植物内生菌抗菌活性物质及其在果蔬采后保鲜中的应用进展
周金伟, 周红丽, 柏连阳, 易有金*,李高阳, 夏 菠, 隆丽林
(1.湖南农业大学食品科技学院/食品科学与生物技术湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410128;2.湖南农业大学植物保护学院,长沙 410128;3.湖南省农业科学院农产品加工研究所,长沙 410128)
植物内生菌抗菌活性物质及其在果蔬采后保鲜中的应用进展
周金伟1, 周红丽1, 柏连阳2, 易有金1*,李高阳3, 夏 菠1, 隆丽林1
(1.湖南农业大学食品科技学院/食品科学与生物技术湖南省重点实验室,长沙 410128;2.湖南农业大学植物保护学院,长沙 410128;3.湖南省农业科学院农产品加工研究所,长沙 410128)
植物内生菌是寄生在植物组织中的一大类群特殊微生物,过去长期被忽略。然而越来越多的研究表明,植物内生菌是新型抗菌药物的宝贵资源,其代谢产物中存在一系列具有多样性结构的抗菌活性化合物。本文对近年来植物内生菌产生的抗菌活性物质及其抗菌效果进行了综述,简要介绍了植物内生菌在果蔬采后保鲜中的应用,同时总结了植物内生菌抗菌活性物质在当前实际研究中所遇到的问题。
内生菌; 抗菌物质; 抗菌活性; 果蔬; 采后保鲜
当前,由各种病原菌引起的疾病正日益危害着人类的健康和生命,而化学药物的滥用加剧了许多致病菌产生耐药性[1]。因此,寻求新型、安全、高效的天然抗菌药物成为当务之急[2]。从微生物次级代谢产物中筛选生物活性物质是新药研究与开发的一个重要途径,为寻找能够产生新型抗菌药物的微生物资源,植物内生菌近年来成为研究的热点[3]。植物内生菌能产生多种抗菌活性物质,且这些物质有许多是尚未开发的新物质[4]。本文以化合物结构类型为线索,对近年来植物内生菌产生的抗菌活性物质进行综述,并对植物内生菌在果蔬保鲜中的应用进行简要讨论。
1 植物内生菌产生的抗菌活性物质
1.1 生物碱
生物碱是天然产物中最大的一类化合物,多数具有抗菌活性。
从丹参内生细菌Pseudomonas brassicacearum subsp.neoaurantiaca中分离到1个抗菌生物碱(图1a),该化合物对腐皮镰刀菌和尖孢镰刀菌的MIC值均为50μg/m L[5],能有效保护丹参免受病原真菌的侵染。Du等[6]从鼠尾藻内生真菌Eurotium cristatum中分离出2个新的吲哚类生物碱cristatumins A和D(图1b,c)和2个同系物(图1d,e),其中化合物d和e对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌有很强的抗菌活性,其MIC分别为64和8μg/m L,活性略低于氯霉素(4μg/m L)。
内生曲霉产生的2个生物碱fumigaclavine C(图1g)和pseurotin A(图1h)对大肠杆菌和绿脓假单胞菌等病原细菌的抗菌效果显著[7]。藏红花内生青霉产生的吡咯生物碱(图1i)对白念珠菌、新型隐球菌和红色毛癣菌的MIC80介于16~64μg/mL[8]。从马钱子内生真菌Gliocladium sp.的发酵物中发现的二酮哌嗪生物碱(图1j)在43.4μg/mL时对藤黄微球菌有很强的抗菌活性[9]。
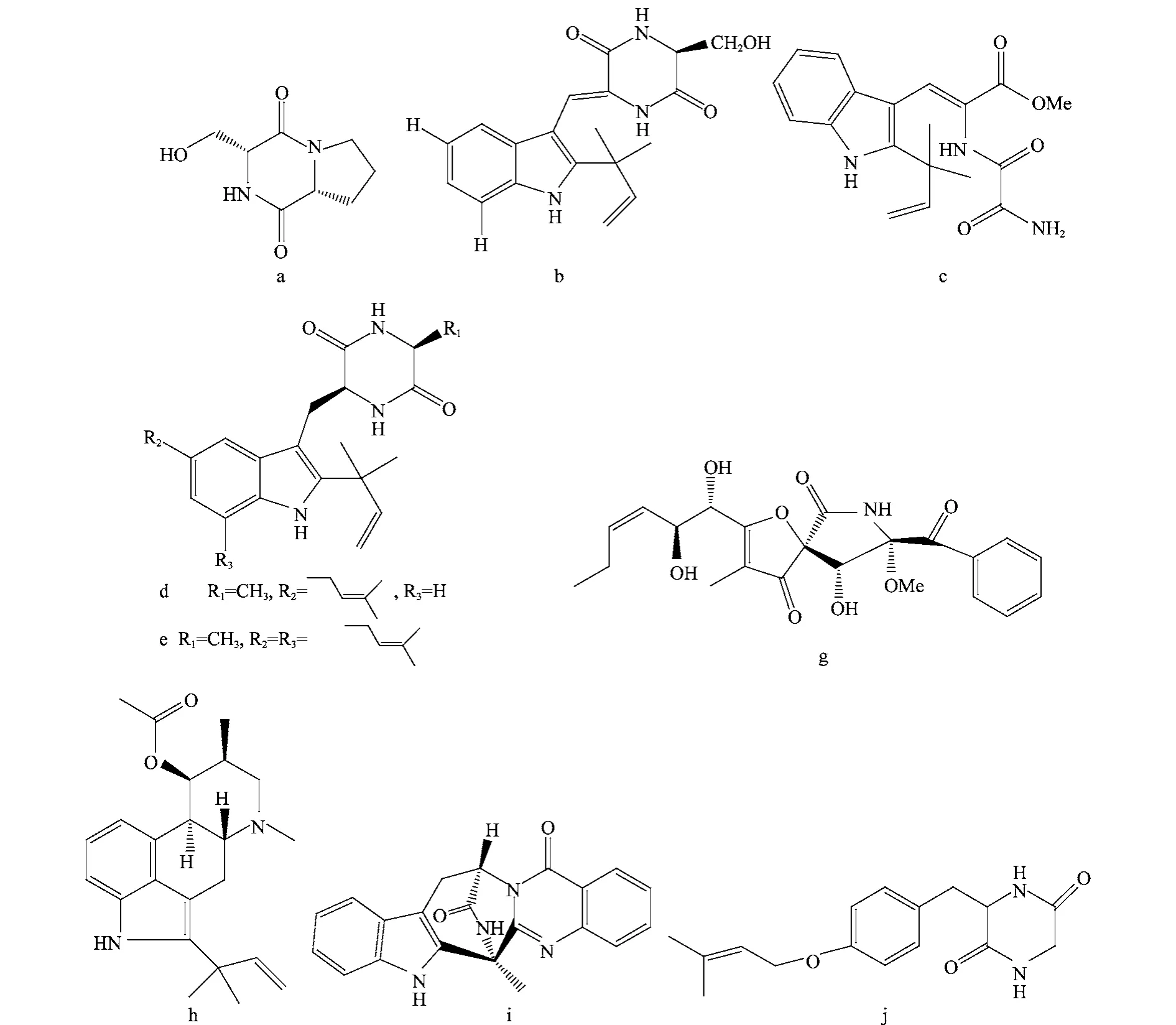
图1 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的生物碱类化合物(a~j)Fig.1 Antimicrobial alkaloids(a-j)from endophytes
1.2 萜类
内生木霉能产生2个新倍半萜化合物(图2c, d),对大肠杆菌、葡萄球菌和皮炎单孢枝霉的最小抑制剂量为25~150μg/disk[10]。
Gao等[11]从内生黄青霉中获得2个具有广谱抗菌活性的新四环二萜conidiogenones H和I(图2e,f)。褐藻内生真菌Aspergillus wentii产生的二萜化合物(图2g)对白念珠菌的MIC为16μg/m L[12]。重楼内生菌Pichia guilliermondii产生的三萜化合物烟曲霉酸(图2h)对9个供试细菌的MIC为1.56~50μg/mL,对稻瘟病菌孢子萌发的IC50为7.20μg/mL[13]。此外,从内生真菌Ulocladium sp.的发酵物中分离出3个具有抗菌活性的新的混合萜类tricycloalternarenes F-H(图2i~k)[14]。
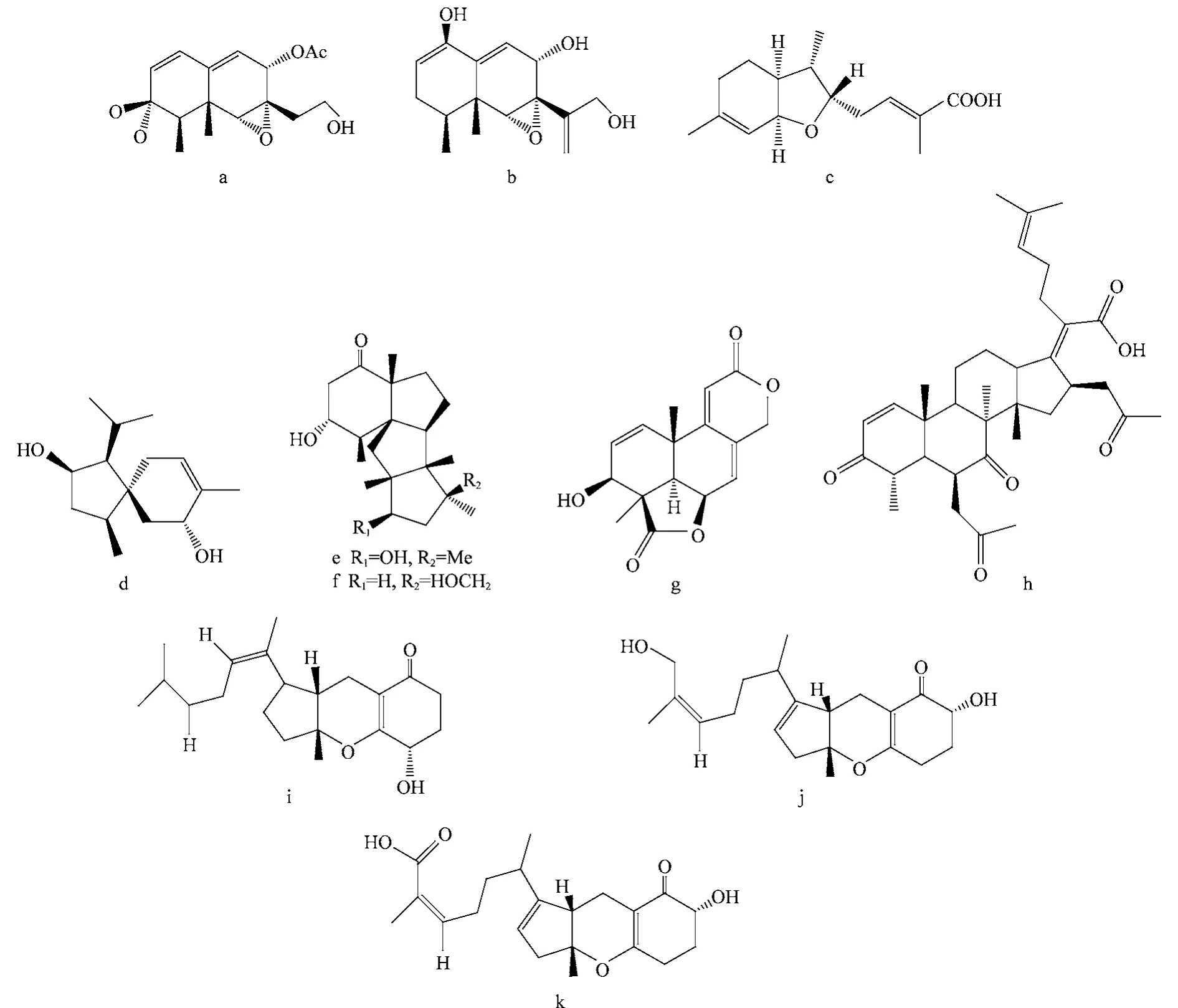
图2 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的萜类化合物(a~k)Fig.2 Antimicrobial terpenoids(a-k)from endophytes
1.3 肽类
微生物产生的肽类物质由非核糖体合成,大多具有抗菌活性。
从Catunaregam tomentosa中获得的内生真菌Curvularia geniculata能产生1个新的肽类-聚酮化合物curvularides B(图3a),对白色念珠菌有抑菌活性[15]。该化合物与抗真菌药物氟康唑联合使用时能发挥协同效应,有望开发成新的抗真菌药物。
乌拉尔甘草内生根瘤菌产生的环二肽化合物(图3b),对大肠杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草芽胞杆菌的MIC为250~500μg/mL[16]。苦丁茶内生芽胞杆菌产生的bacillomycin D(n-C14,iso-C15)(图3c,d)对禾谷镰刀菌等植物病原真菌有强烈抑制作用[17]。
1.4 甾体类
甾体类化合物广泛存在于植物体内,植物内生菌寄生在植物组织中,其代谢产物中往往也含有甾体类化合物,以麦角甾烷型骨架居多[18]。
Gao等[19]从内生黄青霉中分离到2个甾体化合物penicisteroids A(图4a)和anicequol(图4b)。化合物(图4a)为四羟基甾体,两个化合物在浓度为20μg/disk时对黑曲霉和芸苔链格孢菌的抑菌圈直径介于6~18 mm。
从药用植物乌头中获得一株内生拟茎点霉,由其发酵液中分离到2个新甾体化合物(14β,22E)-9,14-dihydroxyergosta-4,7,22-triene-3,6-dione(图4c)、(5α, 6β,15β,22E)-6-ethoxy-5,15-dihydroxyergosta-7,22-dien-3-one(图4d)和3个已知化合物calvasterols A(图 4e)、calvasterols B(图4f)及ganodermaside D(图4g)。5个化合物对白色念珠菌、黑曲霉、稻瘟病菌、燕麦镰刀菌、紧密着色芽生菌和毛癣菌具有抗菌活性[20]。
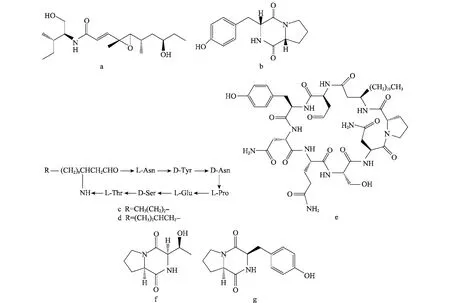
图3 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的肽类化合物(a~g)Fig.3 Antimicrobial peptides(a-g)from endophytes
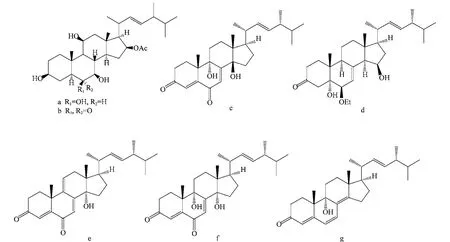
图4 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的甾体类化合物(a~g)Fig.4 Antimicrobial sterides(a-g)from endophytes
1.5 醌类
天然醌类是具有对醌型或邻醌型结构的一类化合物,以萘醌和蒽醌化合物居多[25]。
从Salsola oppostifolia中获得的内生真菌Coniothyrium sp.能产生4个羟基蒽醌化合物(图5g~j),均具有广谱抗菌活性[21]。此外,从红树内生拟茎点霉中分离出1个新的四氢蒽醌衍生物(图5k),对金黄色葡萄球菌和甲氧西林抗药性葡萄球菌的MIC分别为128和64μg/mL[22]。
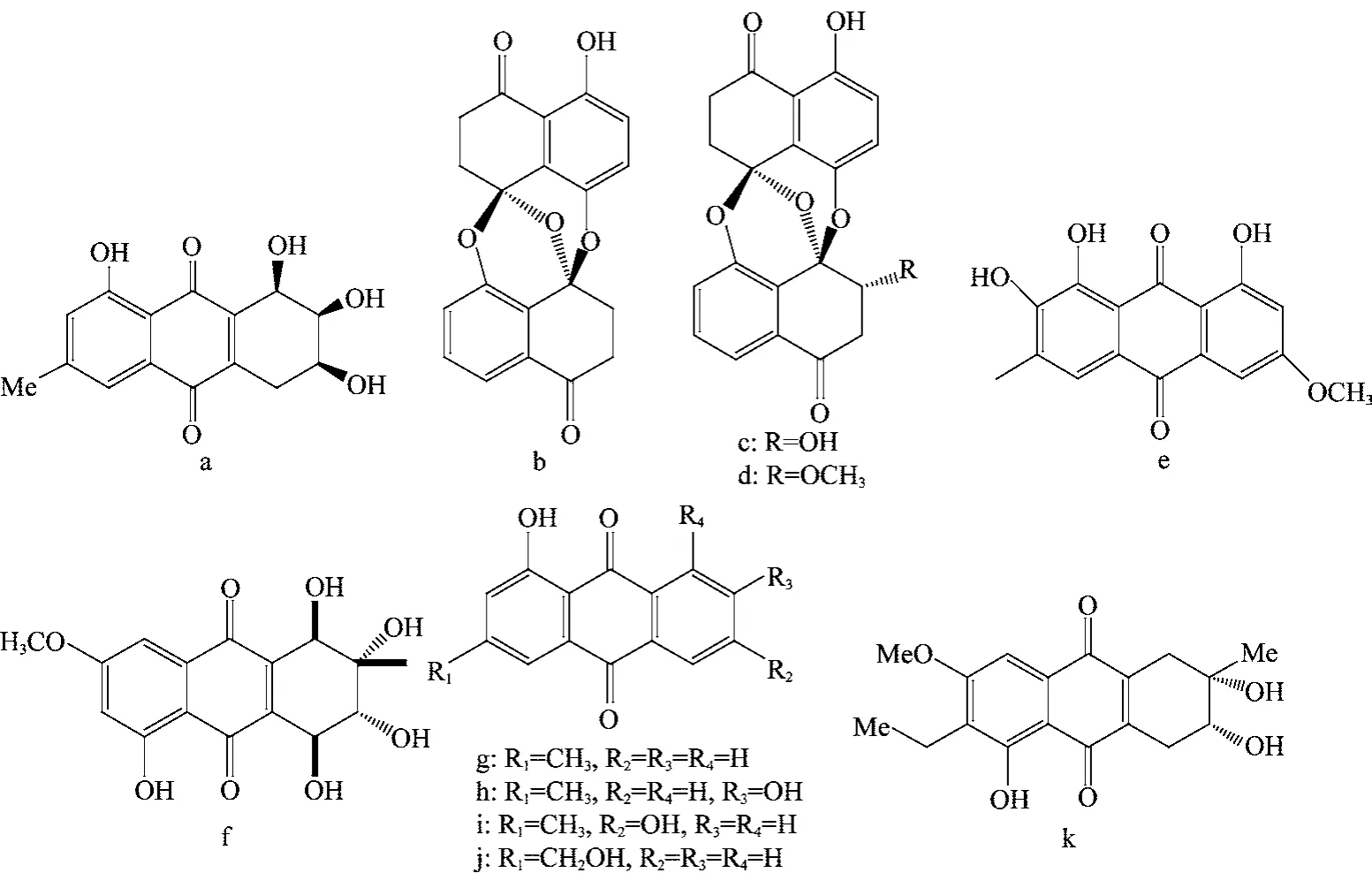
图5 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的醌类化合物(a~k)Fig.5 Antimicrobial quinones(a-k)from endophytes
1.6 酚及酚酸类
内生菌代谢所产生的酚及酚酸类化合物通常具有抗菌活性。
芒果内生真菌Pestalotiopsis mangiferae产生的新化合物(图6a)对枯草芽胞杆菌、肺炎克雷伯菌和大肠杆菌的MIC为0.039~5μg/mL[23]。垂丝海棠内生甘蓝链格孢菌能产生3个广谱抗菌化合物alternariol(图6b)、alternariol 9-methyl ether(图6c)和altechromone A (图6d)[24]。Botryorhodines A和B(图6e,f)来自内生真菌Botryosphaeria rhodina的代谢产物,这两个化合物对多种植物病原真菌有抑制作用[25]。
Siddiqui等[26]从内生真菌Microdiplodia sp.中获得3个新的酚类化合物(图6g~i),3个化合物对嗜肺军团菌和葡萄黑粉菌有抑菌活性。从植物Cistus monspeliensis中分离到一株内生真菌Phomopsis sp.,其产生的2个新的酚类化合物phomochromone A和B(图6j,k)在浓度为1 mg/mL时,对大肠杆菌、巨大芽胞杆菌、灰霉菌和葡萄黑粉菌的抑菌圈半径为5~8 mm[27]。
1.7 异香豆素衍生物
由元宝槭(Acer truncatum Bunge)叶子中获得一株内生真菌Exserohilum sp.,该菌能产生2个新的异香豆素衍生物exserolides C和F(图7a,b)和1个已知物(图7c),其中化合物(图7a)和(图7c)抗真菌活性较好,化合物(图7b)抗细菌效果显著[28]。
Oliveira等[29]从内生真菌Xylaria sp.和Penicillium sp.的发酵液中获得3个双氢异香豆素(图7d~f),其中一个(图7d)为新化合物,对植物病原真菌C.cladosporioides、C.sphaerospermum的最小抑制量分别为10和25μg,另两个化合物(图7e,f)的最小抑制量为5~10μg。
从草本植物Fagonia cretica中获得的内生真菌Microdochium bolley能产生3个新的异香豆素衍生物(图7g~i)。在50μg/disk时,图7g所示化合物对病原真菌Microbotryum violaceum的抑菌圈半径为7 mm,图7h和图7i所示化合物对大肠杆菌、巨大芽胞杆菌和葡萄黑粉菌的抑菌圈半径为6~9 mm[30]。
1.8 酯类
植物内生菌产生的天然酯类以内酯居多。
从野生地黄内生真菌Massrison sp.中分离到3个新的抗真菌酯类化合物:massarigenin D(图8a)、spiromassaritone(图8b)和paecilospirone(图8c),化合物b的活性最强,对白色念珠菌、新型隐球菌、红色毛癣菌和烟曲霉菌的MIC80为0.25~4μg/mL[31]。

图6 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的酚类化合物(a~k)Fig.6 Antimicrobial phenols(a-k)from endophytes

图7 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的醌类化合物(a~i)Fig.7 Antimicrobial quinones(a-i)from endophytes
印度楝内生真菌Phomopsis sp.能产生5个具有广谱抗真菌活性的十环内酯化合物(图8d~h)[32]。褐藻内生真菌产生的化合物(图8i)对金黄色葡萄球菌、沙门氏菌等多种致病细菌的MIC介于6.25~100μg/m L[33]。
Pyrenocines J-M(图8j~m)是从内生真菌Phomopsis sp.中获得的新化合物,4个化合物均有很强的抗细菌活性[34]。此外,藤黄果内生蕈青霉能产生3个内酯化合物penicillone(图8n)、pyrenocines A和B(图8o,p),对M.gypseum的MIC分别为64、128和32μg/mL[35]。
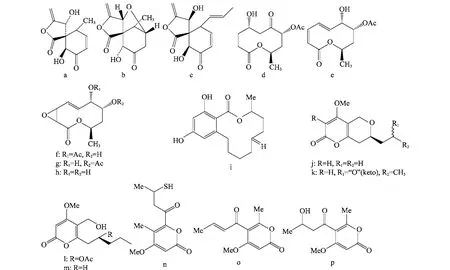
图8 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的酯类化合物(a~p)Fig.8 Antimicrobial esters(a-p)from endophytes
1.9 几丁质酶
从玉米植物组织中分离到6株内生芽胞杆菌,其产生的几丁质酶,对串珠镰刀菌的防治率介于54.2%~79.6%[36]。花生内生放线菌能分泌3种几丁质酶,分子量分别为80.8、78和76 k Da。3种酶对Rhizoctonia solani、Fusarium oxysporum、Alternaria alternate等7种植物病原真菌均有抗菌活性[37]。此外,Lee等[38]从热带植物N.ampullaria和N.mirabilis中分离出26株内生菌,多数能产生具有抗菌活性的几丁质酶。
1.10 葡聚糖酶
从盾叶薯蓣(Dioscorea zingiberensis)的根茎中分离到一株内生枯草芽胞杆菌SWB8,其产生的β-1,3和β-1,4-葡聚糖酶对金黄色葡萄球菌、粪肠杆菌等9种病原菌有抗菌活性[39]。从芦苇中分离出3株内生真菌Choiromyces aboriginum、Stachybotrys elegans和Cylindrocarpon sp.,其产生的外切-β-1,4-葡聚糖酶、内切-β-1,4-葡聚糖酶和β-1,3-葡聚糖酶对病原真菌Fusarium graminearum、Pythium aphanidermatum、Rhizoctonia cerealis、R.solani、Sclerotium rolfsii菌丝的生长有抑制作用[40]。
1.11 挥发性物质
Muscodor sutura是从Prestonia trifidi中分离到的一个新的内生菌属,其产生的罗汉柏烯(图9a)、chamigrene(图9b)、异石竹烯(图9c)等挥发性化合物对烟曲霉菌、灰霉菌、褐斑病菌等多种植物病原真菌有广谱抗菌作用[41]。从裂榄木(Bursera simaruba)叶中分离到一株内生真菌Muscodor yucatanensis,其产生的辛烷、2-甲基丁基乙酸酯、2-戊基呋喃、石竹烯(图9d)和香橙烯(图9e)等挥发性化合物对Guignardia mangifera、Colletotrichum sp.、Phomopsis sp.有致死作用[42]。内生真菌Oxyporus latemarginatus分离自辣椒(Capsicum annum L.),其产生的挥发性化合物5-戊基-2-糠醛(图9f)对链格孢菌、葡萄孢菌、炭疽病菌的抑制率介于13%~85%[43]。此外,齿舌兰内生拟茎点霉能产生桧萜(图9g)、苯乙醇、正丁醇和丙酮等挥发性抗菌成分[44]。
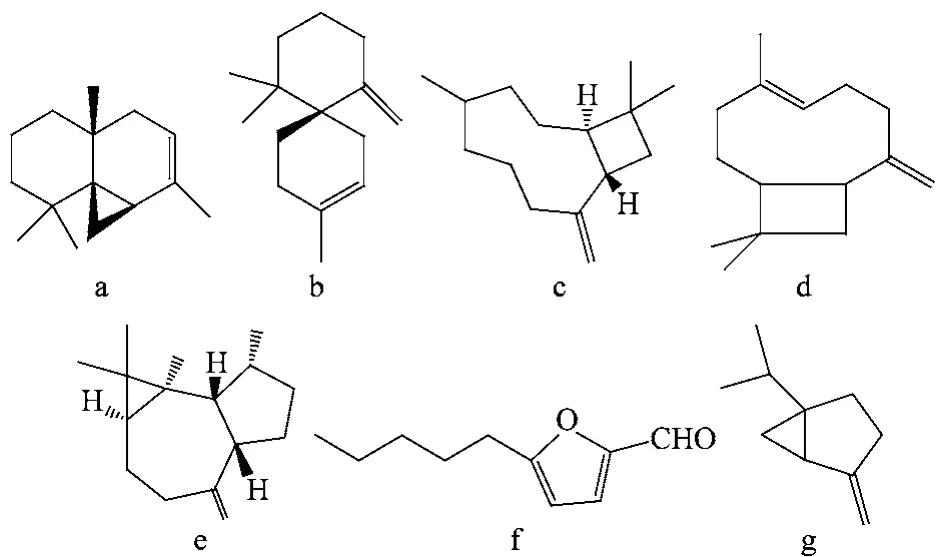
图9 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的挥发性化合物(a~g)Fig.9 Antimicrobial volatile compounds(a-g) from endophytes
1.12 其他类
内生真菌Phomopsis sp.能产生4个新的具有抗菌活性的α-吡喃酮化合物phomopsinones A-D(图10a~d)[45]。从白衫内生真菌Botryosphaeria dothidea KJ-1中获得3个新化合物(图10e~g),对大肠杆菌、枯草芽胞杆菌、金黄色葡萄球菌和蜡样芽胞杆菌有抗菌活性[46]。
Cryptosporioptide(图10h)是从内生真菌Cryptosporiopsis sp.中获得的一个聚酮类化合物,在50μg/disk时对B.megaterium的抑菌圈半径为9 mm[47]。从葡萄叶中获得的内生菌Acremonium byssoides能产生4个新化合物acremines H,I,L, N(图10i~l),在浓度为1 mmol/L时,对Plasmopara viticola孢子萌发的抑制率为30.4%~69.4%[48]。
Senadeera等[49]从内生真菌Dothideomycete sp.中分离到1个新的聚酮化合物(图10m),该化合物对甲氧西林抗药性金黄色葡萄球菌有明显抑菌活性。此外,印度楝内生真菌Nigrospora sp.能够产生2个solanapyrone同系物solanapyrones N和O(图10n,o),对黑曲霉、葡萄孢菌和岛青霉的MIC介于31.25~250μg/mL[50]。
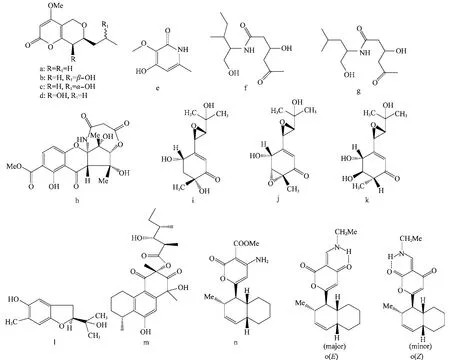
图10 内生菌产生的具有抗菌活性的其他类化合物(a~o)Fig.10 Other antimicrobial compounds(a-o)from endophytes
2 植物内生菌在果蔬采后保鲜中的应用
水果蔬菜营养丰富,但其在采后储藏过程中易受到病原菌感染而腐烂。据统计,在发达国家因采后病害导致的果蔬腐烂达20%~25%,而我国的果蔬损失率高达25%~30%[5152]。目前,果蔬在储藏过程中多采用化学杀菌剂进行采后病害的防治[53],然而化学杀菌剂的长期使用导致病原菌产生抗药性,且农药残留严重威胁着人类健康。植物内生菌作为重要的生防微生物,可通过接种内生菌菌体或其产生的抗菌物质等方式发挥防病功效[54],减轻或消除化学杀菌剂带来的不良影响。
2.1 植物内生菌菌体防治保鲜
Lai等[55]从山豆根(Sophora tonkinensis)中分离到一株内生多黏类芽胞杆菌,该菌对Penicillium digitatum引起的柑橘类水果采后绿霉病有较好的防治效果。当该菌的接种量达到1×109cfu/mL时,绿霉病的发病率降低到18.3%,且接种后水果的紧实度、可溶性固形物、维生素C含量以及可滴定酸度等生理指标未发生改变。Shi等[56]研究了内生细菌恶臭假单胞菌的变种MGP1对木瓜炭疽病的防治效果,发现MGP1对木瓜炭疽病的最大防治率达63%。此外, Shi等[57]进一步研究了木瓜炭疽病与木瓜内生细菌恶臭假单胞菌MGY2的互作效应,发现MGY2处理后木瓜的发病率和病变直径显著降低,且MGY2能通过提高木瓜苯丙氨酸氨裂解酶、过氧化氢酶、过氧化物酶等抗病相关酶的活性和基因表达量以及总酚含量等方式增强宿主的抗病性。Wang等[58]研究了内生枯草芽胞杆菌EB-28对西红柿腐烂致病菌灰霉病菌的防治效果,发现EB-28对灰霉病的防治效果显著,其体外和体内防治率分别为71.1%和52.4%。
2.2 植物内生菌产生的抗菌物质防治保鲜
Nodulisporium spp.是从Lagerstroemia loudoni分离到的一株内生真菌,该菌能产生31种挥发性化合物。其发酵液对柠檬绿霉病、来蒙青霉病和柑橘青霉病的防治效果显著,最低防治浓度分别为50、60和60 g[59]。从辣椒(Capsicum annum L.)中获得一株内生真菌Oxyporus latemarginatus,其固体发酵产物能有效防治葡萄孢菌引起的苹果采后腐烂,采用50 g固体发酵产物处理后,苹果的防治率达98.4%,其产生的主要抗菌活性物质为5-戊基-2-糠醛(134)[43]。从越南肉桂(Cinnamomum loureirii)中获得的内生真菌Nodulisporium sp.能产生榄香烯、1-甲基-1,4-环己二烯、芹子烯和α-芹子烯等挥发性成分,对B. cinerea引起的苹果灰霉病和P.expansum引起的苹果青霉病均有很好的防治效果[60]。此外,黄海东等[61]从云雾龙胆中分离到一株内生短小芽胞杆菌LD-b1,其发酵液对苹果腐烂病菌病斑直径仅为对照的13.7%。
3 结语与展望
自从Stierle等[62]首次从内生菌Pestalotiopsis microspore代谢产物中分离出抗癌物质紫杉酚以来,从内生菌次级代谢产物中寻找新型天然药物引起了人们的广泛关注。越来越多的研究表明,植物内生菌能够产生种类丰富的天然活性物质,这些物质大多具有抗菌活性[46]。因此植物内生菌产生的次级代谢产物为解决日益突出的病原菌耐药性,开发高效、低毒、环保的抗菌药物开辟了一条新途径。植物内生菌作为一个天然抗菌活性物质库,其研究潜力巨大。目前对于内生菌的研究尚处于初级阶段,许多问题有待解决[63]。除继续从传统植物内生菌中寻找新的抗菌活性物质外,从特殊生境条件下的内生菌中筛选抗菌物质越来越受到青睐[18]。目前对于内生菌的研究还仅局限于可培养内生菌,然而有些内生菌在人工培养基中无法生长,因此限制了活性物质的筛选[1]。如何利用现代技术手段最大程度的模拟宿主环境,从而筛选更多的内生菌及其活性产物成为当前面临的一大难题[64]。植物内生菌与宿主植物在长期进化过程中形成了共生关系,植物内生菌能产生与宿主植物相同的代谢产物[65],然而其代谢产物是如何进行调控,内生菌与宿主之间如何进行信号传递和基因交流目前尚不清楚。
植物内生菌活性产物种类繁多,然而许多活性产物尤其是新型未知的功能成分由于其含量太低,当前的技术手段无法检测,从而制约了新型药物的发现。内生菌代谢产物受培养条件的影响较大,如何优化内生菌培养条件,获得高产菌株以实现工业化生产仍需继续探索。当前,有关内生菌活性产物构效关系的研究相对较少,有些产物的抗菌活性较低或毒性较高,因此有必要对其进行结构修饰,以增强或降低其生物活性,使其更好地服务于人类和生态环境。
植物内生菌易受外界环境影响,将其用于果蔬采后病害防治时,其防治效果是否稳定,是否会引起果蔬生理发生变化,是否会产生有害成分仍需进一步研究。此外,采用内生菌活性物质进行果蔬采后防治时,由于其发酵周期长、活性成分含量低以及现代分离纯化技术尚不成熟等因素的制约,其生物防治剂多处于研发阶段,成果转化和应用率较低[66]。
我国幅员辽阔,植物资源丰富,因此有众多植物内生菌资源有待开发,尤其是对海洋植物以及处于特殊生境条件下的植物内生菌的研究较少。但生命科学以及现代分析检测技术的不断发展,必将加速推进植物内生菌抗菌活性物质的筛选步伐。
[1] Guo B,Wang Y,Sun X,et al.Bioactive natural products from endophytes:a review[J].Applied Biochemistry and Microbiology,2008,44(2):136-142.
[2] Liu Changhong,Zou Wongxin,Lu Hong,et al.Antifungal activity of Artemisia annua endophyte cultures against phytopathogenic fungi[J].Journal of Biotechnology,2001,88(3):277-282.
[3] 杨春平,韩小美,韩江涛,等.冬青卫矛内生放线菌YDGl7菌株发酵液抑菌活性研究[J].农药学学报,2008,10(1):53-63.
[4] Li Haiyan,Chen Qing,Zhang Yanli,et al.Screening for endophytic fungi with antitumour and antifungal activities from Chinese medicinal plants[J].World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2005,21:1515-1519.
[5] Li Xiaojun,Tang Haoyu,Duan Jiali,et al.Bioactive alkaloids produced by Pseudomonas brassicacearum subsp.neoaurantiaca,an endophytic bacterium from Salvia miltiorrhiza[J].Natural Product Research,2013,27:496-499.
[6] Du Fengyu,Li Xiaoming,Li Chunshun,et al.Cristatumins AD,new indole alkaloids from the marine-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium cristatum EN-220[J].Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2012,22(14):4650-4653.
[7] Pinheiro E A A,Carvalho J M,dos Santos D CP,et al.Antibacterial activity of alkaloids produced by endophytic fungus Aspergillus sp.EJC08 isolated from medical plant Bauhinia guianensis[J]. Natural product Research,2013,27(18):1633-1638.
[8] Zheng Chengjian,Li Lin,Zou Jingping,et al.Identification of a quinazoline alkaloid produced by Penicillium vinaceum,an endophytic fungus from Crocussativus[J].Pharmaceutical Biology,2012,50(2):129-133.
[9] Koolen H H F,Soares E R,da Silva F M A,et al.An antimicrobial diketopiperazine alkaloid and co-metabolites from an endophytic strain of Gliocladium isolated from Strychnos cf.toxifera[J]. Natural product Research,2012,26(21):2013-2019.
[10]Wu Shaohua,Zhao Lixing,Chen Youwei,et al.Sesquiterpenoids from the endophytic fungus Trichoderma sp.PR-35 of Paeonia delavayi[J].Chemistry&Biodiversity,2011,8(9):1717-1723.
[11]Gao Shushan,Li Xiaoming,Zhang Yi,et al.Conidiogenones H and I,two new diterpenes of Cyclopiane class from a Marine-Derived endophytic fungus Penicillium chrysogenum QEN-24S[J].Chemistry&Biodiversity,2011,8:1748-1753.
[12]Sun Haofen,Li Xiaoming,Meng Li,et al.Asperolides A-C, tetranorlabdane diterpenoids from the marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Aspergillus wentii EN-48[J].Journal of Natural Product,2012,75(2):148-152.
[13]Zhao Jianglin,Mou Yan,Shan Tijiang,et al.Antimicrobial metabolites from the endophytic fungus Pichia guilliermondii isolated from Paris polyphylla var.yunnanensis[J].Molecules,2010,15(11):7961-7970.
[14]Wang Quanxin,Li Chunshun,Yang Xiaoli,et al.Tricycloalternarenes F-H:three new mixed terpenoids produced by an endolichenic fungus Ulocladium sp.using OSMAC method[J].Fitoterapia, 2013,85:8-13.
[15]Chomcheon P,Wiyakrutta S,Aree T,et al.Curvularides A-E:antifungal hybrid peptide-polyketides from the endophytic fungus Curvularia geniculata[J].Chemistry-A European Journal,2010,16:11178-11185.
[16]Wang Lei,Zheng Chengdong,Li Xiaojun,et al.Cyclo(pro-tyr) from an endophytic rhizobium isolated from Glycyrrhiza uralensis [J].Chemistry of Natural Compound,2012,47:1040-1042.
[17]Zhao Zhenzhen,Wang Qiushuo,Wang Kaimei,et al.Study of the antifungal activity of Bacillus vallismortis ZZ185 in vitro and identification of its antifungal components[J].Bioresource Technology,2010,101:292-297.
[18]戈惠明,谭仁祥.共生菌—新活性天然产物的重要来源[J].化学进展,2009,21(1):30-46.
[19]Gao Shushan,Li Xiaoming,Li Chunshun,et al.Penicisteroids A and B,antifungal and cytotoxic polyoxygenated steroids from the marine alga-derived endophytic fungus Penicillium chrysogenum QEN-24S[J].Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2011, 21:2894-2897.
[20]Wu Shaohua,Huang Rong,Miao Cuiping,et al.Two new steroids from an endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp.[J].Chemistry&Biodiversity,2013,10(7):1276-1283.
[21]Sun Peng,Huo Juan,Kurtán T,et al.Structural and stereochemical studies of hydroxyanthraquinone derivatives from the endophytic fungus Coniothyrium sp.[J].Chirality,2013,25(2):141-148.
[22]Klaiklay S,Rukachaisirikul V,Phongpaichit S,et al.Anthraquinone derivatives from the mangrove-derived fungus Phomopsis sp.PSU-MA214[J].Phytochemistry Letters,2012,5 (4):738-742.
[23]Subban K,Subramani R,Johnpaul M.A novel antibacterial and antifungal phenolic compound from the endophytic fungus Pestalotiopsis mangiferae[J].Natural Product Research, 2013,27(16):1445-1449.
[24]Gu Wen.Bioactive metabolites from Alternaria brassicicola ML-P08,an endophytic fungus residing in Malus halliana[J]. World Journal of Microbial&Biotechnology,2009,25(9):1677-1683.
[25]Abdou R,Scherlach K,Dahse H M,et al.Botryorhodines A-D,antifungal and cytotoxic depsidones from Botryosphaeria rhodina,an endophyte of the medicinal plant Bidens pilosa[J].Phytochemistry,2010,71(1):110-116.
[26]Siddiqui I N,Zahoor A,Hussain H,et al.Diversonol and blennolide derivatives from the endophytic fungus Microdiplodia sp.:absolute configuration of diversonol[J].Journal of Natural Product,2011,74(3):365-373.
[27]Ahmed I,Hussain H,Schulz B,et al.Three new antimicrobial metabolites from the endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp.[J]. European Journal of Organic Chemistry,2011,2011(15):2867-2873.
[28]Li Ruxin,Chen Shenxi,Niu Shubin,et al.Exserolides A-F, new isocoumarin derivatives from the plant endophytic fungus Exserohilum sp.[J].Fitoterapia,2014,96:88-94.
[29]Oliveira C M,Regasini L O,Silva G H,et al.Dihydroisocoumarins produced by Xylaria sp.and Penicillium sp.,endophytic fungi associated with Piper aduncum and Alibertia macrophylla[J].Phytochemistry Letters,2011,4(2):93-96.
[30]Zhang Wen,Krohn K,Draeger S,et al.Bioactive isocoumarins isolated from the endophytic fungus Microdochium bolleyi [J].Journal of Natural Product,2008,71(6):1078-1081.
[31]Sun Zhenliang,Zhang Ming,Zhang Jifa,et al.Antifungal and cytotoxic activities of the secondary metabolites from endophytic fungus Massrison sp.[J].Phytomedicine,2011,18(10):859-862.
[32]Wu S H,Chen Y W,Shao S C,et al.Ten-membered lactones from Phomopsis sp.,an endophytic fungus of Azadirachta indica[J].Journal of Natural Product,2008,71(4):731-734.
[33]Yang Ruiyun,Li Chunyuan,Lin Yongchen,et al.Lactones from a brown alga endophytic fungus(No.ZZF36)from the South China Sea and their antimicrobial activities[J].Bioorganic&Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2006,16(16):4205-4208.
[34]Hussain H,Ahmed I,Schulz B,et al.Pyrenocines J-M:Four new pyrenocines from the endophytic fungus,Phomopsis sp. [J].Fitoterapia,2012,83(3):523-526.
[35]Rukachaisirikul V,Kaeobamrung J,Panwiriyarat W,et al.A new pyrone derivative from the endophytic fungus Penicillium paxilli PSU-A71[J].Chemical&Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 2007,55(9):1383-1384.
[36]Bressan W,Figueiredo J E F J.Chitinolytic Bacillus spp.isolates antagonistic to Fusarium moniliforme in maize[J].Journal of Plant Pathology,2010:343-347.
[37]Haggag W M,Abdallh E G J.Purification and characterization of chitinase produced by endophytic Streptomyces hygroscopicus against some phytopathogens[J].Microbiological Research,2012,2(5):145-151.
[38]Lee J M,Tan W S,Ting A S Y.Revealing the antimicrobial and enzymatic potentials of culturable fungal endophytes from tropical pitcher plants(Nepenthes spp.)[J].Mycosphere, 2014,5(2):364-377.
[39]Jin Zhixiong,Zhou Wei,Wang Ya,et al.Antibacterial effect and cytotoxicity ofβ-1,3-1,4-glucanase from endophytic Bacillus subtilis SWB8[J].Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2011,51(11):1527-1537.
[40]Cao Ronghua,Liu Xiaoguang,Gao Kexiang,et al.Mycoparasitism of endophytic fungi isolated from reed on soilborne phytopathogenic fungi and production of cell wall-degrading enzymes in vitro[J]. Current Microbiology,2009,59(6):584-592.
[41]Kudalkar P,Strobel G,Riyaz-Ul-Hassan S,et al.Muscodor sutura,a novel endophytic fungus with volatile antibiotic activities[J].Mycoscience,2012,53(4):319-325.
[42]Macías-Rubalcava M L,Hernández-Bautista B E,Oropeza F, et al.Allelochemical effects of volatile compounds and organic extracts from Muscodor yucatanensis,a tropical endophytic fungus from Bursera simaruba[J].Journal of Chemical Ecology,2010,36(10):1122-1131.
[43]Lee S O,Kim H Y,Choi G J,et al.Mycofumigation with Oxyporus latemarginatus EF069 for control of postharvest apple decay and Rhizoctonia root rot on moth orchid[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2009,106(4):1213-1219.
[44]Singh S K,Strobel G A,Knighton B,et al.An endophytic Phomopsis sp.possessing bioactivity and fuel potential with its volatile organic compounds[J].Microbial Ecology,2011,61 (4):729-739.
[45]Hussain H,Krohn K,Ahmed I,et al.Phomopsinones A-D:Four new pyrenocines from endophytic fungus Phomopsis sp. [J].European Journal of Organic Chemistry,2012,2012(9):1783-1789.
[46]Xiao J,Zhang Q,Gao Y Q,et al.Secondary metabolites from the endophytic Botryosphaeria dothidea of Melia azedarach and their antifungal,antibacterial,antioxidant,and cytotoxic activities[J].Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2014,62(16):3584-3590.
[47]Saleem M,Tousif M I,Riaz N,et al.Cryptosporioptide:A bioactive polyketide produced by an endophytic fungus Cryptosporiopsis sp.[J].Phytochemistry,2013,93:199-202.
[48]Arnone A,Assante G,Bava A,et al.Acremines H-N,novel prenylated polyketide metabolites produced by a strain of Acremonium byssoides[J].Tetrahedron,2009,65(4):786-791.
[49]Senadeera S P D,Wiyakrutta S,Mahidol C,et al.A novel tricyclic polyketide and its biosynthetic precursor azaphilone derivatives from the endophytic fungus Dothideomycete sp.[J].Organic &Biomolecular Chemistry,2012,10(35):7220-7226.
[50]Wu Shaohua,Chen Youwei,Shao Shicheng,et al.Two new solanapyrone analogues from the endophytic fungus Nigrospora sp.YB-141 of Azadirachta indica[J].Chemistry&Biodiversity,2009,6(1):79-85.
[51]Droby S.Improving quality and safety of fresh fruit and vegetables after harvest by the use of biocontrol agents and natural materials[C].International Symposium on Natural Preservatives in Food Systems,2005,709:45-52.
[52]黄应维,徐匆,马锞,等.果蔬微生物保鲜技术的研究进展[J].现代食品科技,2013,29(6):1455-1458.
[53]Chen Hua,Xiao Xiang,Wang Jun,et al.Antagonistic effects of volatiles generated by Bacillus subtilis on spore germination and hyphal growth of the plant pathogen,Botrytis cinerea[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2008,30(5):919-923.
[54]Mousa W K,Raizada M N.The diversity of anti-microbial secondary metabolites produced by fungal endophytes:an interdisciplinary perspective[J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2013,4:65.
[55]Lai Kaiping,Chen Shaohua,Hu Meiying,et al.Control of postharvest green mold of citrus fruit by application of endophytic Paenibacillus polymyxa strain SG-6[J].Postharvest Biology and Technology,2012,69(2):40-48.
[56]Shi Jingying,Liu Aiyuan,Li Xueping,et al.Identification of endophytic bacterial strain MGP1 selected from papaya and its biocontrol effects on pathogens infecting harvested papaya fruit [J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2010,90 (2):227-232.
[57]Shi Jingying,Liu Aiyuan,Li Xueping,et al.Inhibitory mechanisms induced by the endophytic bacterium MGY2 in controlling anthracnose of papaya[J].Biological Control,2011,56(1):2-8.
[58]Wang Shutong,Hu Tongle,Jiao Yanling,et al.Isolation and characterization of Bacillus subtilis EB-28,an endophytic bacterium strain displaying biocontrol activity against Botrytis cinerea Pers [J].Frontiers of Agriculture in China,2009,3(3):247-252.
[59]Suwannarach N,Kumla J,Bussaban B,et al.Biofumigation with the endophytic fungus Nodulisporium spp.CMU-UPE34 to control postharvest decay of citrus fruit[J].Crop Protection, 2013,45(3):63-70.
[60]Park M S,Ahn J,Choi G J,et al.Potential of the volatile-producing fungus Nodulisporium sp.CF016 for the control of postharvest diseases of apple[J].Plant Pathology Journal,2010,26 (3):253-259.
[61]黄海东,李晓雁,杨红澎,等.龙胆内生菌的分离鉴定及其对苹果腐烂病菌的诂抗作用[J].食品工业科技,2012,33(6):215-218.
[62]Stierle A,Strobel G,Stierle D.Taxol and taxane production by Taxomyces andreanae,an endophytic fungus of Pacific yew [J].Science,1993,260(5105):214-216.
[63]马养民,赵洁.植物内生真菌抗菌活性物质的研究进展[J].有机化学,2010,30(2):220-232.
[64]Clardy J,Fischbach M A,Walsh C T.New antibiotics from bacterial natural products[J].Nature Biotechnology,2006,24 (12):1541-1550.
[65]Strobel G,Daisy B,Castillo U,et al.Natural products from endophytic microorganisms[J].Journal of Natural Product, 2004,67(2):257-268.
[66]吴忠红,杜鹃,王刚霞,等.植物内生菌在果蔬保鲜中的研究进展[J].生物技术进展,2013,3(6):399-402.
(责任编辑:田 喆)
Progress in antimicrobial products from endophytes and their application in the preservation of postharvest fruits and vegetables
Zhou Jinwei1, Zhou Hongli1, Bai Lianyang2, Yi Youjin1, Li Gaoyang3, Xia Bo1, Long Lilin1
(1.Hunan Provincial Key Laboratory of Food Science and Biotechnology/College of Food Science and Technology, Hunan Agricultural University,Changsha 410128,China;2.College of Plant Protection,Hunan Agricultural University,Changsha 410128,China;3.Institute of Agro-product Processing Science and Technology, Hunan Provincial Academy of Agricultural Sciences,Changsha 410128,China)
Endophytes are microorganisms residing in the tissues of living plants which are relatively unstudied for a long time.However,more and more researches have proven that endophyte are precious sources of novel antimicrobial products.Presently a number of antimicrobial natural products belong to diverse structural classes have been isolated from endophytes.This review summarizes the antimicrobial products produced by endophytes and their antimicrobial effects.Besides,the application of endophytes in post-harvest fruits and vegetables is briefly discussed.The prospects and existing problems of isolating natural products from endophytes are also discussed.
endophytes; antimicrobial products; antimicrobial activity; fruits and vegetables;postharvest preservation
S 476.8
A
10.3969/j.issn.0529-1542.2015.06.004
2014-12-05
2014-12-29
国家科技支撑计划项目(2015BAD16B00,2015BAD16B01);国家自然科学基金项目(31071738,31000827);长沙市科技局项目(K1308044-21);湖南省研究生科研创新项目(CX2013B310);湖南省自然科学基金项目(09JJ3032)
*通信作者 E-mail:yiyoujin@126.com

