一个充分下降的杂交共轭梯度法
□江羡珍,陈永福,冯华丽,孙玉辉
(玉林师范学院 数学与信息科学学院,广西 玉林 537000)
一个充分下降的杂交共轭梯度法
□江羡珍,陈永福,冯华丽,孙玉辉
(玉林师范学院 数学与信息科学学院,广西 玉林 537000)
对无约束优化问题,基于文献[6]的WYL公式和文献[8]的MFR公式,给出了一个杂交共轭梯度法公式,并建立相应的算法. 在不依赖于任何线搜索的条件下,算法的每一步迭代都可以产生一个充分下降方向,且在标准Wolfe线搜索之下可以证明此杂交共轭梯度法是全局收敛的。最后其数值测试结果表明所给的杂交方法是有效的.
无约束优化;杂交共轭梯度法;充分下降;全局收敛
1 引言
共轭梯度法是求解大规模非线性无约束优化问题min{f(x)|x∈Rn}的有效方法之一,其中f∶Rn→R为一阶连续可微函数.其迭代公式的一般形式为

其中gk=Δf(xk),dk为搜索方向,αk是沿搜索方向dk由某种非精确线搜索产生的步长,βk为方向调控参数,不同的βk对应不同的共轭梯度法.著名的βk计算公式[1-5]有:
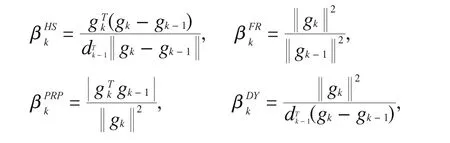
与以上公式对应的共轭梯度法分别称为HS方法、FR方法、PRP方法和DY方法.其中,PRP方法和HS方法被公认为是数值效果较好的共轭梯度法,而FR方法和DY方法则具有良好的收敛性质.近年来,许多学者在以上公式的基础上对βk进行了改进,得出了一些既保证收敛又有良好数值表现的新算法[6-13].文献[6]对PRP方法进行了改进,得到如下新的βk公式

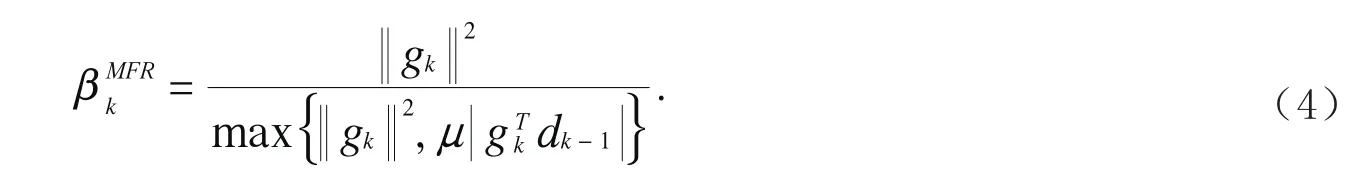
由此公式所产生的算法在不依赖于任何线搜索条件下,每一步迭代总可以产生一个充分下降方向.基于文献[6,8]等的研究,为了充分利用WYL公式良好的数值表现和MFR公式良好的下降性质,本文将这两种方法进行杂交得到如下共轭梯度法公式
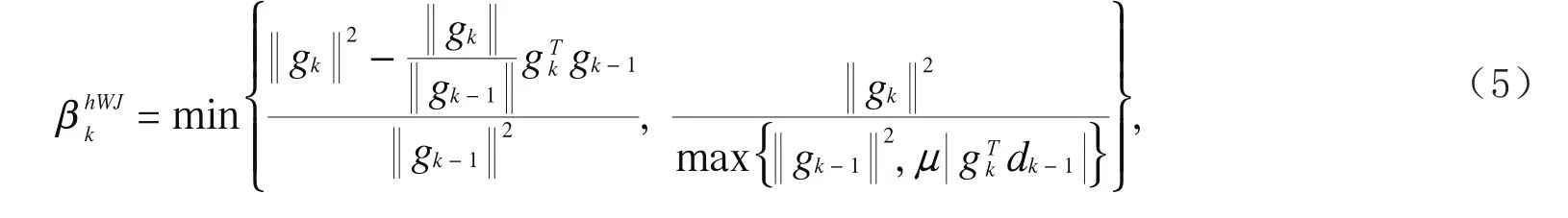
基于公式(5),本文在第二部分建立一个新的算法,并证明由算法所产生的方向满足充分下降条件;第三部分在标准Wolfe非精确线搜索条件下证明算法的全局收敛性;最后对算法进行数值测试.
2 算法及性质
算法框架A
初始步 任取初始点x1∈Rn,∀ε>0,0<δ<σ<1,d1=g1,k:=k+1
步骤1 若‖gk‖<ε 则停止.否则,由某一个非精确线搜索求得步长αk.
返回步骤1.
下面的引理说明由算法框架A所产生的搜索方向满足充分下降条件.
引理1对于任意的k≥1,设搜索方向dk由算法框架A产生,则有且

3 全局收敛性
为了证明新算法的全局收敛性,下面给出本文所采用线搜索条件和所需的两个常规假设.
标准Wolfe非精确线搜索条件:
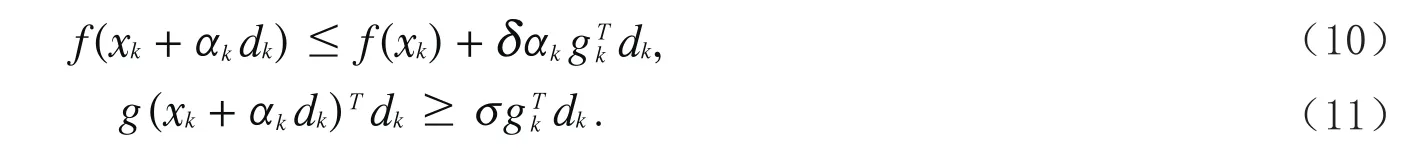
两个常规假设:
(H1)水平集∧={x∈RN|f(x)≤f(x1)}有界,其中x1为初始点.
(H2)在水平集∧的一个邻域内,f(x)连续可微,且其梯度函数gk满足Lipsschitz条件,即存在常数L>0,对∀x, y∈U,有‖g(x)-g(y)‖≤L‖x-y‖.
下面的引理所给出的是著名的Zoutendijk条件[14].
引理2设假设(H1)和(H2)成立,考虑迭代公式xk+1=xk+αkdk,其中搜索方向dk满足步长αk满足Wolfe线搜索准则(10)和(11),则

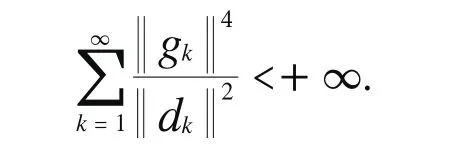
该引理在文献[9]中的第二章已给出具体的证明.
定理1 假设(H1)和(H2)成立,步长αk满足Wolfe线搜索准则(10)和(11),则算法A或有限步终止于gk=0,或产生无穷点列{xk},使得
证明:若定理1不成立,则有‖gk‖>0,于是存在常数γ>0使得由(2)式得
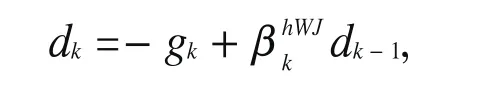
两边平方后,得
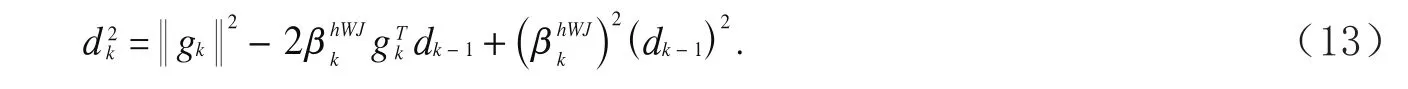
又由(7)式可得
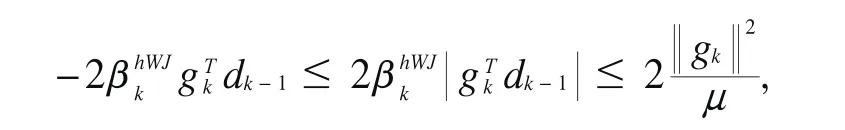
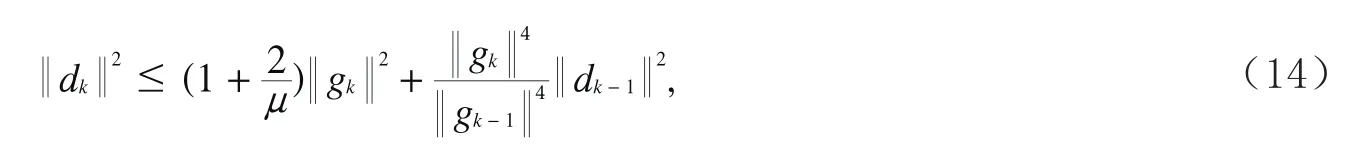
两边除以‖gk‖4得
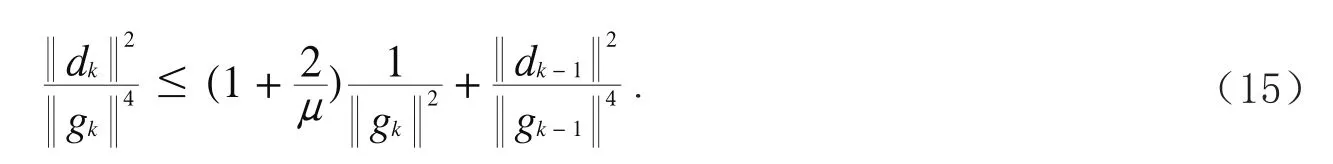
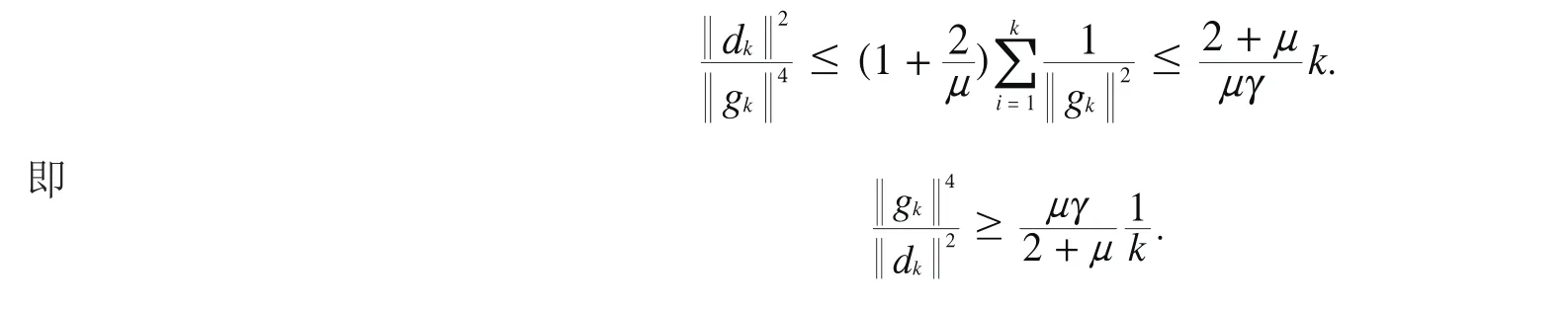
由此可知
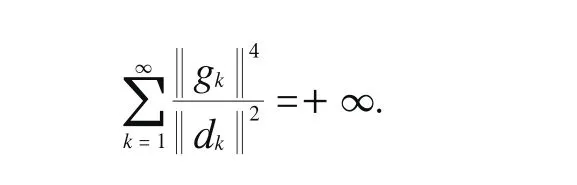
3 数值试验
为检验算法A的实际数值效果,我们对常用的无约束测试问题集文[15]中的34个问题共94个算例进行模拟测试.并将测试结果与如下方法进行比较:
所有测试都在标准Wolfe线搜索准则下完成.方法测试的环境为Matlab 7.5,Win7.0操作系统,Pentium(R) Dual-Core CPU T4400 1.90GHz2.43GB内存.参数选取如下:σ=0.1,δ=0.03,μ=10.75.算法的终止准则为以下二者情形之一:(1)‖gk‖>10-6(2)Itr>1000终止准则(2)出现时认为该方法对这个数值例子失效,并记“F”.
NF/NG/Itr/Tcpu依次表示目标函数值计算次数、梯度计算次数、迭代次数及消耗CPU时间.数值结果详见Table 1.同时,我们还采用先进的Dolan和More[16]的性能图对试验效果进行刻划,从图1-4可以看出本文的算法在所测试的94个算例中总体效果比其余三个方法稍好.
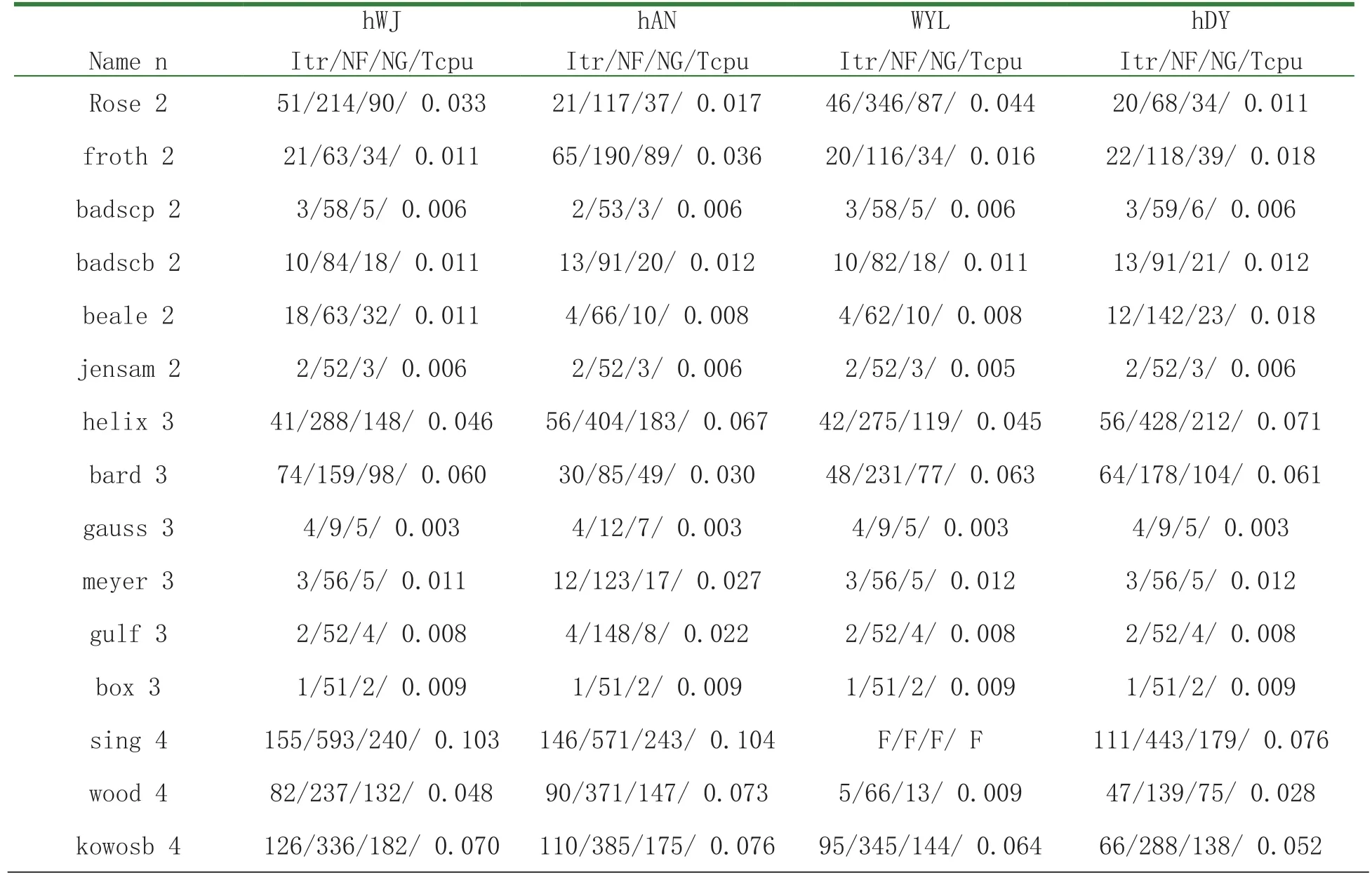
Table1:数值试验报告
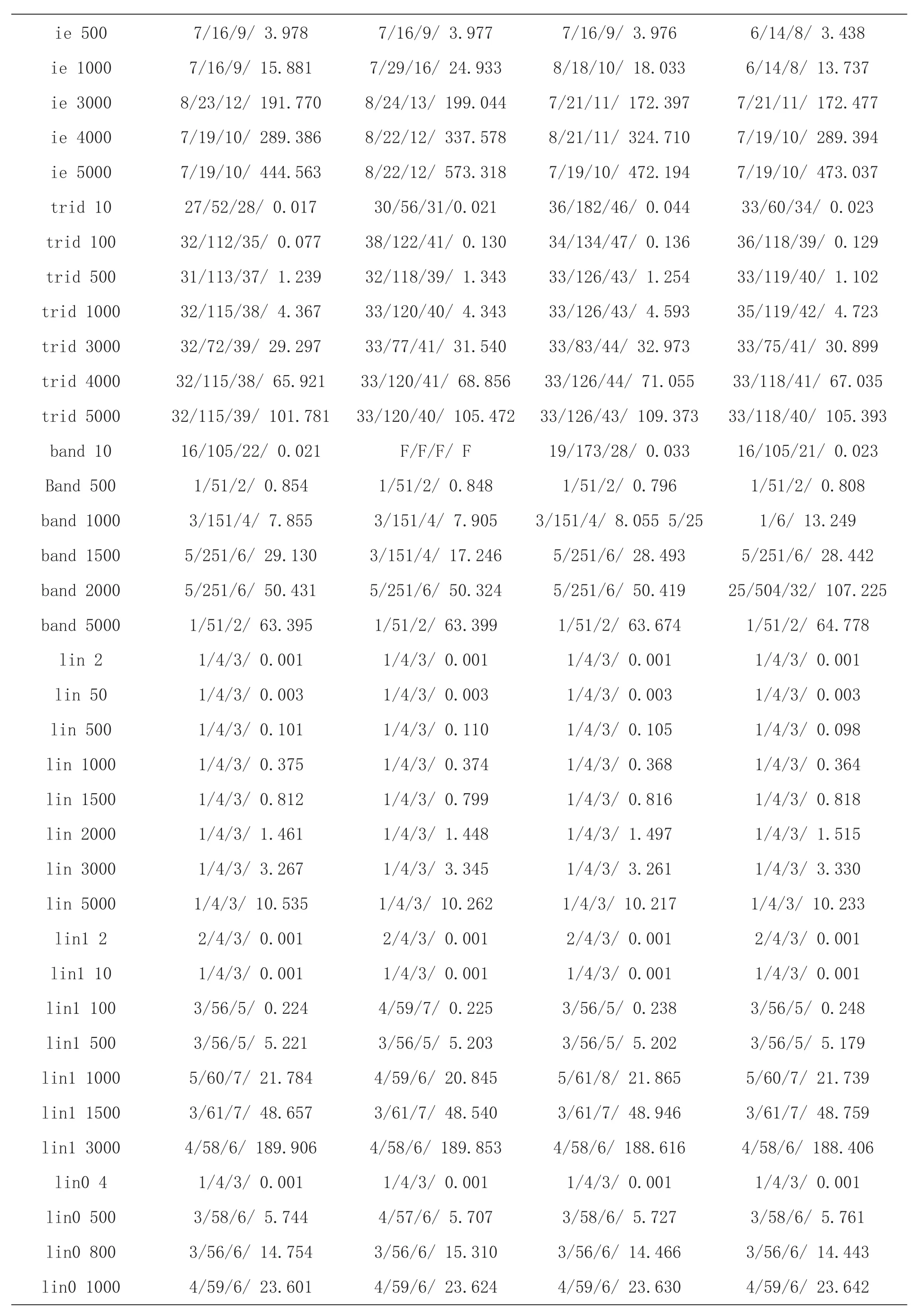
ie 5007/16/9/ 3.9787/16/9/ 3.9777/16/9/ 3.9766/14/8/ 3.438 ie 10007/16/9/ 15.8817/29/16/ 24.9338/18/10/ 18.0336/14/8/ 13.737 ie 30008/23/12/ 191.7708/24/13/ 199.0447/21/11/ 172.3977/21/11/ 172.477 ie 40007/19/10/ 289.3868/22/12/ 337.5788/21/11/ 324.7107/19/10/ 289.394 ie 50007/19/10/ 444.5638/22/12/ 573.3187/19/10/ 472.1947/19/10/ 473.037 trid 1027/52/28/ 0.01730/56/31/0.02136/182/46/ 0.04433/60/34/ 0.023 trid 10032/112/35/ 0.07738/122/41/ 0.13034/134/47/ 0.13636/118/39/ 0.129 trid 50031/113/37/ 1.23932/118/39/ 1.34333/126/43/ 1.25433/119/40/ 1.102 trid 100032/115/38/ 4.36733/120/40/ 4.34333/126/43/ 4.59335/119/42/ 4.723 trid 300032/72/39/ 29.29733/77/41/ 31.54033/83/44/ 32.97333/75/41/ 30.899 trid 400032/115/38/ 65.92133/120/41/ 68.85633/126/44/ 71.05533/118/41/ 67.035 trid 500032/115/39/ 101.78133/120/40/ 105.47233/126/43/ 109.37333/118/40/ 105.393 band 1016/105/22/ 0.021F/F/F/ F19/173/28/ 0.03316/105/21/ 0.023 Band 5001/51/2/ 0.8541/51/2/ 0.8481/51/2/ 0.7961/51/2/ 0.808 band 10003/151/4/ 7.8553/151/4/ 7.9053/151/4/ 8.055 5/251/6/ 13.249 band 15005/251/6/ 29.1303/151/4/ 17.2465/251/6/ 28.4935/251/6/ 28.442 band 20005/251/6/ 50.4315/251/6/ 50.3245/251/6/ 50.41925/504/32/ 107.225 band 50001/51/2/ 63.3951/51/2/ 63.3991/51/2/ 63.6741/51/2/ 64.778 lin 21/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.001 lin 501/4/3/ 0.0031/4/3/ 0.0031/4/3/ 0.0031/4/3/ 0.003 lin 5001/4/3/ 0.1011/4/3/ 0.1101/4/3/ 0.1051/4/3/ 0.098 lin 10001/4/3/ 0.3751/4/3/ 0.3741/4/3/ 0.3681/4/3/ 0.364 lin 15001/4/3/ 0.8121/4/3/ 0.7991/4/3/ 0.8161/4/3/ 0.818 lin 20001/4/3/ 1.4611/4/3/ 1.4481/4/3/ 1.4971/4/3/ 1.515 lin 30001/4/3/ 3.2671/4/3/ 3.3451/4/3/ 3.2611/4/3/ 3.330 lin 50001/4/3/ 10.5351/4/3/ 10.2621/4/3/ 10.2171/4/3/ 10.233 lin1 22/4/3/ 0.0012/4/3/ 0.0012/4/3/ 0.0012/4/3/ 0.001 lin1 101/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.001 lin1 1003/56/5/ 0.2244/59/7/ 0.2253/56/5/ 0.2383/56/5/ 0.248 lin1 5003/56/5/ 5.2213/56/5/ 5.2033/56/5/ 5.2023/56/5/ 5.179 lin1 10005/60/7/ 21.7844/59/6/ 20.8455/61/8/ 21.8655/60/7/ 21.739 lin1 15003/61/7/ 48.6573/61/7/ 48.5403/61/7/ 48.9463/61/7/ 48.759 lin1 30004/58/6/ 189.9064/58/6/ 189.8534/58/6/ 188.6164/58/6/ 188.406 lin0 41/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.0011/4/3/ 0.001 lin0 5003/58/6/ 5.7444/57/6/ 5.7073/58/6/ 5.7273/58/6/ 5.761 lin0 8003/56/6/ 14.7543/56/6/ 15.3103/56/6/ 14.4663/56/6/ 14.443 lin0 10004/59/6/ 23.6014/59/6/ 23.6244/59/6/ 23.6304/59/6/ 23.642
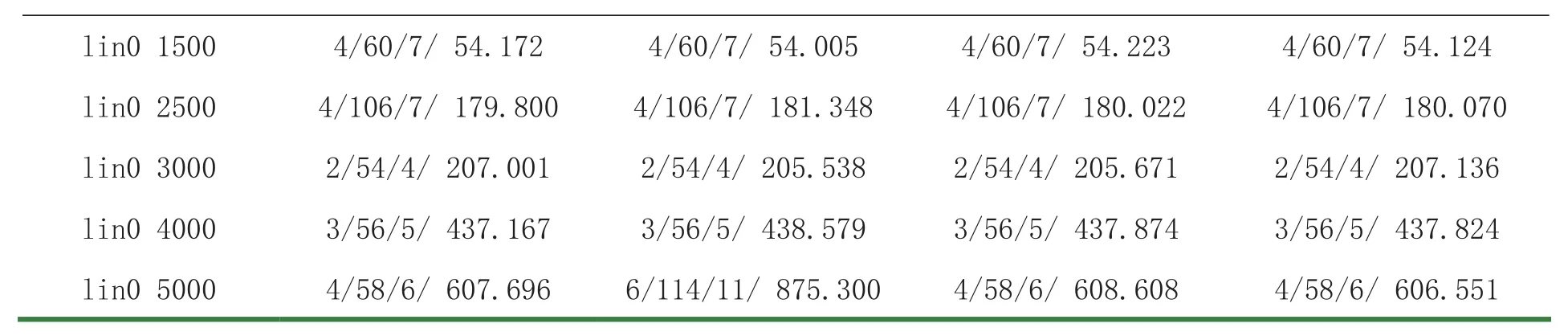
lin0 15004/60/7/ 54.1724/60/7/ 54.0054/60/7/ 54.2234/60/7/ 54.124 lin0 25004/106/7/ 179.8004/106/7/ 181.3484/106/7/ 180.0224/106/7/ 180.070 lin0 30002/54/4/ 207.0012/54/4/ 205.5382/54/4/ 205.6712/54/4/ 207.136 lin0 40003/56/5/ 437.1673/56/5/ 438.5793/56/5/ 437.8743/56/5/ 437.824 lin0 50004/58/6/ 607.6966/114/11/ 875.3004/58/6/ 608.6084/58/6/ 606.551
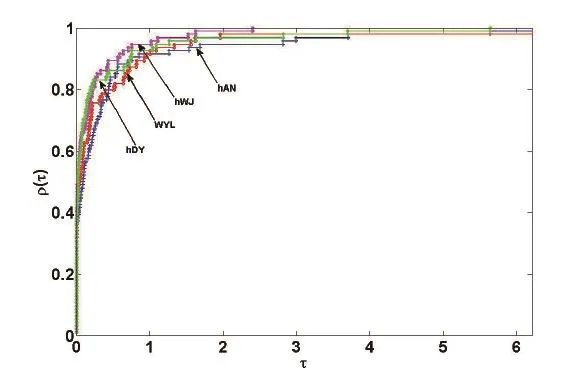
图1:计算时间比较
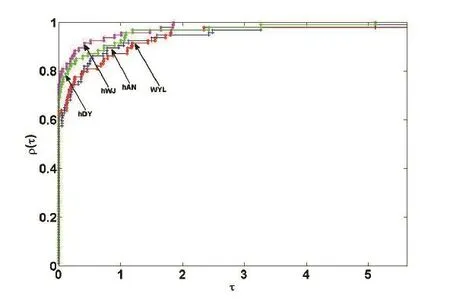
图2:函数计算次数比较
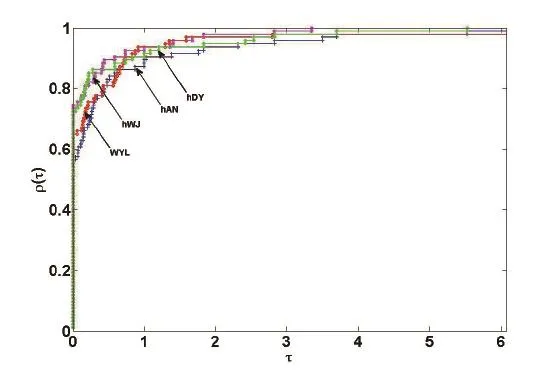
图3:梯度计算次数比较
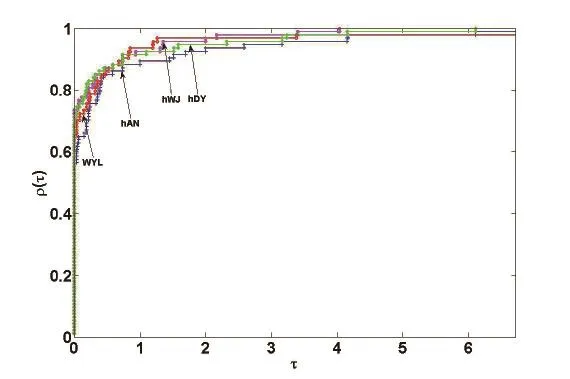
图4:迭代次数比较
Abstract:In this paper, Based on the WYL formula in [6] and the MFR formula in [8], a hydrid conjugate gradient method is proposed for unconstrained optimization. It can generates sufficient descent condition at each iteration without any line search , and converges globally for nonconvex minimization if the Wolfe line search is used. Some elementary numerical experiments are reported, which show that the proposed method is promising.
[1]Fletcher R., Reeves C.. Function minimization by conjugate gradients[J]. Computer Journal, 1964, 7: 149-154.
[2]Polak E., Ribière G.. Note surla convergence de directions conjugèes[J]. Rev. Francaise Informat Recherche Operationelle 3e Anne`e, 1969, 16(3): 35-43.
[3]Polyak B. T.. The conjugate gradient method in extreme problems[J]. USSR Computational Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 1969, 9: 94-112.
[4]Hestenes M. R, Stiefel E.. Method of conjugate gradient for solving linear equations[J]. Journal of Research of National Bureau of Standards, 1952, 49: 409-436.
[5]Dai Y. H., Yuan Y. X.. A nonlinear conjugate gradient method with a strong global convergence property[J]. SIAM Journal on Optimization, 1999, 10: 177-182.
[6]Wei Z.X., Yao S.W.. and Liu L. Y. The convergence properties of some new conjugategradient methods[J]. Applied Mathematics and computation, 2006, 183: 1341-1350.
[7]Dai Y.H., Yuan Y.X.. An efficient hybrid conjugate gradient method for unconstrained optimization[J]. Annals of Operations Research, 2001,103: 33-47.
[8]Jiang X.Z., Jian J.B.. A sufficient decent Dai-Yuan type nonlinear conjugate gradient method for unconstrained optimization problems[J]. Nonlinear Dyn; 2013, 72: 101-112.
[9]N..Andrei. Hybrid conjugate gradient algorithm for unconstrained optimization[J], J. Optim. Theory Appl. 2009,141:249–264.
[10]Yuan G. L., Lu X. W.. A modified PRP conjugate gradient method[J], Ann. Oper. Res., 2009, 166: 73–90
[11]江羡珍,简金宝,马国栋.具有充分下降性的两个共轭梯度法[J],数学学报,2014,57(2):365–372.
[12]江羡珍,韩麟,简金宝. Wolfe线搜索下一个全局收敛的混合共轭梯度法[J]. 计算数学,2012,34(1):103-112.
[13]戴或红,袁亚湘. 非线性共轭梯度法[M].上海:上海科学技术出版杜,2000.
[14]Zoutendijk G.. Nonlinear programming computational methods, In: Abadie, J.(ed.) Integer and Nonlinear Programming, North-Holland, Amsterdam, 1970.
[15]Mor`e J. J., Garbow B. S.. Hillstrome K. E., Testing unconstrained optimization software[J].ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software, 1981, 7: 17-41.
[16]Dolan E. D, Mor`e J. J.. Benchmarking optimization software with performance profiles[J]. Math. Program, 2002, 91: 201-213.
【责任编辑 谢文海】
A Hydrid Conjugate Gradient Method with Sufficient Decent Property
JIANG Xian-zhen, CHEN Yiong-fu, FENG Hua-li, SUN Yu-hui
(School of Mathematics & Information Science, Yulin Normal University, Yulin, Guangxi 537000)
unconstrained optimization; hydrid conjugate gradient method; sufficient descent; global convergence
O224
A
1004-4671(2015)05-0025-09
2015-05-27
广西自然科学基金项目(2013GXNSFFAA019009);广西高校大学生创新创业计划项目(201410606034)。
江羡珍(1968~),广西陆川人,玉林师范学院数学与信息科学学院教授,研究方向:最优化理论与方法。

