重庆市高血压和糖尿病患者社区健康管理现状及影响因素研究
张彦琦,张 玲,易 东,石 凯,刘 岭,周 亮,伍亚舟
重庆市高血压和糖尿病患者社区健康管理现状及影响因素研究
张彦琦,张玲,易东,石凯,刘岭,周亮,伍亚舟
目的了解重庆市高血压和糖尿病患者的社区健康管理现状,并探讨其影响因素。方法于2014年7月,采用方便抽样法,在重庆市沙坪坝区24个社区的社区卫生服务中心(站)中抽取居民1 200名。采用自行设计的问卷对纳入居民进行调查,内容包括居民的一般情况、慢性病患病情况及社区健康管理利用情况。共发放问卷1 200份,回收1 036份,因问卷填写不合格剔除15份,最终获得有效问卷1 021份。结果1 021名居民的实际糖尿病患病率为11.9%〔122/1 021,95%CI(10.0%,13.9%)〕,实际高血压患病率为29.3%〔299/1 021,95%CI(26.5%,32.1%)〕。居民对社区健康管理的知晓率为77.8%(794/1 021),不同患病情况居民的知晓率比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。居民的社区健康管理接受率63.8%(651/1 021),不同患病情况居民接受率比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。不同患病情况居民对健康管理作用的认知、健康管理满意度、健康管理形式比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。健康管理内容中,不同患病情况居民在测量/询问血压和血糖、生活指导、用药指导、体格检查、建立健康档案及其他方面比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);而在随访和健康教育讲座方面比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。多因素非条件Logistic逐步回归分析显示,性别、年龄、自测血糖和血压情况、最近卫生服务机构、患病情况对居民接受社区健康管理的影响有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论居民的高血压和糖尿病患病率较高,而社区健康管理知晓率和接受率较低,高血压和糖尿病患者优于未患病居民。性别、年龄、自测血糖和血压情况、最近卫生服务机构、患病情况是居民接受社区健康管理的影响因素。
健康管理;社区卫生服务;高血压;糖尿病;重庆
张彦琦,张玲,易东,等.重庆市高血压和糖尿病患者社区健康管理现状及影响因素研究[J].中国全科医学,2015,18(28):3473-3477.[www.chinagp.net]
Zhang YQ,Zhang L,Yi D,et al.Status of and influencing factors for the community health management of hypertensive and diabetic patients in Chongqing[J].Chinese General Practice,2015,18(28):3473-3477.
健康管理的理论和实践最早起源于上世纪20年代末的美国,而其在我国的出现和兴起是近10年才开始的[1]。随着慢性非传染性疾病的流行、人口老龄化进程的加快、医疗费用迅速增长所带来经济负担的加重,健康管理在我国的社区卫生服务中显得越来越重要[2],基于社区的慢性病健康管理被WHO认为是控制慢性病和降低医疗费用的有效举措。目前我国的社区健康管理尚处于起步和探索阶段,但高血压和糖尿病的健康管理已经取得了初步成效[3-4]。本研究以重庆市沙坪坝区社区居民为研究对象,了解其社区健康管理利用情况,并探讨其影响因素,以期能为完善社区健康管理机制提供决策依据。
1 对象与方法
1.1研究对象于2014年7月,采用方便抽样法,在重庆市沙坪坝区24个社区的社区卫生服务中心(站)抽取1 200名居民,以其中问卷填写合格的1 021名居民为研究对象。纳入标准:(1)年龄>18周岁;(2)在重庆市主城区居住时间>3年。排除标准:存在语言表达和理解障碍,不能与调查员正常交流,不能正确理解和回答调查员的问题。本研究获得第三军医大学医学伦理委员会批准,所有居民均为自愿参加。
1.2研究方法由第三军医大学600名经过集中培训的三年级本科学生组成24个调查小组,分配到24个社区,在社区卫生服务中心(站)采用自行设计的问卷对到卫生服务中心(站)就诊或咨询的社区居民进行面对面调查。问卷内容包括居民的一般情况、慢性病患病情况(糖尿病和高血压患者需二级以上医院确诊)、社区健康管理利用情况。共发放问卷1 200份,回收1 036份,因问卷填写不合格剔除15份(重要项目填写缺失10份、重要项目答案矛盾5份),最终获得有效问卷1 021份,问卷有效回收率为85.1%。
1.4统计学方法采用Epidata 3.0软件进行数据录入,采用SPSS 13.0统计软件进行数据分析。计数资料以相对数表示,组间比较采用χ2检验;居民接受社区健康管理的影响因素分析采用多因素非条件Logistic逐步回归分析。以P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2 结果
2.1不同患病情况居民的一般资料1 021名居民中,单纯糖尿病患病率为5.2%〔53/1 021,95%CI(3.8%,6.6%)〕,单纯高血压患病率为22.5%〔230/1 021,95%CI(19.9%,25.1%)〕,糖尿病合并高血压患病率为6.8%〔69/1 021,95%CI(5.3%,8.3%)〕;实际糖尿病患病率为11.9%〔122/1 021,95%CI (10.0%,13.9%)〕,实际高血压患病率为29.3%〔299/1 021,95%CI(26.5%,32.1%)〕。不同患病情况居民的一般资料见表1。
2.2不同患病情况居民健康管理利用情况比较居民对社区健康管理的知晓率为77.8%(794/1 021),不同患病情况居民的知晓率比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。社区健康管理的接受率为63.8%(651/1 021),不同患病情况居民的接受率比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。不同患病情况居民对健康管理作用的认知、健康管理满意度、健康管理形式比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。健康管理内容中,不同患病情况居民在测量/询问血压和血糖、生活指导、用药指导、体格检查、建立健康档案及其他方面比较,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05);而在随访和健康教育讲座方面比较,差异无统计学意义(P>0.05,见表2)。
2.3居民接受社区健康管理影响因素的多因素非条件Logistic逐步回归分析以是否接受健康管理为应变量,以居民一般资料为自变量,进行多因素非条件Logistic逐步回归分析。结果显示,性别、年龄、自测血糖和血压情况、最近卫生服务机构、患病情况对居民接受社区健康管理的影响有统计学意义(P<0.05,见表3)。
3 讨论
本研究纳入居民的实际糖尿病患病率为11.9%〔95%CI (10.0%,13.9%)〕,实际高血压患病率为29.3%〔95%CI (26.5%,32.1%)〕,高于王建生等[6]和王栋等[7]报道的数据,这可能与纳入人群的年龄构成不同有关。另外,居民的社区健康管理知晓率仅为77.8%,且非糖尿病或高血压者低于患病人群;社区健康管理的接受率为63.8%,且高血压合并糖尿病患者和单纯高血压患者高于单纯糖尿病患者和非糖尿病或高血压者。这一结果与柴云等[8]报道的高血压和糖尿病患者的社区卫生服务利用率分别为81.4%和56.9%的结果一致,但高于李园等[9]报道的城市高血压规范管理率为63.3%的结果。这可能与患病人群的卫生服务需求有关,也可以表明重庆沙坪坝区的社区卫生服务机构对高血压健康管理的实施更优。提示社区健康管理服务应提倡“预防为主”“治未病”的健康理念,应提高服务主动性,面对健康人群进行主动宣传和健康教育,以降低慢性病及其并发症的发生。
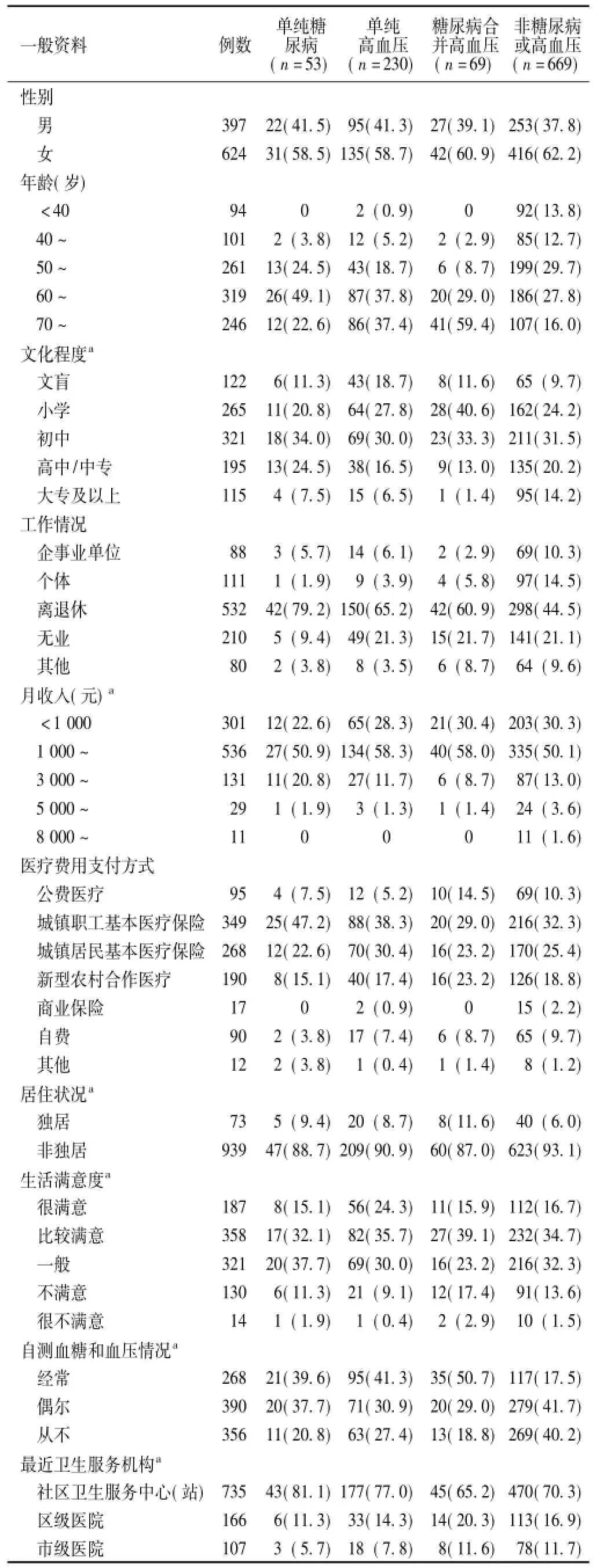
表1 不同患病情况居民的一般资料〔n(%)〕Table 1General data of residents with different diseases
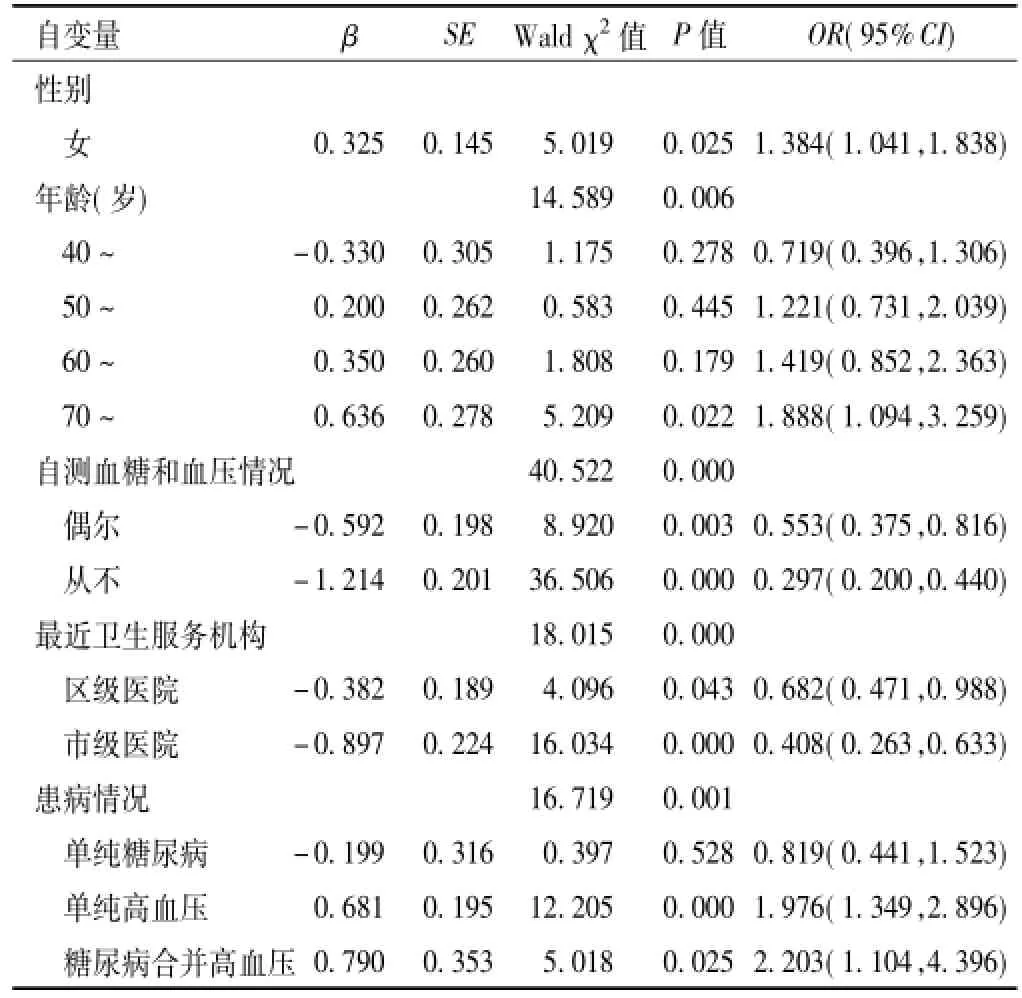
表3 居民接受社区健康管理影响因素的多因素非条件Logistic逐步回归分析Table 3Multivariate non-conditional logistic regression analysis of influencing factorsfortheresidentsacceptingcommunity health management
本研究结果显示,居民接受健康管理的形式主要为门诊,接受较多的健康管理项目为测量/询问血压和血糖、体格检查、生活指导、建立健康档案、用药指导,而随访和健康教育讲座较少。另外,大部分居民对社区健康管理的满意度较高,认为社区健康管理服务的帮助性较大。说明社区健康管理的效果已经得到了居民的认可,但社区卫生服务机构应开展形式多样的健康管理项目,以调动居民的社区健康管理积极性。
多因素分析显示,女性和70岁及以上的居民更倾向于接受社区健康管理;患慢性病居民比无慢性病居民更倾向于接受社区健康管理,尤其是高血压患者,包括单纯高血压和合并糖尿病的患者;而偶尔或从不自测血糖和血压、最近卫生服务机构不是社区卫生服务中心(站)则是居民接受社区健康管理的不利因素。这可能是因为老年女性在社区活动中较为活跃,年龄越大慢性病患病率越高,而患病人群的卫生服务需求更大。值得注意的是社区卫生服务机构的可及性也是影响社区健康管理的因素,这与王栋等[7]的研究结果一致。与部分研究不同的是,本研究结果显示,月收入、文化程度、医疗费用支付方式不是社区健康管理的影响因素[10-12]。

表2 不同患病情况居民健康管理利用情况比较〔n(%)〕Table 2Comparison of the utilization of health management of residents with different diseases
综上所述,重庆市开展的社区健康管理服务已经得到了社区居民的认可,但仍有可完善空间。社区卫生服务机构应走出去,主动开展形式较为多样的健康管理项目和健康促进措施,以调动居民积极性,加强自身健康管理职能,提高健康管理水平和可及性。
[1]Zhao M,Liu FC,Liu WH,et al.Health management in China[J].Int J Cardiol,2014,176(1):234.
[2]郝楠,郭明华.健康管理发展现状及研究进展[J].解放军医院管理杂志,2013,20(6):562-564.
[3]Chen XJ,Gao XL,You GY,et al.Higher blood pressure control rate in a real life management program provided by the community health service center in China[J].BMC Public Health,2014,14 (14):801.
[4]Chao J,Wang Y,Xu H,et al.The effect of community-based health management on the health of the elderly:a randomized controlled trial from China[J].BMC Health Serv Res,2012,12:449.
[5]颜虹.医学统计学[M].2版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2014:277.
[6]Wang JS,Liu SY.Interval estimation of the hypertension prevalence among person aged over 18 years in China[J].Chinese Journal of Health Education,2010,26(11):839-841.(in Chinese)王建生,刘诗瑶.我国18岁以上居民高血压患病率的区间估计[J].中国健康教育,2010,26(11):839-841.
[7]Wang D,Wang J,ZhouYF,et al.Surveyandanalysis on awareness,demands and utilization of community health service in community residents in Nanjing[J].Chinese General Practice,2013,16(4):446-449.(in Chinese)王栋,王洁,周亚夫,等.南京市某社区居民对社区卫生服务知晓、需求及利用情况的调查分析[J].中国全科医学,2013,16(4):446-449.
[8]柴云,汪文新,樊宏,等.成都市高血压和糖尿病患者社区卫生服务利用及其影响因素分析[J].中国慢性病预防与控制,2010,18(3):314-316.
[9]Li Y,Ren DF,Ding PF,et al.Evaluation on programs regarding the community-based management of hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in eight provinces,China[J].Chinese Journal of Epidemiology,2014,35(1):35-39.(in Chinese)李园,任多富,丁萍飞,等.中国8省(自治区)高血压和2型糖尿病患者健康管理服务实施现状[J].中华流行病学杂志,2014,35(1):35-39.
[10]马玉坤,陈长香,李淑杏,等.社区老年人的月收入对自我健康管理的影响研究[J].河北医药,2014,36(17):2681-2682.
[11]Fan H,Wang QY,Wu YY.A comparison of utilization type and influencing factors of the community health service between Nanjing urban and rural residents[J].Chinese General Practice,2013,16(36):4306-4310.(in Chinese)樊宏,王乾元,邬银燕.南京市城郊居民社区卫生服务的利用类型对比及影响因素调查分析[J].中国全科医学,2013,16 (36):4306-4310.
[12]Zhang LF,Jiang RS,Zhou M,et al.Current situation and influencing factors of utilization of urban community health services in Kunming[J].Soft Science of Health,2014,28(7):437-440.(in Chinese)张丽芳,姜润生,周梅,等.昆明市城市社区卫生服务利用现状及影响因素研究[J].卫生软科学,2014,28(7):437-440.
Status of and Influencing Factors for the Community Health Management of Hypertensive and Diabetic Patients in Chongqing
ZHANG Yan-qi,ZHANG Ling,YI Dong,et al.Department of Health Statistics,College of Preventive Medicine,Third Military Medical University,Chongqing 400038,China
Objective To investigate the status of community health management of hypertensive and diabetic patients in Chongqing and its influencing factors.MethodsIn July 2014,we sampled 1 200 residents from 24 community health service centers in Shapingba District of Chongqing using convenience sampling method.We used a self-designed questionnaire to conduct investigation on the enrolled residents.The questionnaire content included general information,the condition of chronic diseases and the utilization of community health management.A total of 1 200 questionnaires were distributed and 1 036 questionnaire were returned,and we at last obtained 1 021 effective questionnaires after the exclusion of 15 unqualified questionnaires.ResultsThe actual diabetes prevalence among the 1 021 residents was 11.9%〔122/1 021,95%CI(10.0%,13.9%)〕,and the actual hypertension prevalence was 29.3%〔299/1 021,95%CI(26.5%,32.1%)〕.The residents'awareness rate of community health management was 77.8%(794/1 021),and residents with different diseases were significantly different(P<0.05)in the awareness rate.The residents'acceptation rate of community health management was 63.8%(651/1 021),and residents with different diseases were significantly different(P<0.05)in the acceptation rate.Residents with different diseases were not significantly different(P>0.05)in the effect of health management,the satisfaction degree with health management and the form of health management.Among health management items,residents with different diseases were significantly different(P<0.05)in blood pressure monitoring/consultation,life guidance,medication guidance,physical examination and the establishment of health record and other aspects;while residents with different diseases were not significantly different(P>0.05)in follow-up and lectures of health education.Multivariate non-conditional logistic regression analysis showed that gender,age,monitor of blood glucose and blood pressure,the nearest health service setting and the state of illness had significant influence on residents accepting community health management(P<0.05).ConclusionResidents have higher prevalence of hypertension and diabetes mellitus,while the awareness rate and acceptation rate of community health management are low,and hypertensive patients and diabetic patients have higher awareness rate and acceptation rate.Gender,age,monitor of blood glucose and blood pressure,the nearest health service setting and the state of illness are influencing factors for residents accepting community health management.
Health management;Community health services;Hypertension;Diabetes mellitus;Chongqing
R 197.1
A
10.3969/j.issn.1007-9572.2015.28.021
2015-06-08;
2015-08-24)
(本文编辑:王凤微)
国家自然科学基金资助项目(81202286,81172773);重庆市自然科学基金资助项目(cstc2012jjA10006)
400038重庆市,第三军医大学军事预防医学院卫生统计学教研室(张彦琦,易东,刘岭,周亮,伍亚舟),健康教育教研室(张玲,石凯)
易东,400038重庆市,第三军医大学军事预防医学院卫生统计学教研室;E-mail:yd_house@hotmail.com

