Application of fuzzy cognitive map in information intelligent push
ZHANG Jia(张佳), XU Sheng-li(徐胜利), DENG Fang(邓方),
(1.School of Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China;2.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Control and Decision of Complex Systems, Beijing 100081, China)
Application of fuzzy cognitive map in information intelligent push
ZHANG Jia(张佳)1,2, XU Sheng-li(徐胜利)1, 2, DENG Fang(邓方)
(1.School of Automation, Beijing Institute of Technology, Beijing 100081, China;2.Key Laboratory of Intelligent Control and Decision of Complex Systems, Beijing 100081, China)
Since computer system functions are becoming increasingly complex, the user has to spend much more time on the process of seeking information, instead of utilizing the required information. Information intelligent push technology could replace the traditional method to speed up the information retrieval process. The fuzzy cognitive map has strong knowledge representation ability and reasoning capability. Information intelligent push with the basis on fuzzy cognitive map could abstract the computer user’s operations to a fuzzy cognitive map, and infer the user’s operating intentions. The reasoning results will be translated into operational events, and drive the computer system to push appropriate information to the user.
fuzzy cognitive map; artificial intelligence; information intelligent push
With the development of computertechnology, powerful computers can provide more information than ever before. The operation of a computer system is more complicated. Therefore, computer users have to spend much more time on seeking information. If information intelligent push is used, the computer system could understand users’ operating intentions and push useful information to users actively[1].Consequently, users will save a lot of operating time, and they will have the time to pay more intention to information itself.
1 Information intelligent push
Information intelligent push[2]introduces artificial intelligence technology into the traditional information push method. The method could change a computer without any thinking ability into an intelligent robot, which could provide service to users actively and help them to use computer quickly and conveniently[3].
The “smart” of information intelligent push reflects in two aspects:
① The system could choose different users’ models and execute different push programs according to different users.
② On the basis of the habits and current operations of users’, the system could infer their intentions, next operations, and push informations needed by users.
The foundation of information intelligent push is that the computer system could understand the user’s operating intention. However, the description of interactions and tasks on a computer system are quite different from the user. Computer system uses accurate defined frame structures to describe the interactions and tasks. By contrast, the description of interaction and the tasks of the user are produced by human brain thinking. It has characteristics of relative vague and arbitrary. The two opposite ways of processing information make the user must adapt to the computer model with the procedure prescribed in advance.
Based on the characteristics ofinformation intelligent push, inferring the user’s operating intention by computer system becomes a difficult problem with information intelligent push. In order to make the information intelligent push come true, it is necessary to find a suitable method to solve this problem. The method could be used to infer users’ intention and help them to complete the follow-up operation. The paper uses a fuzzy cognitive map to solve the problem of user’s intention reasoning in intelligent information push.
2 Fuzzy cognitive map[4]
Fuzzy cognitive map[5-6]is a tool to describe complex systems. It was developed from cognitive maps by KosKo[7]. FCM has an excellent concept representation and reasoning ability for its fuzzy degrees of interrelationships between concepts. A simple FCM which is consisted of six nodes is shown in Fig.1.

Fig.1 Fuzzy cognitive map
According to structural characteristics of the FCM, it could be described as a three parallel group:U={V,E,W}. In the equationV={v1,v2,…,vn} represents a collection of nodes-concepts. Since every node is a state space,Vci(t) is the value of nodeviat timet.E={

Tab.1 Weight between vi and vj in FCM
3 Information intelligent push based on FCM
As FCM has the powerful knowledge representation ability and reasoning ability, FCM is utilized as senior cognition parts in information intelligent push. It will be a senior decision maker in computer system and realize reasoning of users’ operations.
In the process of information intelligent push, firstly, users’ operations are mapped from perceptual space to concept space which gives birth to a set of interactive concepts. The inference engine will load the current user’s model into FCM to reason the intention of the user. The reasoning results will change some concept values in the FCM. The change of concept values will be mapped into the perceptual space in real time and convert to operations. At last, information intelligent push will be completed through the feedback of underlying operating facilities.
3.1 Reasoning mechanism
The reasoning of information intelligent push relies on the recurrence effect of the forward node to the rear node. The reasoning process is described as follows:
The 1×nstate matrixΦuand then×nadjacency matrix Wucould be concluded from a FCM consisted of n nodes at timet[8]:
Φu(t)=(Vc1(t),…,Vcn(t))
The following equation is used to calculate the state of nodes at timet+1.
After these steps, the state of the system at timet+1 will be deduced from the state of timet. The process is repeated until the system enters the final mode.
The reasoning procedure reflects the evolution of the system. (Vc1(t),Vc2(t),Vc3(t), …,Vcn(t)) can be obtained at the end of the reasoning process.
3.2 Information intelligent push model
Event-driven strategy is used in the process of information intelligent push. When the system receives the operation from the users, the operation will be firstly inserted into the event queue and the system responds immediately. Then the system will reason the event and respond to the result of reasoning.
The process of information intelligent push is depicted in Fig.2. Firstly, the user’s operation
will be converted to a state vector as an event, and the vector will be input into a FCM. Then a question is raised: If the event occurs, what the consequence it will lead to? After FCM reasoning, the output state vector exports corresponding results, which is the answer to the question. The outcome state vector is converted into an event. It will drive the system to select appropriate module from the information module library and display it in a human machine system of the computer to achieve the purpose of information intelligent push.
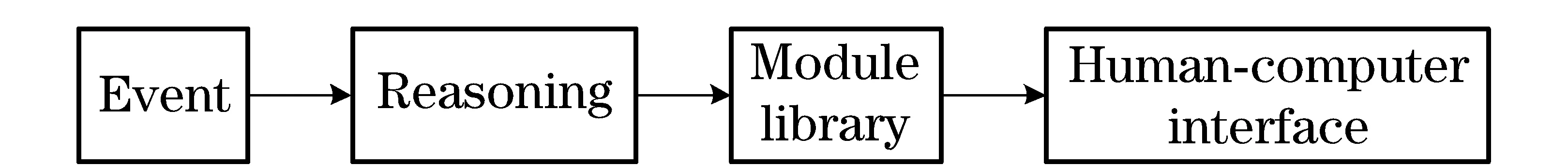
Fig.2 Process of information intelligent push
Fig. 3 is an example of information intelligent push based on FCM in a car navigation device. It is too dangerous to drive the car and operate the navigation device at the same time. However, with the help of information intelligent push, the navigation device can infer the intention of the driver from one operation by the driver and finish the next operations that the driver would do. Therefore, information intelligent push is a smart assistant to help the driver to drive safely.
There are three steps to constructthe FCM of the smart car navigation device.
Step 1 Determine concept-nodes inthe navigation.
Eight concept-nodes, shown in Tab.2, are selected by discussing with some users of the navigation device.

Tab.2 Concept-nodes in the car navigation device
Step 2 Determine the relation between concept-nodes.
If one concept-node influences another, there exists a relationship between them. For example, the user zooms in the map, he may select destination, zoom out, check nearby information, search, or just move map. Therefore, the concept-node named “zoom in” has relationship with the other four concept-nodes. By analyzing each pair of concept-nodes, Fig.3 is gotten. The arrows of edges show the influence direction.
Step 3 Determine the weight values of relation.
The weight value of relation is in the interval of [-1,1]. After an discussion between experts and users, the values shown in Fig.3 are determined.

Fig.3 An example of information intelligent push
In the reasoning process, the initial value of each node is determined by operations as follows: If the operation occurs, the corresponding node will take the value 1; If the operation does not occur, then the value of the corresponding node is 0[9].
The initial nodes’ values engender an event vector. A new event vector, represented the intention of the driver’s operations, is gained by repeated action of the adjacent matrix. The system
火焰是红色的,那人影置身火焰中心,却是漆黑一团,周身仿佛笼罩着一层黑色的雾。人影望着青辰,开口道:“她就在你的身后,你为何不动手?”
will respond to the driver’s subsequent operations and push the required information to the driver.
4 Simulation results analysis
The example, given in section 3.2, is simulated in Matlab. Supposing that the driver takes operation 1, the initial state vectorΦuis
Φu(t)=(1,0,0,0,0,0,0,0)
The adjacent matrix Wuwhich is given by FCM from Fig.3 could be obtained:
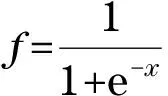
After the simulation, the results are shown in Tab.3 and Fig.4.
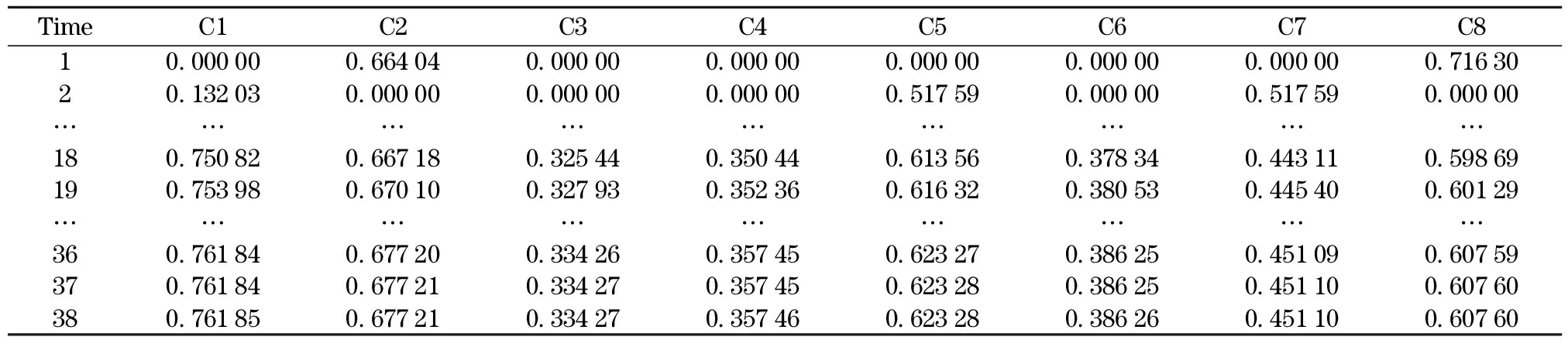
Tab.3 Data of simulation result

Fig.4 Figure of simulation results
From the data in Tab.3 and the trends of nodes’ values in Fig.4, it can be observed that after 37 times of calculation, the reasoning process comes into the final mode.
In the final mode, ifVci>0.5, thenVci=1. IfVci<0.5, thenVci=0. The result state vectorΦuis gained.
Φu(t)=(1,1,0,0,1,0,0,1)
As the intelligent information push is used in the car navigation device, the driver could focus on driving instead of operating the navigation device which will improve the safety.
5 Conclusions
In this paper, the process of information intelligent push has been presented. Obviously, FCM is the core of information intelligent push. The system monitors the user’s operations in real-time and converts them to abstract fact concepts. By the fuzzy mapping relationship of the fact concepts, the system takes real-time reasoning and realizes the information intelligent push by the reasoning results.
The user’s operations can be easily abstracted to a fuzzy cognitive map in a small-scale computer system. However, for large and complex computer systems, it is difficult to concentrate all of the user’s operations into a fuzzy cognitive map[10]. So further discussions about how to divide a massive FCM into a number of small-scale FCMs, integrate several parts of reasoning results and realize quick and exact reasoning are still needed.
[1] Hooi L Y, Osman M A, Idrus R, et al. Acceptance level of push technology-based online shopping widget among Malaysians: application oftechnology acceptance theory[J]. WSEAS Transactions on Business and Economics, 2010, 7: 211-220.
[2] Zhu Ming, Yu Yu, Zhuang Yue, et al. DSP-based intelligent advertising push system[J]. Journal of Data Aguisition & Processing, 2012,27(S2):267-271. (in Chinese)
[3] Duan L, Street W N, Xu E. Healthcare information systems: data mining methods in the creation of a clinical recommender system[J].Enterprise Information Systems, 2011, 5(2): 169-181.
[4] Institute of Public Policy Studies (Ann Arbor, Mich.), Institute of International Studies (Berkeley, Calif.). Structure of decision: the cognitive maps of political elites[M]. Princeton: Princeton University Press, 1976.
[5] Su Xiancheng, Yo Xiaohong, Zhao Zhi. Applications of FCM method to the analysis of space situation[J]. Shipboard Electronic Countermeaseure, 2010, 33(3):57-61. (in Chinese)
[6] Peng Zhen, Tian Liqin, Wu Jiang, et al. Research on complex system modeling and reasoning based on large fuzzy lognitive map[J]. Computer Science, 2013, 40(6): 203-205, 210. (in Chinese)
[7] Kosko B. Fuzzy cognitive maps[J]. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 1986, 24(1): 65-75.
[8] Stylios C D, Groumpos P P. Mathematical formulation of fuzzy cognitive maps[C]∥Proceedings of the 7th Mediterranean Conference on Control and Automation, 1999: 2251-61.
[9] Zhang Guiyun, Ma Xirong, Yang Bingru. Decomposition forfuzzy cognitive maps of complex systems[J]. Computer Science, 2007, 34(4): 129-132.(in Chinese)
[10] Ren Haoli, Luo Fei, Jin Xiaoguang. Study on armament system of system (SoS) measure of performance method based on fuzzy cognitive map[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2009, 21(S2): 68-71. (in Chinese)
(Edited by Wang Yuxia)
10.15918/j.jbit1004-0579.201524.0419
TP 181 Document code: A Article ID: 1004- 0579(2015)04- 0553- 05
Received 2014- 03- 05
Supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (61304254)
E-mail: dengfang@bit.edu.cn
 Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology2015年4期
Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology2015年4期
- Journal of Beijing Institute of Technology的其它文章
- Influence of shear sensitivities of steel projectiles on their ballistic performances
- Triaxial high-g accelerometer of microelectro mechanical systems
- Dynamic modeling and simulation for the rigid flexible coupling system with a non-tip mass
- Multi-constrained model predictive control for autonomous ground vehicle trajectory tracking
- Estimating the clutch transmitting torque during HEV mode-switch based on the Kalman filter
- Optimal tracking control for automatic transmission shift process
