二类油藏分层注聚措施优选
万荣晖

摘 要:萨南开发区油藏属普通稠油油藏,油层存在油层厚度小、连通状况差、层间矛盾大等特点。若采用笼统注聚,非主力油层受层间干扰的影响,吸聚量少,对油井见效晚,开发效果差。因此采用分层注聚技术,使聚合物驱注聚剖面得到有效改善,从而解决主力油层与非主力油层间吸聚量差异大的问题,实现层间合理配注,延长注聚区的有效期,进而提高阶段采收率。采用ECLIPSE软件模拟分层注聚,并给出分层聚驱措施优化,包括分层措施时机优化和分层注聚强度优化,使分层注聚效果达到最优。
关 键 词:稠油油藏;聚驱;分层注聚;措施优化
中图分类号:TE 122 文献标识码: A 文章编号: 1671-0460(2015)07-1531-03
Optimization of Separate-layer
Polymer Injection Measures for TypeⅡReservoirs
WAN Rong-hui
(Northeast Petroleum University, Heilongjiang Daqing 163000, China)
Abstract: Reservoir in Sanan development area is a common heavy oil reservoir; the reservoir has the characteristics of small reservoir thickness, poor connectivity, and big interlayer contradiction and so on. If using the general injection process, because the non-main layer is affected by interlayer interferenc, its absorbing polymer amount is less, so development effect is poor. The separate-layer polymer injection technology can improve the injection profile of polymer flooding, and solve the problem of large absorbing amount difference between main and non-main layers to achieve interlayer reasonable match injection and extend the period of validity of polymer injection region to improve the recovery rate. In this paper, ECLIPSE software was used to simulate the separate-layer polymer injection, and the measures to optimize the stratification of polymer flooding were put forward to achieve the optimal effect of separate-layer polymer injection, including hierarchical measure time and hierarchical injection strength optimization.
Key words: Heavy oil reservoir; Polymer flooding; Separate-layer polymer injection; Optimization measures
聚驅措施优化包括分层、解堵、压裂以及分微相注聚,本文将着重分析分层聚驱措施优化。同水驱采油一样,聚合物驱采油也存在层间矛盾,若采用笼统注聚开采方式,聚合物溶液将主要进入主力油层,因此会对油井见效早;而非主力油层,因受层间干扰的影响,吸聚量少,对油井见效晚,注聚开采效果差。分层注聚能有效改善注聚剖面,使聚合物溶液沿高渗层突进现象得到控制,并解决主力油层与非主力油层吸聚量差异大的问题,使非主力油层得到有效开发,实现层间合理配注,延长注聚区的有效期,可进一步提高采收率[1-5]。
1 试验区地质概况及开发现状
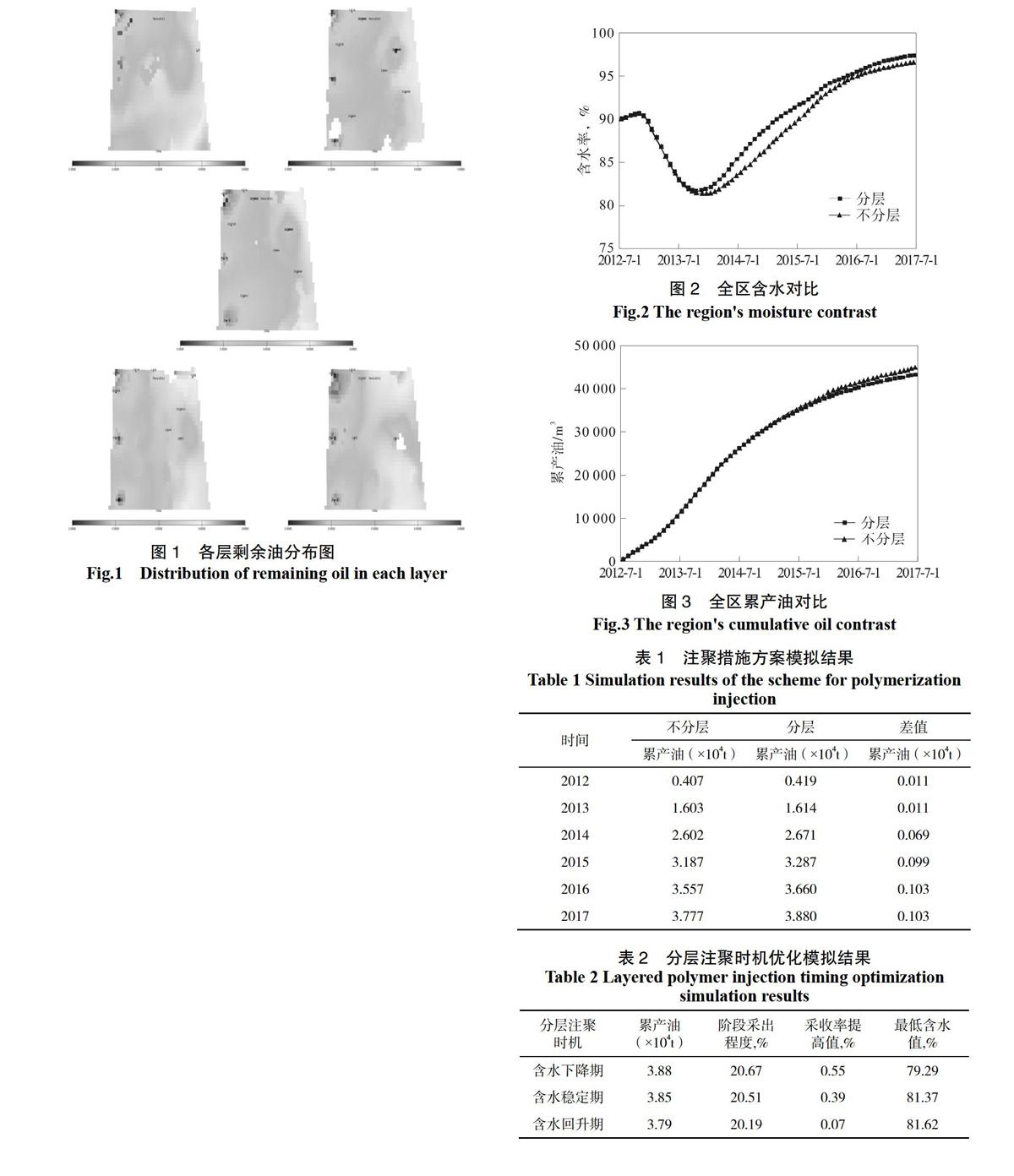
萨南开发区油藏属普通稠油油藏,油层表现为油层厚度小、连通状况差、层间矛盾大等特点。试验区控制面积0.24 km2,孔隙体积39.88×104 m3,地质储量18.77×104 t。中心井区控制面积0.06 km2,孔隙体积9.53×104 m3,地质储量4.59×104 t。试验区葡I5-7、葡II1-3油层纵向上可分6个小层、8个沉积单元。水驱结束后,试验区累产油7.37×104 t,采出程度为39.28%,剩余含油饱和度为50.82%,图1为各层剩余油分布。
南三区中块试验区目的层综合含水率达87.24%,处于高含水期开采阶段。葡I5-7~葡II1-3油层有效厚度水淹比例较高,继续水驱挖潜的难度越来越大,水驱开发的经济效益较差。因此有必要转聚驱并进行聚驱注入参数优化研究,改善二类油层开发效果。
图1 各层剩余油分布图
Fig.1 Distribution of remaining oil in each layer
2 分层措施
对试验区进行两组模拟研究,一组是笼统注聚,一组是分层注聚(将聚合物驱目的层分为PI5+61a-PI7和PII1a-PII3两段)。
不分层方案采取清配清稀最优方案(聚合物分子量950~1 200万,浓度1 100 mg/L,注入速度0.2 PV/a,注入段塞0.64 PV),分层方案为层段一、二的注聚强度均为9 m3/(d·m),分层注聚时机为含水稳定期,模拟结果如表1所示。
图2、图3是分层与不分层含水对比以及累产油对比。数值模拟结果表明:分层注聚后,全区含水略有下降,含水稳定期延长,累产油增产0.103×104 t,阶段采收率比不分层提高0.55%,因此分层注聚效果比不分层好。
3 分层措施时机优化
根据近几年在注入井分层注入方面的做法,以及油层性质与发育状况,将目标层段分为两层,PI5+61a-PI7为层段一,PII1a-PII3为层段二。分别选择含水下降期分层、含水稳定期分层、含水回升期分层三种方案进行模拟计算。同时也考虑对空白水驱进行分层注聚,层段一、二的注聚强度均为9 m3/(d·m)。分层注聚时机优化数值模拟结果如表2所示。
图2 全区含水对比
Fig.2 The region's moisture contrast
图3 全区累产油对比
Fig.3 The region's cumulative oil contrast
表1 注聚措施方案模拟结果
Table 1 Simulation results of the scheme for polymerization injection
时间 不分层 分层 差值
累产油(×104t) 累产油(×104t) 累产油(×104t)
2012 0.407 0.419 0.011
2013 1.603 1.614 0.011
2014 2.602 2.671 0.069
2015 3.187 3.287 0.099
2016 3.557 3.660 0.103
2017 3.777 3.880 0.103
表2 分层注聚时机优化模拟结果
Table 2 Layered polymer injection timing optimization simulation results
分层注聚
时机 累产油
(×104t) 阶段采出程度,% 采收率提高值,% 最低含水值,%
含水下降期 3.88 20.67 0.55 79.29
含水稳定期 3.85 20.51 0.39 81.37
含水回升期 3.79 20.19 0.07 81.62
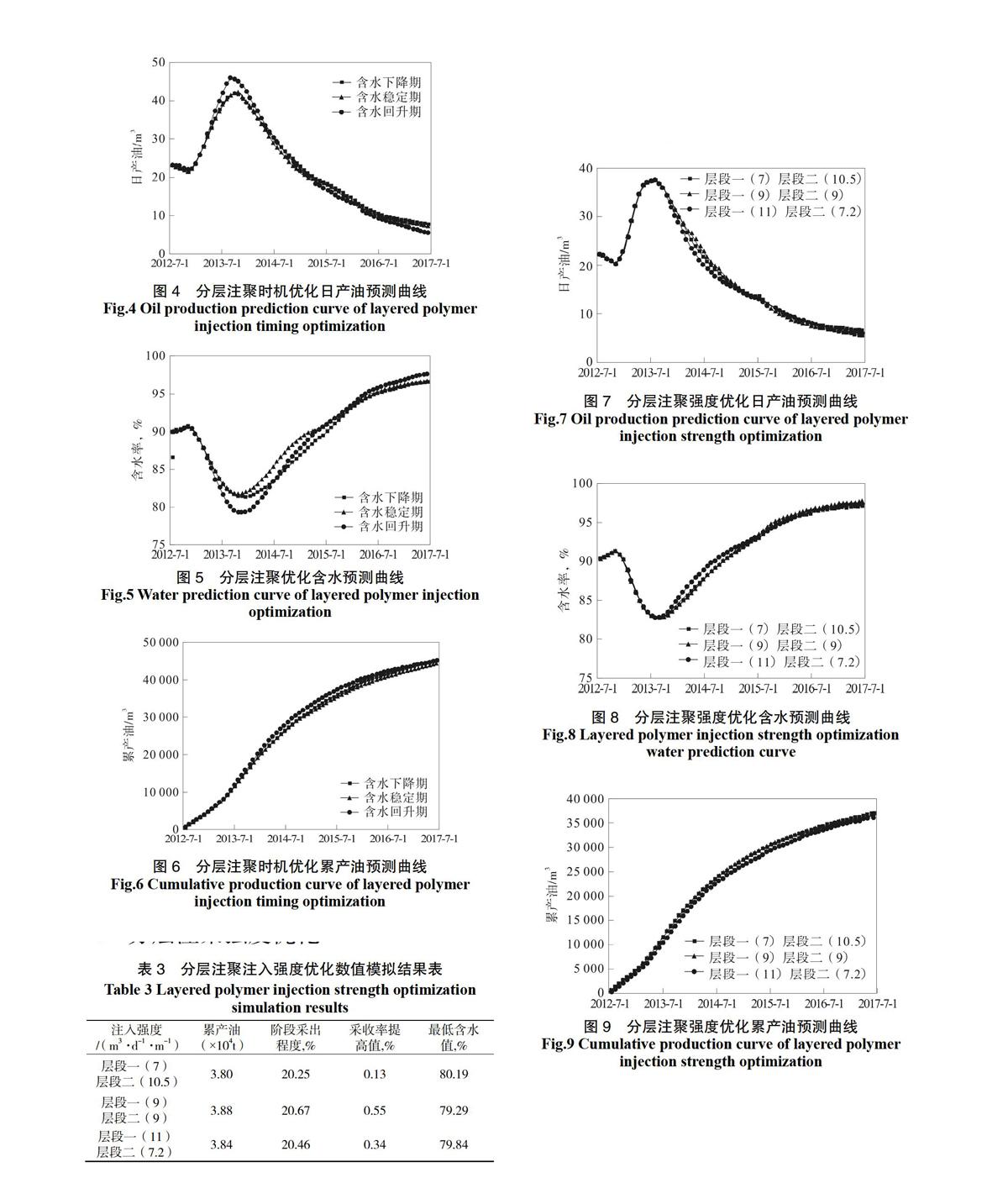
图4是分层注聚时机优化日产油对比曲线,图5是分层注聚时机优化含水对比曲线,图6是分层注聚时机优化累产油对比曲线。数值模拟结果表明:
注入井在含水下降期、含水稳定期、含水回升期实施分层注聚,比不分层注聚采收程度分别提高0.55%、0.39%、0.07%。同时,在含水下降期进行分层注聚开发效果最好,因此分层注聚越早越好。
图4 分层注聚时机优化日产油预测曲线
Fig.4 Oil production prediction curve of layered polymer injection timing optimization
图5 分层注聚优化含水预测曲线
Fig.5 Water prediction curve of layered polymer injection optimization
图6 分层注聚时机优化累产油预测曲线
Fig.6 Cumulative production curve of layered polymer injection timing optimization
4 分层注聚强度优化
表3 分层注聚注入强度优化数值模拟结果表
Table 3 Layered polymer injection strength optimization simulation results
注入强度
/(m3·d-1·m-1) 累产油
(×104t) 阶段采出程度,% 采收率提高值,% 最低含水值,%
层段一(7)
层段二(10.5) 3.80 20.25 0.13 80.19
层段一(9)
层段二(9) 3.88 20.67 0.55 79.29
层段一(11)
层段二(7.2) 3.84 20.46 0.34 79.84
在含水下降期进行分层注聚的基础上,改变层段一、层段二的注聚强度,进行分层注聚注入强度优化数值模拟,结果如表3所示。
另外,图7是分层注聚强度优化日产油对比曲线,图8是分层注聚强度优化含水对比曲线,图9是分层注聚强度优化累产油对比曲线。
图7 分层注聚强度优化日产油预测曲线
Fig.7 Oil production prediction curve of layered polymer injection strength optimization
图8 分层注聚强度优化含水预测曲線
Fig.8 Layered polymer injection strength optimization water prediction curve
图9 分层注聚强度优化累产油预测曲线
Fig.9 Cumulative production curve of layered polymer injection strength optimization
从上述数值模拟结果可以看出:分层注聚强度层段一、层段二均为9 m3/(d·m)比未分层注聚提高0.55%,最低含水值为79.29%。 (下转第1537页)

