肿瘤性贫血患者血清Hepcidin和IL-6及血清铁的表达及意义*
河北省唐山市人民医院血液科(唐山063000) 冯志刚 刘东芳 紫建杰 刘艳芬
肿瘤性贫血患者血清Hepcidin和IL-6及血清铁的表达及意义*
河北省唐山市人民医院血液科(唐山063000) 冯志刚 刘东芳 紫建杰 刘艳芬
目的:探讨肿瘤性贫血患者外周血铁调素(Hepcidin)水平变化及其与白介素-6(IL-6)、血清铁(SI)水平变化的相关性,了解其在肿瘤性贫血中的作用,为临床治疗提供依据。 方法:将肿瘤性贫血患者100例作为观察组,另选择同期来我院体检的人员20例作为对照组。采用酶联免疫法(ELISA)检测患者血清中Hepcidin、IL-6,亚铁嗪终点比色法测定SI浓度,了解Hepcidin与贫血、IL-6的相关性。结果:肿瘤性贫血患者外周血Hepcidin、IL-6浓度均明显高于对照组(P<0.05),SI浓度低于对照组(P<0.05)。随着贫血程度加重,外周血Hepcidin、IL-6浓度升高(P<0.05),SI浓度降低(P<0.05)。肿瘤性贫血患者血清Hepcidin与IL-6成正相关(r=0.33,P<0.05),血清Hepcidin与SI水平呈负相关(r=-0.24,P<0.05),血清IL-6与SI水平呈负相关(r=-0.21,P<0.05)。结论:肿瘤性贫血患者外周血中Hepcidin、IL-6浓度明显升高,Hepcidin与IL-6成正相关,Hepcidin及IL-6在肿瘤性贫血发病中起重要作用,及早降低Hepcidin、IL-6浓度,有助于阻止贫血的发展,为肿瘤性贫血的治疗提供新的策略。
贫血是肿瘤患者的常见合并症,大约有50%的肿瘤患者发生贫血,在晚期肿瘤患者及接受化疗或放疗的患者中,贫血的发生率高达90%。肿瘤和肿瘤治疗相关性贫血已越来越受到重视,贫血不仅影响肿瘤的治疗,更为严重的是严重影响这部分患者的生活质量,其发病机制尚不十分清楚[1],铁调素(Hepcidin)可以通过抑制肠道铁的吸收及单核巨噬细胞系统铁的释放,对铁代谢起负调控作用,在肿瘤性贫血的发病机制中起最关键作用。白介素-6(IL-6)是目前认为刺激Hepcidin合成的最主要的炎症因子,可通过刺激Hepcidin的合成调节铁的代谢,造成贫血的发生。本研究中我们探讨Hepcidin、IL-6与肿瘤性贫血的关系,以进一步揭示肿瘤性贫血的发病机制,为临床治疗提供理论依据。
资料与方法
1 临床资料
1.1 资料来源:观察组:100例,选择我院2012年9月至2014年10月确诊的肿瘤性贫血患者,其中轻中度型贫血(B组)85例,重型贫血(C组)15例。对照组:20例,为我院健康体检者。
1.2 标本采集:空腹抽取静脉血6ml,其中2ml置入生化管中,采用亚铁嗪终点比色法测定血清铁,其余4ml放入血清生化管中室温凝固,离心后收集血清,于-80℃超低温冰箱中保存。
1.3 试剂:人Hepcidin ELISA 检测试剂盒,人IL-6 ELISA检测试剂盒,铁四项试剂均购于上海生工生物有限公司。
1.4 仪器:IMMULITE全自动化学发光分析仪,680型酶标仪等。
2 检测方法 采用酶联免疫法(ELISA)检测患者血清中Hepcidin、IL-6,亚铁嗪终点比色法测定血清铁浓度亚铁嗪终点比色法测定血清铁,按试剂说明书操作。

结 果
1 肿瘤性贫血患者与正常组的IL-6、Hepcidin、血清铁水平比较 见表1。肿瘤性贫血患者外周血IL-6、Hepcidin浓度均明显高于对照组 (P<0.05),血清铁浓度低于对照组(P<0.05)。
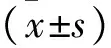
表1 肿瘤性贫血与正常对照组IL-6、Hepcidin、血清铁比较
注:*与对照组比较,P<0.05
2 肿瘤性贫血患者不同程度贫血组IL-6、Hepcidin、血清铁水平比较 见表2。随着贫血程度加重,外周血IL-6、Hepcidin浓度升高(P<0.05),血清铁浓度降低(P<0.05)。
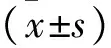
表2 肿瘤性贫血不同程度患者IL-6、Hepcidin、血清铁比较
注:*与对照组比较,P<0.05
3 肿瘤性贫血患者血清Hepcidin、IL-6、血清铁的关系 肿瘤性贫血患者血清Hepcidin与IL-6水平呈正相关(r=0.33,P<0.01);肿瘤性贫血患者血清Hepcidin与血清铁水平呈负相关(r=-0.24,P<0.05);肿瘤性贫血患者血清IL-6与血清铁水平呈负相关(r=-0.21,P<0.05)。
讨 论
肿瘤相关性贫血是指肿瘤直接破坏引起的和肿瘤对机体的侵害和消耗而间接引起的以及在抗肿瘤治疗过程中因药物导致的贫血。恶性肿瘤引起贫血,主要表现为正细胞正色素或小细胞低色素贫血,网织红细胞计数正常或减低,血清铁降低,铁蛋白增高或正常,骨髓铁染色示细胞内铁减少而细胞外铁增多[1],这些表现主要与等负调控因子抑制内源性生成,抑制红系造血及影响铁代谢等有关。其发病机制是多种因素对红细胞生成抑制所致。其发病机制大致分为四类:①促红细胞生成素(EPO)分泌相对不足及作用钝化;②红细胞破坏、寿命缩短;③铁代谢异常及铁限制性红细胞生成;④红系前体细胞增殖受损。以上各类均与细胞因子有关。大量研究显示:IL-6在肿瘤相关性贫血的发生和发展中起一定作用,但其机制不甚清楚。
Hepcidin是近期发现的铁调节蛋白,Sasu等[2]认为Hepcidin浓度与贫血患者的炎症标志物相关,是诊断贫血和判断疗效的有效指标,是铁转运的负性调节剂[2]。随着对IL-6及铁代谢研究的不断深入,发现IL-6在肿瘤相关性贫血发病中起一定作用,IL-6可能通过多种途径诱发贫血的发生:①肿瘤性贫血中多种细胞因子可诱导Hepcidin升高,研究发现IL-6是影响Hepcidin最重要的因素。IL-6基因敲除的小鼠中,在用矿物油处理的炎症过程中未出现Hepcidin升高及低铁血症。体外培养的肝细胞中IL-6可有效诱导Hepcidin产生,而IL-1或TNF-α并不参与这一反应。在健康受试者中输注IL-6后数小时内可诱导Hepcidin产生并导致低铁血症。IL-6-Hepcidin轴在炎症相关性低铁血症中起重要作用[3]。②血清铁浓度依赖于巨噬细胞及肝细胞的铁释放,缺乏Hepcidin或Hepcidin过表达的转基因小鼠中发现Hepcidin是铁释放的抑制因子,可同时抑制肠道铁吸收,炎症状态下,IL-6诱导Hepcidin生成,随之Hepcidin抑制铁释放导致血清铁降低Hepcidin与细胞膜的转铁蛋白分子结合,并且诱导其内化及降解,后者是铁释放的唯一输出方式。Hepcidin浓度越高,浓度则越低,肠细胞、巨噬细胞及肝细胞中铁输出就越少。③肠道铁吸收在炎症状态下被抑制,可能是IL-6及Hepcidin介导的。正常人体内储存铁有400~1000mg,每日造血需要的铁仅1~2mg来源于饮食。真正的铁缺乏可能最终在慢性疾病中出现,尤其在铁储备有限而IL-6水平非常高的儿童患者。④Kemna等研究发现脂多糖(LPS)和IL-6可刺激Hepcidin的表达,在LPS注射人体后可出现IL-6升高,在3~4h后Hepcidin分泌达到了高峰[4],Lee等通过体外细胞培养证实了IL-6可介导Hepcidin mRNA表达增加,认为LPS刺激了IL-6表达,继而导致Hepcidin表达的增加,Hepcidin又通过铁代谢的异常最终引起贫血[5]。
本实验研究结果表明:肿瘤性贫血患者外周血中Hepcidin、IL-6浓度明显升高,血清铁浓度降低,Hepcidin与IL-6成正相关,与血清铁成负相关,Hepcidin及IL-6在肿瘤性贫血发病中起重要作用,及早降低Hepcidin、IL-6浓度,有助于阻止贫血的发展,为肿瘤性贫血的治疗提供了新策略。
[1] Demarmel S, Biasiutti F.Anemia of chronicdisorder pathogenesis,clinical presentation and treatment [J].Ther Umsch,2010,67(2):225-228.
[2] Sasu BJ,Li H,Rose MJ,etal.Serum Hepcidin but not proHepcidin may be an effective maker for anemia of inflammation(AI)[J].Blood Cell Mol DIS,2010,45(2):238-245.
[3] Guenter W,Lawrence T, Goodnoug H.Anemia of chronic disease[J].N Engl J Med,2005,352(10):1011-1023.
[4] Guidi GC,Lech I, Santonastaso C.Advancements in anemias related to chronic andition [J].Clinchem Lab Med,2010,48(13):1217-1226.
[5] Kanda J,Uchiyama T,Tomosugi N,etal.Oncostation M and Leukemia inhibitory factor increase Hepcidin expressin in hepatoma cell lines [J].Int J Hematol,2009,90(6):545-552.
(收稿:2015-01-19)
Clinical significance of serum Hepcidin level and the relationships between Hepcidin level and IL-6,Serum iron levels in patients with cancer-related amemia
Department of Hematology,Tangshan People Hospital of Hebei Province(Tangshan 063000)
Feng Zhigang Liu Dongfang Zi Jianjie et al
Objective:To investigate the clinical significance of serum Hepcidin level and the relationships between Hepcidin level and IL-6,Serum iron levels in patients with cancer-related amemia (CAR) ,and provide experimental evidence for prevention and treatment of CAR. Methods:100 cases in our hospital from September 2012 to October 2014 patients with cancer-related anemia were treated,was set to the observation group, and the other options over the same period 20 cases to the hospital medical staff, served as controls. Serum Hepcidin and IL-6 levels were assayed by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay(ELISA),Serum SI levels were assayer by ferrozine .Results:①The levels of serum Hepcidin and IL-6 compared with the control group increased,but the levels of serum SI decreased, the difference was statistically significant (P<0.05).②Along with the degree of anemia increased,the level of Hepcidin and IL-6 has been rised obviously,but the level of SI has been reduced(P<0.05).③In patients with cancer-related anemia,Hepcidin level were positively correlated with IL-6 level(P<0.05),and Hepcidin and IL-6 levels were negative clrrelated with SI level(P<0.05).Conclusion:The levels of serum Hepcidin and IL-6 compared with the control group increased . Hepcidin level were positively correlated with IL-6 level.The Hepcidin and IL-6 plays an important role in the disease in CAR,and reducing the level of NO as soon as possible,is assist for prevent the progress of anemia.that will provide a new strategy of therapy for CAR.
Neoplasms/complication Anemia/etiology Anemia/blood Iron/metabolism Interleukin-6/metabolism Immunoenzyme techniques
*河北省卫生厅医学科学研究重点课题(20130676)
肿瘤/并发症 贫血/病因学 贫血/血液 铁/代谢 白细胞介素6/代谢 免疫酶技术
R730.6
A
10.3969/j.issn.1000-7377.2015.05.029