Nutritional Properties and Fertilizer Demand Rules of Young Phoebe bournei Forest
Qiu LlU,Minggao CHEN,Jiyou WU*,Chunying DONG,Xiaofei HUANG,Shoucheng HUANG,Aimin TANG,Mingjun HUANG
1.Hunan Academy of Forestry,Changsha 410004,China
2.Jindong Woodland in Yongzhou City,Hunan Province,Yongzhou 426191,China
Nutritional Properties and Fertilizer Demand Rules of Young Phoebe bournei Forest
Qiu LlU1,Minggao CHEN1,Jiyou WU1*,Chunying DONG1,Xiaofei HUANG1,Shoucheng HUANG2,Aimin TANG2,Mingjun HUANG1
1.Hunan Academy of Forestry,Changsha 410004,China
2.Jindong Woodland in Yongzhou City,Hunan Province,Yongzhou 426191,China
This study aimed to investigate the absorption characteristics of nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium,calcium and magnesium and rules in fertilizer demand by young Phoebe bournei forest.The results showed that the nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium and magnesium contents in young Phoebe bournei leaves were increased with the proceeding of growth,but the calcium content was increased.During the growth period,the nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium and magnesium contents were relatively high in June,July and August.This study will help to understand the nutritional characteristics and fertilizer demand rules of young Phoebe bournei forest,thereby providing scientific theoretical guidance for application of fertilizer in Phoebe bournei.
Phoebe bournei;Fertilization;Nutritional characteristics;Fertilizer demand rule
P hoebe bournei(Lauraceae: Phoebe)is an evergreen big tree.It is a valuable timber species unique to China,and is China’s second-class protected plant species[1-2].So far,the exploitation activity of Phoebe bournei,one precious species,is very rare.Most studies focus on population structure,spatial layout,seed dormancy and germination, introduction and cultivation,breeding and photosynthetic and physiological characteristics of Phoebe bournei[3-14].Phoebe bournei is widely distributed in the subtropical evergreen broadleaf forest.It favors warm and humid conditions.In China,Phoebe bournei is one of the most widely distributed Phoebe species in China.
In this study,the absorption and utilization characteristics of nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium,calcium and magnesium and fertilizer demand rules of Phoebe bournei were studied. In addition,the effect of fertilization on growth of Phoebe bournei was investigated.This study will provide certain reference for scientific fertilization in Phoebe bournei.
Materials and Methods
Test material
The test material was 3-year-old Phoebe bournei forest.
Overview on test site
The test site was located in the Jindong Woodland in Yongzhou City,Hunan Province.In the test site,the landscape is composed of sandstone,shale and carbonaceous slate.The test site has deep and fertile soil with high organic matter content.The test site has a subtropical southeast monsoon climate with annualaverage temperature of 17.5℃,absolute maximum temperature of 39.3℃,absolute minimum temperature of-13.6℃,average temperature in January of 6.5℃,average temperature in July of 28.9℃,average annual sunshine time of 159.9 h,average annual rainfall of 1 600-1 900 mm and average relative humidity of 81%.The nursery has analtitude of 200 m and soil pH of 5.0-6.5,which are all suitable for the growth of Phoebe bournei.
Test design
Total five fertilization treatments were arranged (Table 1).The randomized block design was adopted. There were five plots for each treatment,and there were five plants (in a row)in each plot.There was one isolation strip between two adjacent treatments.
Monthly changes in contents of nutritional elements in Phoebe bournei
During May to December,2014,the leaves of young Phoebe bournei forest were sampled in the last third of every month.In the collected leaves,the contents of nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium,calcium and magnesium were determined.
Results and Analysis
Monthly changes in nitrogen content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment
As shown in Table 2,the nitrogen contentin Phoebe bourneileaves showed certain variation rule in different treatment.In all the treatments,the nitrogen content reached the peak in August.And then,with the increase of leaf age,the nitrogen content was reduced.Among the months,the nitrogen contentwas relatively high in June,July,August,September and October.Among the treatments,the nitrogen content was higher in treatment 3 during May to October.
Monthly changes in phosphorus content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment
Table 3 showed that the change in phosphoruscontentin Phoebe bournei leaves showed certain rule in different treatment.The phosphorus content reached the peak in August and September.Among the months,the phosphorus content was relatively high in June,July,August,September,October and November.Among the treatments,the phosphorus content in Phoebe bournei leaves was higher in treatment 3 during May to November.
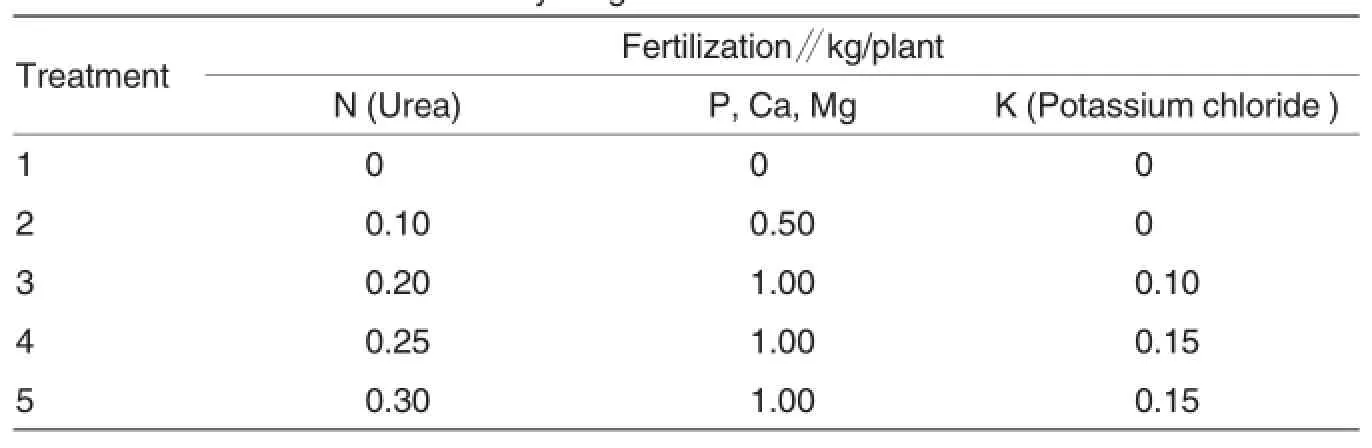
Table 1 Fertilization treatments for young Phoebe bournei forest

Table 2 Monthly changes in nitrogen content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment mg/kg
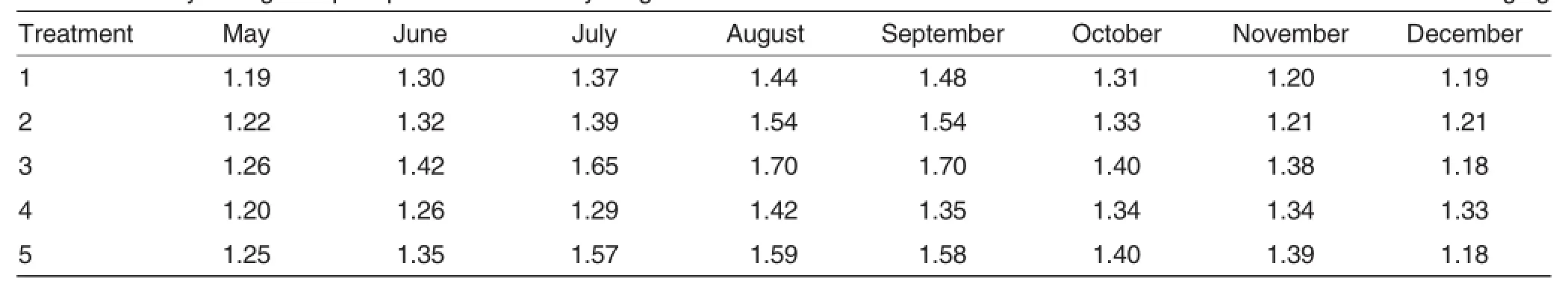
Table 3 Monthly changes in phosphorus content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment mg/kg
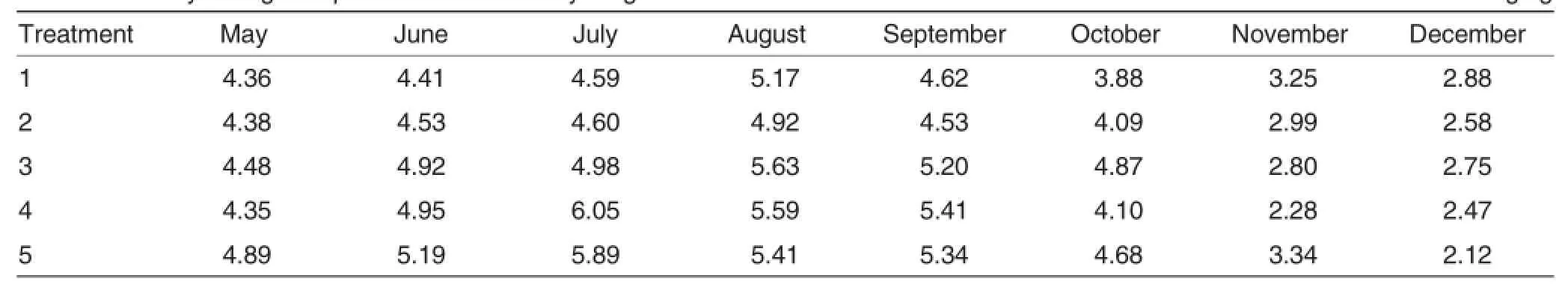
Table 4 Monthly changes in potassium content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment mg/kg
Monthly changes in potassium content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment
As shown in Table 4,the change in potassium contentin Phoebe bournei leaves showed certain rule in different treatment.After the peak,the potassium content was decreased with the increase of leaf age.Among the months,the potassium content was relatively high in June,July,August and September.
Monthly changes in calcium content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment
As shown in Table 5,there were great significant differences in calcium content in Phoebe bourneileaves among different treatments.From a comprehensive point of view,in different treatment,the calcium content in Phoebe bournei leaves was all in-creased with the increase of leaf age. Monthlychangesinmagnesium content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment
Table 6 showed that there were great significant differences in magnesium content in Phoebe bournei leaves among different treatments.In overall,the magnesium content in Phoebe bournei leaves was all increased with the increase of leaf age in different treatment.In June,July and August,the magnesium content was relatively high in all the treatments.

Table 5 Monthly changes in calcium content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment mg/kg

Table 6 Monthly changes in magnesium content in young Phoebe bournei forest under different fertilization treatment mg/kg
Conclusions and Discussion
With the increase of leaf age,the contents of nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium and magnesium in Phoebe bournei leaves were all decreased,but the content of calcium was increased. Generally,content of movable element in plant tissue and organ will gradually decline with the growth of plant,but content of fixed element will be increased with the aging of tissue and organ of plant.Nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium and magnesium are all movable elements,so their contents were decreased with the growth of Phoebe bournei.However,calcium is difficult to be re-transformed or re-utilized,so the content of calcium in Phoebe bournei leaves was increased.
The contents of nitrogen,phosphorus,potassium and magnesium in Phoebe bournei leaves were higher in June,July and August,which was consistent with the higher growth rate of Phoebe bournei during that time.It suggests that the fertilization in Phoebe bournei should be conducted in June.
During the fertilization in Phoebe bournei,more nitrogen element should be applied,and magnesium should be added appropriately.Taking the absorption capacity of young Phoebe bournei forest into account,fertilizer should not be applied too much so as to avoid loss and waste.The specific recipe forapplication ofnitrogen,phosphorus,potassium and magnesium still needs further study.
[1]WU JY(吴际友),CHEN MG(陈明皋),TANG AM(唐爱民),et al.Growth performance of Phoebe bournei generations in seedling stage(闽楠优树子代苗期生长表现)[J].Agricultural Science& Technology,2014,15(7):1188-1190.
[2]LI DL(李栋林),JIN YQ(金雅琴),XIANG QB(向其柏).The geographical distribution,research status and developmental utilization prospect of Phoebe Nees plant resource of our country(我国楠木属植物资源的地理分布、研究现状和开发利用前 景)[J].Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology(福建林业科技),2004,31(1):5-9.
[3]JIANG XM(江香梅),LIN WH(林卫红). Preliminary report on seedling raising of Phoebe bournei(闽楠育苗初报)[J]. Jiangxi Forestry Science and Technology(江西林业科技),2000(4):9-10.
[4]WU DR(吴大荣).A study on seed rain of nanmu(Phoebe bournei)population at Luoboyan Natural Reserve in Fujian(福建省罗卜岩自然保护区闽楠种群种子雨研究)[J].Journal of Nanjing Forestry University(南京林业大学学报),1997,21(1):56-60.
[5]WU DR(吴大荣),WANG BS(王伯荪). Seed and seedling ecology of the endangered Phoebe bournei(Lauraceae)(濒危树种闽楠种子和幼苗生态学研究)[J].Acta Ecologica Sinica(生态学报),2001,21(11):1751-1760.
[6]WU JY,CHEN MG,TANG AM,et al. Growth performance of Phoebe bournei generations in seeding stage[J].Agricultural Science&Technology,2014,15(7):1188-1190,1199.
[7]DONG CY(董春英),CHEN MG(陈明皋),HUANG SC(黄守成),et al.Studies on field sowing practice and the cultivation technology of strong root and seedling of Phoebe bournei(闽楠大田播种育苗及富根壮苗培育技术研究)[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin(中国农学通报),2014,30(16):48-52.
[8]CHEN MG(陈明皋),WU JY(吴际友),SHU Y(舒瑶),et al.Cutting propagation of Phoebe bournei clones(闽楠无性系扦插繁殖试验)[J].Hunan Forestry Science&Technology(湖南林业科技),2014,03:1-3,8.
[9]XIE QH(谢庆宏),WU ZM(吴振明),WU JY(吴际友),et al.The propagation technology ofsoftwood cuttings of Phoebe bournei(闽楠嫩枝扦插繁殖技术研究)[J].Hunan Forestry Science& Technology(湖南林业科技),2011,38(6):43-45.
[10]HUANG MJ(黄明军),CHEN MG(陈明皋),WU JY(吴际友),et al.Study on influence oflighttransmittance of shadeneton growth ofPhoebe bournei seedlings(遮荫网透光度对闽楠苗木生长影响的研究)[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin(中国农学通报),2014,04:8-11.
[11]ZHANG QY(张群英).Effects of density and fertilization on Phoebe bournei seedling growth(密度和施肥对楠木播种苗生长的影响)[J].Journal of Fujian Forestry Science and Technology(福建林业科技),2011,38(2):81-83.
[12]DONG LJ(董立军),ZHU XT(朱晓婷),LIN XZ(林夏珍),et al.Effects of fertil-ization on the growth of three Lauraceae seedlings in containers(施肥对3种樟科植物容器苗生长的影响)[J]. Northern Horticulture(北方园艺),2011,13:73-77.
[13]WANG Y(王艺),WANG XH(王秀花),WU XL(吴小林),et al.Effects of slowrelease fertilizer loading on growth and construction of nutrients reserves of Phoebe chekiangensis and Phoebe bournei container seedlings(缓释肥加载对浙江楠和闽楠容器苗生长和养分库构建的影响)[J].Forest Sciences(林业科学),2013,49(12):57-63.
[14]SHENG J(盛杰),CHEN YH(陈月华),WU JY(吴际友),et al.Study on photosynthetic characteristics of different families of Phoebe bournei at seedling stage(闽楠家系苗期光合特性的研究)[J].Journal of Central South University of Forestry and Technology(中南林业科技大学学报),2015,35(6):45-49.
Responsible editor:Tingting XU
Responsible proofreader:Xiaoyan WU
闽楠幼林营养特性及需肥规律研究
刘球1,陈明皋1,吴际友1*,董春英1,黄小飞1,黄守成2,唐爱民2,黄明军1(1.湖南省林业科学院,湖南长沙410004;2.湖南省永州市金洞林场,湖南永州426191)
为探讨闽楠幼林的氮、磷、钾、钙、镁等营养特性及需肥规律,开展了闽楠幼林施肥研究,结果表明:N、P、K、Mg含量随闽楠生长而下降,而Ca的含量随叶龄增长而上升;6月、7月和8月N、P、K、Mg含量相对较高。该文旨在了解闽楠幼林的营养特性以及所需肥料的规律,为闽楠科学施肥提供理论指导。
闽楠;施肥;营养特性;需肥规律
湖南省林业科技计划项目“闽楠、红椿家具材良种选育与应用”(XLK201406);“闽楠测土配方定量施肥技术研究”。
刘球(1985-),女,湖南安化人,在读博士,助理研究员,从事森林培育方面的研究。*通讯作者,博士,研究员,从事森林培育方面的研究,E-mail:hnforestry@sina.com。
2015-09-19
Supported by Forestry Science and Technology Plan Projects of Hunan Province(XLK201406).
*Corresponding author.E-mail:hnforestry@sina.com
Received:September 19,2015 Accepted:November 5,2015
修回日期 2015-11-05
 Agricultural Science & Technology2015年12期
Agricultural Science & Technology2015年12期
- Agricultural Science & Technology的其它文章
- An lnnovative Strategy for Reciprocal Distant Hybridization between Spartina alterniflora and Rice
- Study on Absorptive Capacity to Formaldehyde and Physiological and Biochemical Changes of Scindapsus aureus Based on the Regulation of LaCl3
- Dynamic Variation in Sugar,Acid,and ASA Contents of‘Ganmi 6’Kiwifruit(Actinidia eriantha Benth)Fruits
- Construction and Development of GMS Agricultural lnformation Network Based on Stakeholder Analysis
- Effects of Different Decolorants on Retention Rate of Total Triterpenes in Fruit and Rattan Stems of Schisandra chinensis(Turcz.)Baill
- Determination of Heavy Metals inDendrobium candidiumWall.ex Lindl.by lCP-MS
