镁铝水滑石的合成及其对VO3-的吸附特性
肖卫红,张青梅,尤翔宇,刘湛(湖南省环境保护科学研究院水污染控制湖南省重点实验室,长沙410004)
镁铝水滑石的合成及其对VO3-的吸附特性
肖卫红,张青梅,尤翔宇,刘湛
(湖南省环境保护科学研究院水污染控制湖南省重点实验室,长沙410004)
摘要:水热合成层间阴离子为CO32-的Mg-Al型水滑石并经过焙烧处理,测试了焙烧前后水滑石对水溶液中VO3-的吸附行为.结果表明:焙烧后的水滑石C-HT对VO3-在35℃时最大吸附量可达95.21 mg/g,远远高于焙烧前水滑石最大吸附容量(31.59 mg/g),可见焙烧处理对水滑石的吸附性能影响显著.VO3-在C-HT上的吸附6 h内可达到吸附平衡,吸附后的C-HT采用碳酸钠溶液脱附可再生,脱附效率达97 %.C-HT对水中VO3-的吸附能力主要在于VO3-与层板间填充的CO32-交换吸附.
关键词:镁铝水滑石;焙烧;阴离子交换;吸附;VO3-
近年来,随着钒工业的快速发展,沉钒等工序的含钒废水排放导致钒水污染严重.含钒废水处理的方法多达10余种[1-5],而应用较多的为化学沉淀法,如氯化铵沉淀法[6]、铁屑沉淀法[7],以及吸附法,如沸石吸附法[8]、活性炭吸附法[9]、阴离子树脂吸附法[10]、壳聚糖[11]等.
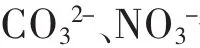
1 实验方法
1.1水滑石的合成
溶液A:将0.3 mol Mg(NO3)2·6H2O及0.1 molAl(NO3)3·9H2O完全溶解在150 mL水中;
溶液B:将50 mL 3 mol/L的Na2CO3溶液和100 mL 3 mol/L的NaOH溶液混合,搅拌均匀;
HT合成:以1滴/秒的速度向B溶液中逐滴加入溶液A,至加入A后的B溶液pH=10左右;滴加完毕后搅拌1 h,再将该溶液转入反应釜中,120℃反应24 h后水洗至中性;过滤,80℃烘干;
C-HT的合成:采用450℃焙烧HT 5 h,得到焙烧后的水滑石,简写为C-HT.
1.2HT及C-HT对水中钒的吸附与脱附
1)吸附等温线测试.分别称取0.1 g HT和0.1 g C-HT作为吸附剂,加入待吸附的100 mL含钒溶液中,pH值为7,分别于15℃、25℃、35℃恒温振荡24 h. VO3-在HT和C-HT上的平衡吸附量Qe可用式(1)计算:



式(2)中:n为吸附剂对VO3-的去除效率.









式(6)中:η为脱附率.
1.3分析方法
2 结果与讨论
2.1吸附等温线
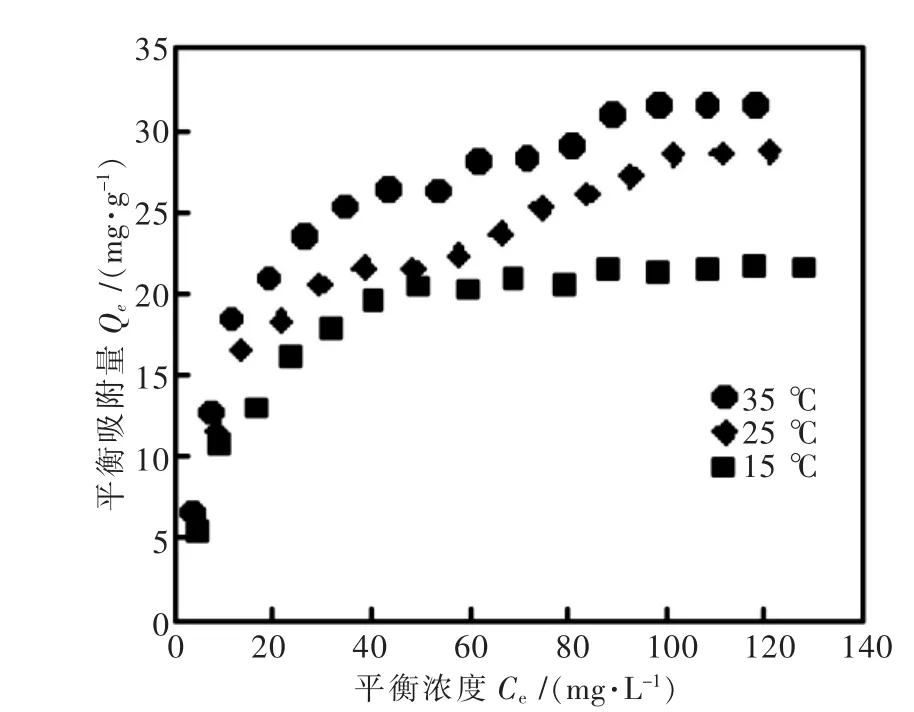
图1 HT对VO3-的吸附等温线Fig.1 Adsorption isotherms of VO3-onto the HT
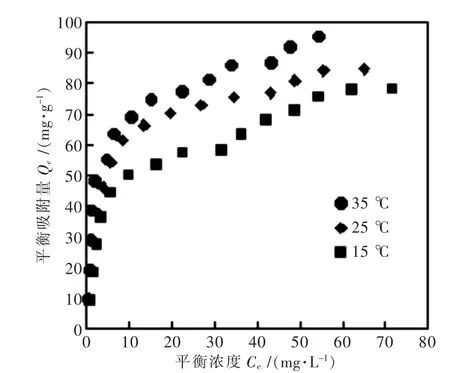
图2 C-HT对的吸附等温线Fig.2 Adsorption isotherms of VO3-onto the C-HT



图3 HT和C-HT对VO3-的吸附效率Fig.3 The adsorption efficiency of VO3-onto HT and C-HT
2.2吸附动力学
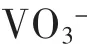

图4 C-HT对VO3-的吸附量随接触时间的变化Fig.4 Adsorption amount of VO3-onto the C-HT
2.3吸附机理探讨
图5(a)为HT的XRD谱图,各衍射峰峰窄而尖,杂峰少而低,表明合成的HT晶相结构完整,结晶度高,具有2个明显的衍射峰(003)和(006),根据已有报道(003)和(006)为层状结构的特征衍射峰[16-17]. 图5(b)为C-HT的XRD谱图,焙烧后(003)和(006)消失,出现了(400)和(440),根据标准JCPDS卡(JCPDS22-700),(400)和(440)为氧化镁和氧化铝的特征峰.
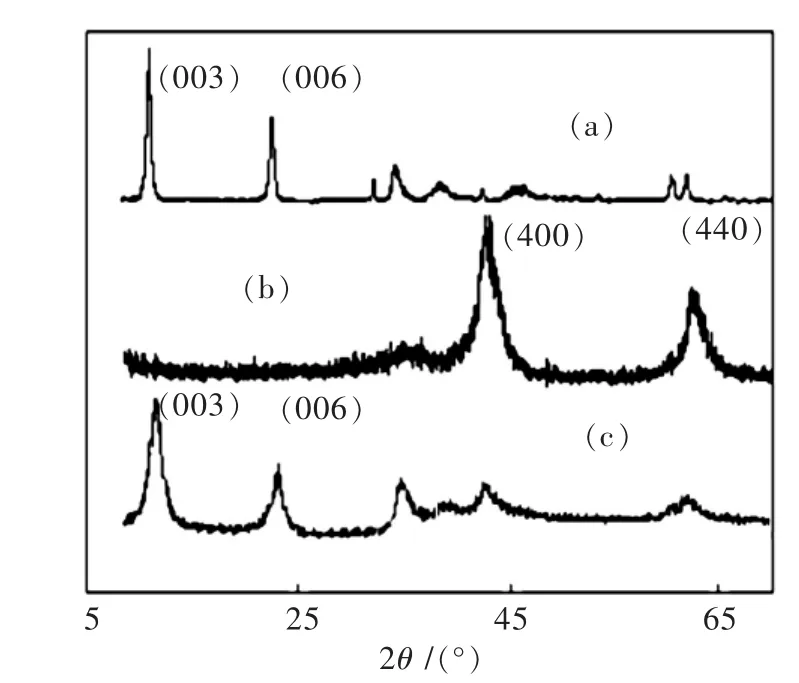
图5 HT(a)、C-HT(b)和V-C-HT(c)的XRD谱图Fig.5 XRD patterns of HT(a),C-HT(b)and V-C-HT(c)

表1 吸附等温线拟合参数Table 1 Adsorption isotherm parameters


图6 Na2CO3溶液对被吸附钒的脱附效率Fig.6 The Desorption efficiency of Na2CO3solution
3 结 论
1)采用水热法合成的镁铝水滑石具有完整的晶相结构,经450℃焙烧5 h形成结晶度较低的氧化镁和氧化铝双金属氧化物固溶体.
参考文献:
[1]Kaczala F,Marques M,Hogland W. Lead and vanadium removal from a real industrial wastewater by gravitational settling/sedimentation and sorption onto Pinus[J]. Bioresource Technology,2009,100(1):235-243.
[2]Abigail P R,Jose A H,Jose R P,et al. Synthesis of protonated chitosan flakes for the removal of vanadium(III,IV and V)oxyanionsfromaqueoussolutionsy[J]. Microchemical Journal,2015,118(5):1-11.
[3]Nosrati S,Jayakumar N S,Hashim M A,et al. Performance evaluation of vanadium(IV)transport through supported ionic liquid membrane[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers,2013,44(3):337-342.
[4]王英.沉钒废水处理技术的研究现状[J].铁合金,2012(6):41-45. [5]包申旭,张一敏,刘涛,等.电渗析处理石煤提钒废水[J].中国有色金属学报,2010,20(7):1440-1445.
[6]关洪亮,王杏林,张璐,等.氯化铵处理含钒废水的研究[J].环境科学与技术,2014,37(5):122-125.
[7]欧阳玉祝,王继徽.铁屑微电解-共沉淀法处理含钒废水[J].化工环保,2002,22(3):165-168.
[8]陈昕,张漪丽.亚铁离子改性沸石对废水中钒(V)的吸附研究[J].湖南师范大学学报(医学版),2009,6(2):5-8.
[9]成应向,罗咏,戴友芝,等.改性活性炭对石煤提钒废水中低浓度NH3-N和V等的吸附[J].环境工程学报,2013,7(9):3455-3460.
[10]张报清,雷霆,方树铭,等.钼酸铵溶液化学沉淀法和离子交换法除钒研究[J].稀有金属,2012,36(3):466-471.
[11]Abigail P R,José A H V,José R P V,et al. Synthesis of protonated chitosan flakes for the removal of vanadium(III,IV and V)oxyanions from aqueous solutions[J]. Microchemical Journal,2015,118(1):1-11.
[12]Miyata S. Physico-chemical properties of synthetic hydrotalcites in relation to composition[J]. Clays Clay Miner. 1980,28:50-55.
[13]任志峰,何静,张春起,等.焙烧水滑石去除氯离子性能研究[J].精细化工,2002,19(6):339-342.
[14]Lazaridis N K,Pandi T A,MatisK A. Chromium(VI)removal from aqueous solutions by Mg-Al-CO3hydrotalcite:sorption-desorption kinetic and equilibrium studies[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research,2004,43(9):2209-2215.
[15]范杰,许昭怡,郑寿荣,等. Mg-Al型水滑石对水溶液中F-的吸附[J].环境化学,2006,25(4):425-428.
[16]王莉娟,焦飞鹏,蒋新宇.焙烧态水滑石吸附水中钒酸根的研究[J].材料导报,2012,26(19):310-316.
[17]郑丽波,叶瑛,季珊珊. Mg/Al型双金属氧化物对六价铬的吸附作用[J].地球化学,2004,33(2):208-214.
Synthesis of the Mg-Al hydrotalcite and its adsorption properties for VO3-
XIAO Weihong,ZHANG Qingmei,YOU Xiangyu,LIU Zhan
(Hunan Research Academy of Environmental Science, Changsha 410004, China)
Abstract:Mg-Al-CO32-hydrotalcite was prepared by hydrothermal method and then calcined. The adsorption behaviors of hydrotalcite for VO3-in the solution before and after calcination were investigated. The results were summarized as follows: The maximum adsorption capacity of hydrotalcite C-HT after calcination for VO3-is 95.21 mg/g at 35℃, much lager than that of hydrotalcite before calcination which is 31.59 mg/g. It shows significant influence of calcination on the adsorption capacity of hydrotalcite. The kinetics of VO3-adsorption onto CHT shows that the time until equilibrium is 6 hour, and C-HT after adsorption is reproducible by desorption of sodium carbonate solution with desorption efficiency of up to 97 %. The adsorption capacity of C-HT for VO3-in the solution is mainly due to the exchange adsorption of VO3-and the CO32-filling between the layers.
Key words:hydrotalcite; synthesis; roasting; sdsorption; VO3-.
作者简介:肖卫红(1966-),女,助理工程师,主要从事水污染控制方面的研究,E-mail:94616944@qq.com.
基金项目:国家环保技术管理项目(2110109);国家科技重大专项“水体污染控制与治理”(2013ZX07504-001-03)
收稿日期:2015-05-20
DOI:10.13264/j.cnki.ysjskx.2015.04.008
文章编号:1674-9669(2015)04-0037-04
中图分类号:TF111.52
文献标志码:A

