越南红河平原区新生代构造应力场特征
Dao Hai Nam,关庆彬,Nguyen The Luan,时溢
(1.吉林大学地球科学学院,吉林长春 130061;2.越南国家科学院地质研究所,越南河内;3.越南国家科学院海洋地质与地球物理研究所,越南河内;4.沈阳地质矿产研究所/中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心,辽宁沈阳 110034)
越南红河平原区新生代构造应力场特征
Dao Hai Nam1,2,关庆彬1,Nguyen The Luan3,时溢4
(1.吉林大学地球科学学院,吉林长春 130061;2.越南国家科学院地质研究所,越南河内;3.越南国家科学院海洋地质与地球物理研究所,越南河内;4.沈阳地质矿产研究所/中国地质调查局沈阳地质调查中心,辽宁沈阳 110034)
红河平原在新生代期间受印度板块、欧亚板块和太平洋板块三大板块的影响,其构造应力场复杂多样.通过研究红河平原新生代构造应力场的变化规律,确定在新生代早期红河平原地区的构造应力场特点为东西的挤压应力场与左旋走滑机制,晚期则转变为南北的挤压应力场与右旋走滑机制,且右旋走滑作用在东南部地区呈增加趋势.红河平原区的这种构造应力场的变化为对红河三角洲的形成和发展提供了条件,控制了红河平原地区的现代构造活动特征.
红河平原;新生代;构造应力场;活动构造;越南
红河平原位于红河盆地的西北部(图1),发育在红河深大断裂带上,形成于新生代,大地构造位置位于华南板块和印度板块之间的碰撞拼合带上.
印度板块与欧亚板块在50Ma前发生碰撞,并极大地改变了亚洲的构造格局[1-2].在新生代期间,构造变形主要有两个阶段:第一阶段是印支板块-华南板块之间的走滑;第二阶段是与华南板块之间碰撞拼贴[3-6](见图2).这个模型得到了中国云南地区所观测的地质现象的验证[5],在这种大的构造背景下,红河断裂带不仅是研究越南地区,而且是整个东南亚地区的构造应力场和变形机制的关键地区.红河断裂带对包括红河平原区在内的红河新生代盆地的形成与发展起着至关重要的作用.
1 红河平原区的新生代构造应力场特征
最近的研究结果[8-22]表明,红河新构造运动经历了两个不同阶段、不同方向的构造应力场.早期(古新世至中新世)构造应力场由最大主应力轴(σ1)近水平,方位为东西向,最小主应力轴(σ3)近水平,方位为南北向,与中间应力轴(σ2)垂直.在此期间,在红河平原形成了构造河谷和下跌地堑(红河平原表现为构造谷下跌地堑型),其方向为北西—南东向(图3、4).巴维山的西南部和三岛北部受到强烈的挤压作用而隆起,抬升后遭受强烈的剥蚀作用,为地势较低的地堑地区提供了沉积物源.在越池的南部形成了南北向的构造应力场,使得红河的流动方向从北西—南东骤然变化为近东西向.
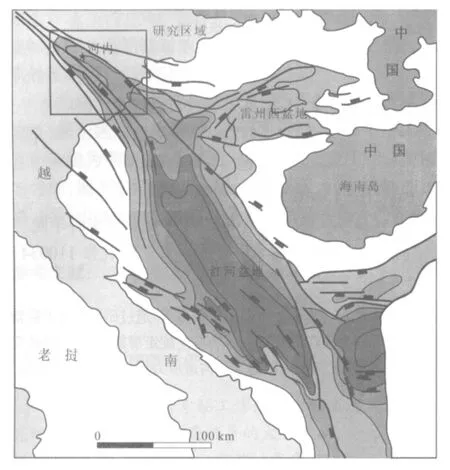
图1 研究区区域构造位置图(据文献[7]修改)Fig.1Regional tectonic map of the study area(Modified from Reference[7])
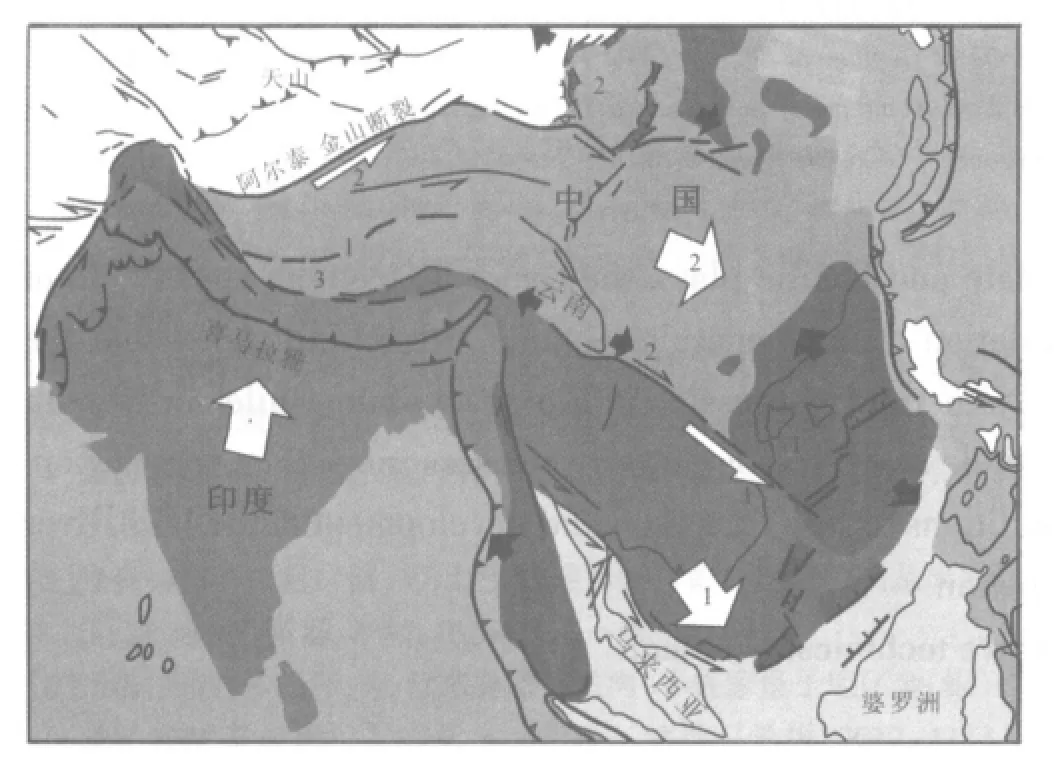
图2 运动学模型(据文献[4])Fig.2Kinematic model(Modified from Reference[4])
晚期(上新世至今)研究区所受的构造应力场由最大主应力(σ1)角度平缓,方位为南北向,最大拉伸轴(σ3)角度平缓,东西走向,中间应力轴(σ2)角度较陡.红河平原地区的内部构造格局十分清晰.在晚期构造应力场的影响下,整个红河构造带的构造格局再次发生改变,使得北西向的断裂构造成为主体构造.越南北部带的东北向东南方向移动,造成东朝-广宁的挤压变形.红河断裂带的西南部(和平-府里)向西北移动形成了南北向的伸展变形带,与红河断裂带毗邻,呈小于45°的锐角相交(图5).Tran Van Thang[11]、Tran Dinh To[24]等认为,红河断裂带的西北段发育右旋走滑断层,红河断裂带东南段发育右旋走滑断层和正断层,以正断层为主,在红河断裂带中的中江地区正断层尤其发育(图6b).在此构造应力场的作用下,在中新世至第四纪期间形成了红河三角洲,北东向断裂与西北向断裂的形成控制了红河流域和其他河流系统.此外,北西向断裂沿顺时针方向的平移移动形成了南-北向的凹陷-裂谷带.
在中新世至第四纪期间,在区域构造应力场背景下,红河平原地区的内部构造格局十分清晰.从越池纬度(红河平原的西北部)最大主应力(σ1)轴逐步从南北向转变为北西—南东向,并有延伸至北部海湾地区.沿着σ1轴的方向,红河平原地区在中新世—第四纪期间断裂构造发育,沿北西—南东向形成地势较低的地堑,并由中心向两侧扩张.因此,新生代期间,特别是在N2—Q阶段,从西北到东南沉积深度逐渐增加(图4),并且西南和东北两个边缘的沉积厚度变化不大,但其中心厚度突然增加进而形成地堑(图3).在这个机制下,形成了延伸到东南地区的地势低洼的地堑,进而形成了红河三角洲(图1).可见,红河三角洲的形成是个相当漫长而复杂的过程.
2 红河平原区新生代的变形特征
在中新世—第四纪期间,其构造应力场一直持续至今,红河平原地区进入复杂并高度分化的构造运动阶段[25-31].早期阶段(古新世—中新世)北西向断裂和东西向断裂是形成和发展为地堑、半地堑的关键作用;晚期阶段(N2—Q)出现北东向断裂和南北向断裂,研究区域分化成单元结构一起运动.
研究区主要的断裂构造包括:北西向断裂、北东向断裂、南北向断裂,这些断裂还包括不同级别的次一级断裂.

图3 红河平原构造剖面图(据文献[23]修改)Fig.3Structural section of Red River Plain(Modified from Reference[23])
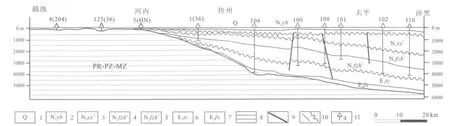
图4 红河平原构造剖面图(据文献[23]修改)Fig.4Structural section of Red River Plain(Modified from Reference[23])
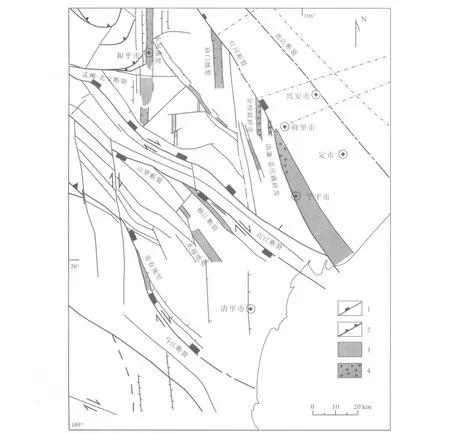
图5 红河西南部和清华地区构造纲要图Fig.5Structural map of SW Red River and Thanh Hoa Plain
第一级断裂包括红河断裂、庐江断裂、斋江断裂,是新生代之前的形成的切过地壳的深大断裂(图3),有着长期和复杂的发展历史.分界构造元素第一级并控制红河三角洲地区的动力变形的特征并发展成为西南隆起带、中心凹陷带和东北隆起带.在现代构造应力场的冲击下,红河断裂带是右行走滑活动机制.此外,红河断裂带的西北段发育右行走滑断层(图6a),但在东南段是右旋正断裂(图6b、c),正断裂越来越发育[12-13,17-21,26].
研究区第二级和第三级断裂构造也比较发达,多沿着红河断裂包括永宁、京门、巴维、山西平行发育.这种断裂分界构造块第一级分成隆起带、凹陷带,但是对第二级和第三级断裂的研究较少,一方面因为它们可能出现的年龄晚(主要是N2—Q阶段),另一个方面是这些断裂的深度不大,通常只发展在新生代的沉积物中.
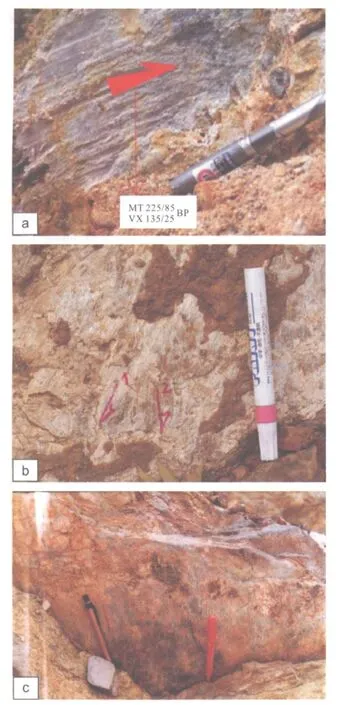
图6 红河正断层Fig.6The Red River normal fault
通过遥感、地貌和地球物理材料,可以发现一系列的南北向断裂带.它们的宽度1~5 km,延伸4~5 km甚至50~60 km.主要有两种类型:伴随着下沉作用的裂谷带和发育在基岩区的构造破碎带(红河平原西南地区的清廉、金榜、庙门).南北向断裂带主要发育在研究区西南部的地势低洼地区,同时受到北西向断裂系统的右旋走滑断层的改造,使得南北向断裂带与红河断裂带呈40~50°锐角相交,主要包括清廉-嘉庆、金榜、庙门、和平-不幕(图5).基本上,这种南北向破碎带是由红河断裂带的西南盘向西北右向移动所形成的南北向的生长带.清廉-嘉庆破碎带下沉并形成裂谷的过程控制了底河近50 km的舒展与蜿蜒弯曲的河道,在下沉区河流仍保持南北方向的流动.或者从和平到不幕-中江之间的的沱河段被南北向破碎带所控制,而在和平地区,沱河的河道则突然转换到北南方向.
3 结论
1)研究区红河平原地区在新生代经历了两个时期:早期东西向挤压应力场与左旋走滑机制;晚期南北向挤压应力场与右旋走滑机制.
2)在构造应力场的影响下,构造运动变化既有水平方向又有垂直方向,形成了复杂的北西、北东和南北向断裂.
3)红河断裂带的主体为右行走滑-正断层.东南段以正断层为主,同时西南段沿顺时针方向平移,形成了红河三角洲.
4)红河断裂带西南盘向西北方向移动形成的裂谷带,主要包括清廉-嘉庆,金榜,庙门,和平-不幕南北向的破碎带.
[1]Molnar P,Taponnier P.Cenozoic tectonics of Asian:Effects of continental collision[J].Science,1975,189:419—426.
[2]Molnar P,Tapponnier P.The collision between India and Eurasia[J]. Scientific American,1977,236(4):30—41.
[3]Tapponnier P,Pelzer G,Ledain A Y,et al.Propagatingextrusion tectonics in Asia:New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology,1982,10:611—616.
[4]Tapponnier P,Peltzer G,Armijo R.On the mechanics of the collision between India and Asia[J].Geol Soc Spec Publ,1986,19:115—157.
[5]Tapponnier P,Lacassin R,Leloup P H,et al.The Ailao Shan/Red River metamorphic belt:Tertiary left-lateral shear between Indochina and South China[J].Nature,1990,343:431—437.
[6]Peltzer G,Tapponnier P.Formation and evolution of strike-slip faults,rift and basin during the India-Asia collision:An experimental approach[J]. Geophys Res,1988,93:15085—15117.
[7]Phung Van Phach.Study of the tectonic phase in the South China Sea Cenozoic sedimentary basin and their relationships with regional tectonic activity[A]//Scienceand TechnologyResearchProjects,VietNamAcademy ofScience and Technology,Ha Noi,2008.
[8]Nguyen Trong Yem.Zoning of recent tectonic stress field of Vietnam[A]//Geology-Resources,Ha Noi,2008,1:8—13.
[9]Nguyen Trong Yem.Regimes of tectonic stress field during Cenozoic in Vietnam[J].Geology,Ha Noi,series A,1996,236:1—6.
[10]Nguyen Trong Yem.Multiphase and coaxial tectonic evolution of Central Viet Nam during Mesozoic and Cenozoic[J].Geology,Ha Noi,1999(11/12):155—163.
[11]Tran Van Thang,Van Duc Chuong.Horizontal displacement of the earth's crust in the Red river fault zone during Pliocene-Quaternary[A]//Geology-Resource,Ha Noi,1996,1:33—46.
[12]Phan Trong Trinh,Briais A,Tapponnier P.Horizontal stress field near ridge transform and transcurrent fault subduction intersection[A]//5th Meeting of the EUG,Strasbourg,1989,OS07—02.
[13]Phan Trong Trinh,Nguyen Trong Yem,et al.Late Cenozoic stress field in North Vietnam from microtectonic measurement[J].Inter Workshop Seis Haz South Asia,1994:182—86.
[14]Phan Trong Trinh,Nguyen Trong Yem,Nguyen Hung,et al.Active faulting and tectonics of North Vietnam[J].Inter Workshop Seis Haz South Asia,1994:186—189.
[15]Phan Trong Trinh,Leloup H P,Tapponnier P,et al.Cenozoic geodynamics in North Vietnam[A]//30th Geological Congress, Proceeding of IGCP383,Ha Noi,1996,7:25—26.
[16]Phan Trong Trinh,Ta Trong Thang,Nguyen Dang Tuc.Deep deformation along the Red River metamorpic zone[J].Geology,Ha Noi, series A,1996,237:52—58.
[17]Phan Trong Trinh,Hoang Quang Vinh,et al.Neotectonic activities of the Red River fault zone and adjacent areas[J].Sciences of the Earth, 2000,22(4):241—252.
[18]Phung Van Phach,Bui Cong Que.Late Cenozoic tectonic activities in North Viet Nam[J].Geology,Ha Noi,1999,13/14:33—41.
[19]Phung Van Phach,Vu Van Chinh.Cenozoic tectonic activities in Red River basin and adjacent area[J].Journal of Marine Science and Technology,2007,3(7):18—30.
[20]Phung Van Phach,Vu Van Chinh.The principal tectonic activities of Tonkin gulf and adjacent area in Cenozoic[A]//Proceeding of Science-Technological Conference on“Vietnam Petroleum Institute:30 Years of Developments and Integration”.Ha Noi,2008,1:94—108.
[21]Nguyen Van Vuong,Ta Trong Thang,Vu Van Tích.A new kinematic model for the Cenozoic deformation along the Red River shear zone: Implication for the Song Hong Basin formation[J].Journal of Geology Series B,Ha Noi,2002,19/20:79—89.
[22]Van Duc Chuong,Tran Van Thang,Van Duc Tung.The evolutional history and mechanical activity of the Red River faults[A]//Proceeding of 14th Scientific Meeting of Hanoi University of Mining and Geology, 2000,2:14—22.
[23]Sevostianov K M,Le Trong Can.Structural geology,oil and gas prospects and plans for the next exploration in Hanoi basin[A]// General Department of Petroleum,Ha Noi,1977.
[24]Tran Dinh To,Duong Chi Cong,Nguyen Dinh Tu.First results of vertical movement study about Red River through(According to leveling net repeated measurement data)[A]//Geology-Resources,Ha Noi,1991: 36—40.
[25]Le Trieu Viet,Tran Van Thang,Nguyen Van Hung.About horizontal displacement in Northwest of Vietnam[A]//Proceeding of the 14th Scientific Meeting of Ha Noi University of Mining and Geology,Hanoi, 2000,2:102—106.
[26]Le Trieu Viet.Tectonic activity of Cao Bang-Tien Yen fault zone in Cenozoic[A]//Proceeding of the 14th Scientific Meeting of Ha Noi University of Mining and Geology,Hanoi,2000,2:110—116.
[27]Harrison T M,Chen Wenji,Leloup P H,et al.An early Miocene transition in deformation regime within the Red River fault zone, Yunnan,and its significance for Indo-Asian tectonics[J].Geophys Res, 1992,97:7159—7182.
[28]Leloup P H,Kienast J R.High temperature metamorphism in a major strike slip shear zone:The Ailao Shan-Red River(P.R.C)[J].Earth Planet Sci Lett,1993,118:213—234.
[29]Le Van Manh,Ta Trong Thang.Red River deep-seated fault zone—An old tectonic suture zone of long development history[J].Sciences of the Earth,Ha Noi,2000,22(4):319—324.
[30]Pham Nang Vu.The Cenozoic deformation of the Red River fault zone[J].Sciences of the Earth,Ha Noi(in Vietnamese with abstract in English),2000,4(22):278—289.
[31]Vu Van Chinh.Active faults during Neotectonic activity in Northeastern Vietnam[A]//Geology-Resources,Ha Noi,1996,1:22—32.
CHARACTERISTICS OF CENOZOIC TECTONIC STRESS FIELD OF THE RED RIVER PLAIN IN VIETNAM
Dao Hai Nam1,2,GUAN Qing-bin1,Nguyen The Luan3,SHI Yi4
(1.College of Earth Sciences,Jilin University,Changchun 130061,China;2.Institute of Geological Science,Viet Nam Academy of Science and Technology, Hanoi,Viet Nam;3.Institute of Marine Geology and Geophysics,Viet Nam Academy of Science and Technology,Hanoi,Viet Nam; 4.Shenyang Institute of Geology and Mineral Resource,CGS,Shenyang 110034,China)
Influenced by the Indo-Australian plate,Eurasian plate and Pacific plate,the Cenozoic tectonic stress field of Red River Plain was complex and diverse.Analysis on the variation of the Cenozoic tectonic stress field shows that the deformation in the Red River region is characterized by east-west sinistral compression in Early Cenozoic,while north-south dextral compression in Late Cenozoic,with an increasing trend of dextral slip compressive stresses in southeastern region. The variation of deformation in the Red River Plain provides conditions for the formation and development of the Red River delta and controls the modern north-south dynamic stress of the region.
Red River Plain;Cenozoic;tectonic stress field;active tectonics;Vietnam
1671-1947(2015)01-0075-06
P546
A
2014-12-19;
2015-02-03.编辑:周丽、张哲.
Dao Hai Nam(1985—),男,硕士研究生,从事构造地质学研究,通信地址吉林省长春市建设街2199号,E-mail//daohainam.mdc@gmail.com

