Scientifi and technical aspects of yogurt fortification A review
Hdi Hshemi GhruieMohmmd Hdi EskndriGholmrez MeshiMohmmd Amin Hnifpour
a Department of Food Science and Technology,College of Agriculture,Shiraz University,Shiraz,Iran
b Fars Pegah Dairy Company,Shiraz,Iran
Abstract Food fortificatio is one of the most important processes for improvement of the nutrients quality and quantity in food.It can be a very cost effective public health intervention.Due to the high consumption rate of dairy products such as yogurt,fortificatio of these products will effectively reduce or prevent diseases associated with nutritional deficiencies The aim of this investigation is to study the technical aspects involved in production of different types of fortifie yogurts and their role in disease prevention and correction of deficiencies In this paper,firstl ,fortificatio is defin d and the main reasons behind carrying out this process are presented and then yogurt production process and a variety of minerals,vitamins,and functional ingredients which are used in the process are briefl discussed.
Keywords: Yogurt fortification Minerals;Vitamins;Fiber
1.Introduction
Considering the importance of food safety and quality,more attention is being paid to the health of consumers[1].However,due to nutrients deficiencie in human societies especially in certain periods of life,embracing,importing,and consumption of fortifie foods is increasing[2].In general,adding one or more essential nutrients to a food and increasing their concentration in that particular food to levels higher than normal is known as fortificatio and is aimed at preventing and correcting deficien cies in one or more nutrients in the society or specifi population groups[3].Nutrition scientists have mentioned that fortificatio of food products using natural resources(fruits,cereal,etc.)is one of the best ways to improve the overall nutrient intake of food with minimal side effects[4].However,compliance notes on the production of fortifie foods with the aim of safeguarding consumers’health and lack of toxicity resulting from the use of this material seem necessary.
Fermentation is a method that has been used for thousands of years to provide longer shelf life for perishable foods and to increase the fl vor and odor of fina food products [5].It is known that fermented foods have been made since Neolithic times.The most famous examples of fermented foods are wine,bread, and cheese.Also, in middle Asian regions, yogurt and other fermented milk products (such as kefi and kumys), traditional alcoholic beverages, vinegar and pickles are common[6].Fermentation is a chemical process in which enzymes break down organic substances into smaller compounds.As the result of fermentation,more digestible,stable and fl vored foods with enhanced nutritional value are produced.Fermentation is carried out by molds,yeast or bacteria.During the growth of these microorganisms,fermented foods are produced incidentally[7].Yogurt is a fermented milk produced byStreptococcus thermophilusandLactobacillus delbrueckiispp.bulgaricus.The production of yogurt as a fermented milk product has been started in the Middle East and spread all over the world.Compared to milk,yogurt is more nutritious and is an excellent source of protein, calcium, phosphorus, ribofl vin, thiamin, vitamin B12,folate,niacin,magnesium and zinc.Since lactose in milk is converted to lactic acid during fermentation and due to the presence of lactose fermenting bacteria in yogurt,lactose intolerant people can consume yogurt without any adverse effect.Moreover, consumption of fermented milk products causes a slight reduction in stomach pH which reduces the risk of pathogen transit and the effects of low gastric juice secretion problem[8].Since fermented milk products are among highly-consumed food in the world, they have been used to deliver nutritional components into human diet.Furthermore,fortificatio of these products such as yogurt,is a good way to improve nutrient intake in daily food products[2].
2.Yogurt consumption and health effects
Obviously,the nutritional value of any material depends on its components.Because of the presence of precious compounds in milk,yogurt is of great importance.Regarding the chemical composition of milk and yogurt,no changes will occur during fermentation.However,the fermentation process causes a beneficia effect on yogurt [9].Table 1 shows the components of full-fat milk,non-fat milk,and the corresponding yogurts[10].
Milk is a physiological liquid containing bioactive and nutrients components which have beneficia effects on the newborn infant’s growth and the digestive system.It may also improve the symbiotic micro flor and the development of lymphoid tissues.Several bioactive compounds are present in milk,notably in fermented milk products,which are of great importance and include certain specifi proteins, vitamins, bioactive peptides,organic acids and oligosaccharides[10].
The consumption of fermented dairy products containing probiotic bacteria would decrease cholesterol absorption [11].Beneficia effects of dairy foods on the body fat and body mass may be caused by whey proteins, medium-chain fatty acids, and the high level of calcium and other minerals.Milk components containing proteins,peptides,probiotic lactic acid bacteria,calcium,and other minerals have a noteworthy effect on the reduction of blood pressure.There are several components in milk fat with functional properties.Sphingolipids and theiractivemetabolites mayexertantimicrobialinfluence either directly or upon digestion.A review of literature revealed that the consumption of recommended level of milk and fermented dairy products,as part of a healthy diet,can result in reducing the risk of many diseases[12].
Fermented dairy products contain adequate levels of certain live and active cultures, namely probiotics that aid to improve the balance of“beneficial versus“undesirable”bacteria in the intestinal tract.Several researches on fermented dairy products showed their effect on the immune system,as well as promoting intestinal health.The impact of consuming fermented products such as yogurt on improving the immunity function in body against carcinogens and harmful toxins is being studied.In order to fin out the effect of milk and dairy products intake in reducing the risk of diseases, clinical investigations have been done on diseases such as GI system diseases,cardiovascular system diseases, musculoskeletal system diseases, urogenital system diseases,immune system diseases,allergy,nervous system diseases,cognitive system diseases,weight control,obesity,aging and dental health[92].
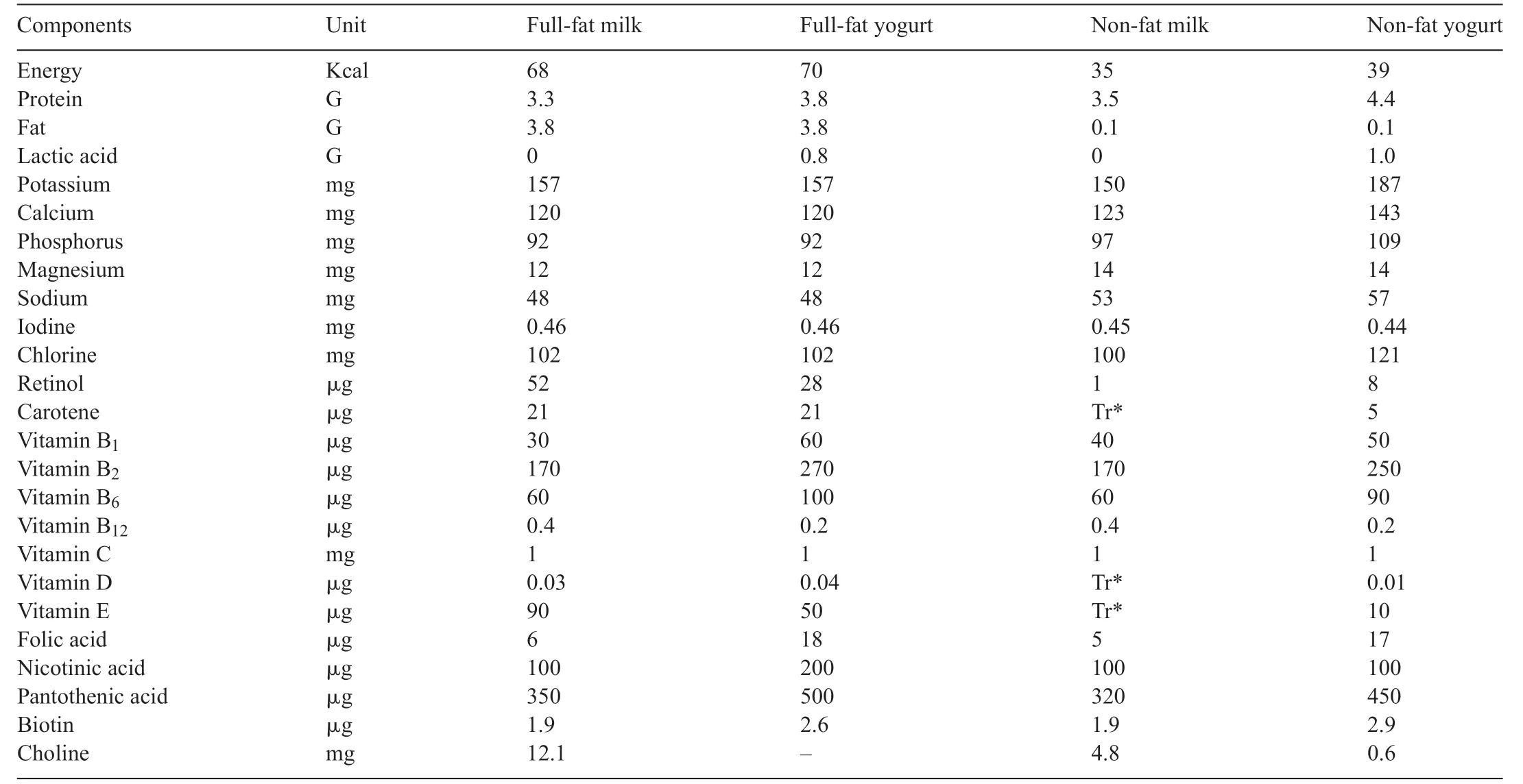
Table 1 Nutritional composition of full-fat milk,non-fat milk and correspondent yogurts(100 g)[10,16].
Such products as yogurt play a potential role in decreasing intestinal disorders and chronic diseases.According to a recent study,several non-nutrient components in yogurt such as sphingolipids, conjugated linoleic acid and butyric acid may play a role as anti-cancer agents[13].The positive effect of probiotics on food allergies in children is another promising area of study.Recent studies in infants have revealed that probiotics not only alter the response to potentially harmful antigens (substances that induce allergies),but also reduce their allergenic potential[14].Fermented dairy products are a good instance of functional foods.Many scientifi studies confir yogurt and other fermented diary products’ functional role which are increasingly advancing the immune system and preventing diseases.Fermented dairy products are good, and in some cases excellent,sources of nutrients namely calcium,protein and potassium[15].
3.Fortification with vitamins
Vitamins are compounds which play a role as cofactors in the body.Fermented milk products such as yogurt can be thought as vitamin sources.However,due to the ability of some starters to synthesize vitamin B that is necessary for their growth,there are different vitamin contents in yogurts.Thus,yogurt and fermented milk products which are produced by strains,may have different vitamins according to the starter that is used[10].
Furthermore, evaluation of vitamins is more difficul since processes like heat treatment,incubation time,temperature and storage conditions change the vitamins content in yogurt[17].
The approximate vitamin content of full fat and nonfat yogurt,and comparison of whole milk and skimmed milk are shown in Table 1 [16].
Vitamin D is vital for appropriate skeletal development which plays a fundamental role in regulating serum calcium and phosphorus concentrations in the body.Due to the photosynthesis of vitamin D in the skin after exposure to solar UV radiation, it is not included in the category of essential nutrient of the body[18].On the other hand,at latitudes above 40◦N or below 40◦S and for several months of the year,no photosynthesized vitamin D is produced in the skin; thus, in order to prevent deficien y,supplementation of vitamin D is required[19,20].Furthermore,the amount of vitamin D produced in the skin as a result of exposure to the sun is limited by application of sunscreen[21].
Diseases such as childhood rickets,osteoporosis and osteomalacia are influence by vitamin D deficien y.It has also been shown that the increase in the risk of developing cancers,osteoporotic fractures, and autoimmune diseases have a direct relationship with vitamin D deficien y[22].
Since vitamin D is a hormone,its receptor,which belongs to the family of steroid/thyroid hormone nuclear receptors,mediate its genomic mechanism of action.Antiproliferative, differentiative and apoptotic effects of this vitamin were observed on prostate cancer cells in vitro[23–25].Concerning the epidemiological studies,vitamin D has negative effects on breast[26]and colon cancers [27].Also, vitamin D deficien y might result in type I diabetes,hypertension,multiple sclerosis and some other cancers [28].Several researches have been conducted on the stability of vitamin D in milk and other dairy products[29–33],which all have claimed that vitamin D is stable during processing and storage.There are not adequate amount of vitamins A and C in low fat dairy products which are not fortified Usually,low fat milk and other dairy products are enriched with vitamin A but not with vitamin C.Fortificatio of dairy products with vitamins A and C leads to improvement in their nutritive quality and consequently,increases their acceptability[34,35].
Vitamin A is toxic in high amounts.But, the provitamins such as carotene are not toxic.It is reported that doses such as 40,000–50,000 and 25,000 IUs are toxic for adults and children respectively [2].So, it is recommended to use β-carotene for fortificatio of dairy products.
Health risks begin to increase, by the intake of more than 100 μg/day of vitamin D.Also, very high doses of vitamin D(more than 250 μg/day) are known to cause tissue and kidney damages [2].Although, Hanson and Metzger reported no adverse effects at level of 250 μg/day of vitamin D, during 5 months of consumption[33].
4.Yogurt fortification with iron
Yogurt is a good source of protein and Ca[36],while dairy products are poor in iron and some other minerals [37].Fortificatio of dairy products with Fe would help nutritional deficiencies Iron-fortifie yogurt has a relatively high iron bioavailability[38].However,before doing any process such as fortification the effects of added iron to yogurt must be assayed.The parameters including oxidation of fat, taste, shelf life and microbial physiology are important, and the sensory quality and overall acceptance of a fortifie yogurt must be ascertained[39–41].Properties of fortifie dairy products are influence by the type of mineral source and the amount of component which is added to the product.Two principal off-fl vors have been created with fortifie yogurt: oxidized fl vor and metallic fl vor,which are due to the catalytic role of iron and the presence of iron salts,respectively[42].
Oxidation of fat occurred in yogurt and milk which were fortifie with ferrous sulfate,ammonium and ferric[43,44],reduced the absorption of this element in the fortifie milk[45].
Fat oxidation in chocolate milk and similar products was not promoted by fortificatio with a ferric polyphosphate–whey protein complex [46].Chocolate milk was fortifie by iron and had acceptable fl vor properties.But other products with ferric chloride or ferrous gluconate were not acceptable.Such oxidation has been effective on sensory characteristics and thiobarbituric acid (TBA) values, which were high in the fortifie milk.Although ferric ammonium citrate increases the oxidation in milk, it is not observed in solid dairy product such as cottage cheese [39].Several researches indicated that the lipid oxidation process evaluated by TBA test was reduced using capsulated iron, compared to uncapsulated iron fortifie yogurt.During three weeks of experiment,no change was found in microcapsulated iron and vitamin C in the fortifie yogurt in terms of sensory parameters and acceptance.Therefore, these researches showed that microcapsules of iron and vitamin C are effective means of fortification and can be used to fortify dairy product without any changes in sensory aspects[47].
Yogurt for tificatio with iron can be an important and effective strategy to control iron deficieny anemia,but adding iron to yogurt still remains a problem.Compared to ferrous sulfate,iron compounds which are water insoluble, are less absorbed.Thus, concerns about their benefi as yogurt fortificant has been increased in the past, especially because the target is young.For many reasons ferric pyrophosphate is one of those compounds that have been widely assayed in many products difficul to fortify such as cereals, salt, rice, infant formulas,and even dairy products.Nonetheless, these data about ferric pyrophosphate will be important in the development of foodfortificatio strategies to figh anemia and iron deficieny in highly vulnerable populations.Chronic overload of iron would cause some adverse effects including,cirrhosis,hepatitis,liver cancer,intestinal irritation,vomiting and diarrhea,articular pain,hormonal disturbance,heart disorder and osteoporosis[89–91].
5.Fortification with calcium
Osteoporosis is a very common disease that affects not only elder women but also elder men and has been related to increased bone fracture risk.Due to the fact that calcium and vitamin D are very important in reducing the risk of fracture, several supplementation researches have examined their effects on bone mass and bone metabolism indices.Still, there are only a few clinical trials examining the effect of these nutrients when supplemented to susceptible population groups via fortifie dairy products.
The sensorial properties of fortifie yogurt should not be influence by using high concentration of minerals.In this regard,Ocak and Rajendram have reported that calcium must be used in micronized type to prevent the adverse impact on the sensorial properties[48].Thus a possible way to enhance the level of minerals in the dairy products is achieved by micronization of the minerals which is mainly due to the fact that ultrafin particles ease dispersion,improve mouth feel,acceptance and texture of dairy products[48].The premium option in calcium fortifie yogurt and dairy products is the application of micronized tricalciumcitrate,whichcangiverisetogoodtechnologicalproperties and nutritional value[16].Indeed,in contrast to calcium,fortificatio with Mg and Zn is not important in developed societies.The tricalcium citrate can be used in yogurts and other dairy products at concentrations of more than 1 g/L calcium[49].
In yogurts and other dairy products, a liquid mineral suspension can be used and the addition of hydrocolloid or starch would result in the stabilization of these suspensions by reducing sedimentation of minerals.All around the world,especially in Europe, where health claims on products are regulated by the new EFSA(European Food Safety Authority)health claim regulation, Mg and Zn offer various options for new fortifie product concepts.By raising the awareness of these minerals and their various beneficia effects on human health,they should gain importance in dairy products as well as calcium and other nutritional ingredients.As technological problem will increase with higher fortificatio levels of mineral, trimagnesium and zinc citrate will be able to prove their superior application in dairy products[49].
6.Fortification with fiber
There is no fibe in yogurt and dairy products.Fiber is a component of the cell wall of fruits, grains, seeds and vegetables[50,51].Fiber of various sources is added to dairy products because of its water-holding capacity and its ability to increase the production yield,reduce the lipid retention,improve textural properties and structure,and reduce caloric content by acting as a bulking agent[52].
Consumption of products containing high fibe may prevent or decrease hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, obesity [53],gastrointestinal disorders [54], coronary heart disease [55,56],diabetes [57,58], and cancer [59].Fortifying yogurt or dairy products with fibe is of increasing interest to create functional foods with health benefit and improve their functionality.Fortifying yogurt with dietary fibe would complement its healthy properties.The maximum acceptable amount of date fibe in fortifie yogurt with potential beneficia health effects is 3%.Many researchers evaluated the effect of dietary fibe on dairy productsandyogurtquality.Theadditionof1.32%oatfibe improved the body and texture of unsweetened yogurt and decreased the overall fl vor quality[60].
7.Fortification with fruits and vegetables
Plants produce a vast amount of secondary metabolites in order to better adapt to the environmental conditions,and protect themselves from microbial attacks and resist both biotic and abiotic stresses.Of these compounds, phenolics have received significan attention in recent years due to their antioxidant,antiinflammator ,anti-mutagenic and anti-clotting power which has been correlated with a declined risk of cardiovascular diseases and cancer development [61–63].The major dietary source of phenolic compounds is fruit [64].It has been suggested that fruit juices[65],powders[66]and extracts have the potential to be used as functional ingredients in the food industry including dairy sector.But, seasonal production of some fruits and vegetables, economic restrictions, and high requirement of fruits in the fresh market, forced researchers to look for alternative strategies for the bio-production of natural compounds similar to anthocyanin and phenolic acids[67].
Plant callus/cell cultures were shown to possess a promising potential for the production of mainly anthocyanin and other phenolic in grapes [68], carrots [69] and cherries [67].Thesein vitrocultures exhibit several advantages over fresh fruit extracts such as possibility of continuous production of natural compounds [67], large scale production depending on specifi needs[70],lower cost and opportunity of manipulating the direction of anthocyanin’s or other phenolic biosynthesis[71,72].
One of the well-known fermented dairy products is yogurt;despite its nutritional characteristics and importance in human diet, it is not being considered as a major source of phenolic compounds[8].The amount of phenolics in dairy products is extremely restricted, which may be because of cattle feed containing high level of phenolics, contamination of food production equipment with sanitizing agents, and bacterial decomposition of proteins in milk.Hence,plant-based additives had been applied to improve the phenolic content of yogurt[8].In another study, yogurt was enriched with acidifie ethanol extracts of four different grape varieties and grape callus which were regarded as functional ingredients[73].
8.Fortification with seed oil containing unsaturated fatty acids and phytosterols
From the perspective of nutrition,unsaturated fatty acids are a nutritional hot topic in oil quality evolution.Compared to animal fat, vegetable oils contain a fatty oil reach in unsaturated fatty acids,mainly linoleic and oleic,which can improve the amount of cholesterol in the plod stream.
Plant sterols compromise a group of compounds which is the focus of research at the moment.They decrease cholesterol absorption and may thus protect against atherosclerosis[74,75].Furthermore,they may have beneficia effects against colon cancer [76,77].To produce functional foods containing elevated levels of plant sterols is the aim of many food companies.On the other hand,for evaluation of their effects on human health at their natural levels,reliable data on plant sterol concentrations in various plant-based foods are needed.
Phytosterols is a white powder insoluble in water and has a melting point of 100–215◦C.Unlike drugs which are basically intestinal,cholesterol is not absorbed intestinally[78].By placing the fat globules in the intestinal cavity,phytosterol prevents absorption of cholesterol in the small intestine[79].These compounds improve type II diabetes,reduce the risk of stomach cancer,inhibit the growth of tumors and enhance inflammator diseases and arteriosclerosis[80].the plant sterols,soy protein and isofl vones in reducing blood cholesterol is meaningful effects.
It seems that due to their strong lipophilic properties, margarine,yogurt,salad dressing,cheese and butter are suitable carriersforphytosterol.Ithasbeenproventhat,comparedtocereals,margarine and phytosterol-enriched dairy products(yogurt and milk)are more effective in lowering cholesterol[81–83].
9.The amount of nutrients needed by different age groups
In selecting micronutrients for society’s different age groups,considering its trophic status and food requirements is of greatimportance.Unfortunately,infants and children are more prone to the deficien y crisis of these materials.In addition to infants and children, other vulnerable groups including, children with malnutrition and adolescents,patients(especially those suffering from HIV/AIDs or Tuberculosis), pregnant and lactating women and people suffering from malnutrition in all ages are of importance.It is obvious that some of these groups have completely different food requirements.
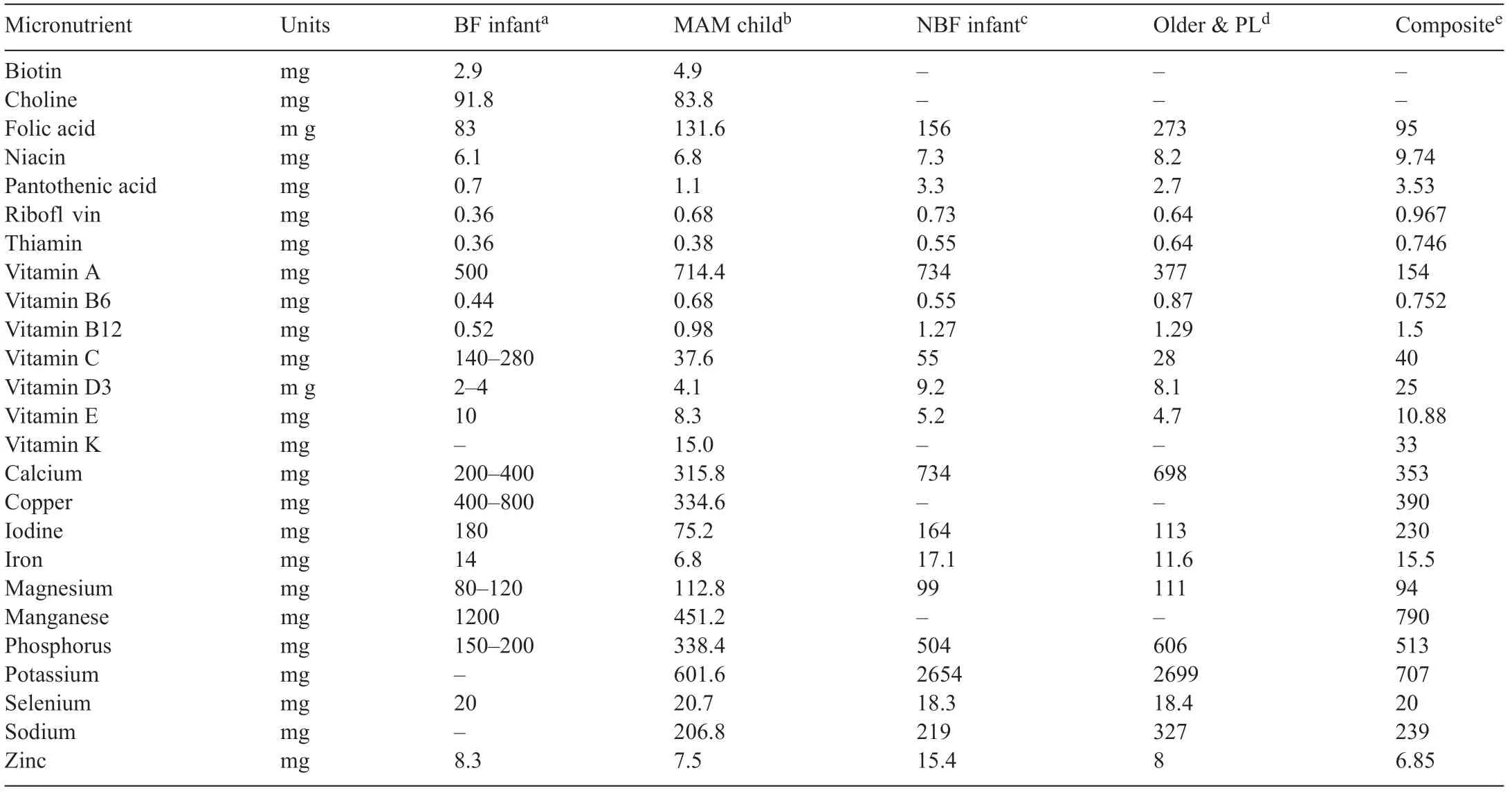
Table 2 Nutrient compounds proposed for fortifie foods(amounts per 100 g food)[84–88].
Several groups,who were expected to be users of any potentially redesigned product-line of FBF,have different micro and macronutrient requirements which have been reported in the existing literature.They include some suggestions for breast and non-breast-fed infants,young children,malnourished children,older children and adults such as pregnant and lactating women.Table 2 presents a summary of these authors’recommendations.
10.Conclusion
Yogurt is the most consumed healthy and nutritious food around the world.Therefore, it offers an appropriate potential to convey nutritious ingredients to human diet.Research shows that most people in developing or underdeveloped countries suffer from micronutrient deficien y and enriched food products can dramatically reduce the nutritional diseases.In this study,a variety of different nutritious components and the manner of using them in dairy products were discussed and the impact of enriched food on preventing or treating disease was shown.This paper shows that food enrichment can prevent or treat most of diseases, especially in young children and it has a significan impact on improving the health of the community.
- 食品科学与人类健康(英文)的其它文章
- GUIDE FOR AUTHORS
- Evaluation of free radical scavenging activity of various extracts of leaves from Kedrostis foetidissima(Jacq.)Cogn.
- Hepatoprotective effect of leaf extracts from Citrus hystrix and C.maxima against paracetamol induced liver injury in rats
- Nutritional status and effect of seaweed chocolate on anemic adolescent girls
- Tea aroma formation

