18F-FDG PET/CT显像在食管癌分期时发现同时性重复癌的价值
周雯,朱湘,王健,徐文贵
(1.天津医科大学药学院,天津市临床药物关键技术重点实验室,天津 300070;2.天津医科大学肿瘤医院分子影像及核医学诊疗科,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市“肿瘤防治”重点实验室,天津 300060)
18F-FDG PET/CT显像在食管癌分期时发现同时性重复癌的价值
周雯1,朱湘2,王健2,徐文贵2
(1.天津医科大学药学院,天津市临床药物关键技术重点实验室,天津 300070;2.天津医科大学肿瘤医院分子影像及核医学诊疗科,国家肿瘤临床医学研究中心,天津市“肿瘤防治”重点实验室,天津 300060)
目的:探讨18F-FDG PET/CT显像在食管癌分期时发现同时性重复癌的价值。方法:回顾性研究171例病理证实的食管癌患者应用18F-FDG PET/CT显像进行分期的影像资料,位于食管癌常见转移部位以外的18F-FDG代谢增高灶,或代谢方式和程度与原发灶明显不一致者,首先考虑同时性重复癌,并根据病灶部位经手术、内镜或穿刺活检等获得病理学结果。结果:171例病理证实的食管癌患者中,病理诊断重复癌35例,其中18F-FDG PET/CT和病理共同诊断阳性的重复癌33例,部位依次为下咽癌14例、肺癌8例、胃癌6例、舌癌2例、乙状结肠癌1例、口咽癌1例,还有1例同时发现乙状结肠癌及胃癌。18F-FDG PET/CT诊断重复癌的灵敏度为94.3%,特异性为94.2%,准确性为94.2%。结论:应用18F-FDG PET/CT显像进行食管癌分期时可以有效发现同时性重复癌,显像阳性患者术前必须进一步明确病变的性质,将会直接影响治疗计划和预后。
食管癌;PET/CT;重复癌;分期
食管癌的5年平均生存率比较低,其分期对预后预测具有重要价值,I期患者的5年生存率>60%,而IV期患者的5年生存率<20%。尽管早期食管癌是可以治愈的,但同时发生的重复癌可能会影响治疗的决策。先前的研究显示食管癌患者发生同时性重复癌并不常见,约为4.3%~11.6%[1]。18F-FDG PET/CT显像已广泛用于食管癌的分期和疗效评价,其在检测食管癌患者远处转移方面较常规影像学具有明显优势,直接影响治疗方案的选择,同时增加了同时性重复癌的检出,目前相关报道尚不多[2-5]。本研究旨在探讨应用18F-FDG PET/CT显像对食管癌术前分期时发现意外同时性重复癌的价值。
1 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料回顾性分析天津医科大学肿瘤医院PET/CT中心2005年4月-2012年12月期间171例病理证实的食管癌患者的18F-FDGPET/CT的影像资料,其中男158例,女13例,年龄36~85岁[(65.38±9.77)岁]。所有患者均未进行食管癌相关的治疗,并于检查前签订18F-FDG PET/CT检查知情同意书。
1.2 方法
1.2.1 显像剂及显像仪器18F-FDG采用美国GE MINItrace回旋加速器自行生产,放化纯度>95%。全身显像采用美国GE Discovery ST PET/CT仪。
1.2.2 检查方法患者于检查前空腹4~6 h,控制其血糖水平<8 mmol/L,安静休息15 min后,于手臂静脉注射18F-FDG,剂量为0.1~0.13 mCi/kg(3.7~4.81 MBq/kg)。期间每15 min口服1.5%造影剂(泛影葡胺)约500 mL,注药后1 h排空膀胱后上机扫描前再次口服500~800 mL对比剂,保持胃壁扩张上机扫描。静卧45~60 min排尿后行全身PET/CT扫描。自颅顶至股骨上端首先行螺旋CT扫描,采集条件:电压120 kV、电流160~200 mA、螺距0.75、球管单圈旋转时间0.8 s;再行3D方式PET全身断层显像,每个床位采集3 min,共6~7个床位。横断面图像用与发射显像同层的CT横断图像进行衰减校正,PET图像重建采用迭代重建的有序子集最大期望值法进行,30个子集,2次迭代。重建图像在XELERIS工作站上与CT图像进行融合,分别得到冠状、矢状、横断面CT、PET及PET/CT融合图像。
1.3 图像分析两名PET/CT医生独立读片分析形成报告,意见不一致时,协商讨论确定结果达到统一。显像上位于食管癌常见转移部位以外的18FFDG代谢增高灶,或代谢的形态和程度与原发食管癌明显不一致者,首先考虑同时性重复癌,并根据病灶部位经手术、内镜或穿刺活检等方法获得病理学结果。根据文献[6]报道的重复癌的诊断依据,(1)每一种肿瘤都是恶性的;(2)各种肿瘤发生于不同部位,彼此独立存在;(3)每种肿瘤都有其形态结构特征,各自的转移途径;(4)除外复发和转移,病理诊断为转移灶的病例未纳入重复癌计数。
1.4 随访可疑同时性重复癌于18F-FDG PET/CT显像后一月内进一步获得病理学诊断。
2 结果
2.1171 例病理证实的食管癌患者临床特征如下
按部位分,发生于食管上段者49例(49/171,28.7%),中段者85例(85/171,49.7%),下段者37例(37/ 171,21.6%);按TNM临床分期分,Ⅰ期46例(46/ 171,26.9%),Ⅱ期59例(59/171,34.5%),Ⅲ期41例(41/171,24.0%),Ⅳ期25例(25/171,14.6%);按病理组织类型分,鳞癌162例(162/171,94.7%),腺癌9例(9/171,5.3%);其中伴发重复癌并经病理学确诊的重复癌33例(33/171,19.3%),发生的部位依次为下咽癌14例、胃癌6例、舌癌2例(图1)、肺癌8例(图2)、乙状结肠癌1例、口咽癌1例,还有1例同时发现乙状结肠癌及胃癌。4例假阳性,其中2例甲状腺高代谢结节,病理证实为甲状腺腺瘤;2例乙状结肠高代谢结节,肠镜病理证实1例为息肉,1例为管状腺瘤(癌前病变)。

图1 食管癌合并舌癌18F-FDG PET/CT显像图Fig 118F-FDG PET/CT imaging of esophageal cancer combined with tongue cancer

图2 食管癌合并左肺癌18F-FDG PET/CT显像图Fig 218F-FDG PET/CT imaging of esophageal cancer combined with left lung cancer
2.2 随访结果171例食管癌患者,36人因死亡等原因失访;68人18F-FDG PET/CT可疑重复癌患者37人进一步获得病理学结果,31人未行病理学检查;余67人经临床和常规影像学随访,2人增强CT分别诊断为肝癌、肾癌并进一步经手术病理证实(表1)。本研究PET/CT诊断重复癌的灵敏度为94.3%,特异性为94.2%,准确性为94.2%。
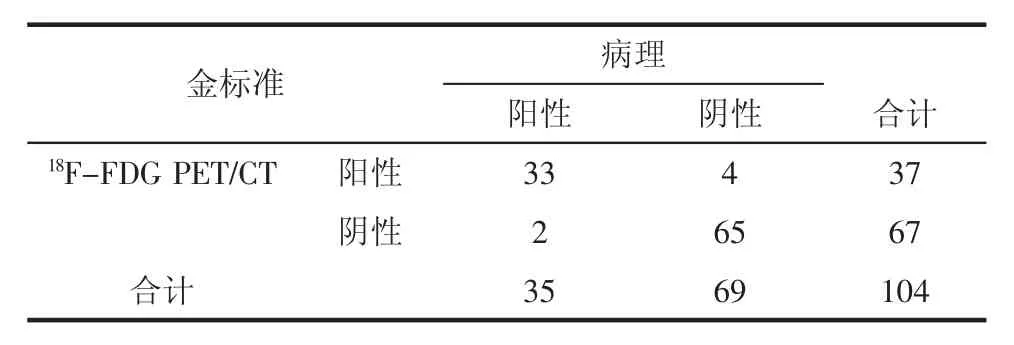
表1 18F-FDG PET/CT诊断重复癌的病理对照结果(n)Tab 1Pathology results of repeat cancer diagnosed by18F-FDG PET/CT
3 讨论
随着影像学技术的不断改进和提高,18F-FDG PET/CT显像在许多肿瘤的评价和疗效判定方面应用越来越多,在检测食管癌患者远处转移方面较常规影像学具有明显的优势,直接影响治疗方案,因此食管癌术前评价发现同时性重复癌的机会也越来越多。新西兰、英国、爱尔兰等国家的学者都针对18F-FDG PET/CT显像发现食管癌的同时性重复癌方面进行了报道[2-4],但西方国家的食管癌病理上主要为腺癌,重复癌多发生于结肠,而在我国等亚洲国家,鳞癌是食管癌的主要病理类型,重复癌的分布有所不同。转移灶与重复癌单纯从影像上难以完全鉴别,本研究依据出现在食管癌常见转移部位以外的高代谢病灶,或其代谢方式和程度与原发病灶明显不一致,初步疑诊为同时性重复癌,最后依据病理学诊断[5-6]。
本研究结果显示食管鳞癌患者最常见的同时性重复癌为头颈部恶性肿瘤,其次为胃癌、肺癌等,与先前日本和香港的研究相一致[1、7-8]。头颈部肿瘤、肺癌和食管癌的黏膜上皮暴露于同样的致癌因素中,导致这些部位容易发生多源癌。众所周知,吸烟、饮酒是食管癌的危险因素[9],且酒精的作用大于吸烟[10],而酒精同时也是头颈部肿瘤、食管癌、胃癌和结肠癌的公认的重要危险因素[11]。饮酒人群患癌危险增高可能与酒精的氧化、甲醛化的代谢过程有关,其中乙醛脱氢酶是这一过程的关键酶,决定了酒精的代谢速度,而且这种酶的活性高低与遗传密切相关。这一观察结果可以解释食管癌和头颈部肿瘤、胃肠道肿瘤之间的密切联系。
尽管18F-FDG PET/CT显像有助于明确可治愈的同时性重复癌,但其与转移癌在影像上难以完全鉴别,依据病灶的部位(食管癌常见转移部位以外)、浓聚的形态和程度,可以进行初步的筛查,最后结果仍旧依赖于病理学检查。同时18F-FDG并非肿瘤特异性显像剂,它的摄取并非总能提示恶性病灶,例如胃食管交界区经常有生理性18F-FDG摄取,而且假阳性也可能是头颈部的淋巴组织增生。最常见的假阳性部位为结肠和甲状腺。结肠的生理性18F-FDG摄取并不少见,可能与其持续蠕动、淋巴组织丰富、结肠壁的白细胞较多有关[12],且结肠的良性疾病和癌前病变、结肠腺瘤和结肠癌之间的SUVmax并无显著差异。甲状腺的18F-FDG摄取约占1.2%~4%,其中恶性病变占14%~47%[13]。但18FFDG PET/CT显像阳性患者在食管癌术前仍必须进一步明确意外高代谢病变的性质,如超声、细针穿刺活检,因为同时性重复癌也可能误诊为转移。重复癌的明确诊断将会直接影响治疗计划和预后,尤其无症状的癌前病变的明确更为重要,虽然不会改变治疗计划和预后,但更具有实际价值,尤其是对于可治愈的食管癌[14]。
本研究亦存在一定的局限性,一些重复癌可能在代谢方式和程度上与食管癌接近,也可以位于常见的转移肿瘤部位,而且本研究所纳入患者未能全部进行腹部增强CT和MRI检查,可能低估了肝癌、肾癌、前列腺癌导致18F-FDG PET/CT假阴性的情况,从而会导致低估食管癌发生同时性重复癌的比例;另外病例数尚较少,且为回顾性研究。综上,应用18F-FDG PET/CT显像进行食管癌分期时可以有效发现同时性重复癌,可以影响进一步治疗方案的选择和患者的预后。
[1]Chen S H,Chan S C,Chao Y K,et al.Detection of synchronous cancersbyfluorodeoxyglucosepositronemissiontomography/ computed tomography during primary staging workup for esophageal squamous cell carcinoma in Taiwan[J].PLoS One,2013,8(11): e8281
[2]Papajík T,Mysliveek M,Sedová Z,et al.Synchronous second primary neoplasms detected by initial staging F-18FDG-PET/CT examination in patients with non-Hodgkin lymphoma[J].Clin Nucl Med,2011,36(7):509
[3]Vyas S,Markar S R,Iordanidou L,et al.The role of integrated F-18-FDG-PET scanning in the detection of M1 disease in oesophageal adenocarcinoma and impact on clinical management[J]. J Gastrointest Surg,2011,15(12):2127
[4]Malik V,Johnston C,Donohoe C,et al.F-18-FDG PET-Detected synchronous primary neoplasms in the staging of esophageal Cancer incidence,cost,and impact on management[J].Clin Nucl Med,2012,37 (12):1152
[5]Choi J Y,Lee K S,Kwon O J,et al.Improved detection of second primary Cancer using integrated[F-18]fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography and computed tomography for initial tumor staging[J].J Clin Oncol,2005,23(30):7654
[6]Hsieh T C,Wu Y C,Sun S S,et al.Synchronous squamous cell carcinomas of the esophagus and renal pelvis[J].Clin Nucl Med,2011,36(11):e171
[7]Kondo N,Tsukuda M,Nishimura G.Diagnostic sensitivity of 18fluorodeoxyglucosepositronemissiontomographyfor detectingsynchronous multiple primary cancers in head and neck cancer patients[J].Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol,2012,269(5):1503
[8]Natsugoe S,Matsumoto M,Okumura H,et al.Multiple primary carcinomaswithesophagealsquamouscellCancer: Clinicopathologic outcome[J].World J Surg,2005,29(1):46
[9]Lin Y S,Totsuka Y,He Yt,et al.Epidemiology of esophageal cancer in Japan and China[J].J Epidemiol,2013,23(4):233
[10]Wu I C,Lu C Y,Kuo F C,et al.Interaction between cigarette,alcohol and betel nut use on esophageal cancer risk in Taiwan[J]. Eur J Clin Invest,2006,36(4):236
[11]Oze I,Matsuo K,Suzuki T,et al.Impact of multiple alcohol dehydrogenase gene polymorphisms on risk of upper aerodigestive tract cancers in a Japanese population[J].Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev,2009,18(11):3097
[12]Grassi I,Castellucci P,Nanni C,et al.Incidental detected increased FDG uptake in bowel and its correlation with histopathological data: our experience in a case series study[J].Curr Radiopharm,2014,7 (2):107
[13]Izumiya M,Yamagishi Y,Nakamura S,et al.A case of metastatic esophageal cancer-endoscopic resection of the primary site following systemic chemotherapies[J].Gan To Kagaku Ryoho,2011,38(7):1167
[14]Yabuki K,Kubota A,Horiuchi C,et al.Limitations of PET and PET/ CT in detecting upper gastrointestinal synchronous cancer in patients with head and neck carcinoma[J].Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol,2013,270(2):727
(2015-06-01收稿)
Value of18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting synchronous primary neoplasms for initial stage of esophageal cancer
ZHOU Wen1,ZHU Xiang2,WANG Jian2,XU Wen-gui2
(1.School of Pharmacy,Tianjin Medical University,Tianjin Key Laboratory on Technologies Enabling Development of Clinical Therapeutics and Diagnostics(Theranostics),Tianjin 300070,China;2.Department of Molecular Imaging and Nuclear Medicine,Cancer Institute and Hospital,Tianjin Medical University,National Clinical Research Center for Cancer,Key Laboratory of Cancer Prevention and Therapy,Tianjin 300060,China)
Objective:To determine the additional clinical value of18F-FDG PET/CT in detecting synchronous neoplasms in initial stage of esophageal cancer.Methods:171 patients with biopsy-proven malignancy of the esophagus underwent18F-FDG PET for initial stage. Synchronous malignancies were defined by abnormal18F-FDG uptake on18FDG-PET which was unlikely due to distant metastases from the primary esophageal lesion depending on intensity and pattern,and confirmed by pathology.Results:Thirty-five synchronous primary neoplasms were identified in 171 patients and 33 neoplasms were PET/CT-positive.Among them.14 neoplasms were discovered in the laryngeal pharynx,8 in the lung,6 in the stomach,2 in the tongue,1 in the sigmoid colon,1 in the oral pharynx and 1 in both stomach and sigmoid colon.The sensitivity,specificity and accuracy of18F-FDG PET/CT were 94.3%,94.2%and 94.2%,respectively.Conclusion:18FFDG PET can detect unexpected synchronous primary neoplasms in patients with esophageal cancer.Sites of pathologic18F-FDG uptake should be confirmed by additional investigations before treatment,because synchronous neoplasms may cause metastases and influence the therapeutic plan.
esophageal cancer;PET/CT;synchronous neoplasms;staging
R735.1+R730.4
A
1006-8147(2015)05-0404-04
周雯(1981-),女,博士,研究方向:药学及核医学;通信作者:徐文贵,E-mail:wwbzzl@sina.com。

