例,T1为14例,T2为10例。病理学分级中低级别28例,高级别26例。本研究获得伦理委员会认可。
1.2试剂和方法
石蜡切片免疫组织化学法染色(Envision二步法)具体步骤如下:1)石蜡切片脱蜡水化;2)自来水冲洗2 min,蒸馏水冲洗2次;3)抗原修复(抗原修复液pH为6.0),水浴锅煮沸20 min之后自然冷却至室温;4)3%H2O2封闭内源性过氧化物酶,室温下30 min;5)PBS缓冲液冲洗3次,每次5 min;6)分别加入购于美国Corixa公司的IMP3鼠单克隆抗体和购于美国Abcam公司的CD44兔单克隆抗体,稀释度均为1:100,4℃冰箱中过夜;7)PBS缓冲液冲洗3次,每次3 min;8)滴加北京中杉金桥公司PV9000两步法试剂盒二抗,分别室温孵育30 min;9)PBS缓冲液冲洗3次,每次5 min;10)美国DAKO公司DAB显色3 min,Mayer's苏木精复染细胞核,逐级酒精脱水,二甲苯透明,中性树胶封片。
1.3结果判断
实验中以PBS代替IMP3和CD44抗体作为阴性对照,分别由两名高级病理医师在光镜下观察染色切片,两者判定结果符合率百分之百。IMP3阳性定位于细胞质,CD44阳性定位于细胞膜。本研究采用半定量的方法对切片免疫组织化学法的染色强度进行评分:无色为0分,浅黄色1分,棕黄色2分,棕褐色3分;再按阳性细胞所占百分比评分:阳性细胞<5%为0分,5%~25%为1分,26%~50%为2分,51%~75%为3分,>76%为4分。将染色程度和阳性细胞百分比的乘积进行评分:0分为阴性(-),<6分为弱阳性,≥6分为强阳性。
1.4统计学分析
采用SAS 9.1统计软件进行处理。计数资料行多独立样本的非参数分析(Kruskcal-Wallis检验)和Spearman相关性检验,计量资料采用单因素方差分析。P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1IMP3和CD44蛋白在复发性膀胱UC中表达特点
IMP3主要在肿瘤组织的细胞质内表达,癌旁组织中无表达(图1)。选取的54例复发性膀胱UC组织中IMP3总阳性表达率为12.96%(7/54),其中9.26%(5/54)弱表达、3.70%(2/54)强表达。6个月内短期复发组25例中高、低级别UC分别为20、5例,25例中IMP3表达占24%(6/25)、均为高级别UC。3年以上较长期首次复发组29例中高、低级别UC分别为6、23例,IMP3表达仅占3.45%(1/29)。IMP3阳性率及表达强度在短期复发组明显高于较长期首次复发组(P=0.024 7,表1)。
CD44蛋白在正常膀胱黏膜基底细胞层强表达,但在表层的尿路上皮细胞无表达,其在膀胱UC中主要在肿瘤组织的细胞膜上表达,同时间质、淋巴细胞和平滑肌也可呈强阳性。54例复发性膀胱UC中CD44阳性率为48.15%(26/54),其中29.63%(16/54)弱表达、18.52%(10/54)强表达(图2)。CD44表达在短期复发组和较长期首次复发组间差异无统计学意义(P=0.237 4,表1)。

图1 复发性膀胱UC中IMP3表达(Envision法×200)Figure 1Expression of IMP3 in recurrent UC of bladder(Envision×200)

表1 短期复发组和较长期首次复发组中IMP3和CD44蛋白表达Table 1Expression of IMP3 and CD44 proteins in the short-term and long-term recurrent groups

图2 复发性膀胱UC中CD44表达(Envision法×200)Figure 2Expression of CD44 in recurrent UC of bladder(Envision×200)
2.2IMP3蛋白表达与膀胱UC患者临床病理特征关系
IMP3阴性、弱阳性和强阳性患者的年龄分别为(65.64±10.03)岁、(61.2±8.53)岁和(69±5.66)岁。IMP3蛋白表达与膀胱UC pT分期(P=0.017 1)和分级(P=0.027 9)呈正相关,即分期、分级越高,IMP3阳性强度越高,而与患者的年龄、性别无相关性(P>0.05,表2)。

表2 IMP3蛋白表达与复发性膀胱UC患者临床病理特征关系Table 2Relationship between the IMP3 protein expression and various clinicopathologic features in the recurrent UC patients
2.3CD44蛋白表达与膀胱UC患者临床病理特征关系
CD44阴性、弱阳性和强阳性患者的年龄分别为(66.64±10.03)岁、(65.47±10.73)岁和(64.81±11.78)岁。CD44蛋白表达与年龄、性别和T分期无相关性(P>0.05),但与病理分级呈负相关,即病理分级越高CD44阳性强度越低(P=0.000 3,表3)。
2.4IMP3与CD44蛋白在复发膀胱UC中表达的相关性
复发性膀胱UC中,7例IMP3阳性表达的患者中5例CD44不表达,IMP3与CD44之间并不存在相关性(P=0.199 0,表4)。

表2 IMP3蛋白表达与复发性膀胱UC患者临床病理特征间的关系(续表2)Table 2Relationship between the IMP3 protein expression and various clinicopathologic features in the recurrent UC patients

表3 CD44蛋白表达与复发性膀胱UC患者临床病理特征关系Table 3Relationship between CD44 protein expression and various clinicopathologic features in the recurrent UC patients
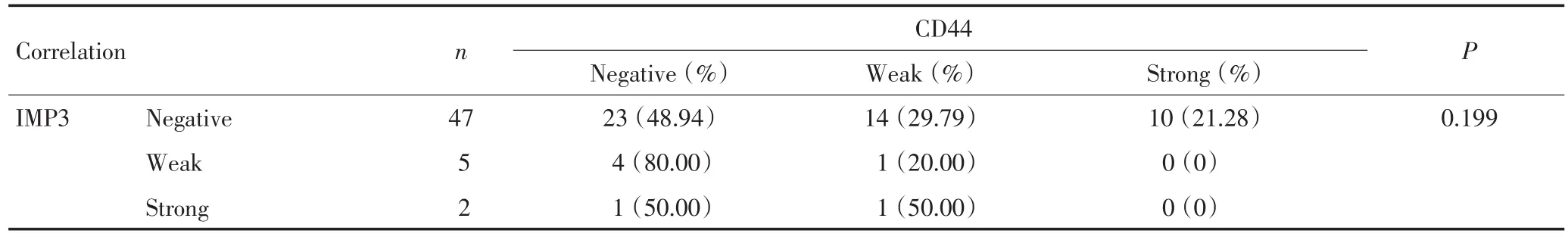
表4 复发性膀胱UC中IMP3与CD44的相关性Table 4Correlation between the expression of IMP3 and CD44 proteins in recurrent UC patients
3 讨论
IMP3在多种恶性肿瘤中过表达,且与部分肿瘤的早期复发有关,如胃癌[7]、上尿道UC[8]等。IMP3在膀胱UC中的表达情况虽有一些报道,但表达率差别较大。Sitnikova等[6]研究表明在浅表性膀胱UC中IMP3表达的阳性率为19.6%,而在转移性膀胱UC中的阳性率高达93%。我国何学军等[9]报道,在膀胱UC活检、部分和全切标本中IMP3阳性率为62.5%(33/48),且IMP3在浅表组(46.15%)、低级别组(46.43%)中的表达明显低于其在固有肌层浸润组(81.82%)、高级别组(85.00%)中的表达。本研究发现,在复发性膀胱UC活检标本中IMP3表达率较低,仅12.96%(7/54)且基本上都表达于短期复发的高级别膀胱UC患者中。本研究短期复发组的25例患者中16例未发生固有肌层浸润,其中Ta期10例、T1期6例,5例为低级别,说明只根据分期、分级很难准确预测患者的短期复发情况。本研究表明,在复发性膀胱UC患者中IMP3表达与肿瘤病理分期、分级呈正相关,且表达率和表达强度在短期复发组中要高于较长期首次复发组患者。
IMP3是一种mRNA结合蛋白,Vikesaa等[10]报道在HeLa细胞中IMP3可以结合到CD44 mRNA上使其表达稳定,从而增强HeLa细胞的黏附能力,促进侵袭伪足的形成。在肝癌中的研究发现IMP3可以联合标
准型CD44(CD44s)作为判断患者预后的新指标,两者共同高表达预示患者的不良预后[11]。Szarvas等[12]报道在侵袭性膀胱UC中IMP3蛋白的表达预示着预后不良且与CD44蛋白并无直接关系。CD44蛋白在膀胱UC中的研究结果差别较大,主要集中在CD44s和变异性CD44(CD44v6)上。Lipponen等[13]研究表明CD44s在膀胱UC肿瘤细胞非基底层的表达增强与不良预后有关,而在基底层和非基底层CD44v6高表达的患者生存率较高,但Sugino等[14]认为在早期膀胱UC中CD44基因高表达,而其丢失与肿瘤细胞获得侵袭性相关,Matuschek等[15]则认为CD44s mRNA高表达和CD44v6 mRNA低表达与良好预后相关。本研究表明,在我国复发性膀胱UC中,CD44表达与肿瘤病理分级呈负相关,但在短期复发和较长期首次复发两组患者中的表达并无差别,并且与IMP3表达无相关性。在膀胱UC中IMP3作用的分子机制很可能不是通过结合CD44 mRNA来发挥的。
综上所述,IMP3可以作为新的指标联合肿瘤病理分期、分级等因素共同预测膀胱UC患者经尿道肿瘤电切术后短期复发的高危性,但IMP3作用的具体分子机制还有待进一步探究。
[1]Siegel RL,Miller KD,Jemal A.Cancer statistics,2015[J].CA Can⁃cer J Clin,2015,65(1):5-29.
[2]Han SJ,Zhang SW,Chen WQ,et al.Analysis of the status and trends of bladder cancer incidence in China[J].Oncology Prog⁃ress,2013,11(1):89-95.[韩苏军,张思维,陈万青,等.中国膀胱癌发病现状及流行趋势分析[J].癌症进展,2013,11(1):89-95.]
[3]Witjes JA,Compérat E,Cowan NC,et al.EAU guidelines on muscle-invasive and metastatic bladder cancer:summary of the 2013 guidelines[J].Eur Urol,2014,65(4):778-792.
[4]Babjuk M,Burger M,Zigeuner R,et al.EAU Guidelines on non -muscle-invasive urothelial carcinoma of the bladder:update 2013[J].Eur Urol,2013,64(4):639-653.
[5]Yaniv K,Yisraeli JK.The involvement of a conserved family of RNA binding proteins in embryonic development and carcino⁃genesis[J].Gene,2002,287(1-2):49-54.
[6]Sitnikova L,Mendese G,Liu Q,et al.IMP3 predicts aggressive superficial urothelial carcinoma of the bladder[J].Clin Cancer Res,2008,14(6):1701-1706.
[7]Okada K,Fujiwara Y,Nakamura Y,et al.Oncofetal protein,IMP-3,a potential marker for prediction of postoperative perito⁃neal dissemination in gastric adenocarcinoma[J].J Surg Oncol,2012,105(8):780-785.
[8]Lee DJ,Xylinas E,Rieken M,et al.Insulin-like growth factor messenger RNA-binding protein 3 expression helps prognostica⁃tion in patients with upper tract urothelial carcinoma[J].Eur Urol,2014,66(2):379-385.
[9]He XJ,Liu WG,She SY,et al.Expression of insulin-like growth factor II mRNA-binding protein 3 in transitional cell carcinoma of the bladder and its clinical significance[J].Clin Med China,2011,27(1):82-85.[何学军,刘文刚,佘绍逸,等.胰岛素样生长因子II mRNA结合蛋白3在膀胱移行细胞癌的表达及意义[J].中国综合临床杂志,2011,27(1):82-85.]
[10]Vikesaa J,Hansen TV,Jønson L,et al.RNA-binding IMPs pro⁃mote cell adhesion and invadopodia formation[J].EMBO J,2006,25(7):1456-1468.
[11]Hu S,Wu X,Zhou B,et al.IMP3 combined with CD44s,a nov⁃el predictor for prognosis of patients with hepatocellular carcino⁃ma[J].J Cancer Res Clin Oncol,2014,140(6):883-893.
[12]Szarvas T,vom Dorp F,Niedworok C,et al.High insulin-like growth factor mRNA-binding protein 3(IMP3)protein expres⁃sion is associated with poor survival in muscle-invasive bladder cancer[J].BJU Int,2012,110(6 Pt B):E308-317.
[13]Lipponen P,Aaltoma S,Kosma VM,et al.Expression of CD44 standard and variant-v6 proteins in transitional cell bladder tu⁃mours and their relation to prognosis during a long-term fol⁃low-up[J].J Pathol,1998,186(2):157-164.
[14]Sugino T,Gorham H,Yoshida K,et al.Progressive loss of CD44 gene expression in invasive bladder cancer[J].Am J Pathol,1996,149(3):873-882.
[15]Matuschek C,Lehnhardt M,Gerber PA,et al.Increased CD44s and decreased CD44v6 RNA expression are associated with bet⁃ter survival in myxofibrosarcoma patients:a pilot study[J].Eur J Med Res,2014,19:6.
(2014-12-26收稿)
(2015-03-30修回)
IMP3 and CD44 protein expression in recurrent bladder urothelial carcinoma
Muhan LI1,Tianying XING2,Huiying HE1
Huiying HE;E-mail:huiyinghe@bjmu.edu.cn
Objective:To evaluate the expression of IMP3 and CD44 proteins in recurrent urothelial carcinoma(UC)and to determine the correlation between the two proteins.Methods:Data from transurethral resection of bladder(TURB)cancer cases between January 2002 and December 2012 were reviewed.Of the 54 UC recurrent cases in this study,one group of 25 had experienced recurrence within 6 months after surgery,and the other group of 29 had their first recurrence after more than 3 years.IMP3 and CD44 immunoreactivities were increased,which correlated with the clinicopathologic parameters.The relationship between IMP3 and CD44 protein expressions was also explored.Results:Six of the 25 short-term recurrent UC cases were tested positive for IMP3 and all belonged to high-grade UC.Among the 29 long-term recurrent patients,only one case of low-grade UC tested positive for IMP3.IMP3 expression rate[24%(6/25)]and intensity[weak staining at 16%(4/25)and strong staining at 8%(2/25)]were higher in the short-term recurrent group than those in the long-term group,which had an expression rate of 3.45%(1/29)and intensity rates for weak staining at 3.45%(1/29)and without strong staining(0/29).No difference was observed in the CD44 expression between the two groups.In addition,the high expression of IMP3 correlated with higher tumor stage and grade,whereas the CD44 expression tended to be inversely correlated with the tumor grade in recurrent UC patients.Furthermore,no correlation existed between the expression of IMP3 and CD44 proteins in the bladder carcinoma specimens.Conclusion:IMP3 exhibited a significantly higher expression rate in short-term recurrent UC specimens than in the long-term recurrent cases.Therefore,IMP3 could be used as a novel marker,together with the other factors including tumor stage and grade,for predicting the high risk of short-term recurrence in UC patients who underwent TURB.
urothelial carcinoma of bladder,recurrence,IMP3,CD44,immunohistochemistry

10.3969/j.issn.1000-8179.20142132
①北京大学医学部基础医学院病理学系(北京市100191);②北京大学第三医院泌尿外科
*本文课题受国家自然科学青年科学基金项目(编号:81001135)资助
贺慧颖huiyinghe@bjmu.edu.cn
1Department of Pathology,Peking University School of Basic Medical Science,and2Department of Urology,The Third Hospital of Peking University,Beijing 100191,China
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China for Young Investigators(No.81001135)
李沐寒专业方向为泌尿男性生殖系统肿瘤进展分子机制。
E-mail:limuhan8816@163.com

