高阶脉冲变时滞BAM神经网络的周期解
吴春雪
高阶脉冲变时滞BAM神经网络的周期解
吴春雪
(烟台大学数学与信息科学学院,山东烟台264005)
神经网络的诸多功能主要体现在其动力学特征中,而周期解问题则是其动力学行为研究中很重要的一部分.许多情况下,考虑神经网络的脉冲效应是必要而具有实际价值的.本文利用重合度理论中的Gaines-Mawhin延拓定理和微分不等式技巧,研究一类具脉冲干扰的高阶BAM神经网络模型的周期解问题,在要求激活函数有界的前提下,得到其周期解存在的充分条件.
重合度理论;BAM神经网络;周期解;脉冲
1987年和1988年由Kosko提出双向联想记忆(BAM)神经网络[1-2],这类神经网络在图像信号处理、自动控制、人工智能、联想记忆、解最优化等方面具有广泛的应用.关于BAM神经网络模型解的存在性及稳定性问题,目前已经有不少研究成果,见文献[3-11].
由于高阶神经网络有着许多优良的性质,强收敛率和高储存量等,吸引了许多学者的关注.大多研究BAM神经网络的文献中,或只考虑时滞模型[12],或只考虑脉冲模型[13],本文在已有文献的基础上,利用重合度理论和微分不等式的技巧对高阶脉冲时滞BAM神经网络进行研究,得到了周期解的存在性定理.
1 预备知识
引理1(Gaines-Mawhin延拓定理)[14]设X是Banach空间,L为指标为零的Fredholm算子,Ω为X中有界开集,N:Ω→X连续映射且在¯Ω是L-紧的,如果下列条件成立:
(1)Lx≠λNx,∀x∈∂Ω∩DomL,∀λ∈(0,1);
(2)QNx≠0,∀x∈∂Ω∩KerL;
(3)deg{JQN,Ω∩KerL,0}≠0,
则方程Lx=Nx在DomL∩¯Ω中至少存在一个解.对于任意非负整数q,令
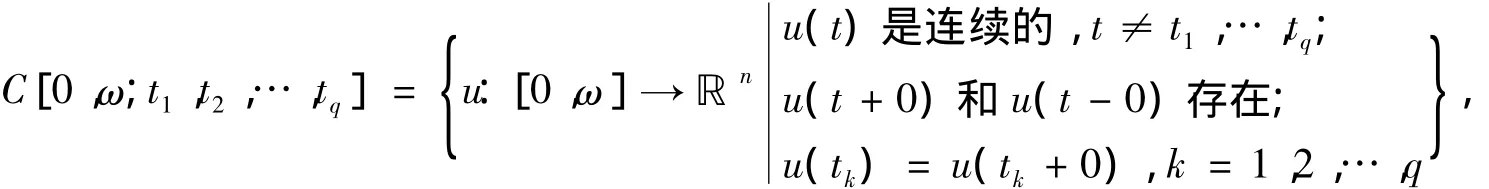
令X={u∈C[0,ω;t1,t2,…,tq]|u(t)=u(t+ω)},Z=X×ℝ(n+m)×(q+1),
下面介绍符号标记.

2 主要结果
我们考虑如下网络模型

其中模型的神经网络方面的意义见文献[15]和[16].
假设下面条件成立:
(H1)函数fjil(u),gijl(u)满足Lipschitz条件,即存在常数>0,使得

对于任意的u1,u2∈ℝ,u1≠u2,i=1,2,…,n,j=1,2,…,m;
(H2)存在一个正整数q,使得

(H3)ai(t)>0,bj(t)>0,ci(t),dj(t),pjil(t),qijl(t)和τjil(t),σijl(t)都是T周期函数,且时滞0≤τjil(t)≤τ,0≤σijl(t)≤σ(i=1,2,…,n,j=1,2,…,m,l=1,2,…,s);
(H4)存在正常数Mijl,Nijl使得
|fijl(u)|≤Mijl,|gijl(u)|≤Nijl,∀u∈ℝ,i=1,2,…,n,j=1,2,…,m,l=1,2,…,s.
定理1假设条件(H1)~(H4)成立,则系统(1)至少有一个T-周期解.
证明取L:DomL∩X→Z,Lu=(u',Δu(t1),…,Δu(tq),0),
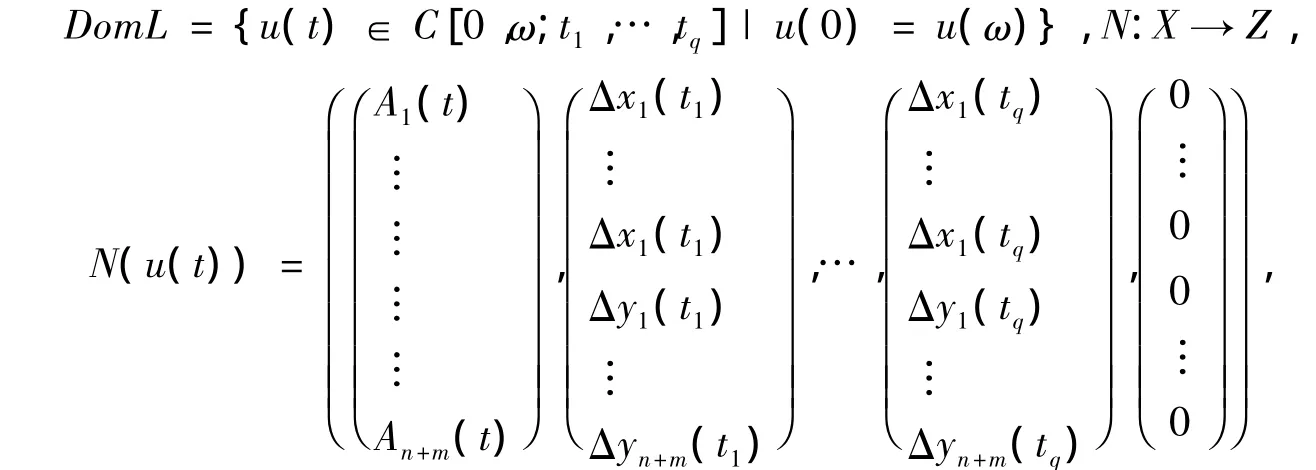
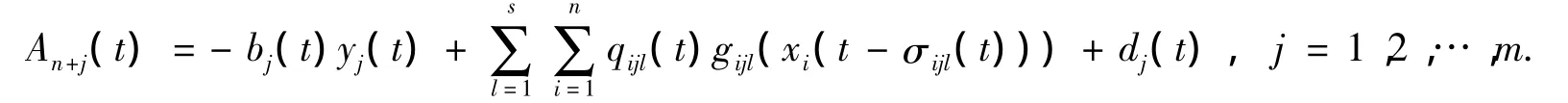
考虑相应算子方程Lx=λNx,λ∈(0,1),有
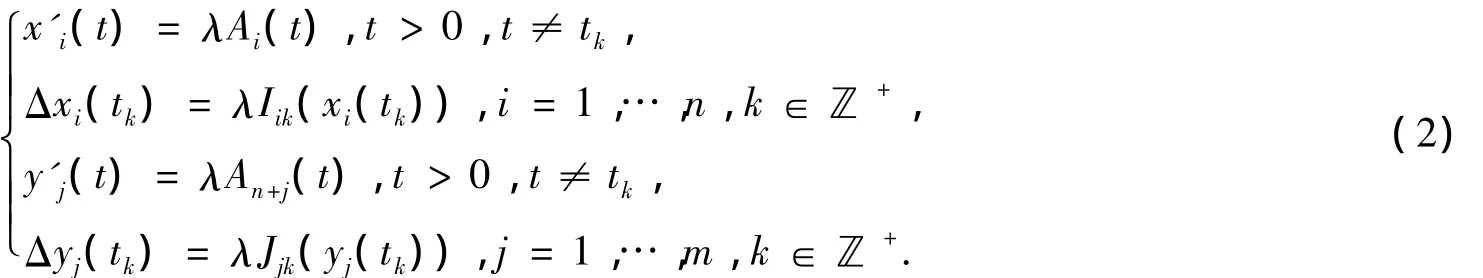
假设u(t)=(x1(t),x2(t),…,xn(t),y1(t),y2(t),…,ym(t))T∈X是系统(2)的对于某个λ∈(0,1)的解,在区间[0,ω]上积分式(2),于是获得

整理得

令ξi∈[0,ω](≠tk),k=1,…,q,使得,i=1,2,…,n.则利用式(3)和H¨oder不等式,有
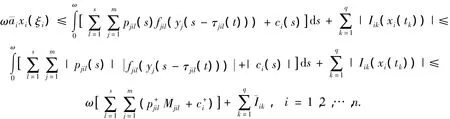
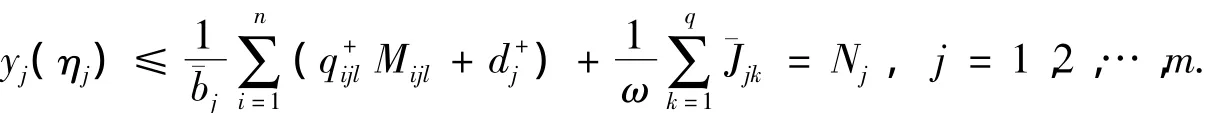
根据式(2)和(3)有

方程(2)两边同乘xi(t)且在[0,ω]上积分,由于
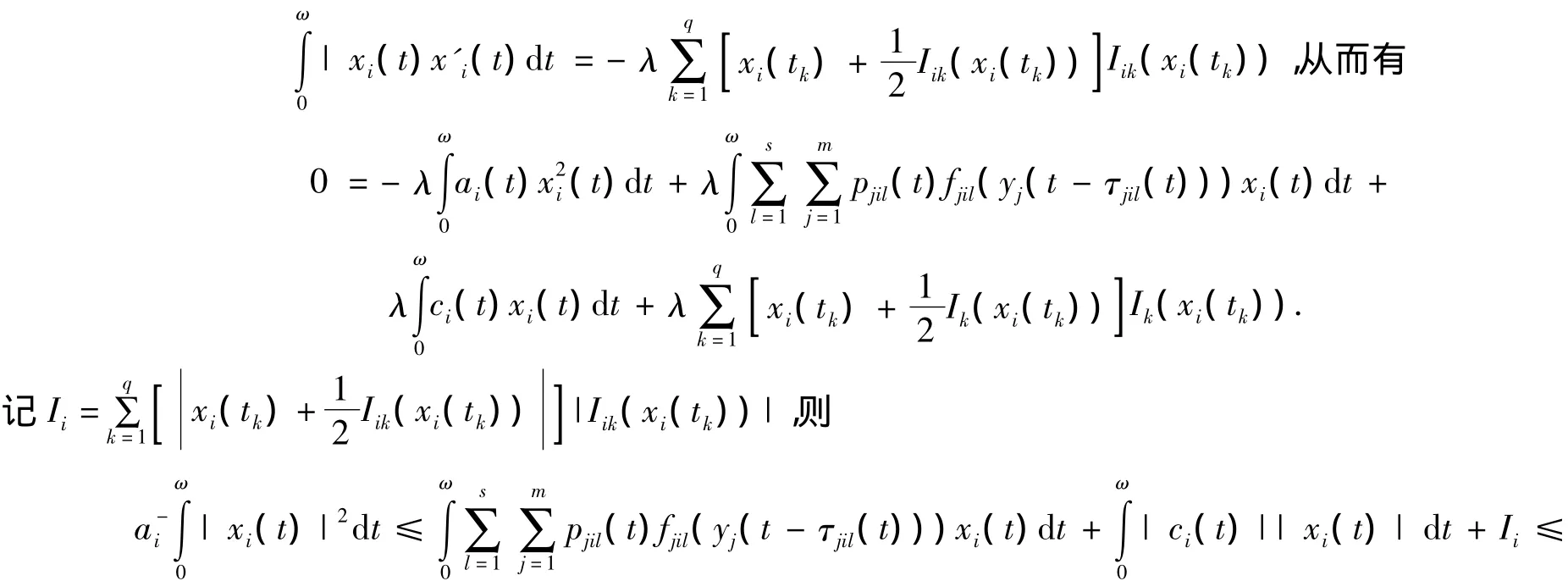
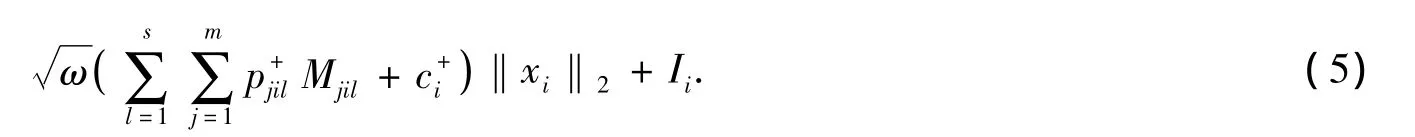
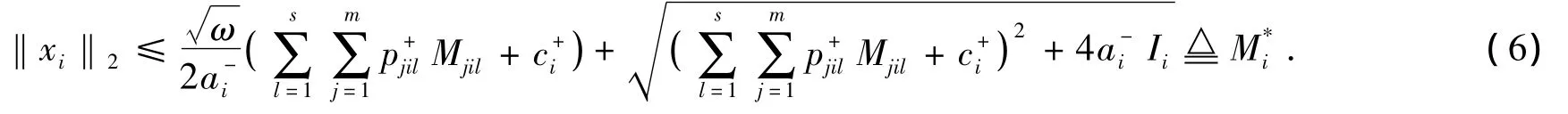
同理可得‖yj‖2≤.
将式(6)代入式(4)得
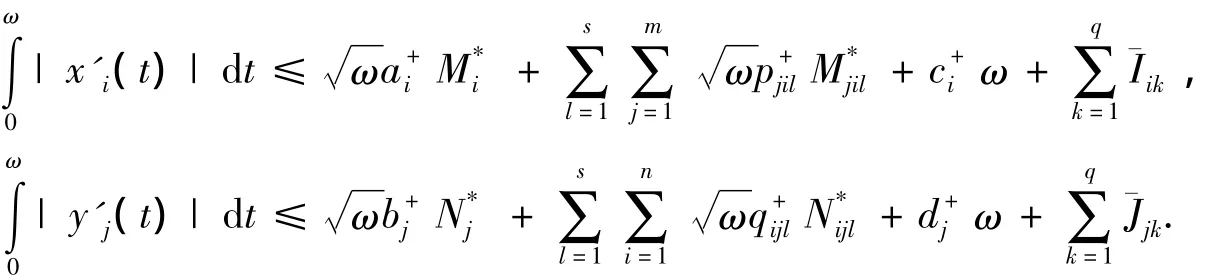

取Ω={u(t)∈X|‖u‖<H*},显然满足引理1的条件(1),当u∈∂Ω∩ℝn+m,u是ℝn+m中常向量且,则QNu=(E1,E2,…,En,En+1,…,En+m)T.
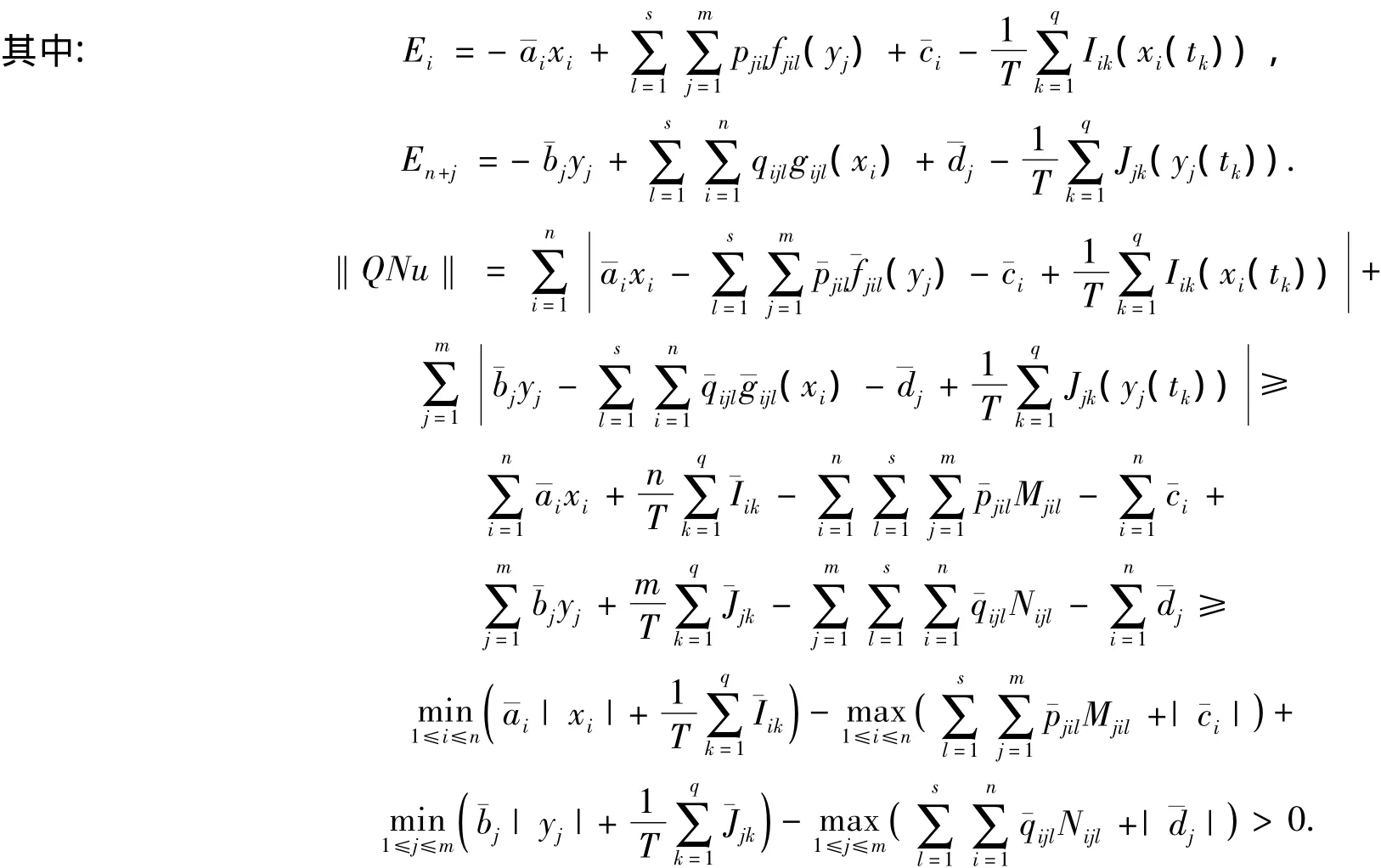
因此,对于u(t)∈∂Ω∩KerL,满足引理1中的条件(2).
定义一个连续函数H:DomL×[0,1]→X满足H(μ,u)=-μx+(1-μ)QNu,这里u(t)是ℝn+m中的常向量且μ∈[0,1],因此‖H(x1,…,xn,y1,…,ym,μ)‖>0.
选择J为恒等映射,有deg{JQN,Ω∩KerL,0}=deg{-u,Ω∩KerL,0}≠0满足引理1中的条件(3).
于是Ω满足引理1中所有条件,方程(1)至少有一个ω周期解.
参考文献:
[1]Kosko B.Adaptive bi-directional associative memories[J].Appl Opt,1987,26(23):4947-4960.
[2]Kosko B.Bi-directional associative memories[J].IEEE Trans Syst Man Cybernet,1988,18:49-60.
[3]Wang Qi,Wang Rui,Zheng Zhaoyue.2Nweighted pseudo almost periodic solutions for CNNs with variable and distributed delays[J].Mathematica Applicata,2014,27(1):73-81.
[4]Agarwal R P,Andrade B D,Cuevas C.Weighted pseudo-almost periodic solutions of a class of semilinear fractional differential equations[J].Nonlinear Ana,2010,11:3532-3554.
[5]Chen Xiaoxing,Hu Xiangyang.Weighted pseudo almost periodic solutions of neutral functional differential equations[J].Nonlinear Analy,2011,12:601-610.
[6]Ding Wei,Wang Linghai.2Nalmost periodic attractors for Cohen-Grossberg-type BAM neural networks with variable coefficients and distributed delays[J].J Math Anal Appl,2011,373:322-342.
[7]Gui Zhanji,Ge Weigao.Periodic solutions of nonautonomous cellular neural networks with impulses[J].Chaos,Solitons and Fractals,2007,32(5):1760-1771.
[8]Li Yongkun.Global exponential stability of BAM neural networks with delays and impulses[J].Chaos,Solitons and Fractals,2005,24:279-285.
[9]Song Qiankun,Wang Zidong.An analysis on existence and global exponential stability of periodic solutions for BAM neural networks with time-varying delays[J].Nonlinear Analysis,2007:1224-1234.
[10]Lou Xuyang,Cui Baotong,Wu Wei.On global exponential stability and existence of periodic solutions for BAM neural networks with distributed delays and reaction-diffusion terms[J].Chaos,Solitons and Fractals,2008,36:1044-1054.
[11]Li Yongkun.Existence and stability of periodic solution for BAM neural networks with distributed delays[J].Applied Mathematics and Computation,2004:847-862.
[12]Gopalsamy K,He Xuezhong.Delay-independent stability in bi-directional associative memory networks[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,1994,5:998-1002.
[13]Gui Zhanji,Yang Xiaosong,Ge Weigao.Periodic solution for nonautonomous bidirectional associative memory neural networks with impulses[J].Neurocomputing,2007,70:2517-2527.
[14]Gaines R E,Mawhin J L.Coincidence Degree and Nonlinear Differential Equations[M].New York:Springer Verlag,1977: 1-50.
[15]Ho W C,Liang Jinling,Lam J.Global exponential stability of impulsive high-order BAM neural networks with time-varying delays[J].Neural Networks,2006,19:1581-1590.
[16]Zhang Jie,Gui Zhanji.Periodic solutions of nonautonomous cellular neural networks with impulses and delays[J].Nonlinear Analysis:RWA,2009,10:1861-1903.
Periodic Solution of Impulsive High-order BAM Neural Networks with Time-varying Delays
WU Chun-xue
(School of Mathematics and Information Science,Yantai University,Yantai 264005,China)
The information processing function of neural networks mostly reflects in its dynamic characteristics.The periodic solution problem is one of the most important parts in the research of neural network dynamic actions in many cases.It is necessary and practically valuable to consider the impulse effect of neural networks.In this paper,by using the continuation theorem of Mawhin’s coincidence degree theory and differential inequalities,sufficient conditions are obtained for the existence of periodic solution of higher-order BAM neural networks with variable delays and impulses under the requirement of boundedness of involved functions.
coincidence degree;BAM neural network;periodic solution;impulse
O175
A
(责任编辑 李春梅)
1004-8820(2015)03-0157-05
10.13951/j.cnki.37-1213/n.2015.03.001
2014-09-25
吴春雪(1976-),女,黑龙江双城人,讲师,博士,研究方向:微分方程.

