细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4在日本血吸虫免疫逃避中的作用及其机制研究
唐春莲,申志琴,严玲霞,刘晓宏
细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4在日本血吸虫免疫逃避中的作用及其机制研究
唐春莲,申志琴,严玲霞,刘晓宏
目的 探讨细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4(CTLA-4)在日本血吸虫免疫逃避中的作用及其机制。方法 雌性BALB/c小鼠随机分成3组,即正常对照组、感染对照组和抗CTLA-4单克隆抗体(Anti-CTLA-4 mAb)组。各感染组每只小鼠经腹部皮肤感染日本血吸虫尾蚴40条,感染2周后,Anti-CTLA-4 mAb组每只小鼠连续3 d腹腔注射300 μg anti-CTLA-4 mAb,对照组注射等体积的PBS。感染后6周杀鼠冲虫,计数每只小鼠虫荷及每克肝脏虫卵数。流式细胞术检测各组小鼠脾淋巴细胞中调节性T细胞(CD4+CD25+Tregs)百分比。ELISA法检测各组小鼠脾淋巴细胞培养上清中细胞因子IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-5和IL-10的含量。肝组织石蜡切片HE染色观察感染组小鼠肝脏虫卵肉芽肿病理变化。结果 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb组减虫率为18.99%,脾淋巴细胞中CD4+CD25+Tregs百分比显著升高(P<0.05)。Anti-CTLA-4 mAb组脾细胞培养上清中细胞因子IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-5和IL-10的含量均高于感染对照组,肝脏虫卵肉芽肿直径较感染对照组明显增大。结论 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb使用同时增强Th1型和Th2型免疫反应,有利于机体清除日本血吸虫但以损伤机体为代价。研究结果提示宿主CTLA-4利于日本血吸虫免疫逃避。
日本血吸虫; 细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白4; 免疫逃避; 细胞因子
Supported by the Schistosomiasis Control Project from Hubei Provincial Health and Family Planning Commission(No. WJ2015XB016) Corresponding author: Liu Xiao-hong, Email: 494527907@qq.com
血吸虫病是一种常见的人兽共患寄生虫病,全球76个国家至少23亿人感染血吸虫[1],我国主要是日本血吸虫。寄生虫具有免疫逃避功能能在宿主体内长期存在,其逃避机制可能与抗原伪装、序列变异等相关[2]。新近研究证实,细胞毒性T淋巴细胞相关蛋白-4(cytotoxic T-lympnocyte-associated protein 4,CTLA-4)与病原体逃避宿主免疫攻击有关,如HIV感染患者,感染利什曼原虫后导致CD4+CTLA-4+调节性T细胞比例明显增高,导致原虫复发[3]。实验性脑疟原虫模型中,FOXP3+细胞损伤了抗原特异性CD4+T细胞及CD8+T细胞反应,因此利于疟原虫逃避宿主免疫攻击。而FOXP3+细胞调节的保护作用依赖于CTLA-4[4]。CTLA-4在日本血吸虫免疫逃避中的作用尚无报道。本文采用CTLA-4 mAb,观察其在日本血吸虫免疫逃避中的作用及其机制。
1 材料与方法
1.1 实验动物分组及处理 18只6~8周龄雌性BALB/c小鼠购自湖北省疾病预防控制中心,随机分成3组,每组6只。即正常对照组、感染对照组、Anti-CTLA-4 mAb组。日本血吸虫阳性钉螺(购自江西省寄生所)光照下逸出尾蚴,各感染组每只小鼠经腹部皮肤感染尾蚴40条。感染后2周,抗体组每只小鼠连续3 d腹腔注射300 μg anti-CTLA-4 mAb,对照组注射等体积的PBS。感染后6周剖杀所有小鼠。
1.2 试剂器材 调节性T细胞染色试剂盒试剂盒购自eBioscience公司;细胞因子IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-5、IL-10检测试剂盒购自eBioscience公司;流式细胞仪(FACSCalibur型)购自美国Becton Dickinson公司。
1.3 虫荷及每克肝脏虫卵计数 日本血吸虫感染后6周,剖杀各感染组小鼠。生理盐水灌注冲虫[5],计算各感染组每只小鼠虫荷及减虫率。称取各感染组每只小鼠肝脏右叶0.5 g,研磨,5% KOH 20 mL 37 ℃消化2 h,取250 μL计数,重复4次取平均值,计算每克肝脏虫卵数。剩余肝组织用于病理学检测。
1.4 脾细胞流式细胞术检测无菌取脾,根据文献报道的方法[6]制备单个脾淋巴细胞悬液。以含10%胎牛血清的RPMI-1640培养液重悬,显微镜下计数淋巴细胞数量,调整其浓度为5×106/mL。流式细胞术染色使用小鼠调节性T细胞染色,其中CD4抗体、CD25抗体和Foxp3抗体分别以异硫氰酸荧光素、别藻青蛋白和藻红蛋白标记。流式细胞仪检测脾淋巴细胞中CD4+CD25+Tregs的百分比。
1.5 脾细胞培养上清中细胞因子检测 无菌取脾,研磨,制备脾淋巴细胞悬液并调整细胞浓度至5×106/mL,置37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱培养72 h,收集上清液。双抗体夹心ELISA法检测脾细胞培养上清中细胞因子IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-5和IL-10的水平,根据标准曲线计算待测样品中特定细胞因子含量(pg/mL)。
1.6 病理学检测 用于病理学检测的肝组织经10%福尔马林固定后,石蜡包埋。切片,厚度约5 μm,常规HE染色,观察各感染组小鼠肝脏虫卵肉芽肿的变化。
2 结 果
2.1 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb对小鼠体内虫荷及每克肝脏虫卵数的影响 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb使用组虫荷及每克肝脏虫卵数明显低于感染对照组(P<0.05)(表1)。

表1 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb对小鼠体内虫荷及每g肝脏虫卵数的影响Tab.1 The effect of anti-CTLA-4 mAb on the worm burden and eggs per gram liver in BALB/c mice
注:数值均为均数±标准差。N代表每组6只小鼠。*与感染对照组比较,P<0.05。
Note:All results were presented as mean ± S.D; n represents 6 mice in each group. *P<0.05, versus infected control group.
2.2 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb对脾淋巴细胞中CD4+CD25+Tregs百分比的影响 CTLA-4表达于CD4+CD25+Tregs,为了研究日本血吸虫感染模型中CTLA-4在CD4+CD25+Tregs中的作用,流式细胞术检测各组小鼠脾淋巴细胞中的CD4+CD25+Tregs百分比。既然Foxp3是CD4+CD25+Tregs的特异性标志,因此,用CD4+CD25+Foxp3+T 细胞表示CD4+CD25+Tregs。无菌取抗体处理组和对照组小鼠脾脏,常规制备脾淋巴细胞悬液,小鼠调节性T细胞染色试剂盒抗体标记。流式检测结果见图1,anti-CTLA-4 mAb组脾淋巴细胞中CD4+CD25+Tregs比例明显高于对照组(P<0.05)。
2.3 脾细胞培养上清中细胞因子的含量 Anti-CTLA-4 mAb组脾淋巴细胞中细胞因子IFN-γ、IL-4、IL-5和IL-10的含量均明显高于感染对照组(图2)。

正常对照组(A), 感染对照组(B)和Anti-CTLA-4 mAb组 (C).P2门为CD4+CD25+T细胞在脾淋巴细胞中的百分比,Q2-2为P2门中的Foxp3+T细胞的百分比(即CD4+CD25+Foxp3+%)。
Normal control (A), infected control (B) and anti-CTLA-4 mAb (C). Upper panels, the cells in P2 gate denote the percentage of CD4+CD25+T cells in splenic lymphocytes. The cells in Q2-2 gate in the lower panels denote the percentage of Foxp3+lymphocytes in P2 gate.
图1 流式细胞染色显示CD4+CD25+Tregs在脾淋巴细胞中的的百分比。
Fig.1 FACS analysis demonstrates the percentage of CD4+CD25+Tregs in splenocytes
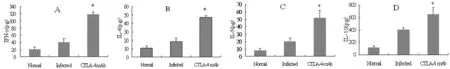
* 与感染对照组比较,P<0.05。* P<0.05, versus infected control group.图2 BALB/c小鼠脾细胞培养上清中IFN-γ(A)、IL-4(B)、IL-5(C)和IL-10(D)的含量Fig.2 The expression of IFN-γ, IL-4, interleukin-5 and IL-10 in splenic lymphocytes culture supernatant
2.4 肝组织病理切片结果 肝组织HE染色结果见图3,anti-CTLA-4 mAb组肝组织虫卵肉芽肿直径(503.2±53.6)较感染对照组(356.8±43.6)增大,组间差异有统计学意义。
3 讨 论
CTLA-4为共刺激分子,与CD28分子结构具有76%的同源性。CTLA-4能竞争性抑制CD28分子与B7复合物结合,防止CD28分子促进T细胞激活[7]。CTLA-4最重要的功能是抑制T细胞激活,CTLA-4基因缺陷小鼠出现淋巴增殖及多器官淋巴细胞浸润,出生后3~4周死亡[8]。Blank等[6]报道,采用抗CTLA-4单克隆抗体(anti-CTLA-4 mAb)能增强机体的免疫反应,有利于机体抗黑色素瘤免疫反应。CTLA-4在转移性的黑色素瘤患者中,有利于肿瘤细胞的免疫逃避,使用相应抗体阻断则有利于病情改善[9]。Martins等[10]报道,锥虫感染模型中采用anti-CTLA-4 mAb有利于机体对病原体的清除,使寄生虫血症下降及利于宿主存活。本实验证实,anti-CTLA-4 mAb使用时机体对日本血吸虫的清除率为18.99%。CTLA-4可能有利于日本血吸虫在宿主体内的免疫逃避。

感染对照组(A)、anti-CTLA-4 mAb组(B)Infected control group (A), anti-CTLA-4 mAb group (B).图3 各感染组虫卵肉芽肿Fig.3 Schistosoma egg granuloma in infected groups
既然CTLA-4表达于CD4+CD25+Tregs,则很容易认为其免疫逃避作用是通过CD4+CD25+Tregs来实现的。本实验使用流式方法检测anti-CTLA-4 mAb对CD4+CD25+Tregs的影响,结果显示:CD4+CD25+Tregs不降反升,表明CTLA-4在日本血吸虫免疫逃避中的作用不是通过CD4+CD25+Tregs来实现的,Suarez N等[11]也报道,封闭CD4+CD25+Tregs与CTLA-4阻断为不同的作用机制,两者能起协同作用利于机体清除肿瘤。抗CTLA-4抗体作用的靶点在于增强效应T细胞的反应或者增强其对CD4+CD25+Tregs的抵抗。
CTLA-4为抑制性受体,能提高效应T细胞激活的阈值[12],用相应抗体阻断后,则能使各种类型细胞增殖及各种类型细胞因子分泌增加。本实验证实,anti-CTLA-4 mAb引起脾细胞培养上清中细胞因子IFN-γ明显上升。Hoffman等[13]报道,Th1型免疫反应对机体清除日本血吸虫很重要。因此,抗体使用后的杀虫效应可能是通过增强Th1型免疫反应来实现的。
病理组织学检测结果显示,与感染对照组相比较,anti-CTLA-4 mAb及联合组单个虫卵肉芽肿直径明显增大。虫卵肉芽肿主要是由日本血吸虫卵引起的Th2型免疫反应[14],anti-CTLA-4 mAb导致Th2型细胞因子上升,因而引起虫卵肉芽肿反应增强。Torino F等[15]报道,anti-CTLA-4 mAb具有明显地抗肿瘤反应,同时加重对机体的病理损伤。Anti-CTLA-4 mAb增强机体免疫反应有利于机体清除寄生虫的同时,以对机体的损伤增强为代价。
[1]Colley DG, Bustinduy AL, Secor WE, et al. Human schistosomiasis[J]. Lancet, 2014, 383(9936): 2253-2264.
[2]Higgins MK, Carrington M. Sequence variation and structural conservation allows development of novel function and immune evasion in parasite surface protein families[J]. Protein Sci, 2014, 23(4): 354-365.
[3]Vallejo A, Abad-Fernández M, Moreno S, et al. High levels of CD4+CTLA-4+Treg cells and CCR5 density in HIV-1-infected patients with visceral leishmaniasis[J]. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis, 2015, 34(2): 267-275.
[4]Haque A, Best SE, Amante FH, et al. CD4+natural regulatory T cells prevent experimental cerebral malaria via CTLA-4 when expandedinvivo[J]. PLoS Pathog, 2010, 6(12): e1001221.
[5]Tang CL, Lei JH, Wang T, et al. Effect of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells on the immune evasion ofSchistosomajaponicum[J]. Parasitol Res. 2011, 108(2): 477-480.
[6]Mo HM, Liu WQ, Lei JH, et al.Schistosomajaponicumeggs modulate the activity of CD+4CD+25Tregs and prevent development of colitis in mice[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2007, 116(4): 385-389.
[7]Dilek N, Poirier N, Hulin P, et al. Targeting CD28, CTLA-4 and PD-L1 costimulation differentially controls immune synapses and function of human regulatory and conventional T-cells[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e83139.
[8]Waterhouse P, Penninger JM, Timms E, et al. Lymphoproliferative disorders with early lethality in mice deficient in Ctla-4[J]. Science, 1995, 270(5238): 985-988.
[9]Matikas A, Mavroudis D. Beyond CTLA-4: novel immunotherapy strategies for metastatic melanoma[J]. Future Oncol, 2015, 11(6): 997-1009.
[10]Martins GA, Tadokoro CE, Silva RB, et al. CTLA-4 blockage increases resistance to infection with the intracellular protozoanTrypanosomacruzi[J]. J Immunol, 2004, 172(8): 4893-4901.
[11]Suarez N, Alfaro C, Dubrot J, et al. Synergistic effects of CTLA-4 blockade with tremelimumab and elimination of regulatory T lymphocytesinvitroandinvivo[J]. Int J Cancer, 2011, 129(2): 374-386.
[12]Egen JG, Kuhns MS, Allison JP. CTLA-4: new insights into its biological function and use in tumor immunotherapy[J]. Nat Immunol, 2002, 3(7): 611-618.
[13]Mendez S, Reckling SK, Piccirillo CA, et al. Role for CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells in reactivation of persistent leishmaniasis and control of concomitant immunity[J]. J Exp Med, 2004, 200(2): 201-210.
[14]Tian Z, Wang XY, Zhou YF, et al.SchistosomajaponicumscFv-IL18 fusion DNA ameliorates hepatic fibrosis in schistosomiasis-infected mice via improving local concentration of IL-18 in liver[J]. Exp Parasitol, 2013, 134(4): 447-454.
[15]Torino F, Barnabei A, De Vecchis L, et al. Hypophysitis induced by monoclonal antibodies to cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4: challenges from a new cause of a rare disease[J]. Oncologist, 2012, 17(4): 525-535.
Effect and mechanism of CTLA-4 on the immune evasion ofSchistosomajaponicumin mice
TANG Chun-lian,SHEN Zhi-qin,YAN Lin-xia,LIU Xiao-hong
(DepartmentofClinicalLaboratory,WuchangHospital,Wuhan430063,China)
In order to explore the effect and mechanism of cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) on the immune evasion ofSchistosomajaponicum(S.japonicum) in mice, the 18 female BALB/c mice were divided randomly into 3 groups: normal control, infected control and anti-CTLA-4 mAb-treated group. Each mouse in infected control and anti-CTLA-4 groups was challenged with 40 cercarie ofS.japonicum. Mice in anti-CTLA-4 mAb group were treated with 300 μg of anti-CTLA-4 mAb for 3 days consecutively, equal volume PBS as control. At 6 weeks post-infection, all mice were succumbed to measure worm burden and eggs per gram liver. The levels of IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-10 were detected by sandwich-ELISA. Flow cytometry was performed to measure the percentages of CD4+CD25+tregs in splenic cells. Liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin to detect egg granuloma. The results showed that reduction rate of worm burden in anti-CTLA-4 mAb group were 18.99%. Compared with that of control group, the percentage of CD4+CD25+Tregs was extremely higher in anti-CTLA-4 mAb group. The egg granuloma size in anti-CTLA-4 mAb group were extremely larger than those of infected control group, while the levels of IFN-γ, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10 in anti-CTLA-4 mAb group were extremely higher than those of control group. It’s indicated that anti-CTLA-4 mAb favors the host to clearS.japonicumby enhancing Th1 type immune response, but at the cost of elevated pathological damage by enhancing Th2 type immune response. It hints that CTLA-4 contribute to the escape ofS.japonicumfrom the host immune responses.
Schistosomajaponicum; CTLA-4; immune evasion; cytokines
刘晓宏,Email: 494527907@qq.com
武汉市武昌医院检验科,武汉 430063
10.3969/j.issn.1002-2694.2015.11.016
R383
A
1002-2694(2015)11-1061-04
2015-05-08;
2015-08-26
湖北省卫生和计划生育委员会血防专项(No. WJ2015XB016)资助

