Hepatoprotective effect of leaf extracts from Citrus hystrix and C.maxima against paracetamol induced liver injury in rats
Arumugam Abirami,Gunasekaran Nagarani,Perumal Siddhuraju
Bioresource Technology Lab,School of Life Sciences,Department of Environmental Sciences,Bharathiar University,Coimbatore 641 046,Tamil Nadu,India
Abstract The present investigation is aimed to evaluate the hepatoprotective effects of Citrus hystrix and Citrus maxima(Red and White variety)methanolic leaf extracts on paracetamol induced toxicity.Leaf extracts were given in the dose of 200 mg/kg body weight for 7 days and toxicity was induced by paracetamol(2 g/kg)on day 5.Silymarin(100 mg/kg body weight)was used as reference standard.On the 7th day animals were sacrifice and liver function markers(ALT,AST,ALP),total bilirubin and total protein in blood serums and hepatic antioxidants(SOD,CAT,GSH and GPx)in liver homogenate were estimated.The leaf extracts restored the liver function markers and hepatic antioxidants to the normal level than elevated levels noticed on paracetamol control at P <0.001.Reversal of hepatoarchitecture has also been registered.The present study shows that C.hystrix and C.maxima leaf extracts possess hepatoprotective action against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity.©2015 Beijing Academy of Food Sciences.Production and hosting by Elsevier B.V.All rights reserved.
Keywords: Citrus hystrix;Citrus maxima;Paracetamol;Silymarin;Hepatoprotection
1.Introduction
Liver is the prime organ associated with various stages of metabolic and physiologic homeostasis of the organism.Free radicals,alcohol,xenobiotics,food additives and pollutants are the major risk factors which lead to hepatitis,cirrhosis and alcoholic liver diseases [1].Treatment of diseases associated with the liver is necessary,and must be done with proper and extensive care.There are few conventional drugs that can stimulate liver function and offer hepatic protection or help in the regeneration of hepatic cells but they are proved to be hepatotoxic at particular dose [2].Acetaminophen (N-acetyl-p-aminophenol,paracetamol)induced toxicity in rats is one of the widely used experimental model to evaluate the hepatoprotective activity of plant extracts [3,4].At therapeutic doses, paracetamol is considered a safe drug.However, it can cause hepatic necrosis, nephrotoxicity, extra hepatic lesions, and even death in humans and experimental animals when taken in overdose[5].There is a need to evaluate natural compounds as effective alternatives.
Citrus hystrix(C.hystrix) DC (commonly known as Kaffi lime) andCitrus maxima(C.maxima) L are giant citrus(commonly known as Pummelo) originated from South East Asia, India and cultivated throughout the tropical and temperate regions for the fruits.C.hystrixis pear-shaped, bumpy,greenish yellow fruit with acidic fl vor with very thorny bush,aromatic leaves and fruits.The leaves are strongly aromatic,one or two fresh leaves can be torn, chopped and used as a spice and for various fl voring purpose in Southeast Asian and Thai dishes.Also, small pieces of fresh leaves are added with butter milk to prevent the peroxidation of lipids due to the presence of associated bioactive compounds i.e.polyphenols and enhance the digestive system of stomach.It is used as traditional medicine for headache,flu fever,sore throats,bad breath and indigestion[6].The regular use of rubbing fresh leaves on the teeth and gum could aid in dental health.Many active compounds were isolated from leaves of this plant such as phenolic acids, fl vonoids, limonoids, coumarins, glycerolipids andαtocopherol.They possess various pharmaceutical effects such as anti-tumor,antimicrobial,anti-inflammatio and antioxidant activities[7–11].
C.maximafruit is the largest of all citrus variety.It is globose,pear-shaped with 11–14 segments.The pulp appears as white or pinkish red with spindle-shaped juice sacks that separate easily from one another and sweetish-acidic fl vor.The leaves are large 5–10 cm×2–5 cm long size,ovate to elliptical shape,frequently emarginated,obtusely acute apex and dotted glandular[12].Traditionally leaves are used in the treatment of convulsive cough,cholera,epilepsy and hemorrhagic diseases.Leaves possess the important classes of phytochemicals such as alkaloids,saponins and carbohydrates[13].The major essential oils such asDL-limonene,E-citral,1-hexene-4-methyl and Z-citral were analyzed through GC–MS in the leaves and they exhibit antifungal, antiaflatoxigeni and antioxidant activity [14].The leaves exhibit a variety of pharmaceutical effects such as antioxidant, hepatoprotection, anticancer, antimicrobial, antihyperglycemic,antidepressant,anti-inflammatio andanalgesicactivity[15–19].Hence,the aim of the present study was to investigate and compare the hepatoprotective effects of crude methanolic extracts ofC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red and White)leaves on paracetamol induced acute liver toxicity in rats.The protective effects were compared with silymarin, a well known hepatoprotective agent against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity.
2.Materials and methods
2.1.Chemicals
Paracetamol (Cipla Ltd., Baddi, Himachal Pradesh, India),detection kits for alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartate transaminase (AST) and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) (Agappe Diagnostics Ltd.,Ernakulum,Kerala,India)were obtained for the studies.All the other chemicals were obtained from HiMedia Laboratories(Mumbai,Maharashtra,India).
2.2.Preparation of test drugs
The leaves ofC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red and White)fruits were collected from Mayiladuthurai,Nagai district,Tamil Nadu during the month of April 2010.The leaves were cleaned with tap water to wash out the sand particles, dried in oven at 40◦C and ground into fin powder using laboratory blender(Remi Anupam Mixie Ltd.,Mumbai,Maharashtra,India).The powdered samples were extracted by stirring 100 mL 80:20 of aqueous methanol at 25◦C for 48 h and filterin through Whatmann No.4 filte paper.The residues were reextracted with 75 mL of aqueous methanol for 3 h.The solvent of the combined extract was dried at 40◦C.They were dissolved in 0.5%carboxy methyl cellulose(CMC)in(fi ed dose in mg)/10 mL concentration and administrated to the desired volumes according to the body weight of animals to the respective groups.
2.3.Animals housing and feeding conditions
Male Sprague-Dawley (SD) rats were procured from the Small Animal Breeding Centre, College of Veterinary and Animal Sciences, Kerala Agricultural University, Mannuthy,Thrissur, Kerala.Swiss albino mice were procured from animal house of Nandha College of Pharmacy and Research Institute, Erode, TN, India.The animals were provided with adequate environmental conditions(temperature 24±2◦C;relative humidity 40–60%; and 12:12 light:dark cycle) with the standard commercial pellets(M/s.Hindustan Lever Ltd.,Mumbai, Maharashtra, India) and purifie water ad libitum.All the experiments were performed with the permission from Institutional Animal Ethics Committee(688/2/C-CPCSEA)and were in accordance with the guidelines of CPCSEA.
2.4.Acute toxicity studies
The healthy Swiss albino mice (20–25 g) fasted for 3–4 h(provided only with water) and were randomly transferred to fi e groups (n=3/group).They were fed orally with extracts in the dose range of 5, 50, 300 and 2000 mg/kg body weight(b.w.)post esophagus(p.o.)with the control of 0.5%CMC.The study was carried out as per OECD guidelines-423(acute toxic class method) [20].The animals were observed for any signs of toxicity, morbidity and mortality for the firs 24 h with special attention during the firs 4 h.They were also analyzed for the changes in behavioral,neurological and autonomic profile Further,they were observed for a period of 72 h and till the completion of 14 days.Test dose was calculated as per Naskar et al.[21].
2.5.Hepatoprotective activity
2.5.1.Experimental design and animal grouping
The SD rats weighing 100–150 g were used for the study.Animals were divided into six groups(n=6/group)as follows:
GI–normal control(NC)rats received distilled water 5 mL/kg b.w.p.o./7 days.
GII – paracetamol control (PC) rats received distilled water 5 mL/kg b.w.p.o./7 days(except 5th day).
GIII–rats received the standard drug silymarin 100 mg/kg b.w.p.o./7 days.
GIV–rats received test drug 1(C.hystrixleaves)–200 mg/kg b.w.p.o./7 days.
GV – rats received test drug 1 (C.maxima(Red) leaves) –200 mg/kg b.w.p.o./7 days.
GVI – rats received test drug 1 (C.maxima(White)leaves)–200 mg/kg b.w.p.o./7 days.
All the animals in the groups,GIII–GVI were pre-treated with their respective drugs for 5 consecutive days.On the fift day of experimental period,after the drug administration of respective treatments, all animals except those in GI were administered with paracetamol 2 g/kg b.w.p.o.on the seventh day, after 2 h of respective drug treatments,animals were anaesthetized using diethyl ether inhalation jar.Blood was collected through cardiac puncture and the serum was separated.
2.5.2.Determination of key liver function biochemical markers
Liver function biochemical markers such as ALT,AST,ALP,total bilirubin and total protein have been evaluated in the serum obtained from the experimental animals according to the supplier’s specification from the standard kits.
2.5.3.Determination of key oxidative stress markers
One part of the liver tissue from the sacrifice experimental animals was washed and homogenized (1:10, w/v) in ice-cold 50 mmol/L Tris buffer(pH=7.4).The contents were centrifuged at 10,000×gfor 20 min at 4◦C and the supernatant obtained was analyzed for superoxide dismutase (SOD) [22], catalase(CAT) [23], glutathione (GSH) [24] and glutathione peroxidase(GPx)[25].Lipid peroxidation byproduct malondialdehyde(MDA)was measured in the form of thiobarbituric acid reactive substance(TBARS)by Ohkawa et al.[26].
2.5.4.Histopathological studies
Livers excised after sacrificin the animals were immediately washed with buffer and fi ed in 10% buffered formalin.They were then dehydrated through graded alcohol series,cleared in xylene and embedded in paraffi wax.Sections of 5–6 μm thickness were cut using microtome and stained with hematoxylin–eosin.The histopathological changes were examined under the microscope(Nikon,Japan)and the images were captured at the magnificatio of 10 and 40×.
2.6.Statistical analysis
The values expressed as mean±standard deviation (SD)(n=6).The statistical analysis was carried out by one way analysis of variance(ANOVA)followed by post hoc Dunnett’s multiple comparison test using the SPSS(Statistical Package for the social Sciences)version 13.0(SPSS Inc.,Chicago,IL,USA).Significan difference were analyzed at three levels;P<0.05(significant) 0.01 (most significant and 0.001 (highly signifi cant).
3.Results
3.1.Acute toxicity and dose calculation
Animals showed good tolerance to the testing doses of methanolic extracts of the leaf from theC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red and White)as high as 2 g/kg b.w.p.o.respectively.The highest dose was found to be non-lethal and did not show any noticeable signs of toxicity and mortality for 15 days.Generally 1/10th and 1/5th of lethal dose is chosen for the effective dose calculation;hence,200 mg/kg b.w.for all the samples has been scrutinized as test doses.In addition, none of the toxic signs have been found with the selected test doses until the end of the study period.
3.2.Effect of leaves from C.hystrix and C.maxima on serum biochemical parameters
The estimation of enzymes in the serum is a useful quantitative marker of the extent and type of hepatocellular damage.The rats administered with overdose of paracetamol(2 g/kg) caused significan liver damage and necrosis of cells as evidenced by the elevated serum hepatic enzymes (ALT,AST and ALP) and reduced level of protein and increased level of total bilirubin (Table 1).The level of enzyme markers ALT, AST and ALP in normal rats were found to be 61.9±4.43, 79.43±2.74, 159.77±3.68 IU/L respectively; as expected,paracetamol intoxication made their elevation to 4.3,3.6 and 1.95-fold increment with the values of 266.93, 288.77 and 312.4 IU/L respectively.This indicate the hepatic injury and loss of structural integrity.Pre-treatment with leaf extracts significantl (P<0.001) reduced their elevations with the normal values in the range of 79.97–90.20, 93.10–114.5, and 186.13–210.80 IU/L for ALT,AST and ALP respectively.Treatments with methanolic extracts of leaf indicate the stabilization of plasma membrane as well as repair of hepatic tissue damage caused by paracetamol.
Similarly, a distorted pattern for other markers by 2.9-fold increased bilirubin and 2.1-fold decreased protein content was observedin PCratsco mpared to the NCrats(2.18vs.0.74 mg/dL for bilirubin; 4.79 vs.9.63 mg/dL for protein content)anticipate the impaired liver function (Table 1).Significan(P<0.001)restoration of these markers by the interventionsC.hystrixleaves extract (CHL),C.maxima(Red) leaves extract CMRL andC.maxima(White) leaves extract CMWL to the comparable level of normal control and silymarin pre-treated rats was registered by table values.Hepatocellular necrosis or membrane damage lead to very high levels of serum AST and ALT released from liver to circulation,low level of protein and high level of bilirubin respectively.

Table 1 Effects of methanolic extracts of leaves from C.hystrix and C.maxima(Red and White)fruits on liver functioning of paracetamol intoxicated SD rats.
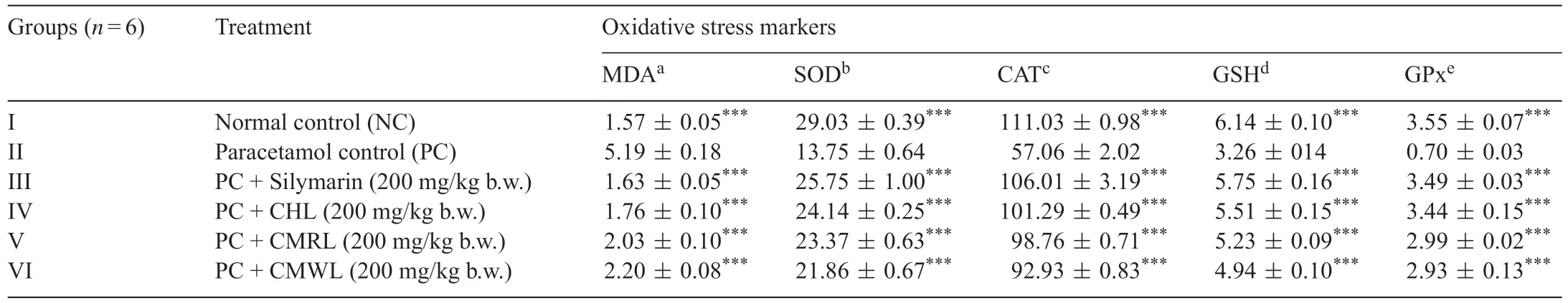
Table 2 Effects of methanolic extracts of leaves from C.hystrix and C.maxima(Red and White)fruits on oxidative stress of paracetamol intoxicated SD rats.
3.3.Effect of methanolic extracts of leaf from C.hystrix and C.maxima on liver biochemical parameters
Liver biochemical parameters like SOD (52.6%)(13.75 U/mg protein), CAT (48.6%) (57.06 μmol of H2O2decomposed/mg protein), GPx (80%) (0.70 U/mg protein) and GSH(47%)(3.26 μg/mg protein)were reduced and lipid peroxidation(3.3-fold)(5.19 nmol MDA/mg protein)were increased in paracetamol induced rats (2 g/kg) compared to normal control(Table 2).Pretreatment with CHL,CMRL and CMWL extracts brought back these oxidative stress markers in the range of 1.76–2.20 nmol MDA/mg protein, 21.86–24.14 U/mg protein,92.93–101.29 μmol of H2O2decomposed/mg protein,4.94–5.51 μg/mg protein, 2.93–3.44 U/mg protein for MDA,SOD, CAT, GSH and GPx respectively, which is on par with normal control rats and significantl different(P<0.001)from the paracetamol intoxicated rats.Glutathione removes free radical species such as hydrogen peroxide,superoxide radicals and maintains membrane protein thiols.
3.4.Effect of methanolic extracts of leaves from C.hystrix and C.maxima on histopathology
Histopathological liver sections of rats from all the six experimental groups are shown in Fig.1A–F and they provide supportive evidence of biochemical analysis.The primary aim is to understand how tissues are organized at all structural levels,including the molecular and macromolecular,the entire cell and intercellular substances and tissues and organs.In this,liver sections from normal control rats(Fig.1A(magnificatio under 10×)) organized into lobules which are roughly hexagonal in shape, with portal triads at the vertices and a central vein in the middle.Within each lobule, hepatocytes are arranged into hepatic cords running radiantly from the central vein and are separated by adjacent sinusoids.Portal tracts showed unremarkable portal veins, bile ducts and no signs for inflammation necrosis or fibrosi or toxic changes.Liver sections from paracetamoltreatedrats(Fig.1B(magnificatio under10×))showed vacuolization of hepatocytes,mild sinusoidal dilation,mild portal tract inflammation fatty changes and necrosis.Pretreatment with silymarin,C.hystrixleaf andC.maxima(Red)leaf extracts in paracetamol intoxicated rats showed recovery of the hepatocytes from necrosis indicating that sample extracts preserved the structural integrity of the hepatocellular membrane and liver cell architecture damaged by paracetamol which was confirme by histopathological examination.Liver sections of the rats treated with methanolic extract ofC.maxima(White)leaf and intoxicated paracetamol(Fig.1F(magnificatio under 10×))showed moderate hepatoprotective activity and the hepatocytes shows normal sinusoids,cytoplasmic clearing and focal ballooning and binucleation.
4.Discussion
Plant medicines play an important role by their various formulations for the treatment of various diseases.Some have been analyzed and scientificall validated for their potentials.Here,we designed the experiments to examine the hepatoprotective activity of methanolic extract of leaves from underutilizedC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red and White)for their development into safe natural drug candidates.

Fig.1.Photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin stained histological sections of normal, paracetamol intoxicated, standard and test drug treated rats liver.(1)Normal control (10×), (2) paracetamol treated rat liver (10×), (3) silimarin+paracetamol treated rat liver (10×), (4) C.hystrix leaf extract+paracetamol treated rat liver(40×),(5)C.maxima(Red)leaf extract+paracetamol treated rat liver(40×),(6)C.maxima(White)leaf extract+paracetamol treated rat liver(40×).(N,nucleus; H, hepatocytes; CV, central vein; NC, necrosis; SD, sinusoidal dilation, FC, fatty change; V, vacuole; PRI, portal tract inflammation B, ballooning and binucleation).
Paracetamol (acetaminophen) is widely consumed as an antipyretic drug that is safe in therapeutic doses but can cause fatal hepatic damage in human and animal at higher toxic doses.Bioactivation of paracetamol by hepatic cytochrome P-450 leads to formation of a highly reactive and toxic metabolite N-acetyl-p-benzoquinone imine(NAPQI).NAPQI is normally detoxifie by conjugation with reduced glutathione (GSH) to form mercapturic acid which is excreted in urine.Toxic overdose of paracetamol depletes hepatic GSH content so that free NAPQI binds covalently to cellular mitochondrial proteins which suppresses mitochondrial fatty acid β-oxidation and results in massive necrosis and apoptosis of hepatocytes[27,28].An obvious sign of hepatic injury is the leaking of cellular enzymes such as ALT,AST and ALP into plasma due to the disturbance caused in the transport functions of hepatocytes.ALT is more specifi to the liver, and it is a better parameter for analyzing hepatic injury.High levels of AST indicate the cellular leakage as well as loss of functional ability of cell membrane in liver.Serum ALP is also related with liver cell damage.High concentration of ALP cause serious hepatic damage in paracetamol treated rats[29].Liver is the major source of most of the serum proteins.Bilirubin is a product of heme within the reticuloendothelia system;its elevation in the blood stream can be adduced to over production,increased hemolysis,decreased conjugation or impaired bilirubin transport[30].Bilirubin is an index that is used to assess the normal functioning of the liver instead of the extent of hepatocellular injury.
Antioxidant enzymes such as superoxide dismutase(SOD),catalase and glutathione peroxidase(GPx)are very important in protecting organisms from reacting oxygen species.SOD is a defense enzyme,which converts superoxide radicals to hydrogen peroxide.Catalase is a hemeprotein found in peroxisomes of eukaryotic cells that catalyses the conversion of hydrogen peroxide to water and oxygen.GPx plays a critical role in maintaining balance in the redox status of animals under acute oxidative stress and protect against chemically induced oxidative destruction of lipid and proteins.Lipid peroxidation has been postulated to be the destructive process in liver injury due to paracetamol administration.The increase in MDA level of liver suggests enhanced lipid peroxidation leading to tissue damage and failure of antioxidant defense mechanisms to prevent formation of excessive free radicals.The decrease of glutathione,GPx,SOD and catalase enzyme activity may indicate the toxic effects of reactive oxygen species produced by toxicants.Reduced GSH level was depleted in paracetamol treated group may be due to conjugation of glutathione with NAPQ1 to form mercapturic acid.
The mechanism of hepatoprotection by methanolic extracts ofC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red & White) leaves is due to their antioxidant potential.This suggests that leaf extracts can reduce ROS that may lessen the oxidative damage to the hepatocytes and improve the activities of the liver antioxidant enzymes, thus protecting the liver from paracetamol induced damage.Also, the possible mechanism could be by the stimulation of hepatic regeneration through an improved synthesis of protein or accelerated detoxificatio and excretion.Akachi et al.[31] demonstrated the hepatoprotective effect of polymethoxy fl vonoids such as citromitin,tangeretin and nobiletin from juice ofCitrus depressacould act againstD-Galactosamine induced liver injury in rats.Park et al.[32] evaluated the oral administration of narirutin fraction from the peel ofC.unshiuagainst alcohol induced hepatic damage in rats could block the development of alcoholic fatty liver and hepatic tissue damage.Mahmoud et al.[33] reported that the hepatoprotective effect of limonin from the seed ofC.aurantiumvar bigaradia onD-Galactosamine induced liver injury in rats.They have also been noted as rich phytoconstituents such as dietary phenolics and fl vonoids which are mainly responsible for the antioxidant power.
5.Conclusions
All profile of hepatoprotective analysis indicate theC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red and White) leaves can serve as hepatoprotectants as they restore all the liver function and oxidative stress markers to the desirable levels.Further verifica tion by their histological micrographs reveals the attenuation of liver damage.This is aided by the superior antioxidant potential of the leaf extracts against the sequential events of free radical toxicity by paracetamol.It can be concluded from the observations in our study thatC.hystrixandC.maxima(Red and White) leaf extract may have a protective effect against paracetamol induced hepatotoxicity in rats.However,further studies using more models of experimental hepatic damage are required to elucidate exact molecular and biochemical mechanisms involved and to establish its therapeutic role as a hepatoprotective agent.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Dr.T.Sivakumar,Principal,Nandha College of Pharmacy and Research Institute,Erode,TN,India for necessary permission to carry out the study and Dr.S.Sengottuvelu,Head,Department of Pharmacology,and Mrs.V.Lalitha,Department of Pharmacology,Nandha College of Pharmacy and Research Institute for their support and suggestions.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Evaluation of free radical scavenging activity of various extracts of leaves from Kedrostis foetidissima(Jacq.)Cogn.
- Nutritional status and effect of seaweed chocolate on anemic adolescent girls
- Tea aroma formation
- Scientifi and technical aspects of yogurt fortification A review

