盘形圆弧砂轮曲面磨削几何模型*
彭扬林,戴一帆 ,宋 辞,3 ,石 峰
(1.国防科技大学 机电工程与自动化学院, 湖南 长沙 410073;
2.超精密加工技术湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙 410073;
3.中国科学院 上海技术物理研究所, 上海 200083)
盘形圆弧砂轮曲面磨削几何模型*
彭扬林1,2,戴一帆1,2,宋辞1,2,3,石峰1,2
(1.国防科技大学 机电工程与自动化学院, 湖南 长沙410073;
2.超精密加工技术湖南省重点实验室, 湖南 长沙410073;
3.中国科学院 上海技术物理研究所, 上海200083)
摘要:砂轮外形、加工轨迹、运动轴组合方式、工件摆放方式等的差异都会引起曲面磨削加工模型的变化,加工几何模型是实施曲面磨削首要解决的问题。建立盘形圆弧砂轮的几何模型,通过磨削点法向量匹配,建立工件点和砂轮点的一一映射关系,经过坐标变换可以得到相应的刀具运动轨迹,用于磨削加工。形成统一的盘形砂轮曲面磨削几何模型,并给出刀具运动轨迹的计算流程。该磨削模型适用范围广,有效解决了多种曲面磨削过程的刀具轨迹生成问题,实现了高精度的曲面磨削加工。
关键词:曲面磨削;磨削几何模型;砂轮模型;法向量匹配
常用于曲面磨削加工的砂轮包括杯形砂轮[1-3](圆弧端面或平面端面)、盘形砂轮[4-10](圆周为圆弧面或平面)、球形砂轮[11-12]、局部球形砂轮[13]等。砂轮不同,对应的加工轨迹、加工模型、误差影响类型都会有较大差异,分析方法并不能通用。不同加工轨迹、运动轴组合、工件摆放等,都会引起曲面磨削加工模型的变化,形成不同的加工方式。现主要讨论圆周为圆弧面的盘形砂轮在曲面磨削加工中的加工模型。
曲面按照回转对称性可以分为回转对称曲面和非回转对称曲面。回转对称曲面可以通过母线绕回转轴旋转一周成形,于是可以通过XZ轴联动、插补出母线轨迹,同时C轴回转即可形成回转对称曲面[8,14]。联动轴的变化,如YZC轴组合加工,可以形成平行磨削[3,7,9-11]。砂轮倾角随着曲面法向变化而变化,保证砂轮上磨削点固定,则又形成法向跟踪磨削[3-4]。根据磨削轴和工件轴的夹角又可以区分为垂直轴磨削和斜轴磨削[15-16]。
非回转对称曲面,由于其非回转对称性,无法采用上述方法进行加工,如果将上述的加工方式称为螺旋轨迹加工,则非回转对称曲面只能采用光栅轨迹进行加工。根据所采用联动轴不同、是否斜轴,可衍生出多种加工方式。
相关文献[1,2,5,7-9,12,17]都对加工的几何学模型有一定的研究,但都是针对其特定的加工方式进行,研究不深入、适用范围不广、借鉴意义有限。
1磨削机床系统结构
磨削机床包括五个运动轴,机床如图1所示(1—底座;2—主轴;3—立柱;4—Y轴导轨;5—Z轴导轨;6—A轴转台;7—砂轮;8—C轴转台;9—X轴导轨)。工件安装在C轴转台上,C轴作回转运动,配合XZ二轴联动,可以实现回转对称曲面的加工;XYZ轴联动,或者配合A轴的转动可以实现非轴对称曲面的加工。

图1 磨削机床示意图Fig.1 Schematic diagram of grinding equipment
2砂轮几何模型
砂轮坐标系OgXgYgZg中,砂轮上可能参与磨削的点Pg用参数方程可以表示为式(1),砂轮示意图如图2所示。

(1)
其中,R表示砂轮半径,r表示圆弧半径,U∈[π/2,3π/2]表示圆弧张角,Q∈[-π,0)表示砂轮张角。

图2 砂轮几何模型示意图Fig.2 Schematic diagram of wheel geometric model
由代数学知识可知,该曲面上沿Q方向的切向量可表示为:
nQ=[∂x/∂Q,∂y/∂Q,∂z/∂Q]=[-(R-rcosU)·
sinQ,0,(R-rcosU)cosQ]
(2)
沿U方向的切向量可表示为:
nU=[∂x/∂U,∂y/∂U,∂z/∂U]=[rsinU·
cosQ,rcosU,rsinUsinQ]
(3)
对应pg点处的法向量为:
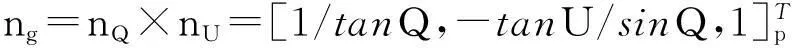
(4)
3曲面加工模型

nwg=S·nw
(5)

图3 曲面磨削加工模型示意图Fig.3 Schematic diagram of curve surface grinding
其中,

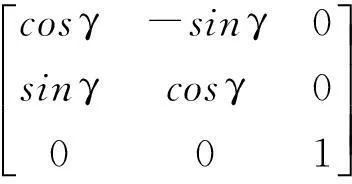
(6)
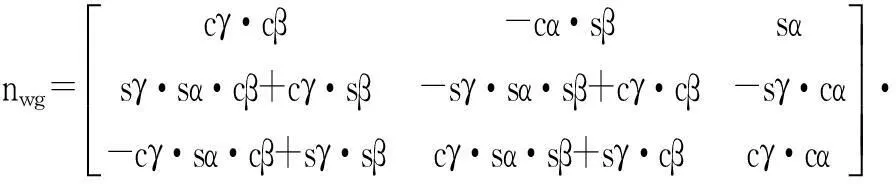
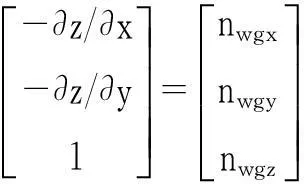
(7)
对于这种由刀具轨迹包络成型的加工方式,最根本的理论就是加工点处工件的单位法向量和砂轮的单位法向量相等或相反(凹面相等,凸面相反)。
于是在点p处,有nwg=ng成立。则有
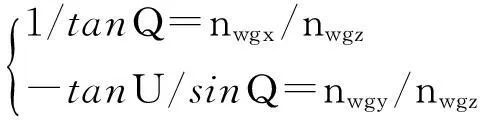
(8)
根据式(8)和式(1)可以得到磨削点p时,对应砂轮上的点在砂轮坐标系中的坐标pg=[xg,yg,zg]T。式(8)中求解反正切时,得到的解值域为[-π/2,π/2],而Q∈[-π,0),U∈[π/2,3π/2],所以角度的求解结果需要进行相位修正。修正方式为:
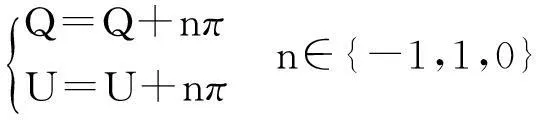
(9)
其中,n取值需要根据定义域实际情况具体确定。
砂轮在工件坐标系中的运动轨迹,可以通过点pg变换到工件坐标系得到,如式(10)所示。
pgw=S-1·pg+T+pT
(10)
其中,平移矩阵T和工件坐标系零点位置选取有关。
4刀具轨迹计算流程
刀具轨迹的计算,就是根据给定的被加工曲面,计算得到磨削刀具的运动轨迹,通过轨迹的包络磨削形成曲面,具体的过程如图4所示。

图4 磨削轨迹计算流程图Fig.4 Calculation flow chart of grinding path
5加工实例
根据上述的磨削几何模型,对一个340mm×340mm双曲面工件进行磨削加工。这是一个回转对称的凸二次曲面,可以通过XZ轴联动,插补出母线轨迹,母线绕回转轴C轴旋转一周成形,得到回转对称双曲面。加工过程、运动轨迹以及磨削面形误差如图5所示,最终磨削面形误差为8.0μm。

(a) 双曲面磨削过程照片(a) Photo of grinding process of hyperboloid

(b) 双曲面磨削轨迹(b) Grinding path of hyperboloid

(c) 双曲面磨削面形误差(c) Figure error of ground hyperboloid图5 双曲面磨削加工过程及面形误差Fig.5 Grinding process and figure error of hyperboloid
对一个340mm×340mm的离轴抛物面工件进行磨削加工时,如果采用工件安装在离轴位置,使用螺旋轨迹进行加工,相当于磨削母镜直径为1070mm口径的回转对称工件,存在要求机床行程大、降低加工效率、影响磨削精度等问题。所以对于此种非回转对称曲面,采用光栅轨迹进行加工更有优势。通过XYZ轴联动,形成曲面的包络轮廓。加工过程、运动轨迹以及磨削面形误差如图6所示,最终磨削面形误差为9.6μm。
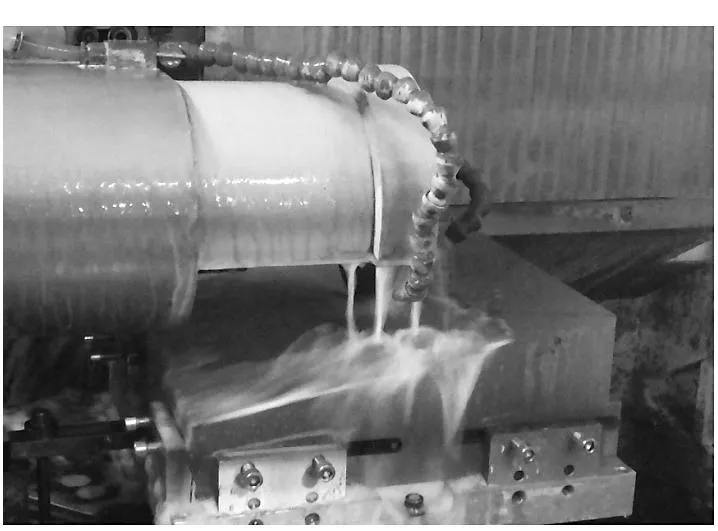

(a) 离轴抛物面磨削过程照片(a) Photo of grinding process of off-axis paraboloid

(b) 离轴抛物面磨削轨迹(b) Grinding path of off-axis paraboloid
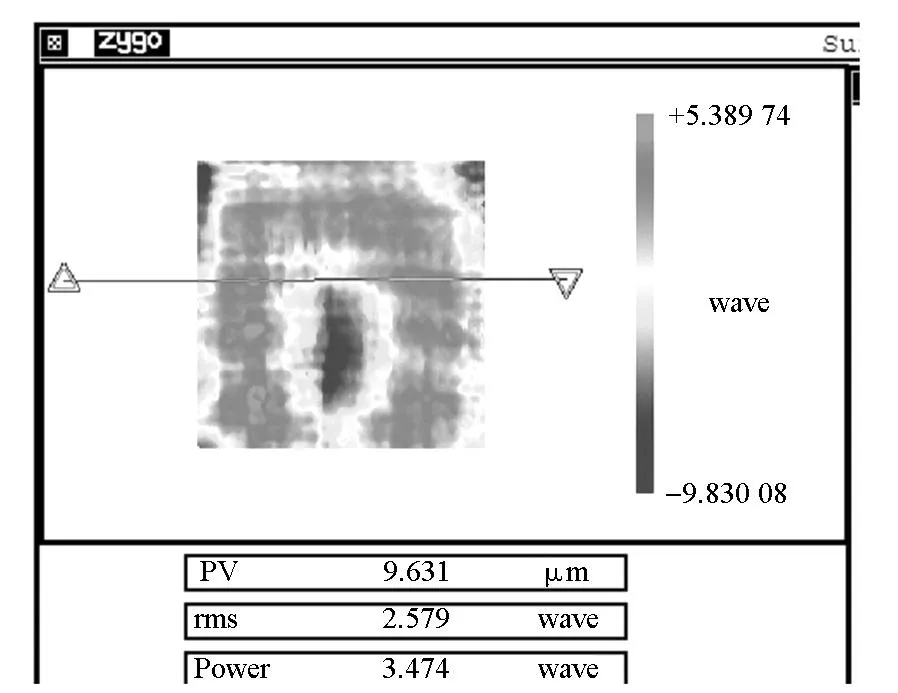
(c) 离轴抛物面磨削面形误差(c) Figure error of ground off-axis paraboloid图6 离轴抛物面磨削加工过程及面形误差Fig.6 Grinding process and figure error of off-axis paraboloid
6结论
基于盘形圆弧砂轮的磨削加工,建立了砂轮的几何模型,通过磨削点法向量匹配推导出工件上加工点和砂轮点的一一映射关系,从而建立加工曲面和刀具运动轨迹之间的几何关系。该模型综合考虑了加工方式、加工轨迹等因素,具有较好的通用性,可以很好指导实际磨削加工的过程。并对同轴的凸双曲面工件和离轴凹抛物面工件进行磨削加工,验证了模型的正确性和有效性,并通过补偿加工获得较好的磨削加工精度。
参考文献(References)
[1]侯海云,蒋天一,胡德金. 五轴磨床加工精密球面的磨削形态及运动分析[J]. 制造技术与机床, 2011, 3:58-63.
HOU Haiyun, JIANG Tianyi,HU Dejin. Topological and kinematic analysis applied for 5-axis spherical precision grinding machine[J]. Manufacturing Technology & Machine Tool, 2011, 3:58-63. (in Chinese)
[2]Kang N H, Li S Y, Zheng Z W. Research on geometric model of grinding large and medium scales optical aspheric surfaces[C]//Proceedings of SPIE, 2006, 6034: 60341B-1-7.
[3]姜晨,郭隐彪,潘日,等. 离轴楔形非球面平行磨削及补偿技术研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2011, 47(3): 193-198.
JIANG Chen, GUO Yinbiao, PAN Ri,et al. Study on method and compensation technology of off-axis wedge aspheric parallel grinding[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 47(3): 193-198. (in Chinese)
[4]Kuriyagawa T, Zahmaty M S S, Syoji K. A new grinding method for aspheric ceramic mirrors[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 1996, 62(4):387-392.
[5]Xie J, Zheng J H, Zhou R M, et al. Dispersed grinding wheel profiles for accurate freeform surfaces[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2011, 51(6):536-542.
[6]Xie J, Zhou R M, Xu J, et al. Form-truing error compensation of diamond grinding wheel in CNC envelope grinding of free-form surface[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2010, 48(9):905-912.
[7]Guo Y B, Chen B K, Zhang Yi, et al. Research on parallel grinding method of non axisymmetric aspheric lens[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 17(1): 149-151.
[8]韩成顺, 董申, 唐余勇. 大型光学非球面超精密磨削的几何模型研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2004, 25(6): 741-745.
HAN Chengshun, DONG Shen, TANG Yuyong. Geometric model of the ultra-precision grinding of large optical aspheric surface[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2004, 25(6): 741-745. (in Chinese)
[9]郭隐彪, 黄元庆, 田波, 等. 非轴对称非球面平行磨削误差补偿技术研究[J]. 机械工程学报, 2002, 38(5): 118-121.
GUO Yinbiao, HUANG Yuanqing, TIAN Bo, et al. Study on compensation of parallel grinding non axisymmetric aspheric surface[J]. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2002, 38(5): 118-121. (in Chinese)
[10]Saeki M, Kuriyagawa T, Lee J S, et al. Machining of aspherical opto-device utilizing parallel grinding method[C]//Proceedings of the American Society for Precision Engineering, 2001, 25: 433-436.
[11]Yeon H, Kuriyagawa T, Sun-Kyu L. Wheel curve generation error of aspheric microgrinding in parallel grinding method[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2006, 46(15):1929-1933.
[12]韩成顺, 董申, 唐余勇. 轴对称非球面超精密磨削的几何模型研究[J]. 光学技术, 2003, 29(3): 329-333.
HAN Chengshun, DONG Shen, TANG Yuyong. Study on geometric model of ultra-precision grinding optical axisymmetric aspheric surface[J]. Optical Technique, 2003, 29(3): 329-333. (in Chinese)
[13]Jiang Z H, Yin Y H. Geometrical principium of fewer-axis grinding for large complex optical mirrors[J]. Science China Technological Sciences, 2013, 56(7):1667-1677.
[14]Lee E S, Baek S Y. A study on optimum grinding factors for aspheric convex surface micro-lens using design of experiments[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools & Manufacture, 2007, 47(3):509-520.
[15]Chen F J, Yin S H, Ohmori H, et al. Form error compensation in single-point inclined axis nanogrinding for small aspheric insert[J]. International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 65(1):433-441.
[16]Chen F J, Yin S H, Huang H,et al. Profile error compensation in ultra-precision grinding of aspheric surfaces with on-machine measurement[J]. International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2010, 50(5): 480-486.
[17]韩成顺, 董申, 唐余勇. 离轴非球面超精密磨削加工几何模型的探讨[J]. 中国机械工程, 2004, 15(17): 1520-1522.
HAN Chengshun, DONG Shen, TANG Yuyong. Modeling of a new ultra-precision grinding method of off-axis aspheric surfaces[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2004, 15(17): 1520-1522. (in Chinese)
http://journal.nudt.edu.cn
Geometric model of curve grinding with disk arc wheel
PENGYanglin1,2,DAIYifan1,2,SONGCi1,2,3,SHIFeng1,2
(1. College of Mechatronics Engineering and Automation, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China;
2. Hunan Key Laboratory of Ultra-precision Machining Technology, Changsha 410073, China;
3. Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai Institute of Technical Physics, Shanghai 200083, China)
Abstract:The differences of wheel shape, machining path, motion axis combinations, and workpiece placed posture, will cause alterations of grinding model, which is the primary problem for the solution to curve generation. A geometric model of disk arc wheel was established; a one-to-one mapping relationship was built between workpiece and grinding wheel through the grinding point normal vector matching. After coordinate transformation, the corresponding machining tool motion trail which can be used for grinding was obtained. The uniform grinding geometry model of curve surface was formed, and the calculating flow of tool path was developed. The model has a wide application range, and can solve the tool path generating problem of multiple type grinding processes, which guarantees a high precision curve surface grinding.
Key words:curve surface grinding; grinding geometric model; geometric model of wheel; normal vector matching
中图分类号:TH161.1
文献标志码:A
文章编号:1001-2486(2015)06-039-04
作者简介:彭扬林(1986—),男,湖南衡阳人,博士研究生,E-mail:pengyanglin2007@126.com;戴一帆(通信作者),男,教授,博士,博士生导师,E-mail:dyf@nudt.edu.cn
基金项目:国家重点基础研究发展计划资助项目(2011CB013204)
收稿日期:*2015-06-01
doi:10.11887/j.cn.201506009

