丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导插管期间熵指数、双频指数和血流动力学的变化
王春林, 胡乃琴, 陈 弘
(江苏省苏北人民医院 麻醉科, 江苏 扬州, 225001)
丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导插管期间熵指数、双频指数和血流动力学的变化
王春林, 胡乃琴, 陈弘
(江苏省苏北人民医院 麻醉科, 江苏 扬州, 225001)
摘要:目的探讨丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导期间熵指数(RE、SE)、双频指数(BIS)和血流动力学的变化。方法选择ASAⅠ~Ⅱ级择期行腹腔镜胆囊切除术患者20例。麻醉诱导:丙泊酚1.5~2 mg/kg、芬太尼3~4 μg/kg和维库溴铵0.1~0.15 mg/kg,当BIS<60、四个成串刺激(TOF)计数以及TOF%均为0时,行气管插管。观察麻醉诱导前即基础值(T1)、病人对指令性反应消失(T2)、气管插管即刻(T3)、插管后1 min(T4)、3 min (T5)和5 min(T6)共6个时点RE、SE、△RE-SE、BIS、平均动脉压(MAP)和心率(HR)的变化。结果插管后MAP 显著高于插管时(P<0.01), 但显著低于基础值(P<0.01); 插管前后HR无显著变化(P>0.05)。RE、SE、△RE-SE和BIS在插管前后差异无统计学意义。结论丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导能减轻气管插管时的心血管反应。在此麻醉诱导方式下, BIS, RE和SE无明显变化,患者对气管插管过程无知晓。
关键词:熵指数; 双频指数; 丙泊酚; 芬太尼; 维库溴铵; 气管插管
气管插管是麻醉诱导过程中最强烈的伤害性刺激,它不仅可引起血流动力学变化,而且可导致麻醉深度改变,引起病人的唤醒反应[1], 甚至发生术中知晓[2]。脑电双频指数(BIS)已被用于气管插管时麻醉镇静深度的监测,气管插管对BIS影响研究较多,但报道[3-7]不一致。熵指数[8]是近年来用于监测麻醉深度的新指标,它包括状态熵(SE) 和反应熵(RE)两个参数,目前关于气管插管对熵指数的影响报道较少。本研究主要观察丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导期间,气管插管对熵指数、BIS以及血流动力学的影响。
1资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
选择ASAⅠ~Ⅱ级在全麻下择期行腹腔镜胆囊切除术患者20例,男11例,女9例,年龄25~60岁,体质量41~78 kg。排除患有心血管疾病、听力障碍、中枢神经系统疾病以及困难气道的患者。本研究经苏北人民医院伦理委员会批准,所有患者均签署知情同意书。
1.2 监测方法
所有患者入手术室后使用多功能监测仪(S/5,Datex-Ohmeda,芬兰)监测心电图、血压、脉搏血氧饱和度(SpO2)、呼气末二氧化碳分压(PETCO2); 熵指数和BIS分别通过熵模块和BIS模块(S/5 M-Entropy、M-BIS,Datex-Ohmeda,芬兰)测定。肌松监测通过肌松模块(S/5 M-NMT,Datex-Ohmeda,芬兰)测定四个成串刺激(TOF)。熵指数电极(Datex Ohmeda Division,Instrumentariam Corp.Helsinki,Finland)和BIS电极(Aspect Medical Systems,Newton,MA)分别置于病人前额正中,两侧眉弓上方、外眼角处,熵指数电极在下,BIS电极在上[9]。
1.3 麻醉方法
患者入室后开放上肢静脉,输入复方氯化钠溶液,诱导期输注速度为10~15 mL/(kg·h)。麻醉诱导:丙泊酚1.5~2 mg/kg,待患者对指令性反应消失 (警觉/镇静评分1~2分) 后给予芬太尼3~4 μg/kg,维库溴铵0.1~0.15 mg/kg,当TOF计数以及TOF%均为0、BIS<60时,行气管插管,气管插管要求一次成功,插管时间不超过30 s。插管后行机械通气,呼吸频率为12次/min,维持PETCO235~40 mmHg。诱导期间如患者出现低血压或心动过缓需要使用麻黄碱、去氧肾上腺素或阿托品处理者退出本研究。
1.4 观察指标
记录麻醉诱导前即基础值(T1)、病人对指令性反应消失(T2)、气管插管即刻(T3)、插管后1 min(T4)、3 min (T5)和5 min(T6)共6个时点平均动脉压(MAP)、心率(HR)、RE、SE、△RE-SE(RE与SE之差)和BIS的数值。术后24 h内随访,询问患者对气管插管过程有无知晓。
1.5 统计学方法
采用SPSS 16.0统计学软件进行分析,计量资料以均数±标准差表示,不同时点比较采用配对t检验,P<0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2结果
血流动力学参数及熵指数和BIS的变化:与T1时比较, T2~T6时MAP显著下降(P<0.01); 与T3时比较,T4~T6时MAP显著升高(P<0.01)。与T1时比较, T3~T6时HR减慢(P<0.01或P<0.05); 与T3时比较,T4~T6时HR无显著变化(P>0.05)。与T1时比较, T2~T6时患者RE、SE、△RE-SE和BIS均显著下降(P<0.01); 与T3时比较,T4~T6时RE、SE、△RE-SE和BIS均无显著变化(P>0.05)。见表1。术后随访,所有患者对气管插管过程均无知晓。
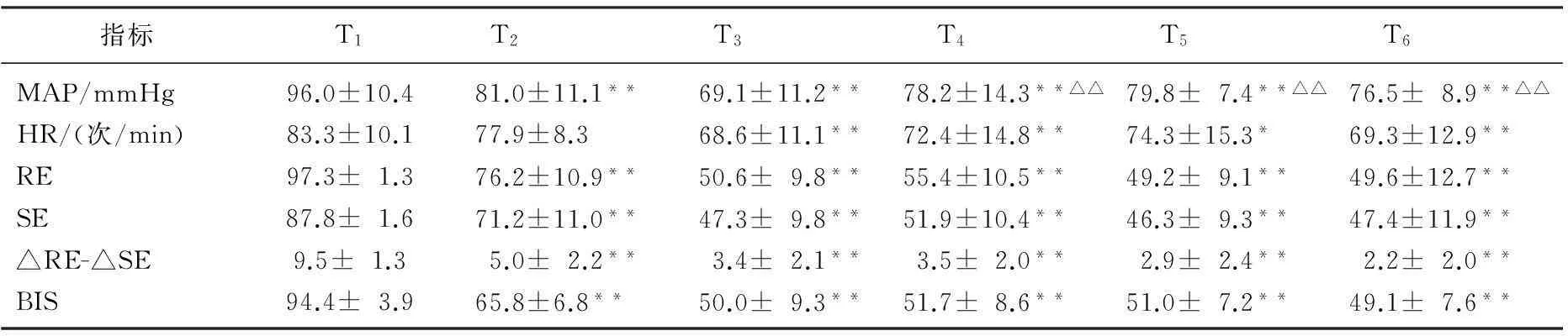
表1 各时点MAP、HR、RE、SE、△RE-SE和BIS的变化
与T1时比较, *P<0.05, **P<0.01; 与T3时比较,△P<0.05, △△P<0.01。
3讨论
气管插管引起心血管反应的机制可能是由于喉镜和气管导管刺激咽喉和气管内感受器,激活交感-肾上腺髓质系统所致。临床上常用丙泊酚和芬太尼诱导来抑制气管插管对血流动力学的影响[3,10]。本研究结果显示,麻醉诱导后由于丙泊酚和/或芬太尼的作用导致MAP和HR的显著下降,气管插管后MAP比插管时显著升高,但仍显著低于基础值,这些变化均在临床可接受的范围以内;气管插管后的HR与插管时相比无显著变化。说明常用剂量丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导能够减轻气管插管引起的血流动力学的改变,与文献报道一致[10]。
尽管气管插管引起的神经反射主要发生在皮层下水平,好像与大脑皮层活性无关,但外周伤害性刺激到达大脑是通过脑干的上行网状激活系统,导致脑电图(EEG)激活[3],引起病人的唤醒反应,甚至发生插管过程的知晓,这往往被人们所忽视。气管插管对脑电参数的影响,由于麻醉诱导所用药物种类、剂量、观察的时点、指标不同,结果也不尽相同[1, 4-7, 11-13]。
Messner等[14]已经证实肌电的活动能够影响EEG和BIS。EEG和EMG的信号范围分别是0.5~30 Hz和30~300 Hz, 而BIS处理的信号低于47 Hz,有部分的重叠,伤害性刺激激活EMG, EMG活动可能被BIS运算法则误认为是EEG活动,引起BIS升高的假象,此种情况下使用NMBD将减少假象,使得BIS降低。熵指数中SE反映皮层EEG的活性,频率范围为0.8~32 Hz,RE是反映皮层EEG和额肌电图(fEMG)的活性,频率范围是0.8~47 Hz, 故△RE-SE主要反映的是fEMG的活性[8]。在丙泊酚-笑气麻醉时,未使用NMBD行气管插管,RE、SE和△RE-SE均升高[11]。丙泊酚-瑞芬太尼麻醉未使用NMBD时,气管插管也引起RE和SE的升高[13]。应用NMBD能减轻置入喉镜引起的RE和△RE-SE增加[5], 而且呈剂量依赖性抑制气管插管导致熵指数的升高[15]。NMBD对麻醉深度监测的影响很可能与麻醉水平有关,也许在深的麻醉水平不明显,因为此时中枢传入和肌电活性被麻醉剂所抑制[5]。
阿片类药物可以通过降低对伤害性刺激的反应,从而影响BIS和熵指数。Guignard等[1]报道在丙泊酚持续靶控输注时,阿片类药物削弱了气管插管时BIS增加的程度。Kawaguchi等[16]研究发现在丙泊酚-罗库溴铵麻醉诱导时,未用雷米芬太尼组气管插管后RE和△RE-SE显著升高,而雷米芬太尼组能抑制气管插管后RE和△RE-SE的升高。本研究发现RE、SE、△RE-SE和BIS在气管插管后均无明显升高,与Sugiura[6]和Gao等[7]的研究结果一致。这可能与使用神经肌肉阻滞药(NMBD)和阿片类药物有关。
综上所述,常用剂量丙泊酚-芬太尼-维库溴铵麻醉诱导能够减轻气管插管引起的血流动力学的改变。此麻醉诱导方式下,患者对气管插管过程无知晓,插管后熵指数和BIS均无显著变化。
参考文献
[1]Guignard B, Menigaux C, Dupont X, et al.The effect of remifentanil on the bispectral index change and hemodynamic responses after orotracheal intubation[J]. Anesth Analg, 2000, 90: 161.
[2]St Pierre M, Landsleitner B, Schwilden H, et al.Awareness during laryngoscopy and intubation: quantitating incidence following induction of balanced anesthesia with etomidate and cisatracurium as detected with the isolated forearm technique[J].J Clin Anesth, 2000, 12(2): 104.
[3]Nakayama M, Ichinose H, Yamamoto S, et al.The effect of fentanyl on hemodynamic and bispectral index changes during anesthesia induction with propofol[J].J Clin Anesth, 2002, 14: 146.
[4]Menigaux C, Guignard B, Adam F, et al.Esmolol prevents movement and attenuates the BIS response to orotracheal intubation[J].Br J Anaesth, 2002, 89: 857.
[5]Hans P, Giwer J, Brichant JF, et al.Effect of an intubation dose of rocuronium on Spectral Entropy and Bispectral Index responses to laryngoscopy during propofol anaesthesia[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2006, 97(6): 842.
[6]Sugiura S, Seki S, Hidaka K, et al. The hemodynamic effects of landiolol, an ultra-short-acting beta1-selectiveblocker, on endotracheal intubation in patients with and without hypertension[J]. Anesth Analg, 2007, 104: 124.
[7]Gao J D, Zhao Y J, Xu C S, et al. Evaluation of entropy for monitoring the depth of anesthesia compared with bispectral index: a multicenter clinical trial[J]. Chin Med J (Engl), 2012, 125(8): 1389.
[8]Viertio-Oja H, Maja V, Sarkela M, et al.Description of the entropy algorithm as applied in the Datex-Ohmeda S/5 Entropy Module[J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, 2004, 48: 154.
[9]王春林, 陈弘, 陶永中, 等. 脑电熵指数和双频指数与丙泊酚镇静深度的相关性观察[J]. 临床麻醉学杂志, 2006, 22: 786.
[10]Shin H Y, Kim J W, Kim A R, et al. The Effects of Lidocaine, Fentanyl, Nicardipine, and Esmolol on Hemodynamic and Bispectral Index Responses during Induction with Thiopental Sodium[J]. Korean J Anesthesiol, 2007, 53: S7.
[11]Aho A J, Yli-Hankala A, Lyytikainen L-P, et al. Facial muscle activity, Response Entropy and State Entropy indices during noxious stimuli in propofol-nitrous oxide or propofol-nitrous oxide- remifentanil anaesthesia without neuromuscular blockade[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2009, 102: 227.
[12]Musialowicz T, Lahtinen P, Pitkanen O, et al. Comparison of Spectral Entropy and BIS VISTA monitor during general anesthesia for cardiac surgery[J].J Clin Monit Comput, 2011, 25: 95.
[13]薛照静, 权翔, 赵晶, 等. 熵指数用于评价全身麻醉患者伤害性刺激强度的可行性分析[J]. 中国医学科学院学报, 2014, 36(1): 68.
[14]Messner M, Beese U, Romstock J, et al. The bispectral index declines during neuromuscular block in fully awake persons[J]. Anesth Analg, 2003, 97: 488.
[15]Kawaguchi M, Takamatsu I, Kazama T.Rocuronium dose-dependently suppresses the spectral entropy response to tracheal intubation during propofol anaesthesia[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2009, 102 (5): 667.
[16]Kawaguchi M, Takamatsu I, Masui K, et al. Effect of landiolol on bispectral index and spectral entropy responses to tracheal intubation during propofol anaesthesia[J]. Br J Anaesth, 2008, 101(2): 273.
Changes of entropy, bispectral index and hemodynamics in tracheal intubation period of anesthesia with propofol, fentanyl and vecuronium
WANG Chunlin, HU Naiqin, CHEN Hong
(DepartmentofAnesthesiology,SubeiPeople′sHospital,Yangzhou,Jiangsu, 225001)
ABSTRACT:ObjectiveTo investigate the changes of entropy, bispectral index and hemodynamics in tracheal intubation period of anesthesia with propofol, fentanyl and vecuronium.MethodsTwenty ASAⅠ~Ⅱpatients scheduled for elective laparoscopic cholecystectomy were enrolled in this study. After simultaneous application of both the entropy and BIS electrode systems, anesthesia was induced with propofol 1.5~2 mg/kg, fentanyl 3~4 μg/kg and vecuronium 0.1~0.15 mg/kg.Endotracheal intubation was performed when the BIS<60 and the train of four stimulation(TOF)=0.The RE, SE, △RE-SE (the difference between RE and SE), BIS, the mean arterial pressure (MAP) and the heart rate (HR) were monitored and recorded respectively at the time points of pre-induction (baseline) (T1), loss of responses to command (T2), tracheal intubation (T3), and 1, 3, 5 minutes after intubation (T4, T5, T6).ResultsCompared with tracheal intubation value, MAP increased significantly after intubation (P<0.01), but significantly decreased when compared with baseline (P<0.01).HR decreased significantly after induction, but there were no significant changes during intubation.RE, SE, △RE-SE and BIS decreased significantly after induction, and there were no significant differences during intubation.ConclusionThe anesthesia induction with propofol, fentanyl and rocuronium can reduce cardiovascular response to tracheal intubation.In this way of anesthesia induction, BIS, RE and SE have no significant changes, and the patients have no awareness of tracheal intubation.
KEYWORDS:entropy; BIS; propofol; fentanyl; vecuronium; tracheal intubation
通信作者:陈弘
收稿日期:2015-05-16
中图分类号:R 614
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1672-2353(2015)24-042-04
DOI:10.7619/jcmp.201524013

