低渗透油藏地层压力保持水平对油水渗流特征的影响
杜玉山,杨 勇,郭迎春,房会春,胡 罡,田选华
(1.中国石化胜利油田分公司地质科学研究院,山东东营257015;2.广东石油化工学院石油工程学院,广东茂名525000;3.成都理工大学油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室,四川成都610059)
·油气采收率·
低渗透油藏地层压力保持水平对油水渗流特征的影响
杜玉山1,杨勇1,郭迎春1,房会春1,胡罡2*,田选华3
(1.中国石化胜利油田分公司地质科学研究院,山东东营257015;2.广东石油化工学院石油工程学院,广东茂名525000;3.成都理工大学油气藏地质及开发工程国家重点实验室,四川成都610059)
油水渗流规律的研究是低渗透油藏水驱开发的关键。相对渗透率曲线能直观反映油水渗流特征,其影响因素研究主要涉及岩石固有性质(润湿性、孔隙结构)、流动介质(油水粘度比)、动力条件(驱替压力梯度及速度)等方面,极少见到地层压力对相对渗透率曲线影响的研究。通过室内流动实验,模拟低渗透油藏地层压力下降过程,建立了不同地层压力保持水平下的相对渗透率曲线,分析了地层压力保持水平对油水渗流特征的影响规律。结果表明,地层压力保持水平下降,孔隙结构非均质性增强,油相相对渗透率下降,水相相对渗透率上升,等渗点左移,油水两相区变窄,残余油饱和度增加,即低渗透油藏渗流规律也存在着应力敏感性特征。分析认为,储层岩石弹性或塑性变形是低渗透油藏油水渗流特征应力敏感性的根本原因,因而提出了储层岩石初始渗透率越低,越应尽早注水保持地层压力开发的低渗透油藏效益开发理念。
低渗透油藏 地层压力保持水平 孔隙结构 油水渗流特征 应力敏感性
相对渗透率曲线可以直观地反映油水在多孔介质中的渗流特征,是油藏工程研究不可或缺的基础资料[1-4]。一般可以通过室内岩心驱替实验来获得相对渗透率曲线[5-12]。前人研究表明,岩石的相对渗透率曲线主要受润湿性、粘度比、孔隙结构以及饱和历程、动力条件(驱替压力或驱替速度)等因素影响[13-25]。室内岩心分析和油气田矿场监测资料研究均表明,在油藏开采过程中地层压力的变化会导致储层岩石发生弹性或塑性应变,从而引起岩石孔隙结构和孔隙体积的变化,进而影响油藏流体的渗流,最终会影响到油气井产能和油气田的开发效果[12-14]。生产实践证实,地层压力的变化对低渗透油藏开发效果的影响尤为敏感[26-37]。由于地层压力的变化会影响岩石的孔隙结构,而岩石的孔隙结构又是影响相对渗透率曲线(油水渗流特征)的一个重要因素,因此,相对渗透率曲线(油水渗流特征)也会间接地受到地层压力保持水平的影响。前人对中、高渗透油藏储层岩石的相对渗透率曲线研究较多[1-25],而对低渗透油藏尤其是关于地层压力对岩石的相对渗透率曲线(油水渗流特征)影响的研究相对较少。为此,笔者通过室内实验,建立了低渗透油藏不同地层压力保持水平的油水两相相对渗透率曲线,明确了低渗透油藏地层压力保持水平对油水渗流特征的影响规律,以期为低渗透油藏高效开发提供理论依据。
1 实验方案
根据前人研究成果[13-25],储层岩石固有性质(润湿性、孔隙结构)、流动介质(油水粘度比)、动力条件(驱替压力梯度及速度)等都是影响油水两相相对渗透率的主要因素。因此,室内实验研究应立足于研究区的实际情况,合理地设计实验方案。
实验岩心实验岩心全部取自胜利油区滨425断块沙四段滩坝砂岩油藏储层的柱塞样品。岩心样品按初始空气渗透率分为1.0×10-3,5.0×10-3和10.0×10-3μm2共3个级别采样。
实验流体实验用油为与地层原油粘度相当的机械油,粘度为7.601mPa·s,实验用水为与储层地层水总矿化度相当的氯化钾溶液,矿化度为170 000mg/L。
实验压力和温度根据油藏埋深(约为2 600 m)及岩石密度(2.3 kg/L)计算得到,岩石骨架承受的上覆压力约为60MPa。因此,实验过程中,始终保持施加在岩心夹持器上的环压为60MPa。根据滨425断块沙四段压力测试资料可知,该油藏的原始地层压力为32MPa,因此,设置实验初始孔隙压力为32MPa。
鉴于实验主要考察地层压力变化对岩心相对渗透率曲线的影响,因此实验可以在常温下进行,设置实验温度保持在25℃左右。
实验步骤实验步骤主要为:①确定孔隙体积。对岩心样品抽真空,饱和模拟地层水,确定孔隙体积和孔隙度;②建立束缚水饱和度。模拟原始地层压力条件,油驱水建立束缚水饱和度;③测定相对渗透率。以流量为1mL/min的恒速水驱油,注入40~50倍孔隙体积的模拟地层水后停止实验,实验过程中记录时间、累积产油量、累积产液量、驱替速度和岩样两端的驱替压差,建立含水饱和度与油水两相相对渗透率关系曲线。
2 实验结果与分析
为了便于说明问题,引入地层压力保持系数来衡量地层压力保持水平的高低,其数值上等于油藏地层压力与原始地层压力的比值。利用该实验方法,获得了不同地层压力保持水平下实际初始空气渗透率分别为1.2×10-3,6.0×10-3和9.0×10-3μm2的岩心样品的油水两相相对渗透率曲线(图1)。
从图1可以看出,地层压力保持水平也是影响低渗透油藏油水渗流特征的主要因素。其主要体现在以下2个方面:一方面,随着地层压力的下降,油相相对渗透率下降速度加快,水相相对渗透率上升速度加快,且相同含水饱和度下的油相相对渗透率降低,水相相对渗透率升高。地层压力保持系数为1.0的油相相对渗透率曲线位置靠上,水相相对渗透率曲线位置靠下;随着地层压力保持系数的减小,油相相对渗透率曲线的位置逐步向下移动,水相相对渗透率曲线的位置逐步向上移动,表明随着地层压力保持水平的下降,储层岩石孔隙结构非均质性增强。分析认为,随着地层压力保持水平的下降,岩石骨架因承受的有效上覆压力增加而发生变形,孔喉半径变小,且小孔喉变形程度较大,大孔喉变形程度相对较小,孔隙结构非均质性增强,储层渗透率降低。
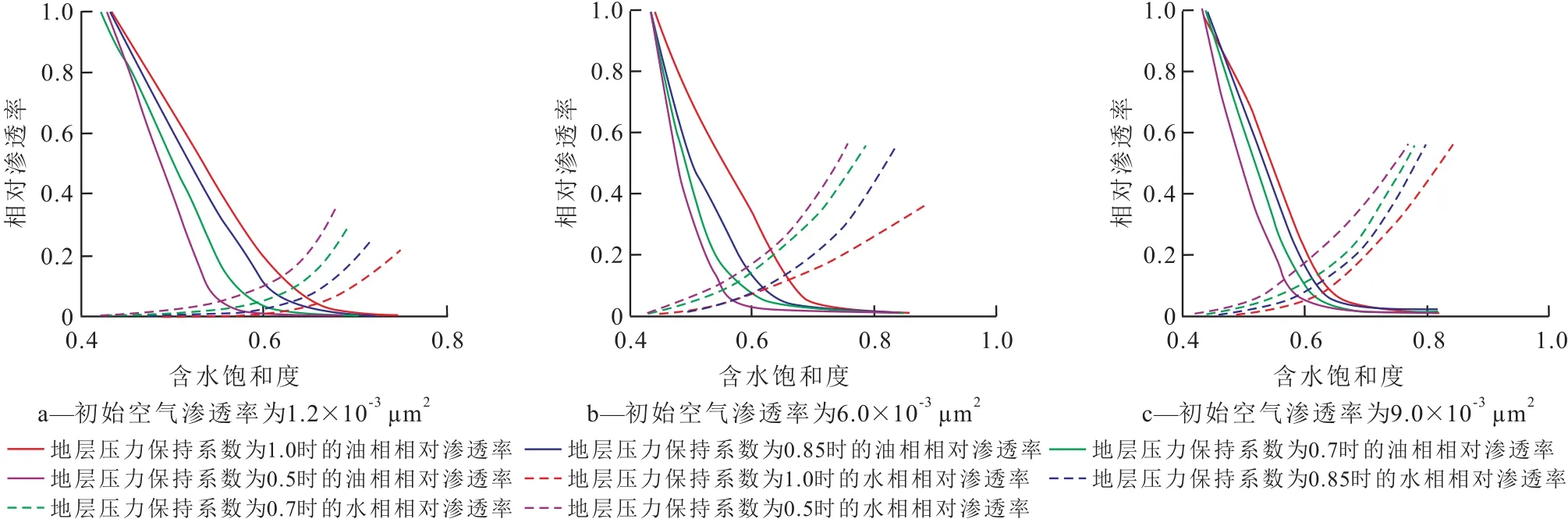
图1 不同地层压力保持水平下的岩心样品油水两相相对渗透率曲线Fig.1 Relative permeability curvesunder different levelsof formation pressuremaintenance
当地层压力下降时,低渗透油藏渗透率随之下降,即低渗透储层岩石表现出应力敏感性特征[27,29,36]。在某一地层压力时,储层岩石的实时渗透率可以看成该地层压力条件下的初始渗透率。实验证实,低渗透油藏储层岩石初始渗透率越低,水相相对渗透率上升速度越大,油相相对渗透率下降速度越大,水驱油效果越差;初始渗透率越低,原油流动需要克服的启动压力梯度越高,油水共存时,越易出水,从而影响采油效果[35-37]。
另一方面,随着地层压力的下降,油水两相相对渗透率曲线的等渗点左移,末端含水饱和度降低。当地层压力保持系数由1.0下降到0.5时,3个不同级别初始空气渗透率的岩心样品的等渗点含水饱和度分别由0.66降至0.55,0.65降至0.54,0.63降至0.57。结果表明,随着地层压力保持水平的下降,等渗点左移,等渗点对应的相对渗透率逐渐增加,水相相对渗透率上升速度增大,油相相对渗透率下降速度增大,水驱油效果变差。
当地层压力保持系数由1.0下降到0.5时,3个不同级别初始空气渗透率的岩心样品末端含水饱和度分别由0.747降至0.678,0.858降至0.762,0.815降至0.757,且末端含水饱和度(残余油饱和度)对应的水相相对渗透率增加,即油水两相区的宽度分别减少了0.069,0.096,0.058。结果表明,随着地层压力保持水平的下降,油水两相共渗区变窄,残余油饱和度上升,水驱油效率下降。
分析认为,当地层压力下降时,会导致储层岩石发生弹性或塑性应变,从而引起岩石孔隙结构和孔隙体积的变化,进而影响原油渗流规律,即地层压力保持水平越低,原油所需克服的启动压力梯度越高,流动越困难,等渗点越靠左,残余油饱和度越高,油水两相共渗区变窄,大量的原油将会滞留在油藏中,水驱油效果变差[35-37]。
3 结束语
通过测试4种不同地层压力保持水平下低渗透油藏储层岩石油水两相相对渗透率曲线可知,束缚水饱和度、残余油饱和度较高,油相相对渗透率在等渗点前期急剧下降,水相相对渗透率较高,是低渗透油藏油水两相相对渗透率曲线的典型特征。随着地层压力的改变,油水两相相对渗透率与含水饱和度的关系会发生变化。
通过室内实验,首次将低渗透油藏的应力敏感性研究由单相流动扩展到两相流动,分析了低渗透油藏油水两相相对渗透率曲线特征及其随地层压力保持水平的变化规律。当油藏地层压力保持水平下降时,由于储层岩石中小孔喉变形程度较大,大孔喉变形程度相对较小,孔隙结构的非均质性增强,从而导致油相相对渗透率下降,水相相对渗透率上升,等渗点左移,油水两相区变窄,残余油饱和度增加,且岩石初始渗透率越低,水相相对渗透率上升速度越大,油相相对渗透率下降速度越大,水驱油效果变差,即低渗透油藏油水渗流特征也存在着应力敏感性。由于低渗透油藏油水渗流规律存在着应力敏感性,因此水驱开发时应立足于超前或早期注水保持原始地层压力开采,以提高驱动压差,减小压敏效应对低渗透油藏开发的不利影响。
[1] 吕渐江,唐海,吕栋梁,等.利用相渗曲线研究低渗气藏水锁效应的新方法[J].天然气勘探与开发,2008,31(3):49-52. Lv Jianjiang,Tang Hai,Lv Dongliang,etal.New researchmethod of water locking effect in low permeability gas reservoir by relative-permeability curve[J].Natural Gas Exploration&Development,2008,31(3):49-52.
[2] 马建国,刘小娟,杜福祥,等.机械振动对岩心相渗曲线的影响[J].西安石油学院学报:自然科学版,1999,14(1):13-15. Ma Jianguo,Liu Xiaojuan,Du Fuxiang,et al.Effects ofmechanical vibration on the relative permeability curve of a core[J].Journal of Xi’an Petroleum Institute:Natural Science Edition,1999,14(1):13-15.
[3] 韩进,甄延忠,张景.安塞油田长10储层渗流特征研究[J].延安大学学报:自然科学版,2013,32(3):61-63. Han Jin,Zhen Yanzhong,Zhang Jing.Research on the characteristics of Chang10 reservoir of Ansai oilfield[J].Journal of Yanan University:NaturalScience Edition,2013,32(3):61-63.
[4] 罗蛰潭,王允诚.油气储集层的孔隙结构[M].北京:科学出版社,1986. Luo Zhetan,Wang Yuncheng.The pore structure ofoiland gas reservoi[rM].Beijing:Science Press,1986.
[5] 张玄奇.油水相对渗透率曲线的实验测定[J].石油钻采工艺,1994,16(5):87-90. Zhang Xuanqi.The laboratorialmeasurement of relative permeability curveofoilandwater[J].OilDrilling&Production Technology,1994,16(5):87-90.
[6] Castillo A F,Perez E R,Rojas JA,et al.Numerical and experimentmodeling of relative permeability in heavy oil reservoirs[R]. SPE 123097,2009.
[7] Ahmadloo F,Asghari K,Yadali Jamaloei B.Experimental and theoretical studies of three-phase relative permeability[R].SPE 124538,2009.
[8] 周凤军,刘忠众,张彩霞.稳态法测定油水相对渗透率的实用方法[J].石油地质与工程,2009,23(2):105-109. Zhou Fengjun,Liu Zhongzhong,Zhang Caixia.Steady statemethod for determining oil-water relative permeability[J].Petroleum Geology and Engineering,2009,23(2):105-109.
[9] 贾振岐,孙念,吴景春,等.特低渗透岩心相对渗透率实验研究[J].特种油气藏,2009,16(1):82-83. Jia Zhenqi,Sun Nian,Wu Jingchun,et al.Experimental study on relative permeability of super-low permeability cores[J].Special Oil&Gas Reservoirs,2009,16(1):82-83.
[10]阳晓燕,杨胜来,李秀峦,等.非稳态法测定稠油油藏相对渗透率实验研究[J].断块油气田,2010,17(6):745-747. Yang Xiaoyan,Yang Shenglai,Li Xiuluan,et al.Experimental study on determining relative permeability of heavy oil reservoir with nonsteady state method[J].Fault-Block Oil&Gas Field,2010,17(6):745-747.
[11]郭平,张涛,朱中谦,等.裂缝—孔隙型储层油水相渗实验研究[J].油气藏评价与开发,2013,3(3):19-22. Guo Ping,Zhang Tao,Zhu Zhongqian,etal.Study on oil-water relative permeability experiments of fractured-porous reservoirs[J]. Reservoir Evaluation and Development,2013,3(3):19-22.
[12]李道品.低渗透油田高效开发决策论[M].北京:石油工业出版,2003. Li Daopin.The decision-making theory of efficiency development in low permeability oil field[M].Beijing:Petroleum Industry Press,2003.
[13]郭沫贞,肖林鹏,张生兵,等.低渗透砂岩油层相对渗透率曲线特征、影响因素及其对开发的影响[J].沉积学报,2008,26(3):445-451. GuoMozhen,Xiao Linpeng,Zhang Shengbing,etal.Features,controls and influence for petroleum development of relative permeability curve in low permeable sandstone reservoirs[J].Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,2008,26(3):445-451.
[14]崔浩哲,姚光庆,周锋德.低渗透砂砾岩油层相对渗透率曲线的形态及其变化特征[J].地质科技情报,2003,22(1):88-91. Cui Haozhe,Yao Guangqing,Zhou Fengde.Type and the variety characteristics of relative permeability curve in low permeable glutenite oil reservoirs[J].Geological Science and Technology Information,2003,22(1):88-91.
[15]赵琳,王增林,吴雄军,等.表面活性剂对超低渗透油藏渗流特征的影响[J].油气地质与采收率,2014,21(6):72-75. Zhao Lin,Wang Zenglin,Wu Xiongjun,et al.Effect of surfactant on seepage characteristics of ultra-low permeability reservoir[J]. Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2014,21(6):72-75.
[16]邵长金,李志航,汪小宇,等.低渗透气藏相对渗透率影响因素的孔隙网络模型[J].天然气工业,2010,30(7):36-38. Shao Changjin,LiZhihang,Wang Xiaoyu,etal.Porenetworkmodeling for the investigation of factors affecting relative permeability of low-permeability reservoirs[J].Natural Gas Industry,2010,30 (7):36-38.
[17]皮彦夫,宋考平,刘丽,等.水驱后聚驱全过程的相对渗透率曲线影响因素分析[J].东北师大学报:自然科学版,2010,42(4):87-91. Pi Yanfu,Song Kaoping,Liu Li,et al.Affecting factor analysis of the relative permeability curve of full term polymer flooding after water drive[J].Journal of Northeast Normal University:Natural Science Edition,2010,42(4):87-91.
[18]阳晓燕,杨胜来,李秀峦.稠油相对渗透率曲线影响因素分析[J].断块油气田,2011,18(6):758-760. Yang Xiaoyan,Yang Shenglai,Li Xiuluan.Affecting factors of relative permeability curve in heavy oil reservoir[J].Fault-Block Oil&Gas Field,2011,18(6):758-760.
[19]蔡玥,赵乐,肖淑萍,等.基于恒速压汞的特低—超低渗透储层孔隙结构特征——以鄂尔多斯盆地富县探区长3油层组为例[J].油气地质与采收率,2013,20(1):32-35. Cai Yue,Zhao Le,Xiao Shuping,et al.Study on pore structure characteristics of super-low permeability and ultra-low permea-bility reservoirs by means of constant-speed mercury intrusion technique-case of oil layers of Chang3 of the Yanchang Formation in Fuxian exploration area of the Ordos Basin[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2013,20(1):32-35.
[20]陈铁龙,唐金星,彭克宗,等.聚合物驱相对渗透率曲线的特征研究[J].西南石油学院学报:自然科学版,1996,18(3):51-56. Chen Tielong,Tang Jinxing,Peng Kezong,et al.Determination method of polymer flooding relative permeability curves[J].Journal of Southwestern Petroleum Institute:Science&Technology Edition,1996,18(3):51-56.
[21]赵益忠,程远方,刘钰川,等.启动压力梯度对低渗透油藏微观渗流及开发动态的影响[J].油气地质与采收率,2013,20(1):67-69,73. Zhao Yizhong,Cheng Yuanfang,Liu Yuchuan,etal.Study on influence ofstart-up pressure gradient tomicro-seepage in low permeability reservoirs and development trends[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2013,20(1):67-69,73.
[22]Erle CDonaldson,Faruk Clvan,Waql UIAlam M.Relative permeability atsimulated reservoir conditions[R].SPE 16970,1988.
[23]Sandberg CR.The effectof fluid flow rate and viscosity on laboratory determinations of oil-water relative permeabilities[R].SPE 709-G,1958.
[24]Downie J.Effect of viscosity on relative permeability[R].SPE 1629-G,1961.
[25]吕伟峰,冷振鹏,张祖波,等.应用CT扫描技术研究低渗透岩心水驱油机理[J].油气地质与采收率,2013,20(2):87-90. LüWeifeng,Leng Zhenpeng,Zhang Zubo,et al.Study on waterflooding mechanism in low-permeability cores using CT scan technology[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2013,20(2):87-90.
[26]王端平,时佃海,李相远,等.低渗透砂岩油藏开发主要矛盾机理及合理井距分析[J].石油勘探与开发,2003,30(1):87-89. Wang Duanping,ShiDianhai,LiXiangyuan,etal.Themain challenges and the reasonable well spacing for the development of low-permeability sandstone reservoirs[J].Petroleum Exploration and Development,2003,30(1):87-89.
[27]张兴焰,闫志军,李淑梅,等.压敏效应对文东异常高压低渗油田开发的影响[J].大庆石油地质与开发,2005,24(2):55-56. Zhang Xingyan,Yan Zhijun,Li Shumei,et al.Influence of pressure-sensitive effects upon developmentofWendong low-permeability oilfield with abnormal high pressure[J].Petroleum Geology&Oilfield Developmentin Daqing,2005,24(2):55-56.
[28]郑浩,马春华.基于正交试验法的低渗透油藏超前注水影响因素分析[J].石油钻探技术,2007,35(5):90-93. Zheng Hao,Ma Chunhua.Analysisof factorsaffecting advancewater injection in low-permeability reservoir by orthogonal experimentmethod[J].Petroleum Drilling Techniques,2007,35(5):90-93.
[29]王道富,李忠兴,赵继勇,等.低渗透油藏超前注水理论及其应用[J].石油学报,2007,28(6):78-81,86. Wang Daofu,Li Zhongxing,Zhao Jiyong,et al.Advance waterflooding theory for low-permeability reservoirs and its application [J].Acta PetroleiSinica,2007,28(6):78-81,86.
[30]Lorenz JC.Stress-sensitive reservoirs[R].SPE 50977,1999.
[31]Farquhar R A,Smart B G D,Todd A C,et al.Stress sensitivity of low-permeability sandstones from the Rotliegendes sandstone[R]. SPE 26501,2001.
[32]Davies JP,Davies DK.Stress-dependentpermeability:characterization andmodeling[R].SPE 71750,2001.
[33]LeiQun,XiongWei,Yuan Jiangru,et al.Analysis of stress sensitivity and its influence on oil production from tight reservoirs[R]. SPE 111148,2007.
[34]Rosalind Archer.Impactofstresssensitive permeability on production dataanalysis[R].SPE 114116,2008.
[35]邓玉珍.低渗透储层应力敏感性评价影响因素分析[J].油气地质与采收率,2010,17(4):80-83. Deng Yuzhen.Factors analysis on stress sensitivity evalutation of low-permeability reservoir[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery-Efficiency,2010,17(4):80-83.
[36]刘丽,房会春,顾辉亮.地层压力保持水平对低渗透油藏渗透率的影响[J].石油钻探技术,2011,39(2):104-107. Liu Li,Fang Huichun,Gu Huiliang.The impactof formation pressuremaintenance on permeability in low permeability reservoirs [J].Petroleum Drilling Techniques,2011,39(2):104-107.
[37]刘丽.低渗透油藏启动压力梯度的应力敏感性实验研究[J].油气地质与采收率,2012,19(2):81-83. Liu Li.Laboratory study on stress sensitivity of threshold pressure gradient in low permeability reservoir[J].Petroleum Geology and Recovery Efficiency,2012,19(2):81-83.
编辑王星
Im pactof formation pressuremaintenanceon oil-water seepage characteristics in low permeability reservoirs
Du Yushan1,Yang Yong1,Guo Yingchun1,Fang Huichun1,Hu Gang2,Tian Xuanhua3
(1.Geoscience Research Institute,ShengliOilfield Company,SINOPEC,Dongying City,Shandong Province,257015,China;2.SchoolofPetroleum Engineering,Guangdong University ofPetrochemical Technology,Maoming City,Guangdong Province,525000,China;3.State Key Laboratory ofOiland GasReservoirGeology and Exploitation,Chengdu University ofTechnology,Chengdu City,Sichuan Province,610059,China)
In low permeability reservoirs,it isessential to exactly know the rule of fluid flow in porousmedia duringwaterflooding development.The relative permeability curvemay intuitively reflect the characteristicsof theoiland water seepage in porousmedia.The study of factors affecting the relative permeability curvemainly focuses on the inherent properties of rock(wettability and pore structure),flow medium(oil and water viscosity ratio),water dynamic condition(displacement pressure gradientand velocity),etc.The impactof the formation pressure on the relative permeability curve in the low permeability reservoirs has seldom been studied.Throughmercury-injection experiment,the decline process of the formation pressurewas simulated,and the relative permeability curves in the low permeability reservoirsunder different levels of formation pressuremaintenancewere established.The variation of the oiland water seepage in the low permeability reservoirs was analyzed.The results of experimental study show thatwhen the heterogeneity of pore structure becomes stronger and the formation pressure goes down,the oil-phase relative permeability declines and thewater-phase relative permeability rises,and also the isotonic pointshifts to the leftand the two-phase region turns narrow,resulting in the increase of residu-al oil saturation.That is,the stress sensitivity exists in the oil-water seepage in the low permeability reservoirs.Analyses have shown that the elastic or plastic deformation in the reservoir rocks is the root cause of the stress sensitivity of the oilwater seepage characteristics.Thus the developmentphilosophy of the low permeability reservoir has been put forward:the lower the initialpermeability of the reservoir rocks is,theearlier thewaterflooding time should be.
low permeability reservoir;formation pressuremaintenance;pore structure;oil-water seepage characteristics;stress sensitivity
TE348
A
1009-9603(2015)03-0072-05
2015-03-12。
杜玉山(1968—),男,山东沂南人,教授级高级工程师,博士,从事油藏开发地质研究及管理工作。联系电话:(0546)8715399,E-mail:sl_dys@126.com。
胡罡(1978—),男,湖北英山人,高级工程师,硕士。联系电话:(0668)2923009,E-mail:hgcdut@126.com。
国家科技重大专项“胜利油田特高含水期提高采收率技术”(2011ZX05011)。

